Download Practice Workbook
Example 1 – Reference Worksheets from Same Workbook
Steps:
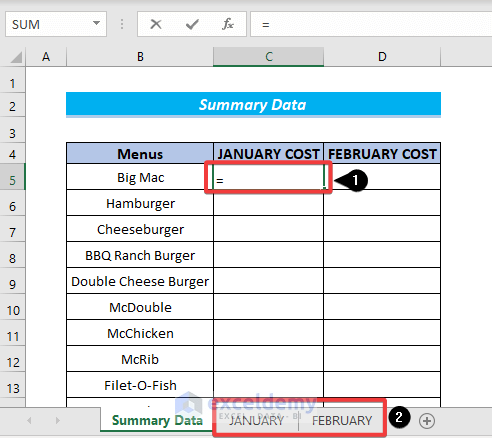
- Click on the desired cell to insert a reference. We have selected cell C5.
- Enter =.
- Select any of the sheets as shown in the image below.
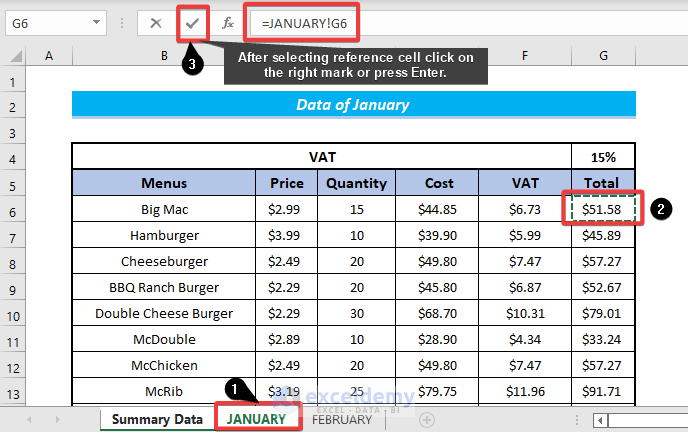
- In the referenced worksheet, choose the cell (cell G6 here) you wish to refer to and press Enter.
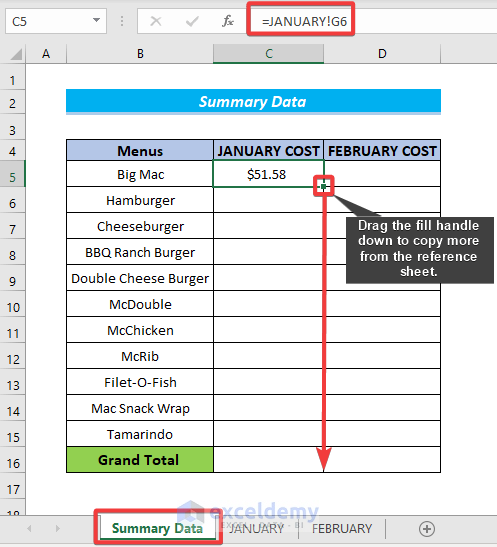
- Drag the fill handle to fill up the rest of the cells in the column.
Read More: Excel VBA Examples with Cell Reference by Row and Column Number
Example 2 – Reference Sheets from Different Workbooks
2.1 Closed Workbook
When you open an additional worksheet and refer to it, you also have to supply the file name with sheet name and cell/range. You have to create a reference for a closed workbook as well as mention the file path.
Steps:
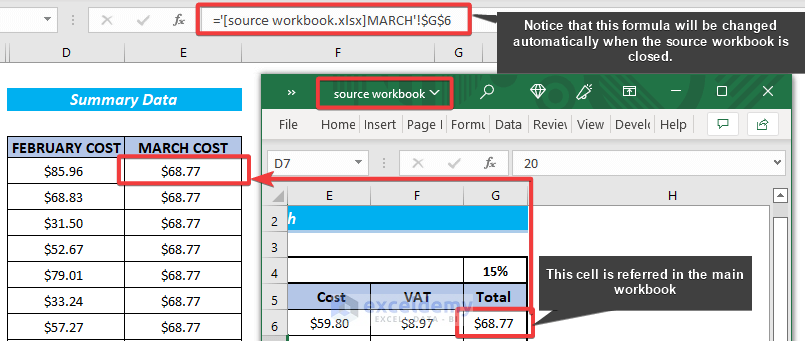
- A reference to cell G6 in the MARCH worksheet of the sample File workbook is provided below. As this file is not opened, the following formula refers to where the file is stored.
='C:\Users\Desktop\MARCH'!$G$6- The following elements are included in the reference:
♣ File Path – the location of the external file is placed
♣ Filename – external workbook name
♣ Sheet Name – the name of the sheet where G6 is located.
♣ Cell/Range Location -the cell (in this case, it is G6).
Note:
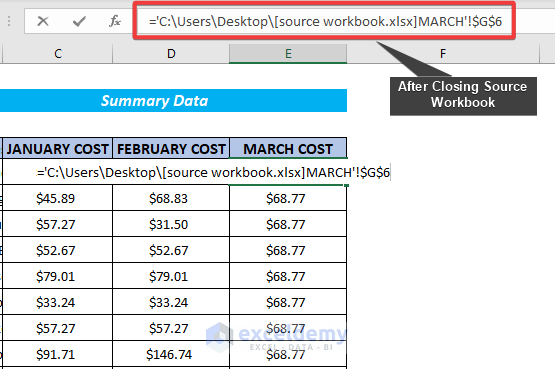
When you create external references to open workbooks and then close them, you will notice that the reference changes automatically. After you close the external workbook, Excel inserts a reference to the file path automatically.
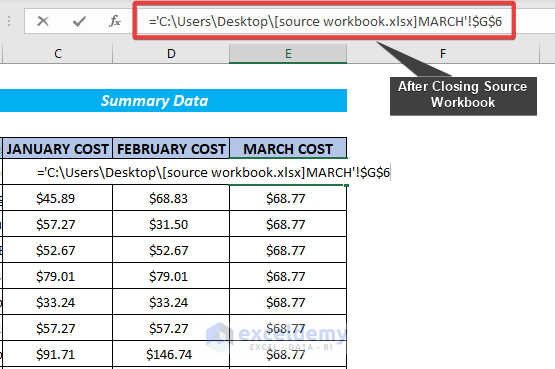
2.2 Opened Workbook
When referencing an external open workbook, you must include the workbook name, worksheet name and cell/range address. The following formula can be used to refer an external open worksheet.
='[FileName]SheetName!CellAddressSteps:
- Click on the desired cell and enter =.
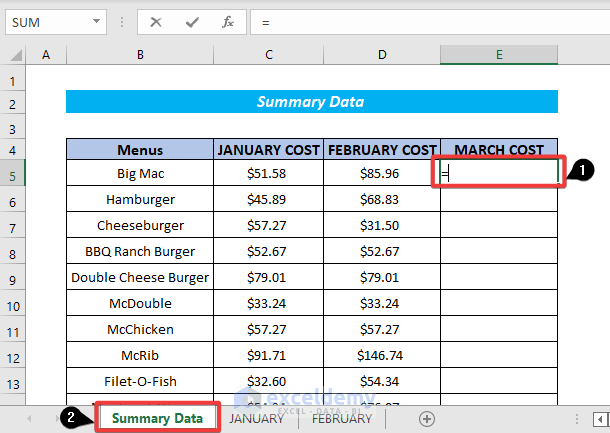
- Select the open workbook after placing the cursor on Excel in the taskbar.
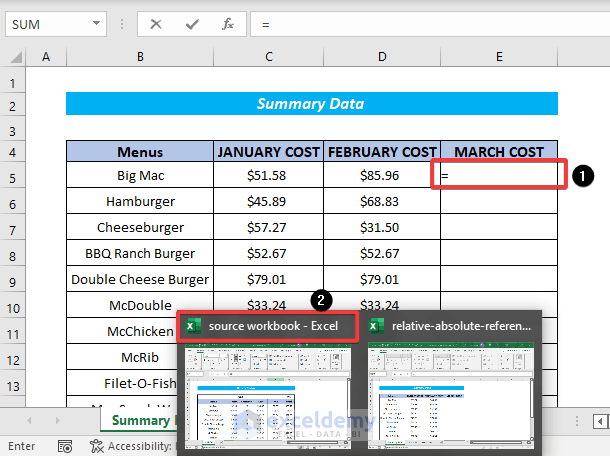
- Select the required cell that you want in the summary table.
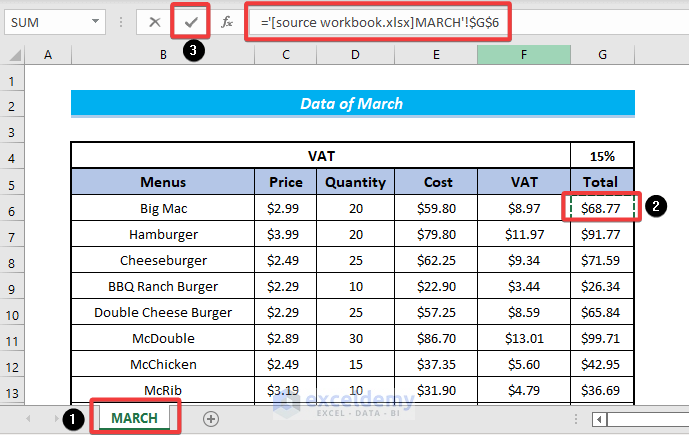
- Use the Fill Handle tool for the remaining cells.
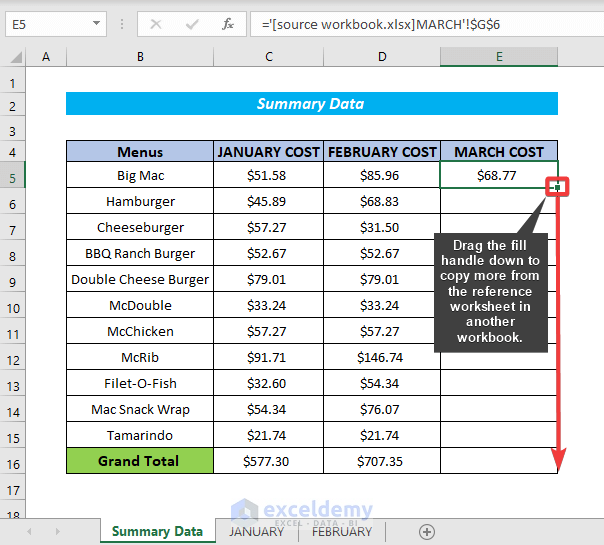
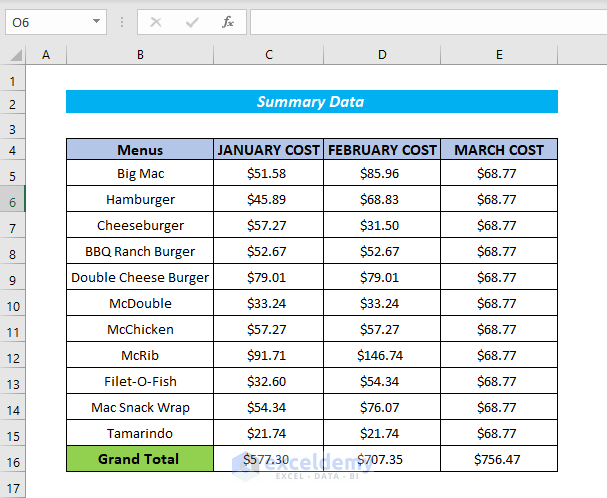
- The cost in March is added to the summary table and the summary table will be displayed as shown in the following image.
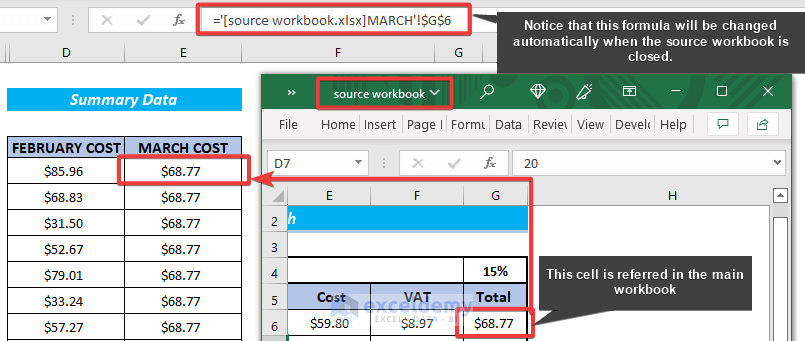
Note: The referencing formula for the opened workbook will automatically be changed by Excel after closing the source workbook.
- Excel has taken the file directory of the source workbook to do the referencing. The fact is that we also have used the very same formula for referencing a cell that is in the closed workbook.
Read More: How to Use Cell Value as Worksheet Name in Formula Reference in Excel
Similar Readings
- How to Reference Text in Another Cell in Excel (14 Ways)
- [Fixed] F4 Not Working in Absolute Cell Reference in Excel (3 Solutions)
- How to Use Variable Row Number as Cell Reference in Excel
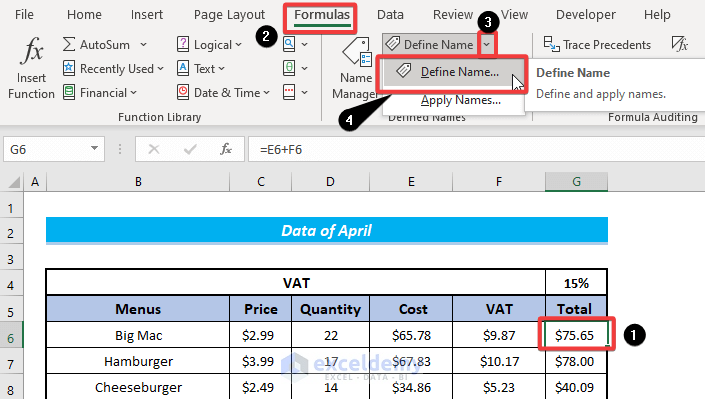
Example 3 – Reference Defined Name from Other Worksheets
Steps:
- Select all of the cells that you wish to include in the named range.
- Navigate to the Formulas tab.
- In the Defined Names group, select the Define Name option.
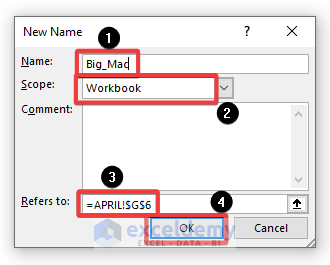
- Give the cell a name in the New Name dialog box, we have used Big-Mac. Remember that there cannot be any spaces in the name.
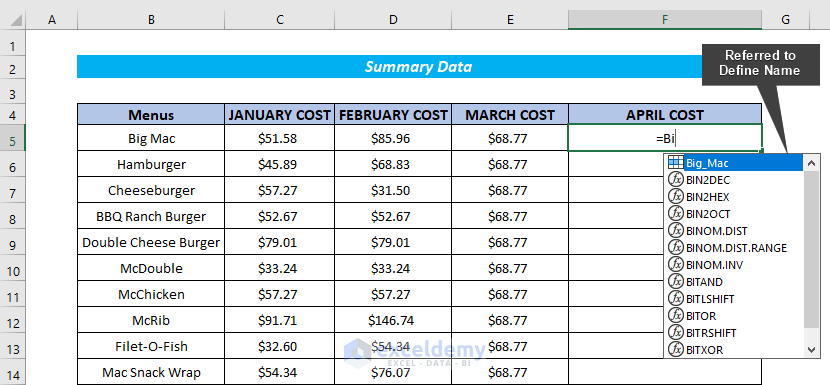
3.1 Same Workbook
- We have named a cell in another workbook. We can call that cell by entering the cell’s name in the summary worksheet.
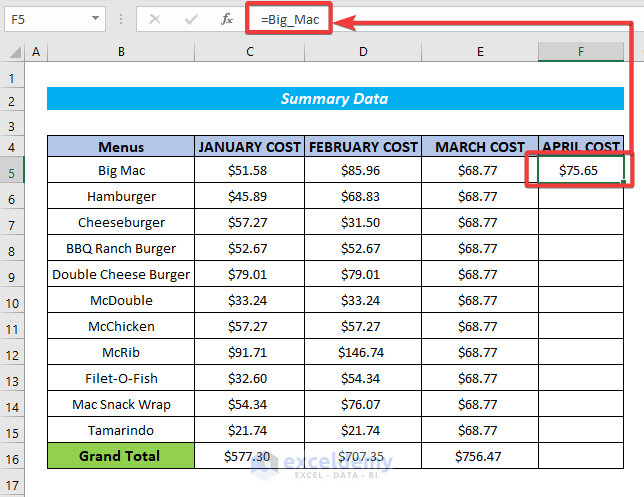
- Press Enter, and it will give a cell value like the image below.
3.2 Other Workbook
3.2.1 Opened Workbook
For example, if we have an Excel workbook named source workbook.xlsx and a named range called Hamburger, we can use the following formula to acquire the total of this cell from another workbook:
='source workbook.xlsx'!HamburgerNote:
If we don’t have space in our workbook, we can use the formula like this:
=sourceworkbook.xlsx!Hamburger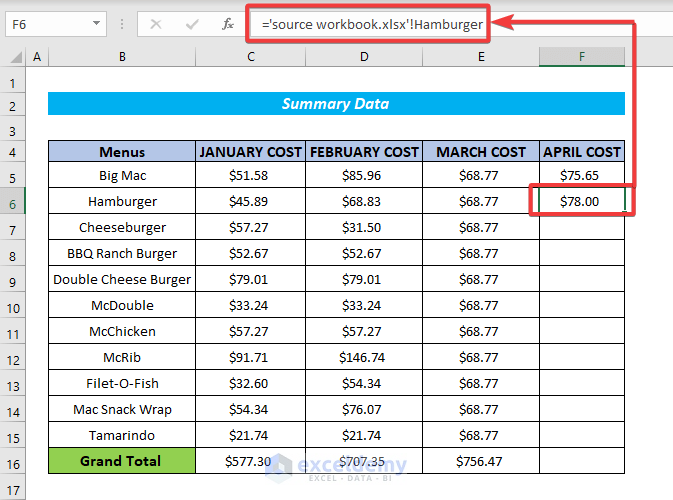
3.2.2 Closed Workbook
If we are accessing a named range in a closed workbook, we must also mention the file location. For example,
='C:\Users\Desktop\source workbook.xlsx'!Hamburger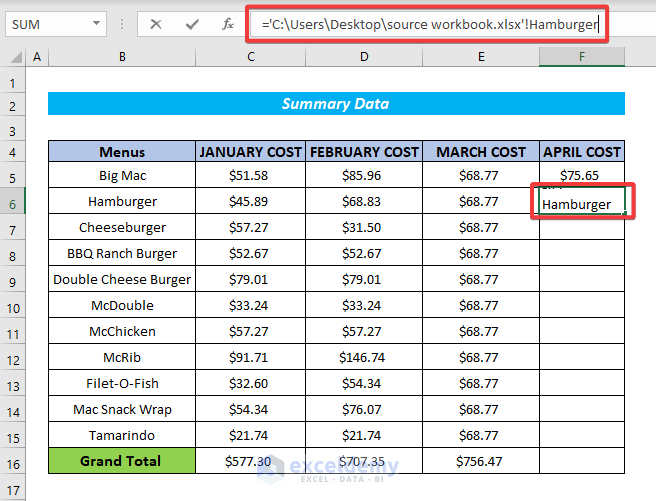
Read More: [Fixed!] Relative Cell Reference Not Working in Excel
Example 4 – Excel Reference Cell in Another Sheet Dynamically Based on Value
We can use references from worksheets in the INDIRECT function.
4.1 Same workbook
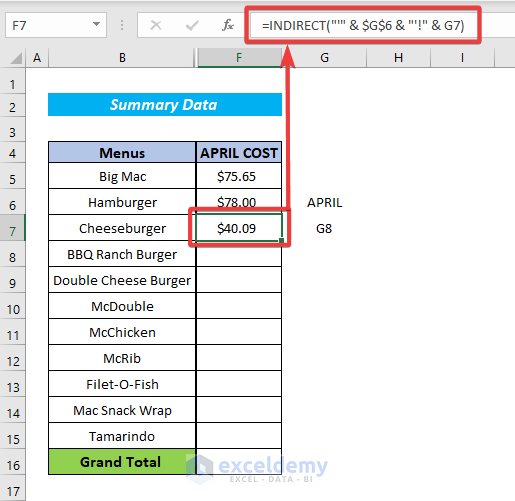
Suppose, we have some vital data in the APRIL worksheet that we want to extract into a Summary Datasheet. Enter the following formula in cell F7.
=INDIRECT("'"&$G$6&"'!"&G7)- Sheet’s name is in $G$6
- Cell to pull data from in G7
Read More: How to Use Cell References in Excel Formula (All Possible Ways)
4.2 Another Workbook
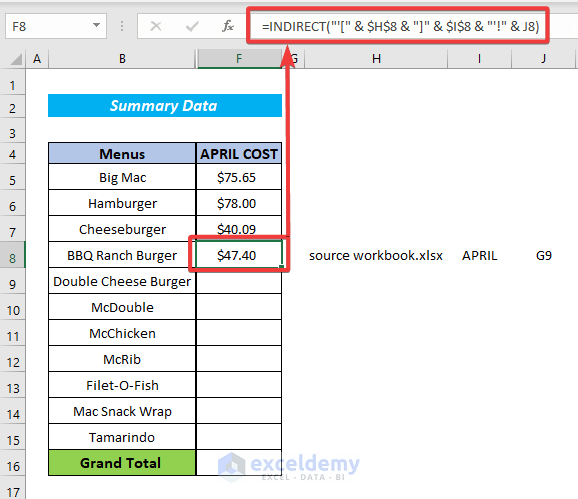
We intend to construct a standard reference to another book (apostrophes are used if our book and/or sheet titles include spaces):
=INDIRECT("'["&$H$8&"]"&$I$8&"'!"&J8)- Book name in $H$8
- Sheet name in $I$8
- Cell address in J8
Read More: Excel VBA: Cell Reference in Another Sheet (4 Methods)
Example 5 – Reference Worksheet by Name in VBA
5.1 Reference with Code Name of Sheet
Even if you change the sheet names, Excel can still recognize the sheets by their code names (sheet1, sheet2, and so on). So, you can reference worksheets using their code names.
Example:
Sheet1.Range("F9").Value = 79>> This macro will return value 79 (numeric value), in cell F9 of sheet1.
5.2 Reference By Sheet Name
If you change the worksheet names, you can still reference them in VBA. In that case, you have to enter the sheet name in double quotes like the following macro.
Example:
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("JANUARY").Range("F9").Value = 79>> This macro will find the worksheet named JANUARY from the workbook and return 79 in cell F9.
5.3 Reference to Currently Viewed Worksheet
If you move from the currently viewed worksheet, you can still reference them in VBA. In that case, you have to use the following macro.
Example:
ActiveSheet.Range("F9").Value = 79>> This macro will find the currently viewed worksheet from the workbook and return 79 in cell F9.
5.4 Reference According to Worksheet Position
If you move among multiple worksheets, you can still reference them according to the worksheet position in VBA. In that case, you have to use the following macro.
Example:
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(1).Range("F9").Value = 79>> This macro will find the first worksheet from the workbook and return 79 in cell F9.
5.5 Reference of Last Worksheet
Whether you move among multiple worksheets, you can still reference them according to the worksheet position in VBA. In that case, you have to use the following macro.
Example:
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(ThisWorkbook.Sheets.Count).Range("F9").Value = 79>> This macro will find the last worksheet from the workbook and return 79 in cell F9.
5.6 Reference Worksheet in Another Workbook
Whether you move among multiple workbooks, you can still reference them in VBA. In that case, you have to use the following macro.
Example:
Workbooks("relative-absolute-references").Worksheets("Summary Data").Range("F9").Value = 79> This macro will find the Summary Data worksheet from the workbook named relative-absolute-references and return 79 in cell F9 in that worksheet.
Related Articles
- Excel VBA: Insert Formula with Relative Reference (All Possible Ways)
- Excel VBA: Get Cell Value from Another Workbook without Opening
- How to Lock a Cell in Excel Formula (2 Ways)
- Reference Another Sheet in Excel (3 Methods)
- How to Use Table Reference with Excel VBA (20 Examples)


