Download Practice Workbook
Download the following workbook.
The MsgBox Function in Excel
Objective:
The MsgBox function is used to create a message box, also known as a dialog box.
Syntax:
MsgBox (Prompt, [Button As VbMsgBoxStyle = vbOkOnly], [Title], [HelpFile], [Context]) As VbMsgBoxResult
Arguments Explanation:
| ARGUMENT | REQUIRED/OPTIONAL | EXPLANATION |
|---|---|---|
| Prompt | Required | A statement displayed in the message box. |
| [Buttons] | Optional | Codes to display buttons and icons in the message box. |
| [Title] | Optional | Title or name of the message box. |
| [HelpFile] | Optional | Index or link assigned to the Help button in the message box. |
| [Context] | Optional | Index or specific topic number of the Help file. |
Return Parameter:
The function returns a statement and defined buttons in the message box.
Button Constants:
| BUTTON CODES | VALUES | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| vbOKOnly | 0 | Shows the Ok button only (Default). |
| vbOKCancel | 1 | Shows OK and Cancel buttons. |
| vbAbortRetryIgnore | 2 | Shows Abort, Retry and Ignore buttons. |
| vbYesNo | 3 | Shows Yes and No buttons. |
| vbYesNoCancel | 4 | Shows Yes, No and Cancel buttons. |
| vbRetryCancel | 5 | Shows Retry and Cancel buttons. |
| vbMsgBoxHelpButton | 16384 | Shows Help Button. |
| vbDefaultButton1 | 0 | Defines the first default button. |
| vbDefaultButton2 | 256 | Defines the second default button. |
| vbDefaultButton3 | 512 | Defines the third default button. |
| vbDefaultButton4 | 768 | Defines the fourth default button. |
| vbMsgBoxRight | 524288 | Right alignment of the text. |
| vbMsgBoxRtlReading | 1048576 | Text reading from the right to the left. |
Icon Constants:
| ICON CODES | VALUES | DESCRIPTION |
| vbCritical | 16 | Displays the critical message icon- Thin white cross inside a red-filled circle. |
| vbQuestion | 32 | Displays the question message icon- White question mark inside a blue-filled circle. |
| vbExclamation | 48 | Displays the warning message icon- Black exclamatory symbol inside a yellow-filled triangle. |
| vbInformation | 64 | Displays the information message icon- The letter ‘i’ in white inside a blue-filled circle. |
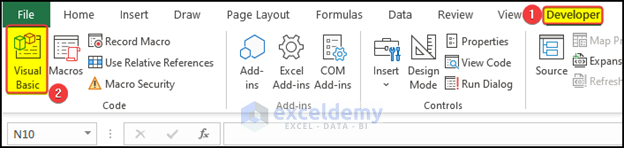
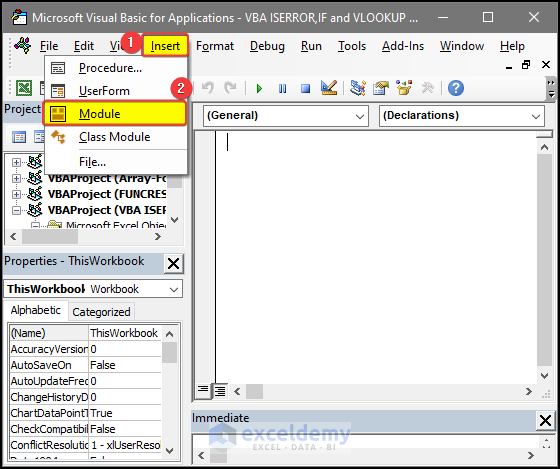
How to Launch the VBA Editor in Excel
- Press Alt+F11 or use the Visual Basic command in the Developer tab.
- Go to Insert > Module, and enter the code.
Note:
If you don’t find the Developer tab on the ribbon, you need to enable it:
Types of VBA MsgBox Functions in Excel: Usage and Return Values
1. vbOKOnly MsgBox – One Option
Only the Prompt argument is used. The function returns the output using the default MsgBox button: vbOKOnly.
The VBA msgbox displays the defined statement and the OK button.
- Run the following code in a new module in the VBA window.
Sub MsgBox_vbOKOnly()
MsgBox "This is an example of default button setting."
End Sub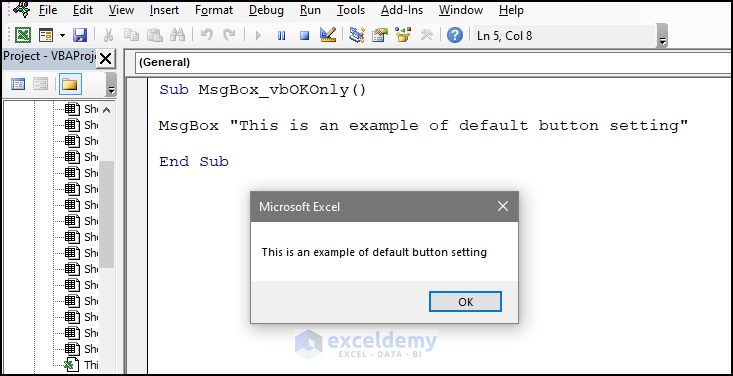
Read More: How to Return a Value in VBA Function (Both Array and Non-Array Values)
2. vbOKCancel MsgBox with the Cancel option
- Copy the code below into the VBA module.
The button code- vbOKCancel is used in the second argument.
Sub MsgBox_vbOKCancel()
MsgBox "Do you want to continue?", vbOKCancel
End Sub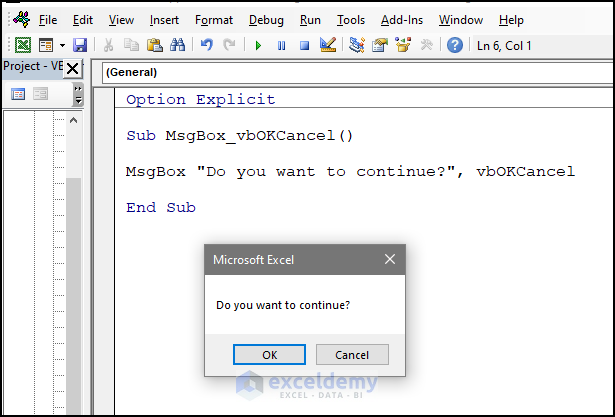
3. vbAbortRetryCancel MsgBox – Three Options
To show the Abort, Retry and Ignore buttons:
- User the following code:
Sub MsgBox_vbAbortRetryIgnore()
MsgBox "What do you want to do?", vbAbortRetryIgnore
End Sub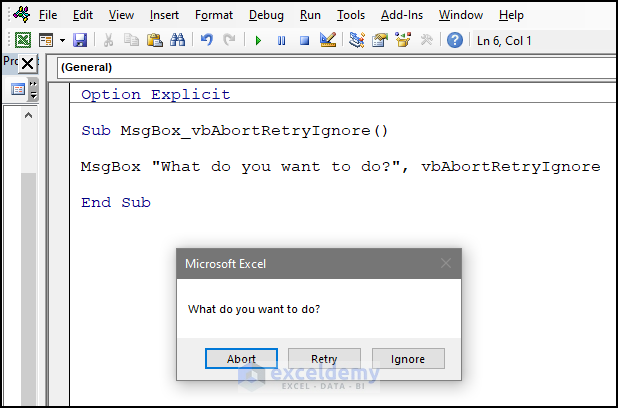
Read More: How to Use VBA Function Procedure with Arguments in Excel
4. vbYesNo Message Box – Two Options
To display Yes and No buttons:
- Use the code:
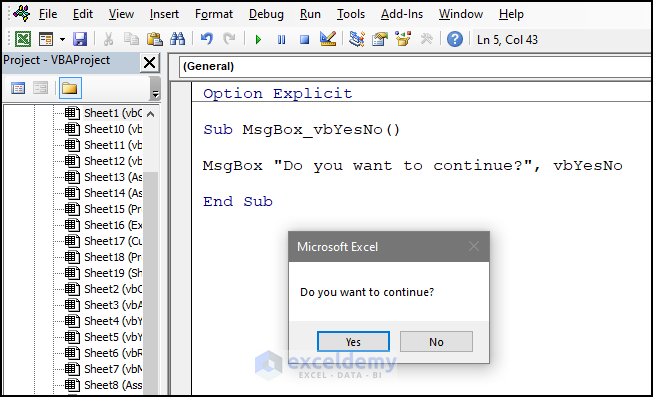
Sub MsgBox_vbYesNo()
MsgBox "Do you want to continue?", vbYesNo
End Sub
5. vbYesNoCancel MsgBox – Two Options and Cancel
To add ’Cancel’ to the Yes and No buttons:
- Use the code:
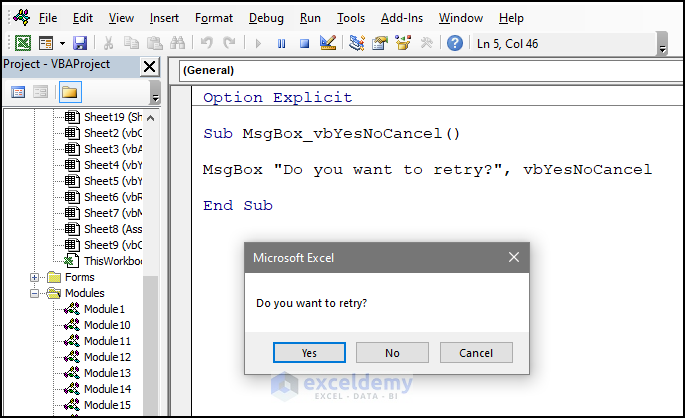
Sub MsgBox_vbYesNoCancel()
MsgBox "Do you want to retry?", vbYesNoCancel
End SubSimilar Readings
- How to Use VBA DateDiff Function in Excel (9 Examples)
- Random Number Excel Formula (5 Examples)
- How to Use VBA Str Function in Excel (4 Examples)
- Use VBA ChDir Function in Excel (4 Suitable Examples)
- How to Use VBA IsError Function (6 Examples)
6. vbCritical – Show Errors
- Use the following code:
MsgBox "An error has occurred", vbCritical
End Sub7. vbQuestion
- Use the following code:
Sub MsgBox_vbCritical()
MsgBox "An error has occurred", vbCritical
End Sub8. vbExclamation
To show a minor input error: (!) inside a yellow-filled triangle:
- Use the code below:
Sub MsgBox_vbExclamation()
MsgBox "An error occurred", vbExclamation
End Sub9. vbDefaultButton – Set the Default Button
9.1 vbDefaultButton1
- Use the code:
Sub DisplayMessageWithDefault1Button ()
MsgBox "Please select a color:", vbQuestion + vbYesNoCancel + vbDefaultButton3, "Select Color"
End SubIf the user presses Enter, Yes will be selected.
9.2 vbDefaultButton2
- Use the code:
Sub DisplayMessageWithDefault2Button()
MsgBox "Please select a color:", vbQuestion + vbYesNoCancel + vbDefaultButton3, "Select Color"
End SubIf the user presses Enter, NO will be selected.
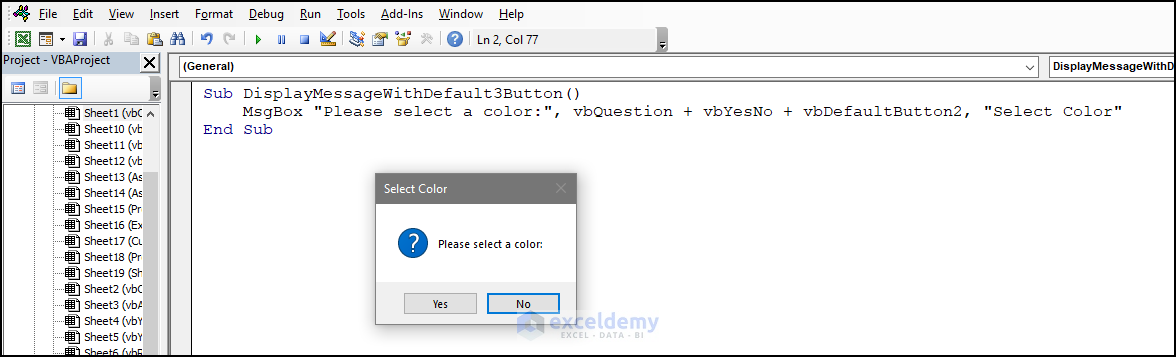
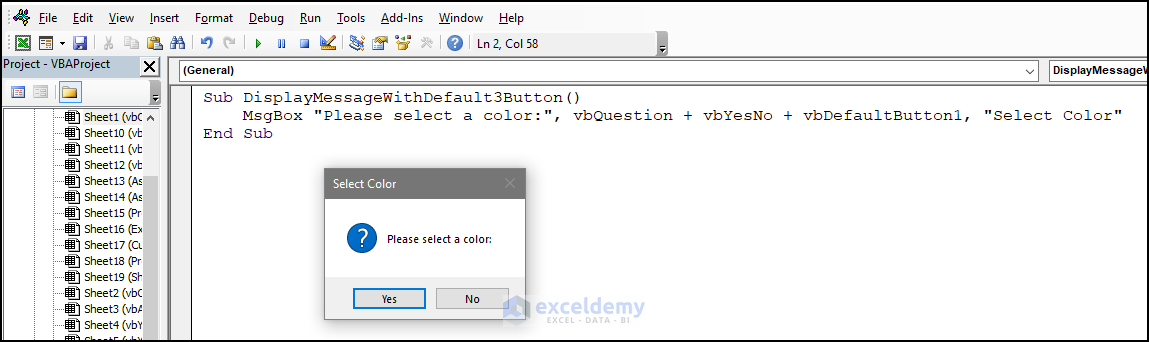
9.3 vbDefaultButton3
- Use the code below.
Sub DisplayMessageWithDefault3Button()
MsgBox "Please select a color:", vbQuestion + vbYesNoCancel + vbDefaultButton3, "Select Color"
End SubIf the user presses Enter, Cancel will be selected.
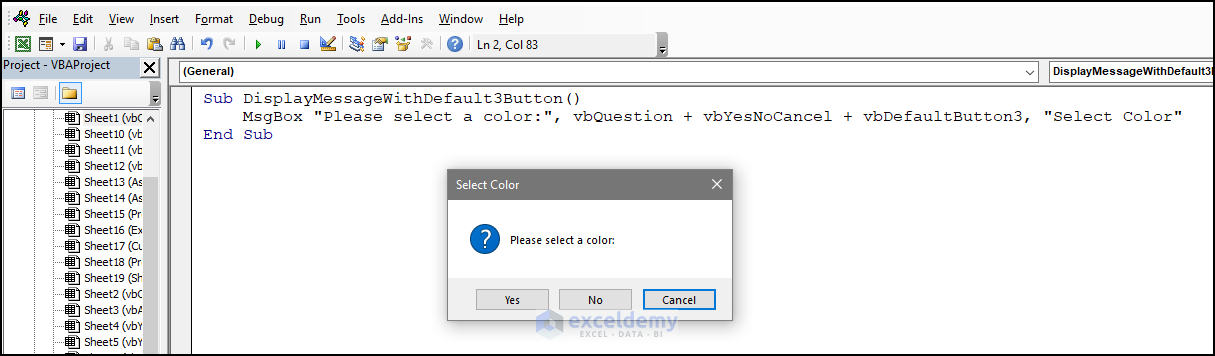
10. vbApplicationModal
To allow interaction with other parts of the Excel interface while the message box is open:
- Use the following code:
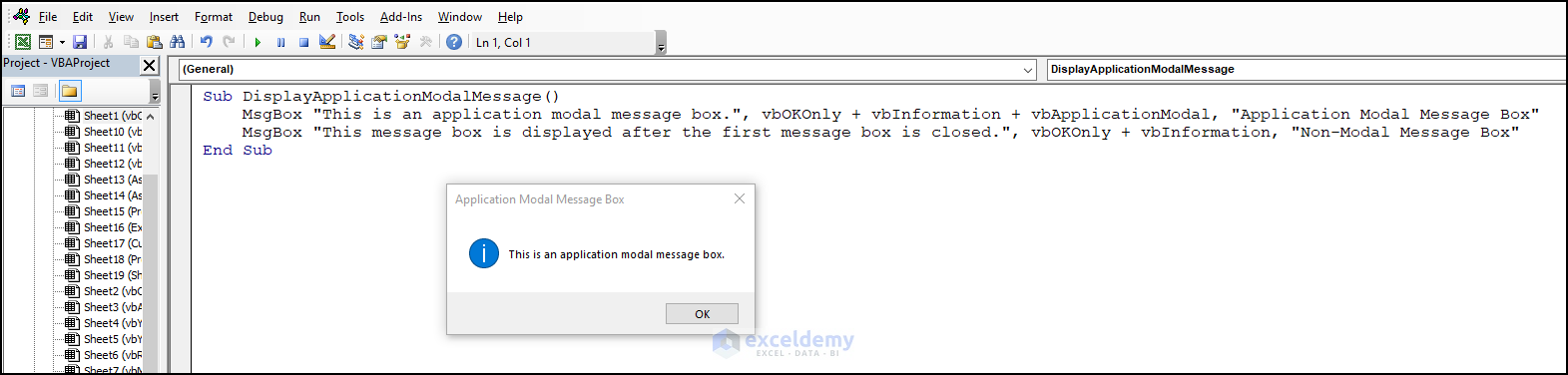
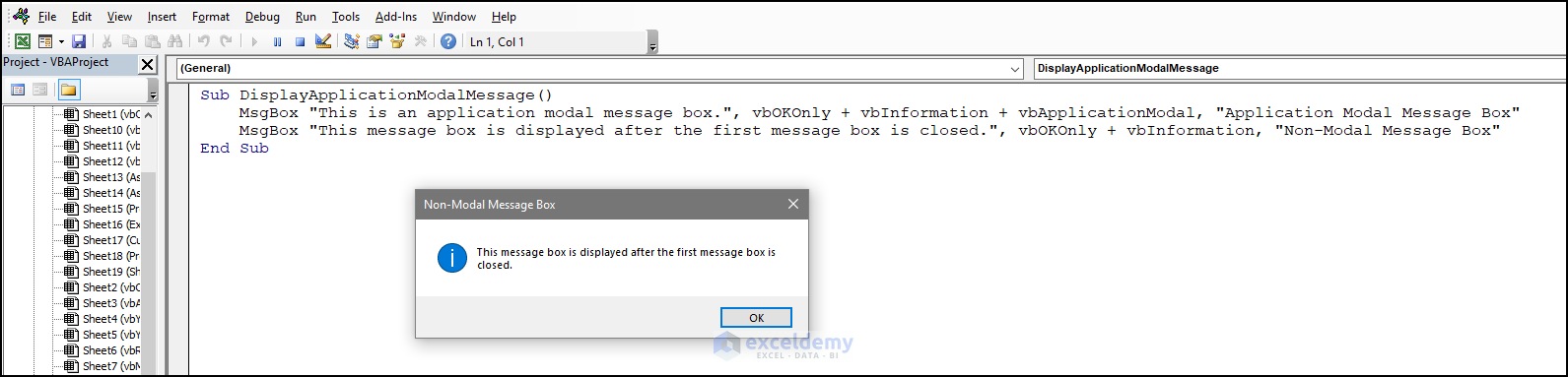
Sub DisplayApplicationModalMessage()
MsgBox "This is an application modal message box.", vbOKOnly + vbInformation + vbApplicationModal, "Application Modal Message Box"
MsgBox "This message box is displayed after the first message box is closed.", vbOKOnly + vbInformation, "Non-Modal Message Box"
End SubYou will be able to interact with other parts of the Excel sheet.
After you close the message box, another box will open.
Similar Readings
- How to Use VBA While Wend Statement in Excel (4 Examples)
- Use VBA UCASE function in Excel (4 Examples)
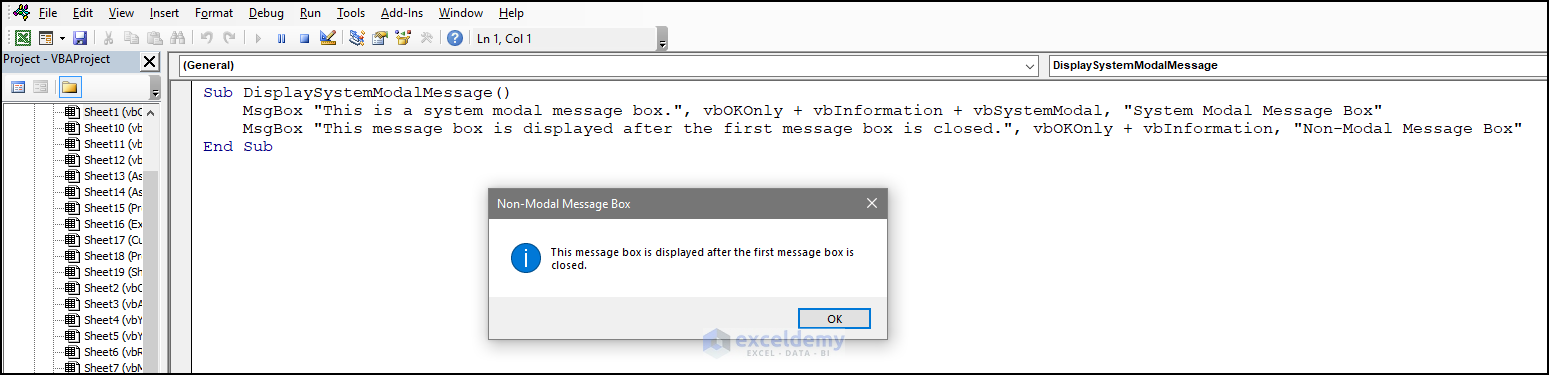
11. vbSystemModal
To restrict interaction to the current tab while the message box is open:
- Use the following code:
Sub DisplaySystemModalMessage()
MsgBox "This is a system modal message box.", vbOKOnly + vbInformation + vbSystemModal, "System Modal Message Box"
MsgBox "This message box is displayed after the first message box is closed.", vbOKOnly + vbInformation, "Non-Modal Message Box"
End Sub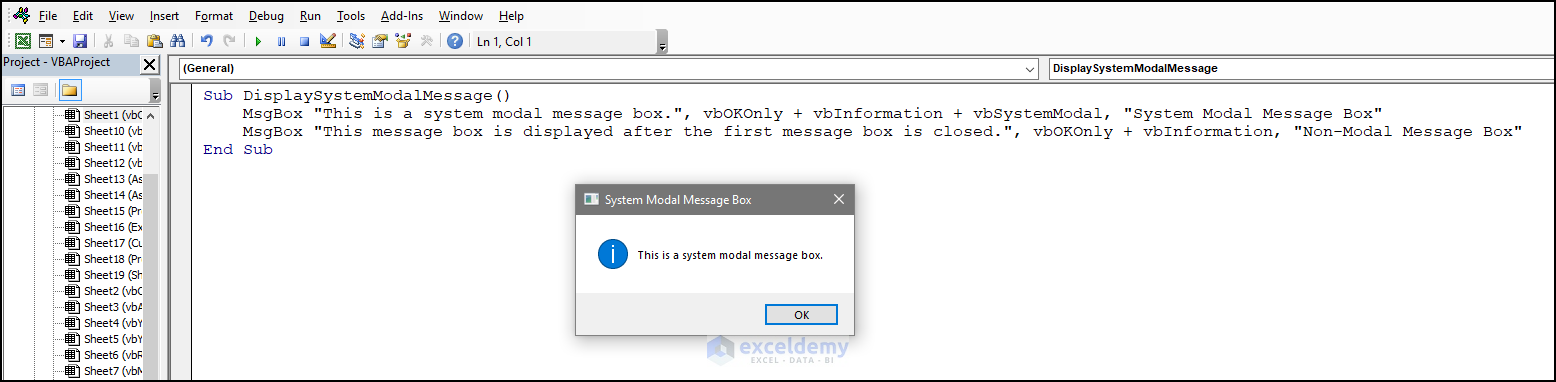
- You need to close the message box to use other parts of the application.
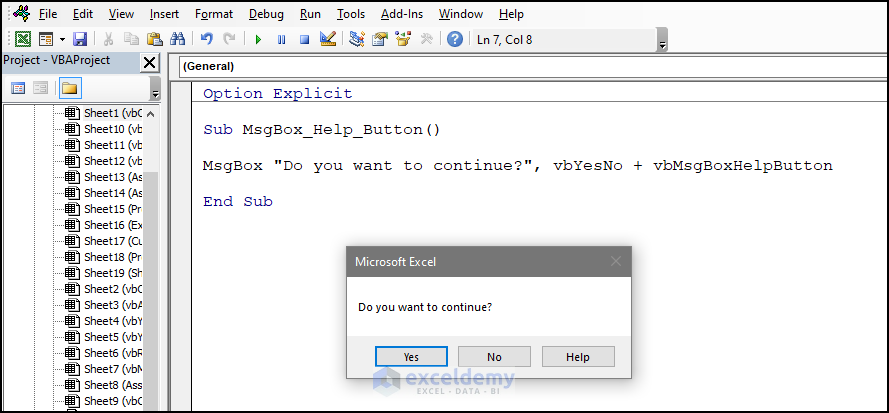
12. vbMsgBoxHelpButton – Show Help Info
To add a Help button:
- Use the code:
Sub MsgBox_Help_Button()
MsgBox "Do you want to continue?", vbYesNo + vbMsgBoxHelpButton
End Sub13. VbMsgBoxSetForeground – Display the Message Box in the Foreground
- Use the code:
Sub DisplayForegroundMessage()
MsgBox "This is a foreground message box.", vbOKOnly + vbInformation + vbMsgBoxSetForeground, "Foreground Message Box"
End Sub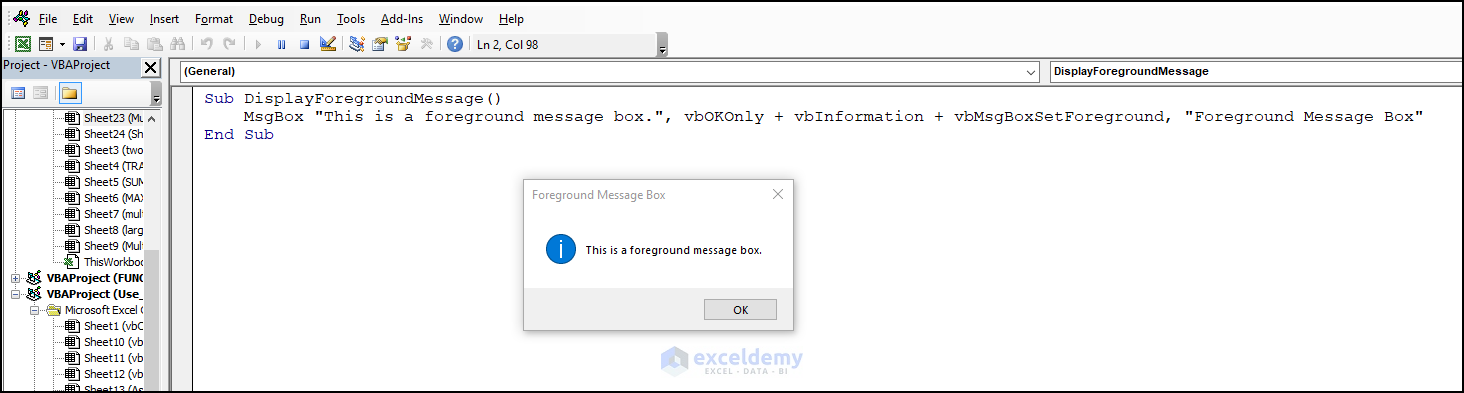
14. vbMsgBoxRight – Align Message Boxes to the Right
- Use the code:
Sub DisplayRightAlignedMessage()
MsgBox "This is a right-aligned message box.", vbOKOnly + vbInformation + vbMsgBoxRight, "Right-Aligned Message Box"
End Sub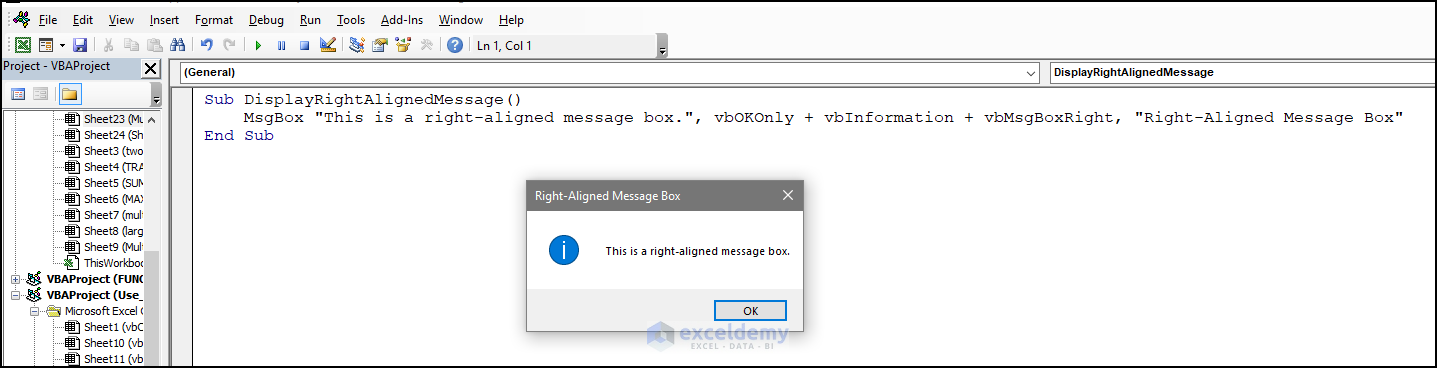
15. vbInformation – Denote Information
To display an icon with the letter ‘i’ inside a blue-filled circle.
- Use the code:
Sub MsgBox_vbInformation()
MsgBox "This is an information box.", vbInformation
End SubUsing Title Argument in the MsgBox Function in Excel
The default title of the message box is Microsoft Excel.
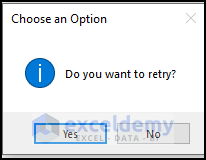
Define a title (”Choose an Option”) by entering it within Double-Quotes (“ “) in the third argument of the MsgBox function.
- For a message box containing Yes and No buttons, use the code:
Sub MsgBox_Title()
MsgBox "Do you want to retry?", vbYesNo + vbInformation, "Choose an Option"
End SubUsing a MsgBox in Excel – 5 Examples
Example 1 – Using the MsgBox Function to Output Information
Steps
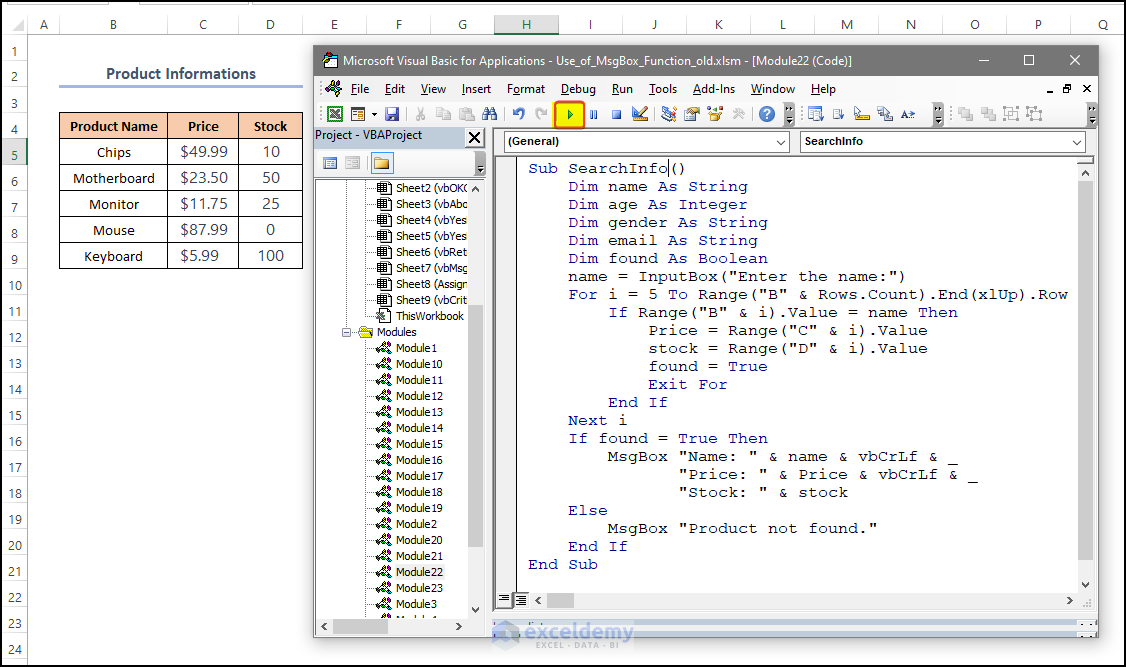
- Consider the dataset below.
- Open the VBA editor in the developer tab and enter the following code in the code window:
Sub SearchInfo() Dim name As String Dim age As Integer Dim gender As String Dim email As String Dim found As Boolean name = InputBox("Enter the name:") For i = 5 To Range("B" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row If Range("B" & i).Value = name Then Price = Range("C" & i).Value stock = Range("D" & i).Value found = True Exit For End If Next i If found = True Then MsgBox "Name: " & name & vbCrLf & _ "Price: " & Price & vbCrLf & _ "Stock: " & stock Else MsgBox "Product not found." End If End Sub
- In the input box, enter “Motherboard”.
- Click OK.
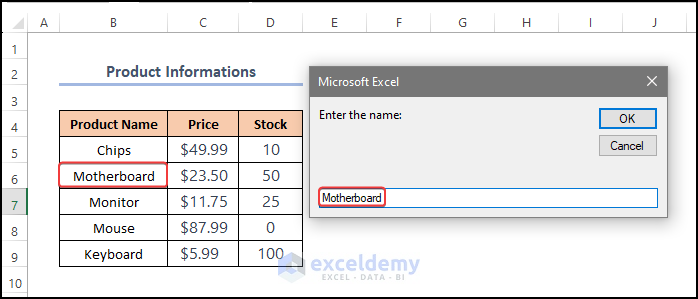
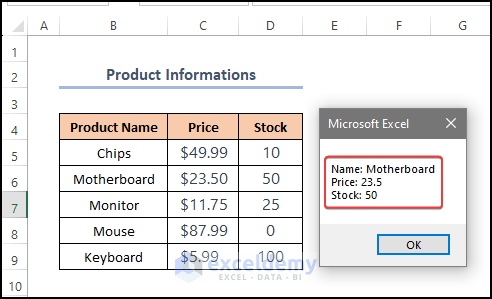
The message box displays Name, Price and Stock of the product.
Example 2 – Using the vbYesNo MsgBox Function to Delete a Specific Row in Excel
Steps
- Consider the dataset below.
- Open the VBA editor in the developer tab and enter the following code in the code window:
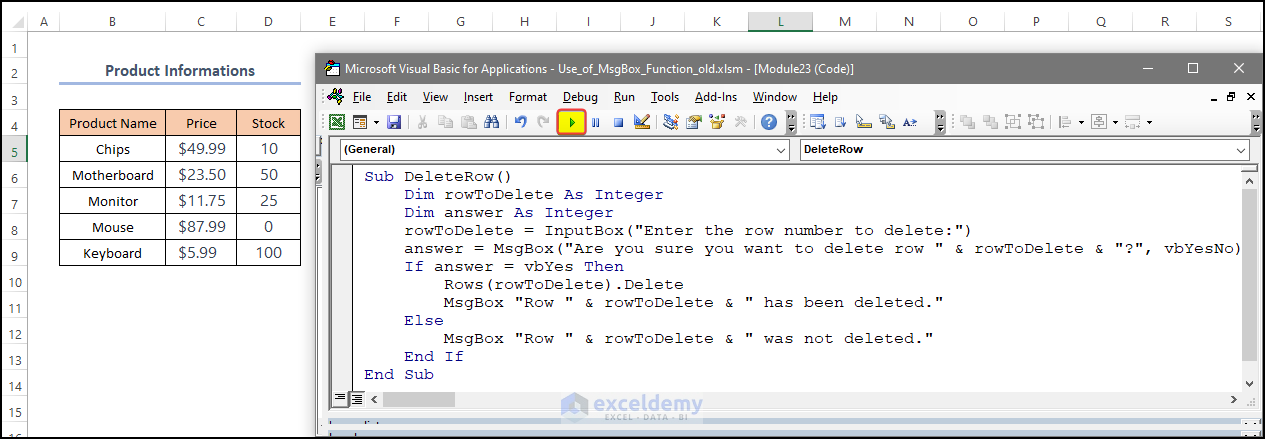
Sub DeleteRow()
Dim rowToDelete As Integer
Dim answer As Integer
rowToDelete = InputBox("Enter the row number to delete:")
answer = MsgBox("Are you sure you want to delete row " & rowToDelete & "?", vbYesNo)
If answer = vbYes Then
Rows(rowToDelete).Delete
MsgBox "Row " & rowToDelete & " has been deleted."
Else
MsgBox "Row " & rowToDelete & " was not deleted."
End If
End Sub- Click Run.
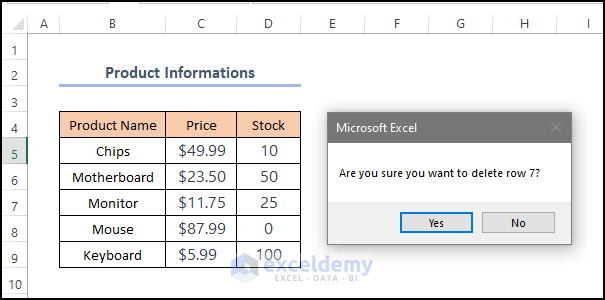
An input box is displayed asking for the row serial number. Enter 7 (here).
- Click OK.
- A confirmation message is displayed. Click Yes.
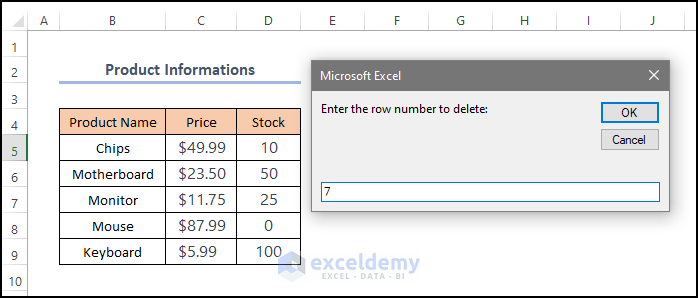
Row 7 was deleted.
- Click OK.
Example 3 – Create a MsgBox with Variables
Steps
- Enter the following code in the VBA Editor and click Run or press F5 to run the code:
Sub MsgBox_Variable()
'variable declaration
Dim button_option As Integer
'(1) create a MsgBox with buttons and Question icon
'(2) assign the options of the MsgBox to the variable
button_option = MsgBox _
("Do you want to exit Excel", vbYesNo + vbQuestion)
'show a MsgBox depending on the value of the variable
If button_option = vbYes Then
MsgBox "Thank you for using this application"
Else
MsgBox "You chose not to exit"
End If
End Sub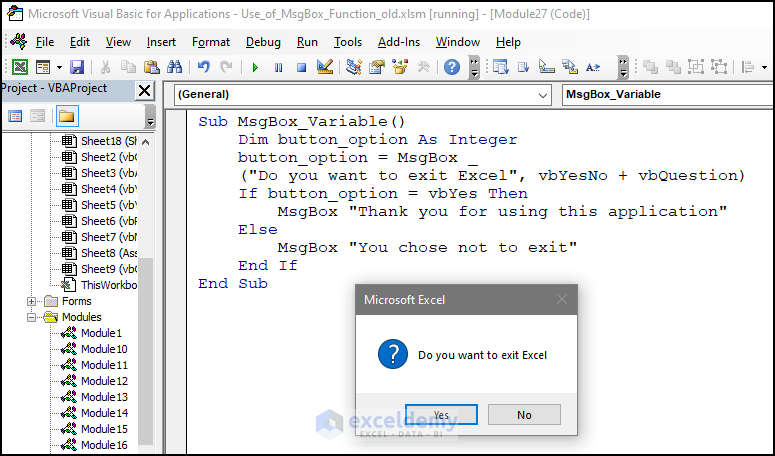
This VBA code creates a MsgBox with a question icon and Yes/No buttons and assigns the users’ selection to the variable button_option. The code displays a different MsgBox depending on the users’ selection. If the user selects Yes, a MsgBox is displayed thanking them for using the application. Otherwise, the MsgBox displays they chose not to exit.
Example 4 – Using a MsgBox to Handle Errors
Steps
- Enter the following code:
Sub Error_Handling()
On Error GoTo Error_Text
Dim int_1, int_2 As Range
Dim Addition As Integer
Set int_1 = Application.InputBox _
("Please insert the first number", Type:=8)
Set int_2 = Application.InputBox _
("Please insert the second number", Type:=8)
Addition = int_1 + int_2
MsgBox "The sum of the numbers is " & Addition
Exit Sub
Error_Text:
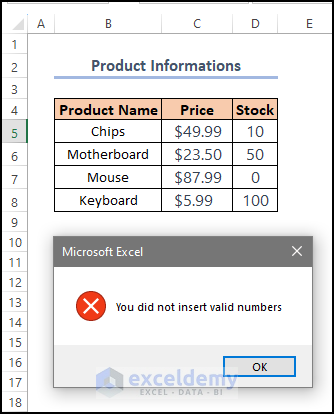
MsgBox "You did not insert valid numbers", vbCritical
End Sub- Run the code.
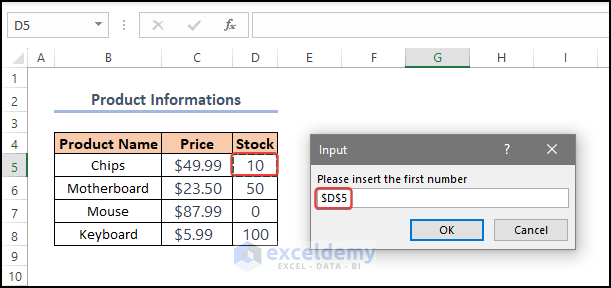
- An input box asks for the first number. Enter it.
- Click OK.
VBA Code Breakdown
Sub Error_Handling(): declares the VBA subroutine: “Error_Handling”.
On Error GoTo Error_Text:
- Sets the error handling for the subsequent lines. If an error occurs, the code moves to the “Error_Text” section of the subroutine.
Dim int_1, int_2 As Range:
- Declares two variables: “int_1” and “int_2” as Range objects. “int_1” is declared as a Variant data type and not as Range. To explicitly declare it as a Range, use the line :
Dim Addition As Integer:
- Declares the variable: “Addition” as an integer data type.
Set int_1 = Application.InputBox(“Please insert the first number”, Type:=8):
- Prompts the user to input the first number by displaying an InputBox. The input value is assigned to the “int_1” variable. The Type argument specifies the input type as a number.
Set int_2 = Application.InputBox(“Please insert the second number”, Type:=8):
- Prompts the user to input the second number by displaying another InputBox. The input value is assigned to the “int_2” variable.
Addition = int_1 + int_2:
- Calculates the sum of the two input numbers and assigns the result to the “Addition” variable.
MsgBox “The sum of the numbers is ” & Addition:
- Displays a message box with the text “The sum of the numbers is [Addition]” where [Addition] is replaced with the value of the “Addition” variable.
Exit Sub:
- Is executed if there are no errors and exits the subroutine.
Error_Text:
- Labels the beginning of the error handling section.
MsgBox “You did not insert valid numbers”, vbCritical:
- Displays a message box with the text “You did not insert valid numbers”. The “vbCritical” argument specifies the type of message box as critical.
- Enter the second number. Here, B5.
- Click OK.
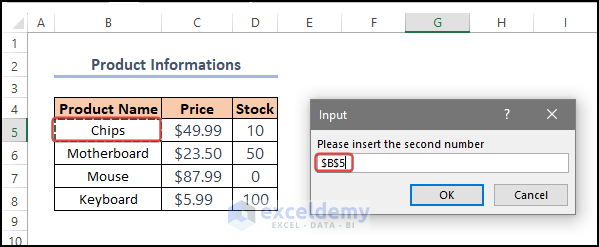
A warning message displays “You did not insert valid numbers”.
D5 contains data in String type. Mixing data types leads to an error.
- Click OK.
- Enter the following code in the VBA Editor and click Run or F5 to run the code:
The code has an error handling declaration to manage any errors. It declares two variables, int_1 and int_2, and assigns user inputs to the variables. It adds the two variables and displays the result using a MsgBox. If an error occurs, it displays a MsgBox with an error message. The code ends with an Exit Sub statement.
Example 5 – Create MsgBox with a Userform
Steps
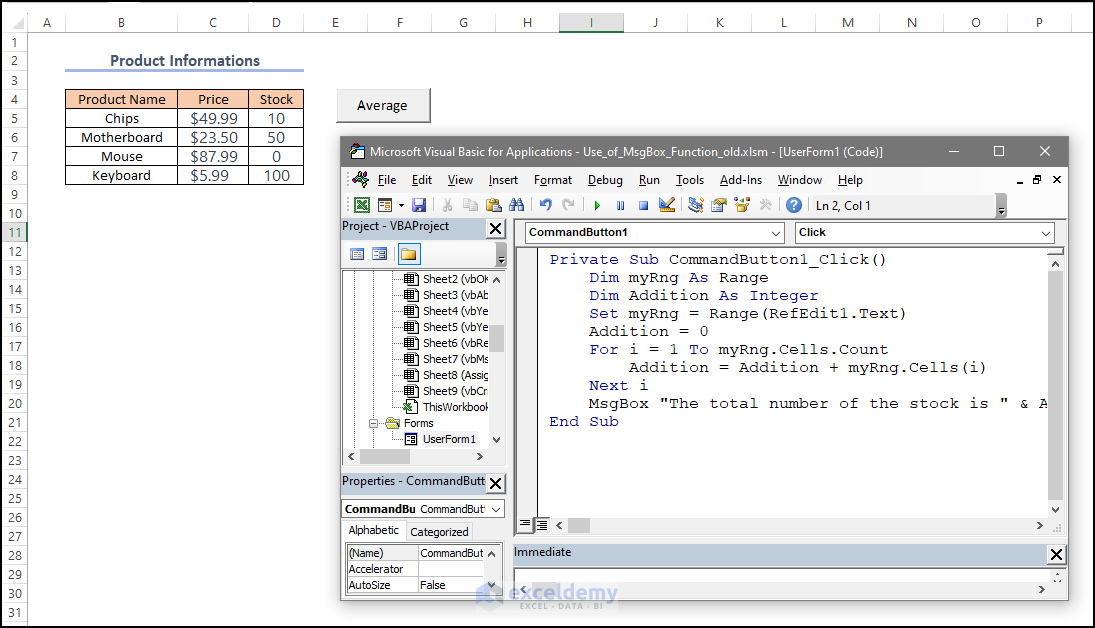
Observe the Userform below:
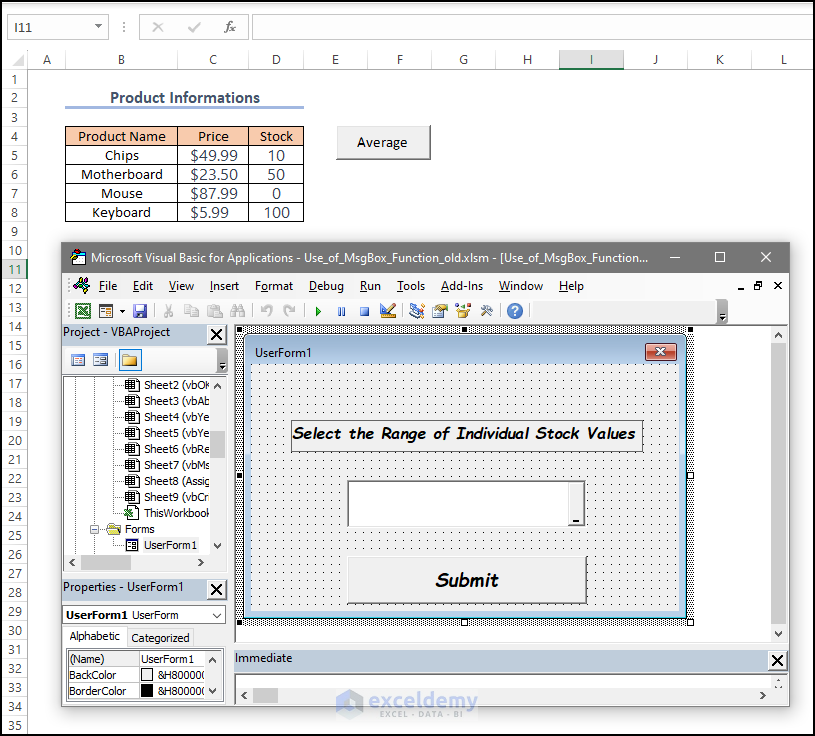
- Double-click the Submit Button to enter the coding section. Enter the following code in the code editor window.
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Dim myRng As Range
Dim Addition As Integer
Set myRng = Range(RefEdit1.Text)
Addition = 0
For i = 1 To myRng.Cells.Count
Addition = Addition + myRng.Cells(i)
Next i
MsgBox "The total number of the stock is " & Addition
End Sub
VBA Code Breakdown
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click():
- Declares a VBA subroutine that will be executed when the user clicks a command button in the worksheet.
Dim myRng As Range:
- Declares the variable: “myRng” as a Range object.
Dim Addition As Integer:
- Declares the variable: “Addition” as an integer data type.
Set myRng = Range(RefEdit1.Text):
- Sets the “myRng” variable to the range of cells that is specified in the RefEdit1 control in the worksheet.
Addition = 0:
- Initializes the “Addition” variable to zero.
For i = 1 To myRng.Cells.Count:
- Starts a For loop that will iterate from 1 to the number of cells in the “myRng”.
Addition = Addition + myRng.Cells(i):
- Adds the value of the i-th cell in the “myRng” range to the “Addition” variable.
Next i:
- The For loop moves to the next iteration.
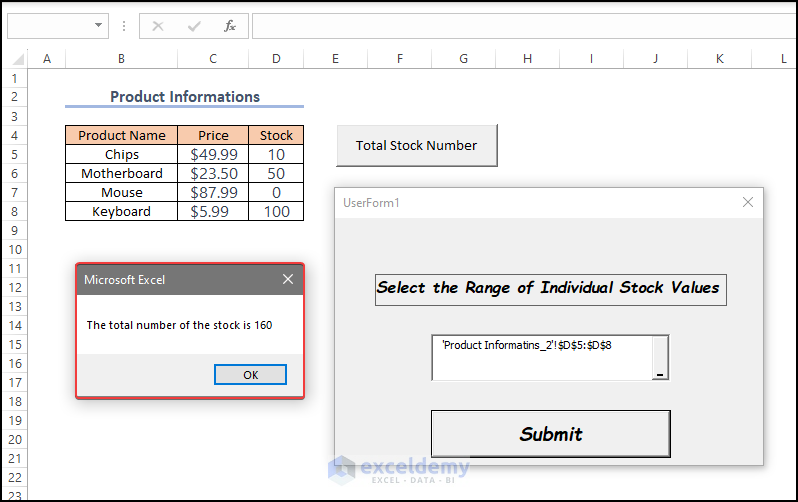
MsgBox “The total number of the stock is ” & Addition:
- Displays a message box with the text “The total number of the stock is [Addition]” ;[Addition] is replaced with the value of the “Addition” variable.
- Enter the code and launch the UserForm.
- Select D5:D8 as the input range.
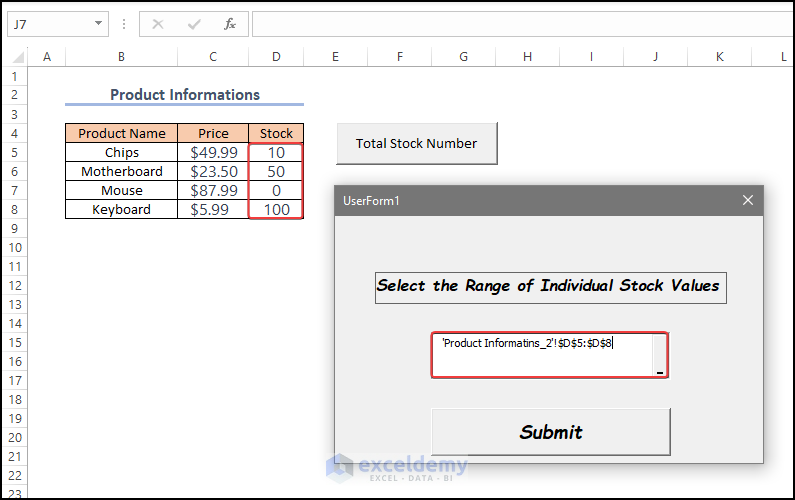
- Click Submit
A message box displays the stock in the selected range.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do I answer a message box in VBA?
You can use the two-way message box function.
- Use the following code in the VBA Userform
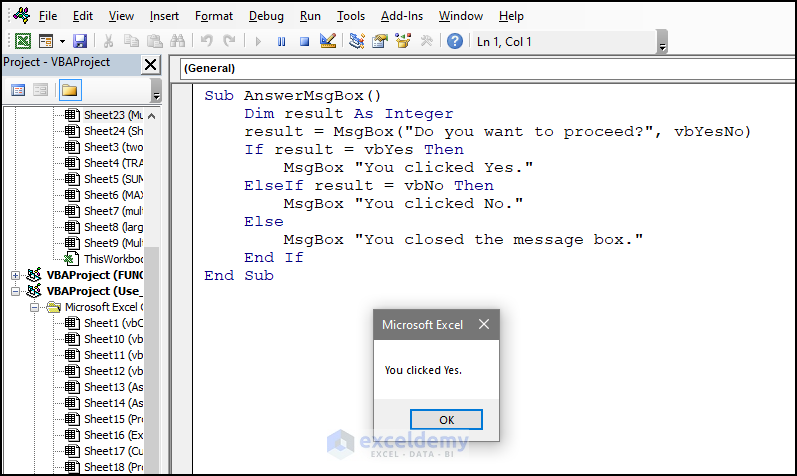
Sub AnswerMsgBox()
Dim result As Integer
result = MsgBox("Do you want to proceed?", vbYesNo)
If result = vbYes Then
MsgBox "You clicked Yes."
ElseIf result = vbNo Then
MsgBox "You clicked No."
Else
MsgBox "You closed the message box."
End If
End Sub- Run the code.
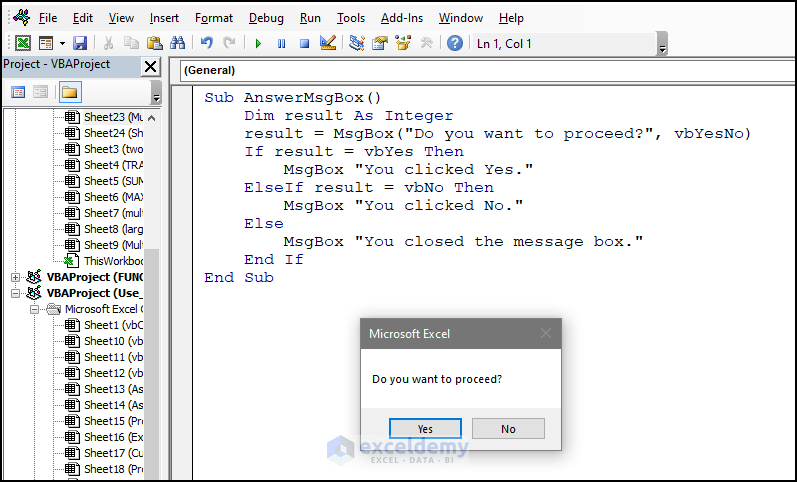
- Click Yes.
2. How Do I Write Multiple Lines in aVBA MsgBox ?
- Use the vbCrLf constant or the vbNewLine constant.
Below is an example:
Sub MultipleLinesMsgBox()
MsgBox "This is line 1" & vbNewLine & "This is line 2" & vbNewLine & "This is line 3"
End Sub
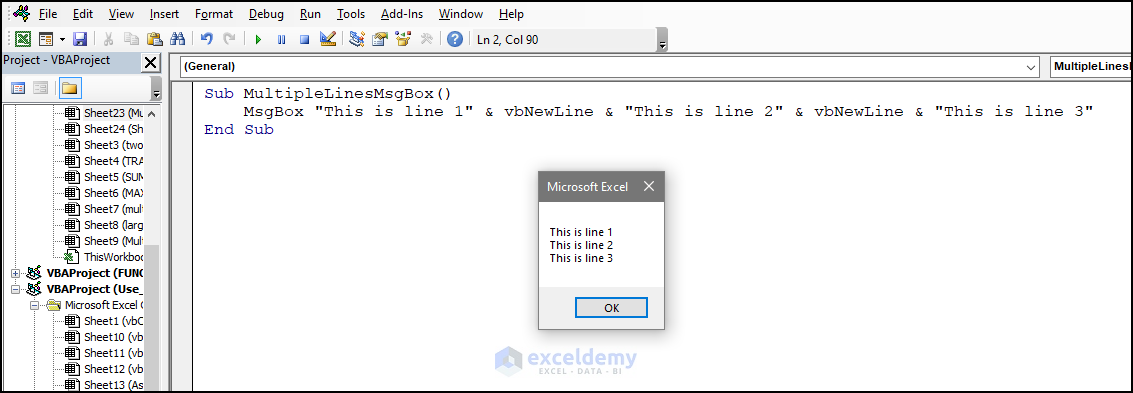
Related Articles
- How to Use VBA Forecast Function in Excel (3 Ideal Examples)
- Call a Sub in VBA in Excel (4 Examples)
- How to Create a Body Mass Index Calculator in Excel Using VBA
- Use VBA Asc Function (5 Practical Examples)
- Use VBA StrComp in Excel (5 Common Examples)