Introduction to Activity Relationship Chart
The foundation for creating any form of plant layout is an Activity Relationship Chart. For this chart to provide a useful plant layout, great care must be taken in its design.
What is Activity Relationship Chart?
An Activity Relationship Chart (ARC for short) is a tabular chart that expresses the closeness rating between all sets of activities or departments. Each pair of departments in an ARC may be given one of six closeness ratings, with nine justifications for each rating (each assigned by a reason code).
Closeness Rating and Basis of the Coding in an Activity Relationship Chart
The relationship chart shows which entities are connected to one another and assesses how important that connection is. The ratings and their closeness are as follows:
| Rating | Closeness |
|---|---|
| A | Absolutely necessary |
| E | Especially important |
| I | Important and core |
| O | Ordinary |
| U | Unimportant |
| X | Prohibited/Undesirable |
The reasons for this closeness rating are expressed with number codes as follows:
| Code | Reason |
|---|---|
| 1 | Flow of Material |
| 2 | Ease of Supervision |
| 3 | Common Personnel |
| 4 | Necessary Contact |
| 5 | Noise |
| 6 | Similar Pieces of Equipment |
Importance of Activity Relationship Chart
The primary goal of the Activity Relationship Chart is to guarantee that the facility you are developing has the shortest possible distance between two pieces of equipment or departments that are crucial to one another. If required prior activity hasn’t been completed, further activities cannot be performed. Putting related facilities closer together and shortening cycle times are the main goals.
How to Create an Activity Relationship Chart in Excel: 4 Steps
We have used Microsoft Excel 365 version here, but you may use any other version according to your convenience. Please let us know if you encounter any problems while using any other versions of Excel.
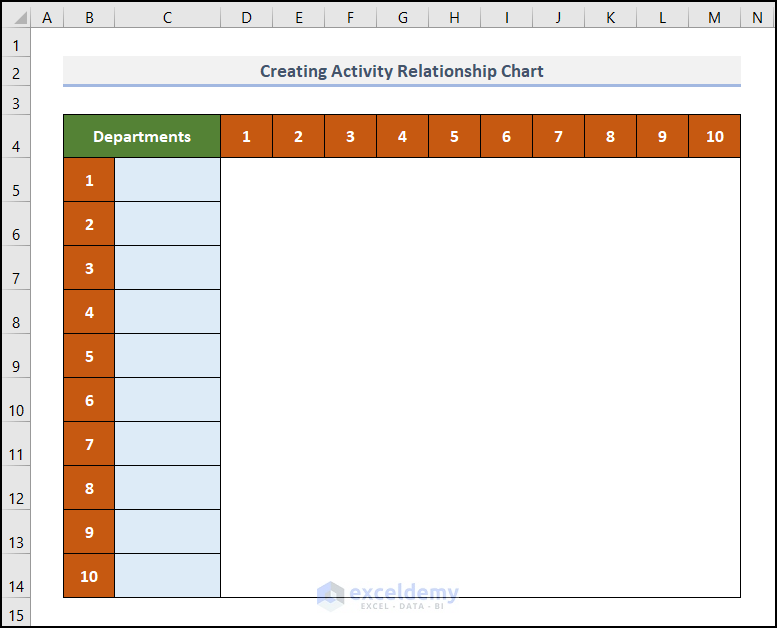
Step 1 – Create Basic Outline
First we create a basic outline where all the elements of the chart are accommodated.
Steps:
- Create a table in the B4:M14 range.
- In cell B4, enter the text Departments.
- Enter 1 to 10 in Column B and in Row 4. These are the serial numbers of the departments which we’ll input in the next step.
- Leave the D5:M14 range blank for future use.
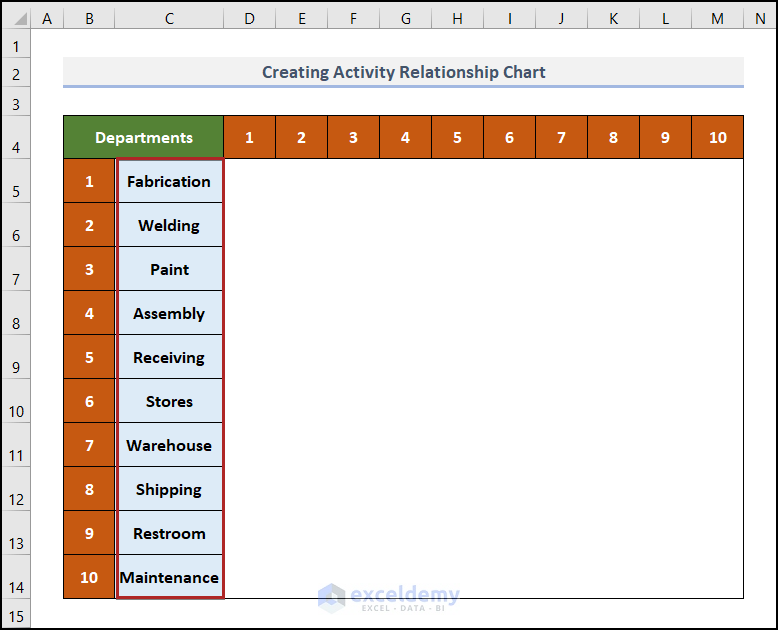
Step 2-Enter Department Names
We’ll use 10 different departments in our sheet.
Steps:
- Enter the name of the departments in the C5:C14 range.
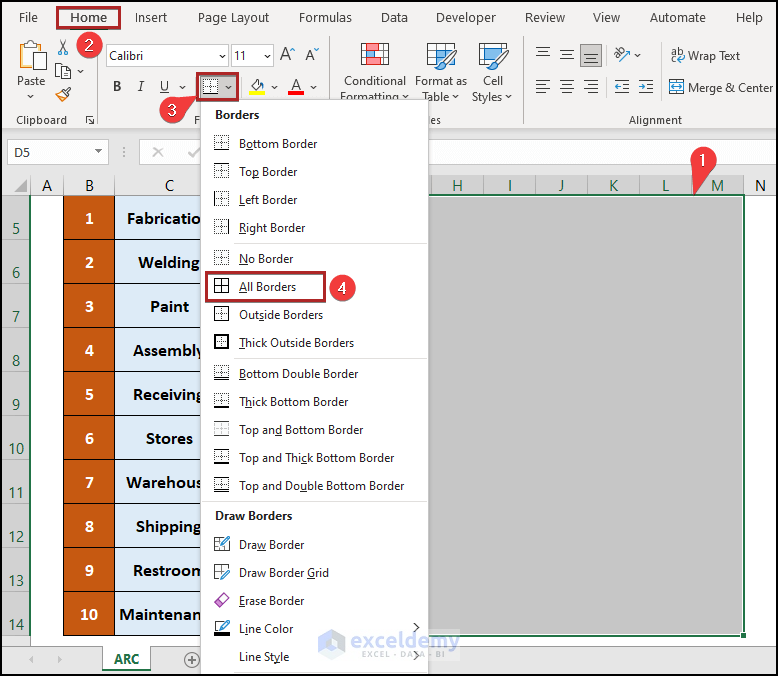
Step 3 – Construct Cell Borders
Now we can create the Activity Relationship Chart.
- Select the cells in the D5:M14 range.
- Go to the Home tab.
- Click on the Borders drop-down from the Font group.
- Select All Borders from the list.
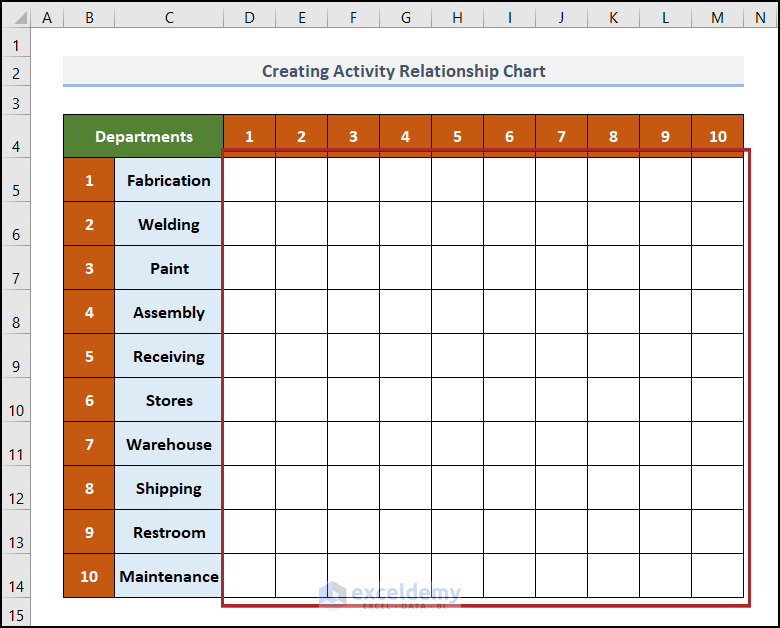
The worksheet now looks like the following image.
- Select the previous range.
- Repeat the previous steps to open the Borders drop-down list.
- This time, select the More Borders option.
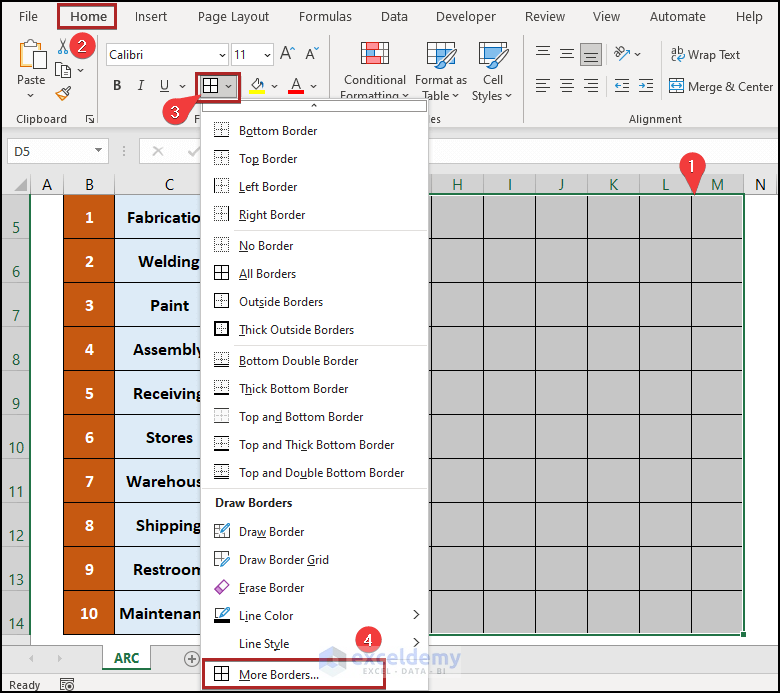
The Format Cells dialog box appears, opening on the Border tab.
- Apply the diagonal border as shown in the image below.
- Click OK.
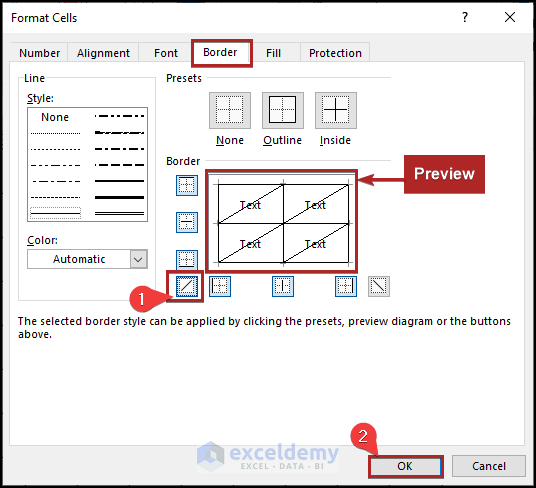
The final result is returned.
Step 4 – Give Closeness Rating and Reasons in Each Cell
Now we can fill in the technical part of this chart. The dataset used is purely fictitious and used only for demonstration purposes.
Steps:
Before inserting the data, we’ll restrict some cells because no data will be contained in them.
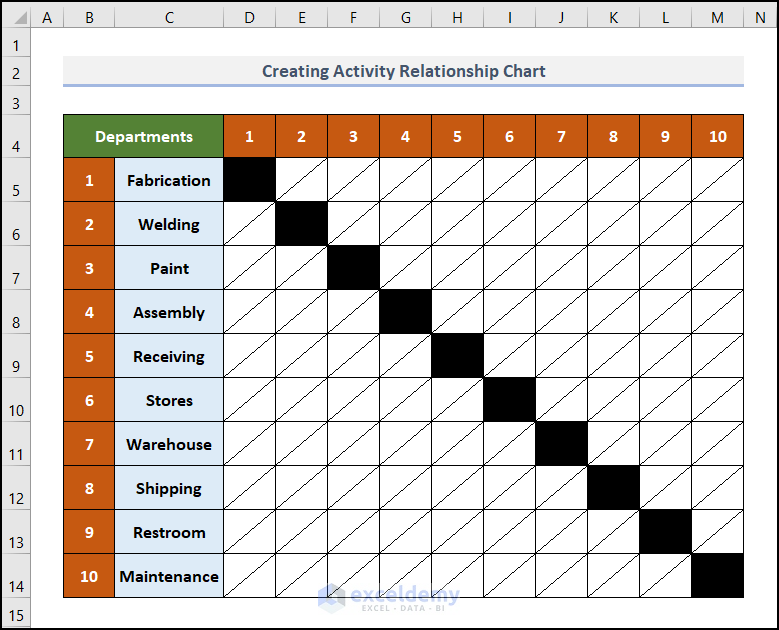
- Select the cells along the diagonal in the D5:M14 range.
- Go to the Home tab.
- Click on the Fill Color drop-down icon in the Font group.
- Select Black from the Theme Colors.
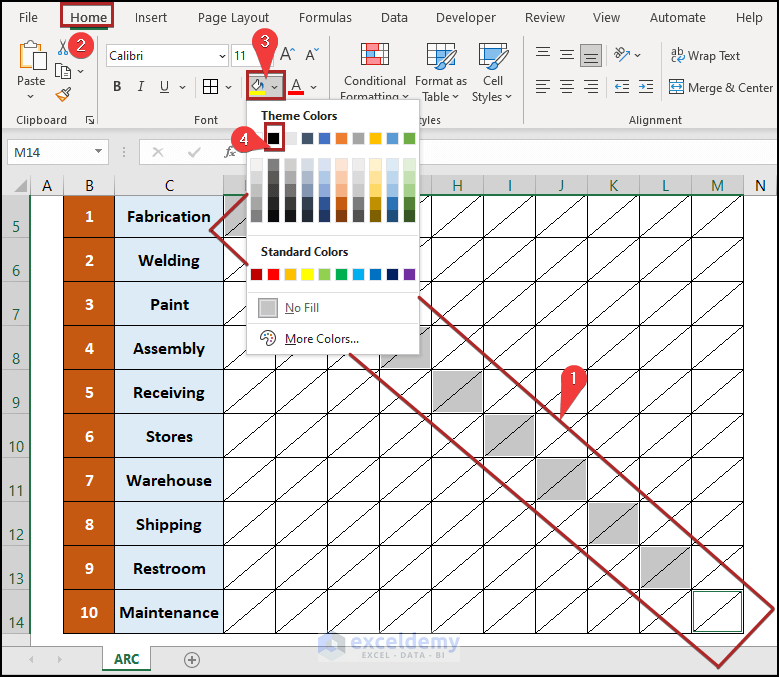
The final look is like something the below.
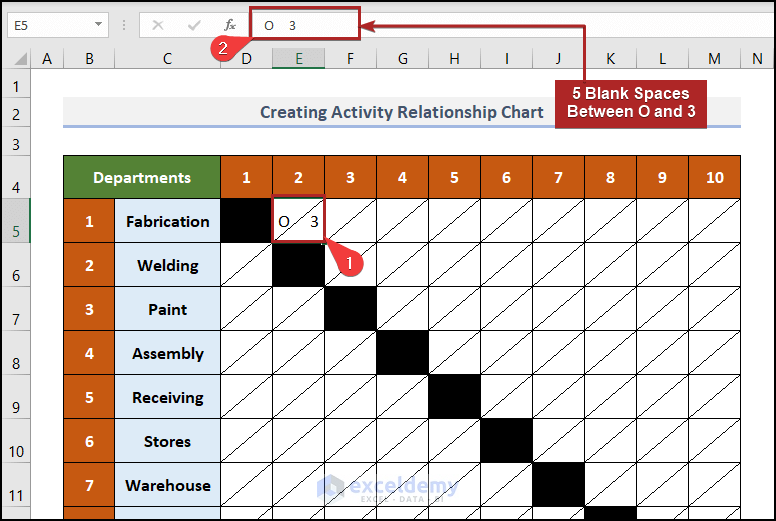
- Select cell E5 and enter the following text:
O 3
We intentionally leave 5 blank spaces between these two letters to accommodate them on both sides of the diagonal border in the cell.
- Press ENTER.
- Similarly, fill up the other cells with correct data.
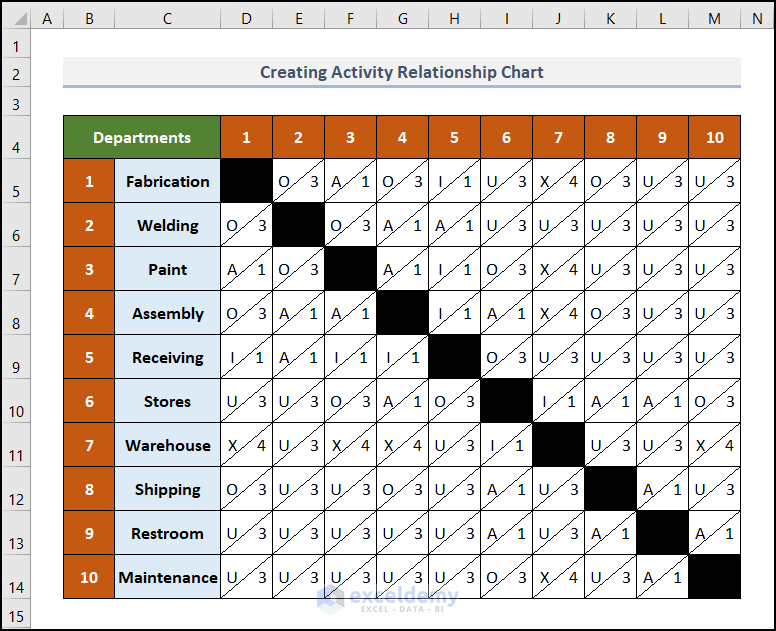
The data is symmetrical along the corners on both sides of the black cells.
To find, for example, the relationship between the Welding and Receiving departments, the serial numbers of these two departments are 2 and 5 respectively, so the result will be found at the intersection of 2 and 5.
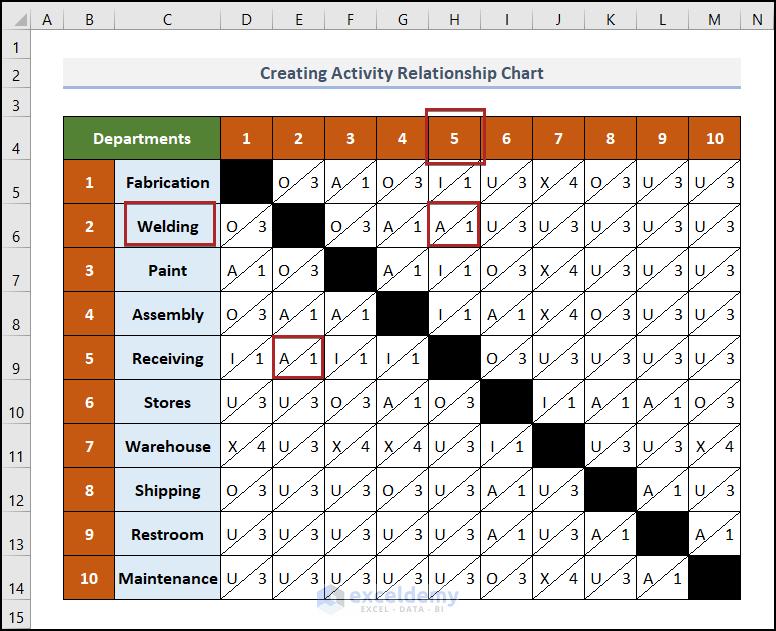
Therefore 2 and 5 intersect with each other twice. In cells E9 and H6, the values are the same. The relationship between these two departments is A1, meaning that their closeness is absolutely necessary.
Related Articles
- How to Create a Weight Loss Graph in Excel
- How to Make a Budget Constraint Graph on Excel
- How to Create Mekko/Marimekko Chart in Excel
- How to Find Intersection of Two Curves in Excel
- How to Show Intersection Point in Excel Graph
<< Go Back to Excel Charts | Learn Excel


