How to Launch the VBA Editor in Excel
- If you don’t see the Developer tab, enable the Developer tab.
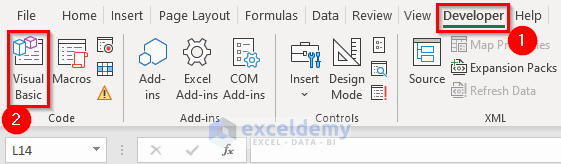
- Select the Developer tab and click on Visual Basic. Alternatively, you can press Alt + F11 to open the Visual Basic Editor.
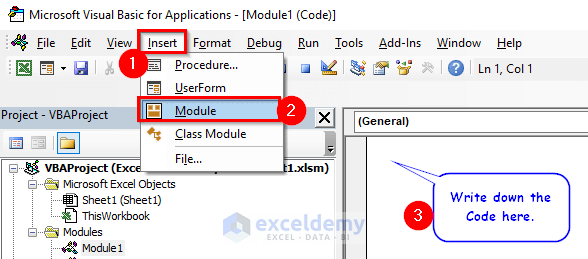
- From the Insert tab, select Module.
Introduction to the VBA Split Function in Excel
- Objective:
The VBA Split function in Excel splits the string into several substrings and returns a one-dimensional array of substrings.
- Syntax:
Split(expression, [delimiter], [limit], [compare])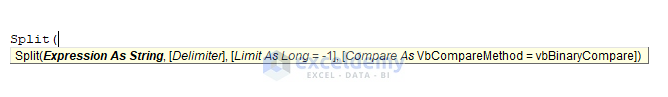
- Arguments Explanation:
| ARGUMENTS | REQUIRED/OPTIONAL | EXPLANATION |
|---|---|---|
| Expression | Required | The string to split based on the delimiter or space. |
| Delimiter | Optional | The character divides the string into parts. |
| Limit | Optional | Number of strings to be returned. |
| Compare | Optional | This argument is used for delimiters that are made up of one or letters. Check the Settings for Compare Argument section for more. |
- Settings for Compare Argument:
| Constant | Value | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| VbBinaryCompare | 0 | Performs a binary comparison. |
| vbTextCompare | 1 | Performs textual comparison. |
| vbDatabaseCompare | 2 | Performs comparison based on information on your database. |
10 Ideal Examples of Using the VBA Split Function in Excel
Example 1 – Split Words from a String
The VBA code will split the string, “We are learning VBA SPLIT Function” and show the sub-strings in a message box.
- Insert the code below in the Module window.
- Press F5 key to run the code.
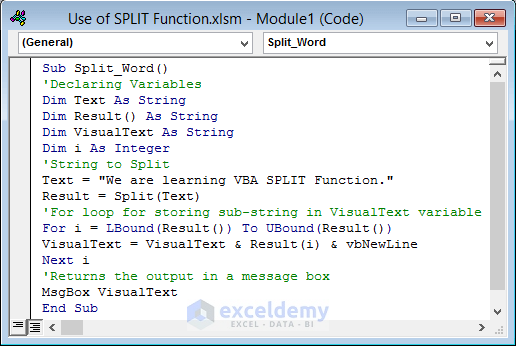
Sub Split_Word()
'Declaring Variables
Dim Text As String
Dim Result() As String
Dim VisualText As String
Dim i As Integer
'String to Split
Text = "We are learning VBA SPLIT Function."
Result = Split(Text)
'For loop for storing sub-string in VisualText variable
For i = LBound(Result()) To UBound(Result())
VisualText = VisualText & Result(i) & vbNewLine
Next i
'Returns the output in a message box
MsgBox VisualText
End SubCode Breakdown
- Here we set the name of the macro as Split_Word. Then, we declared four variables using the Dim All the variables are string types except variable i.
- We have set the string “We are learning VBA SPLIT Function.” in one of the variables (Text). Then applied the SPLIT function to the string using that variable and stored it in a variable named Result.
- Here we have used a For loop where LBound and UBound set the range. LBound is the least length a string can have (0) and UBound returns the maximum length of the string.
- This loop helps us to store the substring in the VisualText Then, we added a MsgBox to return the output in a message box format.
- After running the code, you will see the sub-strings in a message box.
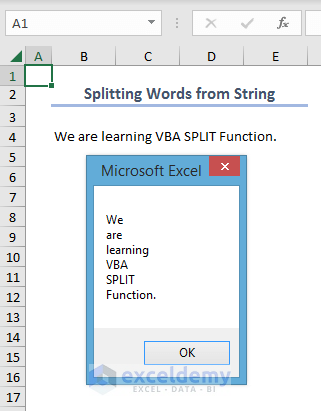
- Since we didn’t mention any delimiter, it assumed each substring ended with a space.
- If you want the output in cells rather than a message box, use the cell number instead of MsgBox.
- The code below splits the string and stores the sub-strings in the range B4:B9.
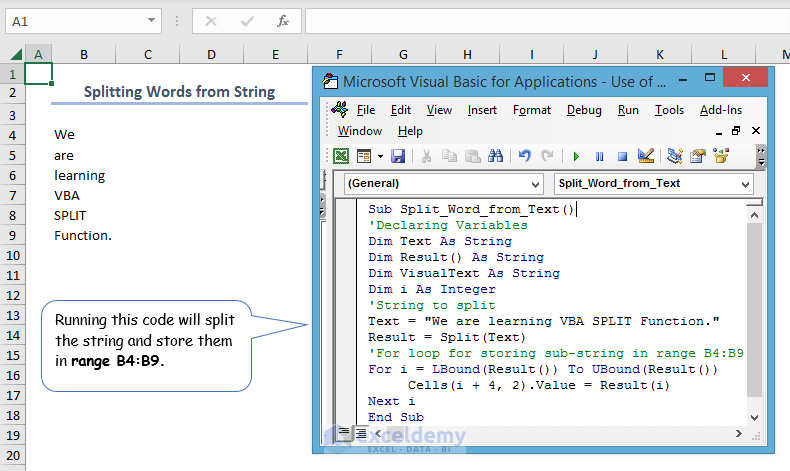
Sub Split_Word_from_Text()
'Declaring Variables
Dim Text As String
Dim Result() As String
Dim VisualText As String
Dim i As Integer
'String to split
Text = "We are learning VBA SPLIT Function."
Result = Split(Text)
'For loop for storing sub-string in range B4:B9
For i = LBound(Result()) To UBound(Result())
Cells(i + 4, 2).Value = Result(i)
Next i
End SubExample 2 – Splitting Words Separated with One Type of Delimiter
If there is no delimiter, then the SPLIT function assumes space as a delimiter. A delimiter can be a comma, a semicolon, or any separating character. We’ll use a comma as the delimiter.
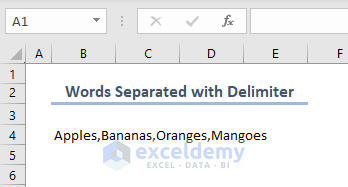
- To split words separated with the comma delimiter, use the following code in the Module window.
- Hit the F5 key to run the code.
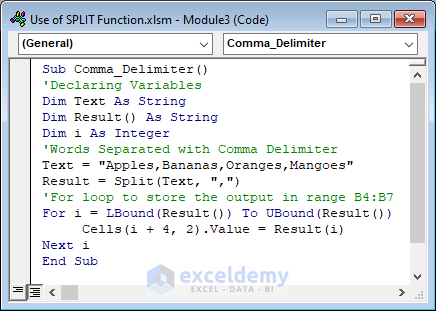
Sub Comma_Delimiter()
'Declaring Variables
Dim Text As String
Dim Result() As String
Dim i As Integer
'Words Separated with Comma Delimiter
Text = "Apples,Bananas,Oranges,Mangoes"
Result = Split(Text, ",")
'For loop to store the output in range B4:B7
For i = LBound(Result()) To UBound(Result())
Cells(i + 4, 2).Value = Result(i)
Next i
End Sub- After running the code, you will see the result below.
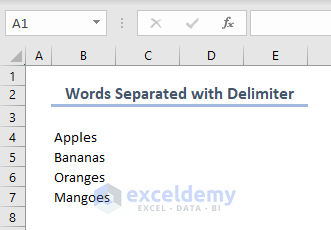
Read More: How to Use VBA Function Procedure with Arguments in Excel
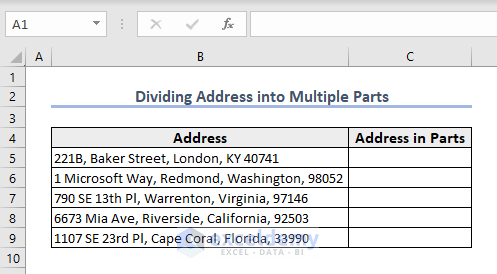
Example 3 – Divide an Address into Parts
Here is an example of a dataset consisting of a few addresses. Each address contains three parts. We’ll split the address into parts and separate them with line breaks.
- To divide the address into three parts, paste the following code in the Module window and save it by pressing Ctrl + S.
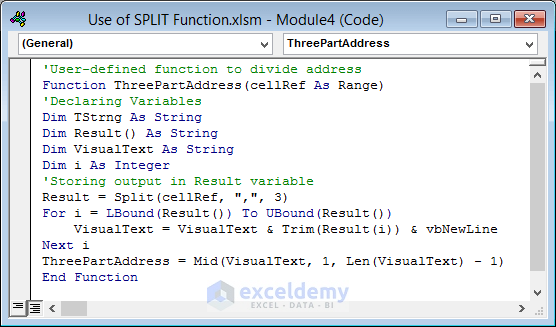
'User-defined function to divide address
Function ThreePartAddress(cellRef As Range)
'Declaring Variables
Dim TStrng As String
Dim Result() As String
Dim VisualText As String
Dim i As Integer
'Storing output in Result variable
Result = Split(cellRef, ",", 3)
For i = LBound(Result()) To UBound(Result())
VisualText = VisualText & Trim(Result(i)) & vbNewLine
Next i
ThreePartAddress = Mid(VisualText, 1, Len(VisualText) - 1)
End FunctionWe have inserted the Limit field in the SPLIT function since we want to divide it into three parts, we have used 3 as the Limit parameter.
We have used VBA LEN and MID functions that return the length of the string and extract the middle value from the text.
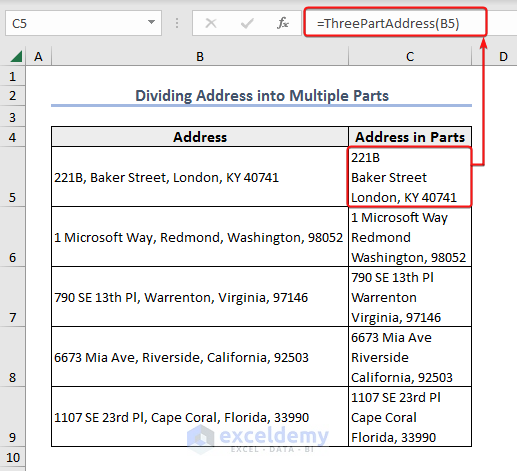
- Use the formula below in Cell C5 and press Enter to see the result.
=ThreePartAddress(B5)- Drag the Fill Handle down to divide all the addresses into three parts.
Example 4 – Count Words in Strings
- To create a function for counting words, paste the following code into the Module window and save it by pressing Ctrl + S.
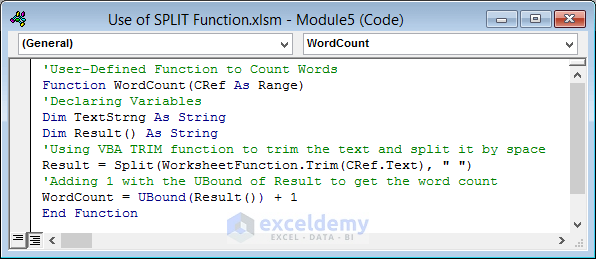
'User-Defined Function to Count Words
Function WordCount(CRef As Range)
'Declaring Variables
Dim TextStrng As String
Dim Result() As String
'Using VBA TRIM function to trim the text and split it by space
Result = Split(WorksheetFunction.Trim(CRef.Text), " ")
'Adding 1 with the UBound of Result to get the word count
WordCount = UBound(Result()) + 1
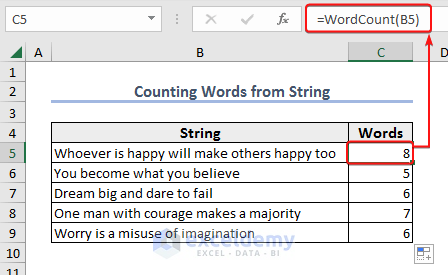
End Function- After saving the code, use the formula below in Cell C5 and press Enter to see the result.
=WordCount(B5)- Drag the Fill Handle down to apply the function to the rest of the cells.
Read More: How to Use VBA RTrim Function
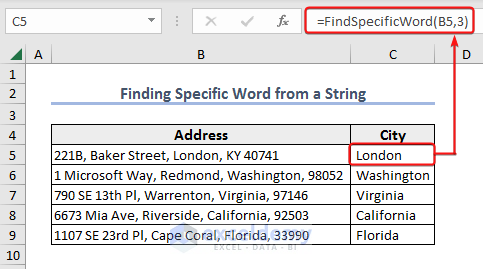
Example 5 – Find a Specific Word from a String
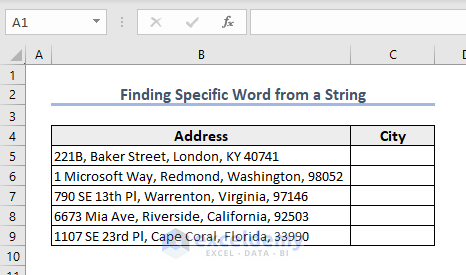
We are using the address dataset for this example. We are going to fetch the name of the city from the address. We will create a function named FindSpecificWord and retrieve the nth word from any string.
- To create the function, paste the following code in the Module window.
- Press Ctrl + S to save the code.
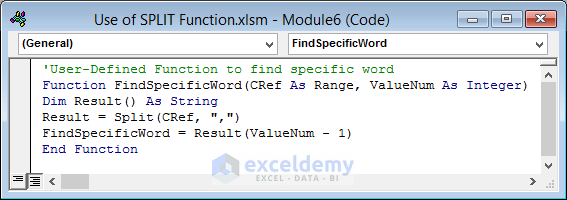
'User-Defined Function to find specific word
Function FindSpecificWord(CRef As Range, ValueNum As Integer)
Dim Result() As String
Result = Split(CRef, ",")
FindSpecificWord = Result(ValueNum - 1)
End FunctionCode Breakdown
- Our function takes two parameters; the CRef (string to split) and the ValueNum (numerical position of the word to find).
- The SPLIT function splits the string by a delimiter comma. It returns the substrings in an array.
- The array index is one less than the total element. You can see our addresses have 4 parts separated by a comma. But the array index number will be one less than that (3). That’s why we have subtracted 1 from the provided value number.
- Insert this formula in Cell C5 and press Enter to see the result.
=FindSpecificWord(B5,3)- Drag the Fill Handle down to extract the city name from the other addresses.
Example 6 – Change the Limit Parameter to Determine the Number of Substrings in an Array
We will split the string “Apples,Bananas,Oranges,Mangoes” and show the result in a message box.
- Use the following code in the Module window.
- Press F5 to run the code.
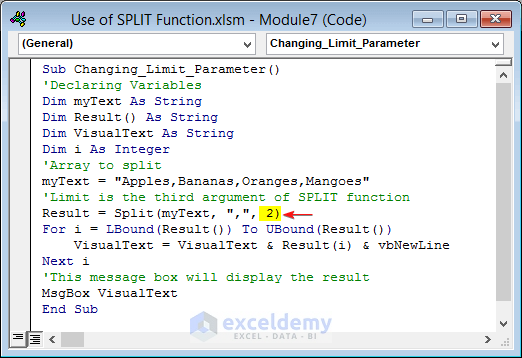
Sub Changing_Limit_Parameter()
'Declaring Variables
Dim myText As String
Dim Result() As String
Dim VisualText As String
Dim i As Integer
'Array to split
myText = "Apples,Bananas,Oranges,Mangoes"
'Limit is the third argument of SPLIT function
Result = Split(myText, ",", 2)
For i = LBound(Result()) To UBound(Result())
VisualText = VisualText & Result(i) & vbNewLine
Next i
'This message box will display the result
MsgBox VisualText
End Sub- After running the code, you will see the two substrings in a message box.
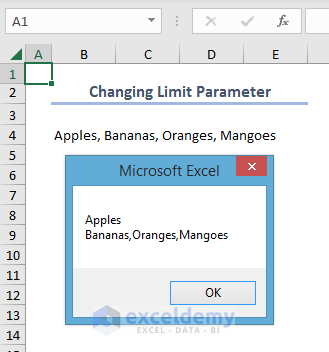
For different limits, you will get different results. We can show them in the following table:
| String | Limit | Output |
|---|---|---|
| “Apples,Bananas,Oranges,Mangoes” | 1 | Apples,Bananas,Oranges,Mangoes |
| “Apples,Bananas,Oranges,Mangoes” | 2 | Apples Bananas,Oranges,Mangoes |
| “Apples,Bananas,Oranges,Mangoes” | 3 | Apples Bananas Oranges,Mangoes |
| “Apples,Bananas,Oranges,Mangoes” | 4 | Apples Bananas Oranges Mangoes |
Example 7 – Copy Data
We will insert an employee’s details in the range B10:E10.
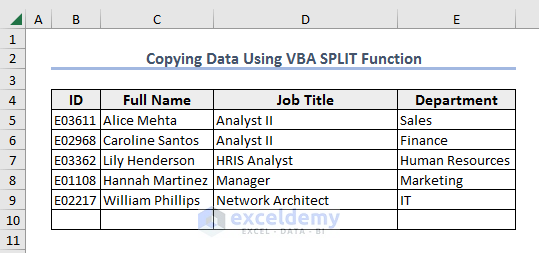
- For inserting information about an employee, use the following code in the Module window.
- Hit the F5 key to run it.
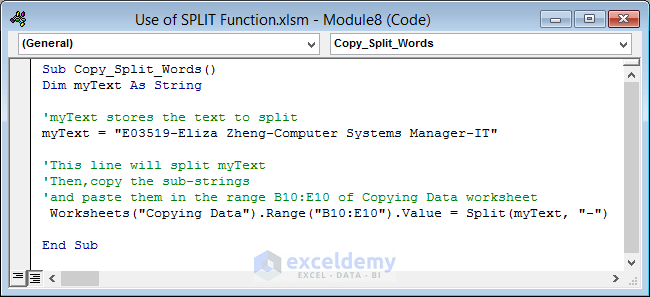
Sub Copy_Split_Words()
Dim myText As String
'myText stores the text to split
myText = "E03519-Eliza Zheng-Computer Systems Manager-IT"
'This line will split myText
'Then,copy the sub-strings
'and paste them in the range B10:E10 of Copying Data worksheet
Worksheets("Copying Data").Range("B10:E10").Value = Split(myText, "-")
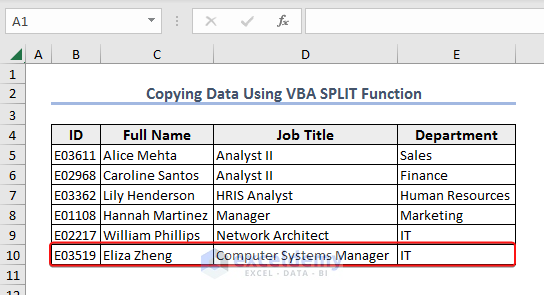
End Sub- After running the code, you will get the following result.
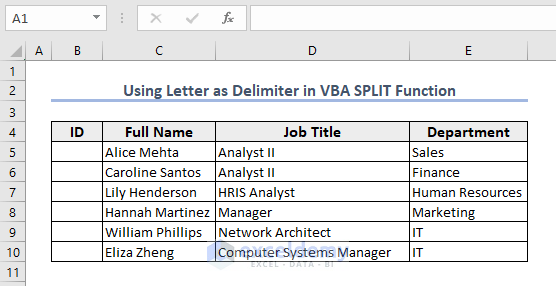
Example 8 – Use a Letter as a Delimiter
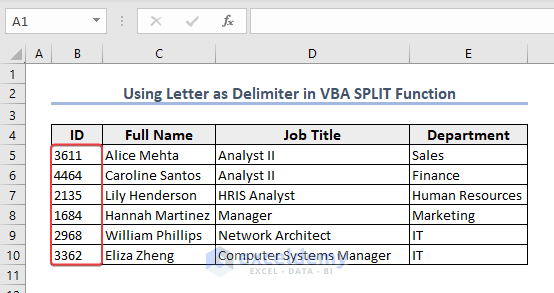
We will insert the IDs of some employees in the range B5:B10 from the string “E03611E04464E02135E01684E02968E03362”. We are using the letter “E” as a delimiter here.
- Use the following code in the Module window.
- Press F5 key to run it.
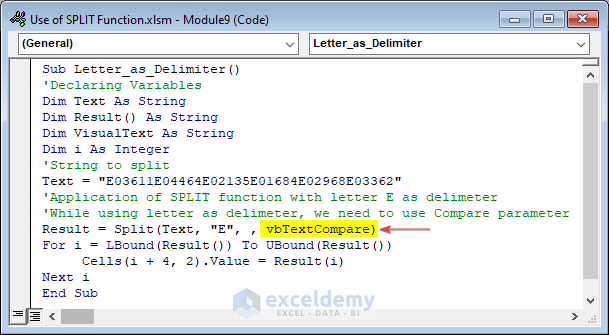
Sub Letter_as_Delimiter()
'Declaring Variables
Dim Text As String
Dim Result() As String
Dim VisualText As String
Dim i As Integer
'String to split
Text = "E03611E04464E02135E01684E02968E03362"
'Application of SPLIT function with letter E as delimeter
'While using letter as delimeter, we need to use Compare parameter
Result = Split(Text, "E", , vbTextCompare)
For i = LBound(Result()) To UBound(Result())
Cells(i + 4, 2).Value = Result(i)
Next i
End SubHere, Split(Text, “E”, , vbTextCompare) contains four arguments. The last argument vbTextCompare helps to split the string by letter “E”.
- We will see the IDs like the picture below.
Different compare arguments show different results. We can show it in the following table.
| String | Delimiter | Type | Result | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| “35e31E43” | e | vbTextCompare | 35 31 43 |
When we need to split by upper or lower case. |
| “35e31E43” | e | vbBinaryCompare | 35 31E43 |
When we need to split by lowercase only. |
Example 9 – Find an Extension
We have some email addresses, and we will extract the emails and their extensions.
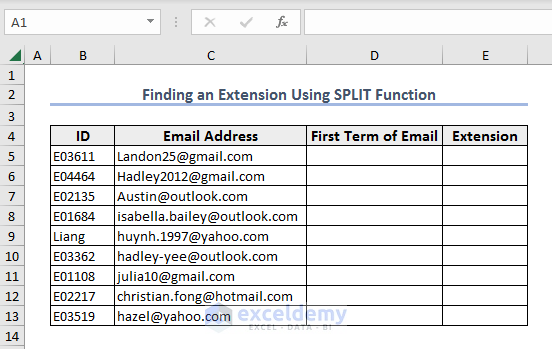
- Use the code below in the Module window.
- Press F5 to run it.
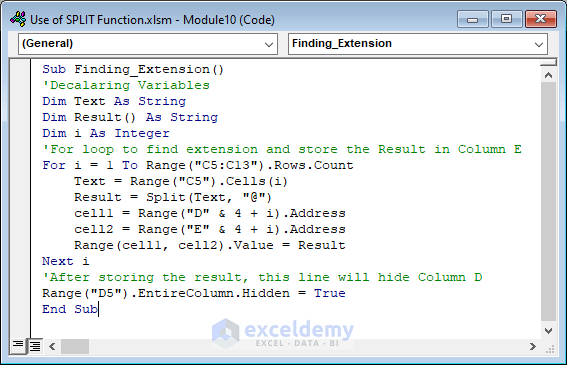
Sub Finding_Extension()
'Decalaring Variables
Dim Text As String
Dim Result() As String
Dim i As Integer
'For loop to find extension and store the Result in Column E
For i = 1 To Range("C5:C13").Rows.Count
Text = Range("C5").Cells(i)
Result = Split(Text, "@")
cell1 = Range("D" & 4 + i).Address
cell2 = Range("E" & 4 + i).Address
Range(cell1, cell2).Value = Result
Next i
'After storing the result, this line will hide Column D
Range("D5").EntireColumn.Hidden = True
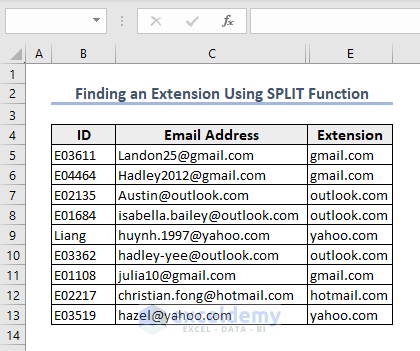
End Sub- You will find the extensions in Column E and the first terms will be hidden (in column D).
What to Do If You Need to Find File Names and Their Extensions?
Use the following VBA code. The code will extract the file name “My Resume” and its extension “.pdf”.
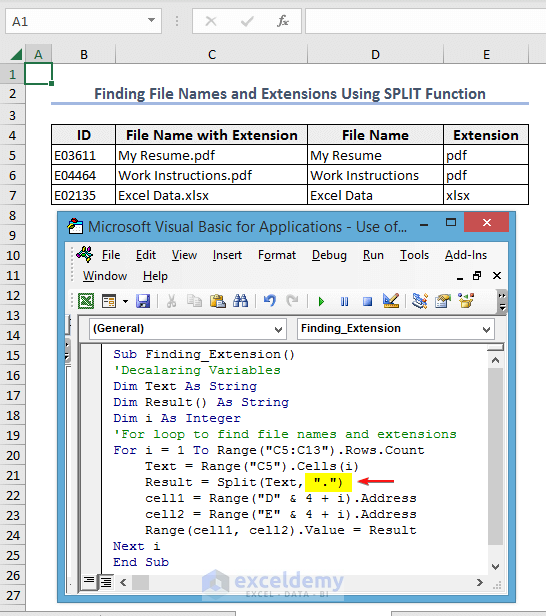
Sub Finding_Extension()
'Decalaring Variables
Dim Text As String
Dim Result() As String
Dim i As Integer
'For loop to find file names and extensions
For i = 1 To Range("C5:C13").Rows.Count
Text = Range("C5").Cells(i)
Result = Split(Text, ".")
cell1 = Range("D" & 4 + i).Address
cell2 = Range("E" & 4 + i).Address
Range(cell1, cell2).Value = Result
Next i
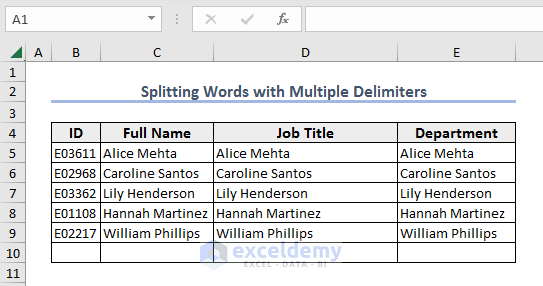
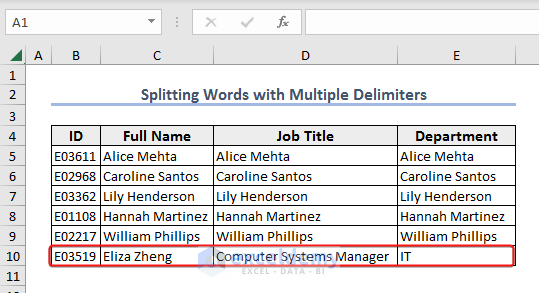
End SubExample 10 – Splitting Words Separated with Multiple Delimiters
The string “E03519,Eliza Zheng-Computer Systems Manager,IT” contains comma (,) and hyphen (-) as delimiters. We will split this string and insert the array in range B10:E10.
- Insert the code below in the Module window.
- Hit the F5 key to run the code.
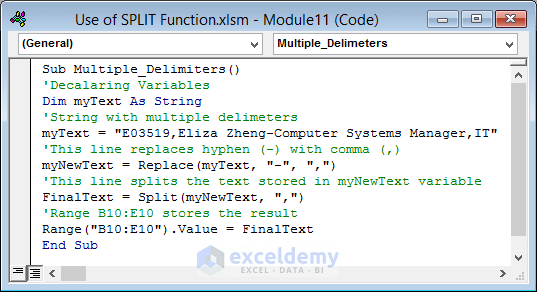
Sub Multiple_Delimiters()
'Decalaring Variables
Dim myText As String
'String with multiple delimiters
myText = "E03519,Eliza Zheng-Computer Systems Manager,IT"
'This line replaces hyphen (-) with comma (,)
myNewText = Replace(myText, "-", ",")
'This line splits the text stored in myNewText variable
FinalText = Split(myNewText, ",")
'Range B10:E10 stores the result
Range("B10:E10").Value = FinalText
End Sub- Here’s the result.
How to Use the Join Function to Reverse a Split in Excel VBA
To explain reverse split, we will use the string “We,are,learning,reverse,split,in,Excel” inside the code. We will place the string in Cell B4. After that, we will split it into an array, then join the sub-strings using space as a delimiter and place the result in Cell B6.
- Insert the code below in the Module window.
- Press F5 key to run it.
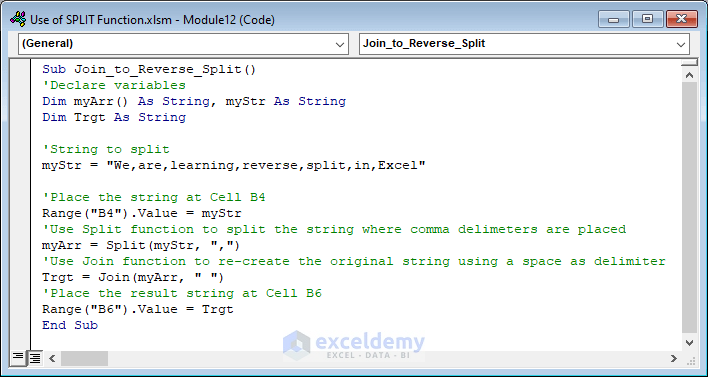
Sub Join_to_Reverse_Split()
'Declare variables
Dim myArr() As String, myStr As String
Dim Trgt As String
'String to split
myStr = "We,are,learning,reverse,split,in,Excel"
'Place the string at Cell B4
Range("B4").Value = myStr
'Use Split function to split the string where comma delimiters are placed
myArr = Split(myStr, ",")
'Use Join function to re-create the original string using a space as delimiter
Trgt = Join(myArr, " ")
'Place the result string at Cell B6
Range("B6").Value = Trgt
End Sub- You will get the following result.

Things to Remember
- The Split function assumes space as the delimiter if you don’t provide the delimiter.
- One must specify the delimiter inside the Split function if the delimiter is not a space.
- The Ubound function finds the maximum length and the Lbound function finds the minimum length of the array.
Download the Practice Workbook
Related Articles
- How to Use VBA Forecast Function in Excel
- Call a Sub in VBA in Excel
- How to Create a Body Mass Index Calculator in Excel Using VBA
- Use VBA Asc Function
- Use VBA StrComp in Excel


