Solution: Change the Status Bar Option to Display the Count Value
- Right-click on the status bar at the bottom of the worksheet interface.
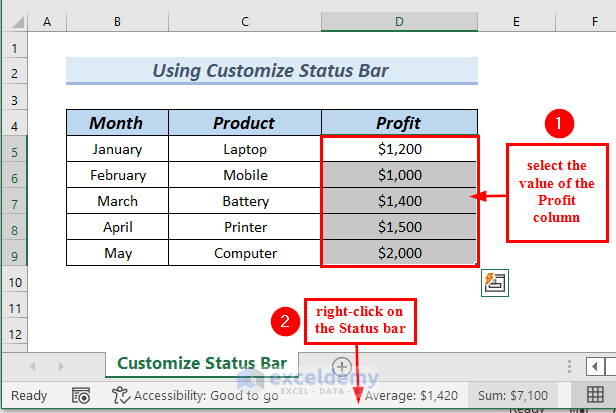
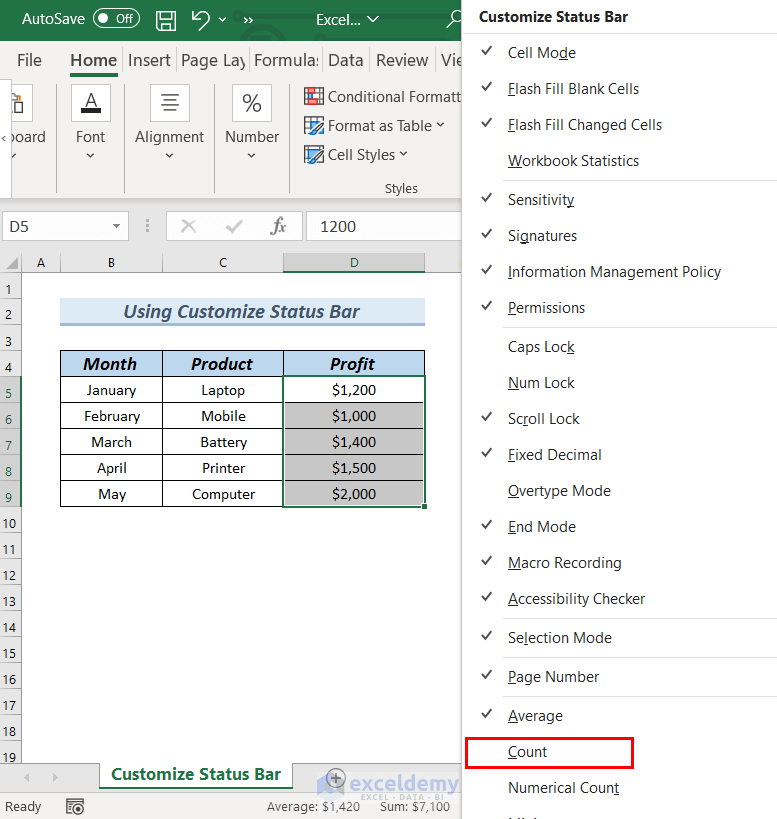
- Select Count from the context menu.
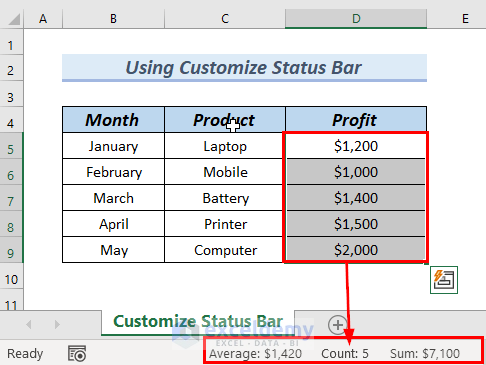
The status bar will now show the total count of the selected cells.
Why is the Status Bar Not Showing Proper Count Values in Excel?
There could be several reasons why the status bar in Excel is not showing proper count values. Here are some common issues and solutions:
1. Proper Range isn’t Selected
The count in the status bar is based on the selected cells. Make sure you have a range of cells selected with the data you want to count.
2. Hidden Rows/Columns
Hiding rows/columns allows users to conceal specific rows of data temporarily. This feature is valuable for focusing on relevant information. When a row or column is hidden within a range, Excel ignores it while showing summary values such as sum, average, and count.
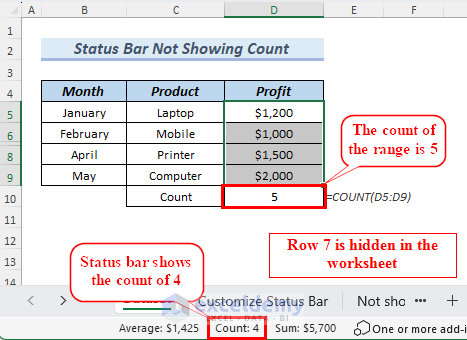
Unhide the hidden columns if you want to see the proper values of count and sum, average, etc.
3. Filtered Data
The Filter feature in Excel also hides specific data from a range. When you select filtered data, the count using a function and a feature from the status bar acts differently.

Removing the filters or selecting all data in the filters results in displaying proper count values in the status bar.
Download Practice Workbook
Frequently Asked Questions
Why isn’t Excel showing sum in status bar?
There are mainly two reasons for the Excel status bar not showing sum:
- The option is disabled in the status bar context menu.
- Selection is not in proper numeric type (e.g. text) to calculate the sum.
How do I display the status bar?
By default, Excel always displays the status bar. In case you don’t have that in your application, turn the Application.StatusBar property True using VBA to display the status bar. You can use other options to hide and unhide the status bar in Excel.
Does the count in the status bar consider cells with errors?
Yes, the count in the status bar counts every error in Excel. The status bar feature takes account of every non-blank value. This includes the errors.
Related Article
<< Go Back to Excel Parts | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

