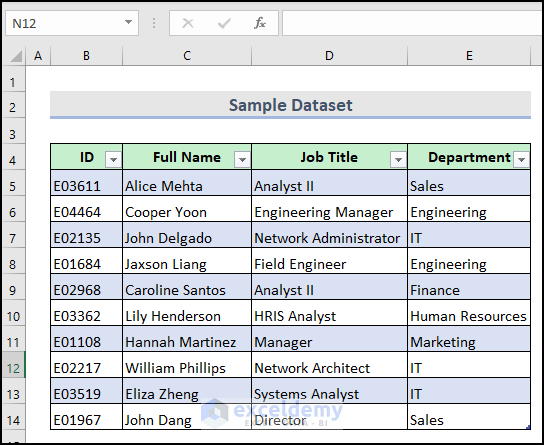
To demonstrate the different ways of deleting rows from an Excel table using VBA, we have a dataset table with 11 rows and 4 columns: ID, Full Name, Job Title, and Department.
Method 1 – VBA Code to Delete Nth Row of Excel Table
Steps:
1.1 Using ListObjects Statement
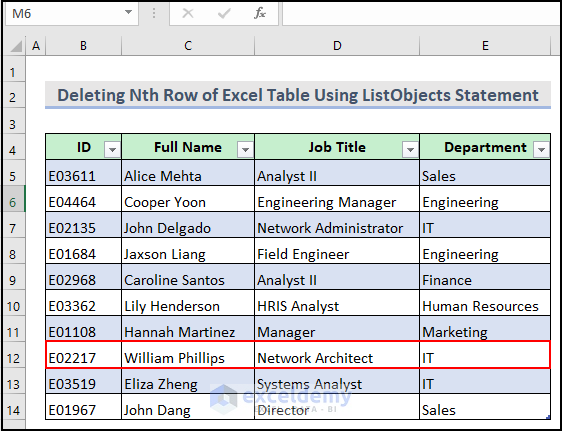
You want to delete the 8th number row in the dataset table.
Steps:
- Enter the following code in the code editor and press F5 to run the entire code.
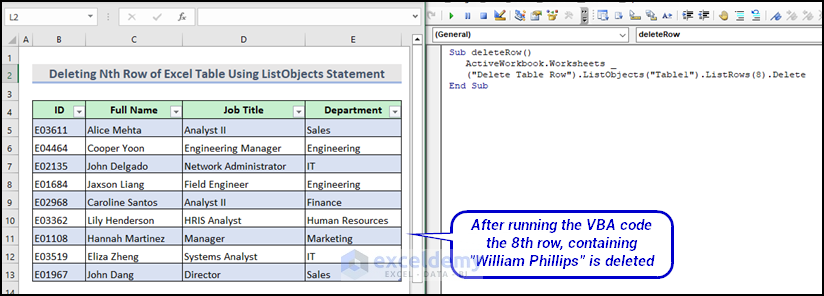
Sub deleteRow()
ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("Delete Table Row").ListObjects("Table1").ListRows(8).Delete
End SubCode Breakdown:
Here,
- ActiveWorkbook refers to the workbook that is currently active in Excel and Worksheets(“Delete Table Row”) refers to the worksheet called “Delete Table Row” in the active workbook.
- ListObjects(“Table1”) refers to a table called “Table1” in the “Delete Table Row” worksheet and ListRows(8) refers to the eighth row of the “Table1” table.
Here is the final output after running the VBA macro.
1.2 Using If Statement
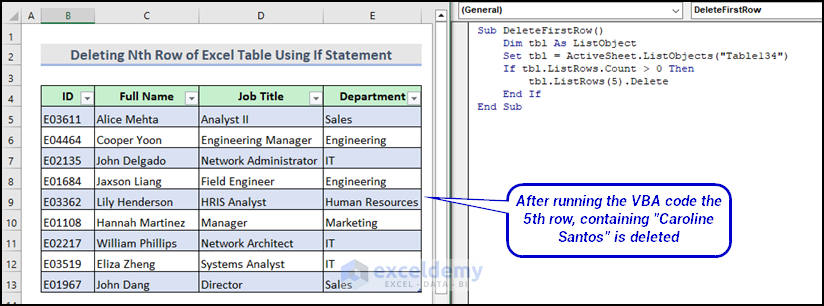
You want to delete the 5th number row in the dataset table. I have attached a demonstrative video here for your better understanding.
Steps:
- Enter the following code in a new module and press F5 to run the entire code.
Sub DeleteFirstRow()
Dim tbl As ListObject
Set tbl = ActiveSheet.ListObjects("Table134")
If tbl.ListRows.Count > 0 Then
tbl.ListRows(5).Delete
End If
End SubCode Breakdown:
Here,
Dim tbl As ListObject- This line declares a variable named tbl as a ListObject data type.
Set tbl = ActiveSheet.ListObjects("Table134")- This line assigns the ListObject for the table named “Table134” in the active sheet to the tbl variable. ListObject is the Excel VBA object that represents a table in a worksheet.
If tbl.ListRows.Count > 0 Then
tbl.ListRows(5).Delete
End If- In this part of the code, it checks if the table has at least one row, and if the table has at least one row, it deletes the fifth row of the table. You can put your preferred row number.
Here is the final output after running the VBA macro.
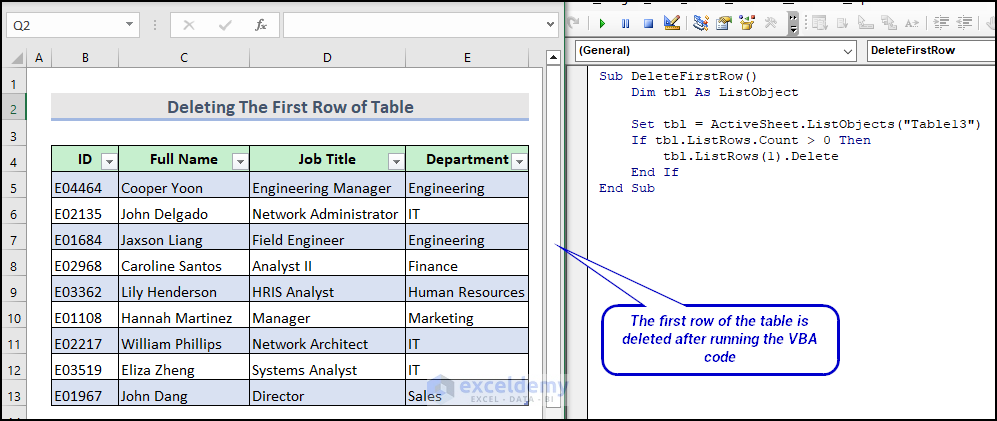
Method 2 – Deleting the First Row from the Table on the Worksheet Using VBA
Below is a demonstrative video here for your better understanding.
Steps:
- Enter a new module and copy and paste the following code. .
Sub DeleteFirstRow()
Dim tbl As ListObject
Set tbl = ActiveSheet.ListObjects("Table13")
If tbl.ListRows.Count > 0 Then
tbl.ListRows(1).Delete
End If
End Sub
- Press F5 to run the entire code
Code Breakdown:
Here,
Dim tbl As ListObject This line declares a variable named tbl as a ListObject.
Set tbl = ActiveSheet.ListObjects("Table13")Assigning tbl variable to the Table13 object on the active sheet. Here, Table13 is the table name of the active sheet. You can put your preferred table name.
If tbl.ListRows.Count > 0 Then
tbl.ListRows(1).Delete
End IfThis If statement checks if there are any rows in the table and deletes the first row of the table.
Here is the final output.
Method 3 – Using VBA Code to Delete Multiple Rows from Table in Excel
Below is a is a step-by-step video for your better understanding.
- Enter a new module and copy and paste the following code.
- Press F5 to run the entire code.
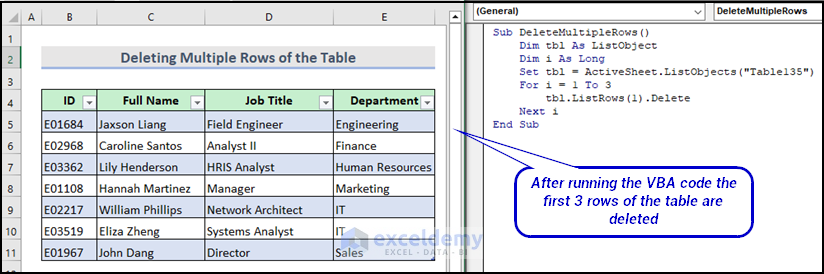
Sub DeleteMultipleRows()
Dim tbl As ListObject
Dim i As Long
Set tbl = ActiveSheet.ListObjects("Table135")
For i = 1 To 3
tbl.ListRows(1).Delete
Next i
End SubCode Breakdown:
Here,
Dim tbl As ListObject
Dim i As LongThese lines declare two variables: tbl as a ListObject data type and i as a Long data type.
Set tbl = ActiveSheet.ListObjects("Table135")This line assigns the ListObject for the table named “Table135” in the active sheet to the tbl variable.
For i = 1 To 3
tbl.ListRows(1).Delete
Next iWe used a For Loop, which loops through the first three rows of the table and deletes the first row of the table.
Here is the final output image after running the VBA macro.
 Read More: How to Delete Multiple Rows with VBA in Excel
Read More: How to Delete Multiple Rows with VBA in Excel
Method 4 – VBA Code to Delete Visible Rows After Filtering
In our table dataset, we have a column named Department. I have filtered the data table by the Department column for the employees who are in the IT department, and I want to delete all of the visible rows after filtering using VBA.
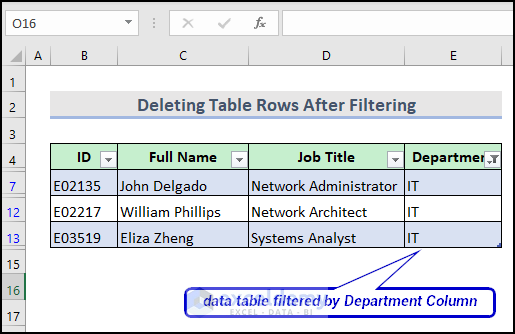
A demonstrative video is here for your better understanding.
- Enter a new module and copy-paste the following code:
Sub DeleteVisibleTableRowsAfterFiltering()
Dim tbl As ListObject
Dim rng As Range
Dim i As Long
Set tbl = ActiveSheet.ListObjects("Table1356")
Set rng = tbl.Range
For i = tbl.ListRows.Count To 1 Step -1
If Not tbl.ListRows(i).Range.EntireRow.Hidden Then
tbl.ListRows(i).Range.EntireRow.Delete
End If
Next i
End Sub- Select the Macro name DeleteVisibleTableRowsAfterFiltering and press Run.
Code Breakdown:
Here,
Dim tbl As ListObject
Dim rng As Range
Dim i As LongThese lines declare three variables: tbl as a ListObject data type, rng as a Range data type, and i as a Long data type.
Set tbl = ActiveSheet.ListObjects("Table1356") This line of code assigns the ListObject for the table named “Table1356” in the active sheet to the tbl variable
Set rng = tbl.Range Here, we are assigning the range of the table to the rng variable.
For i = tbl.ListRows.Count To 1 Step -1
If Not tbl.ListRows(i).Range.EntireRow.Hidden Then
tbl.ListRows(i).Range.EntireRow.Delete
End If
Next iWe executed this loop through each row of the table in reverse order, which checks whether the row is visible after filtering or not. If it is, it deletes the entire row.
Here is the final output.
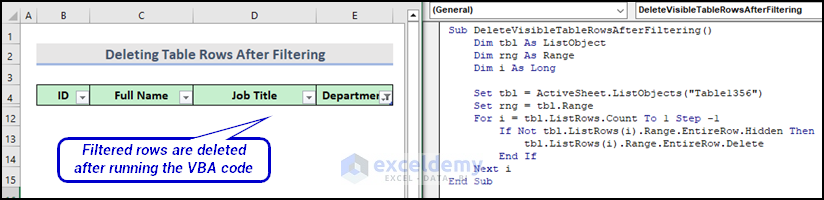
You can now return the hidden rows by selecting the Filter sign in the Department column.
Method 5 – Delete Empty Table Rows with VBA
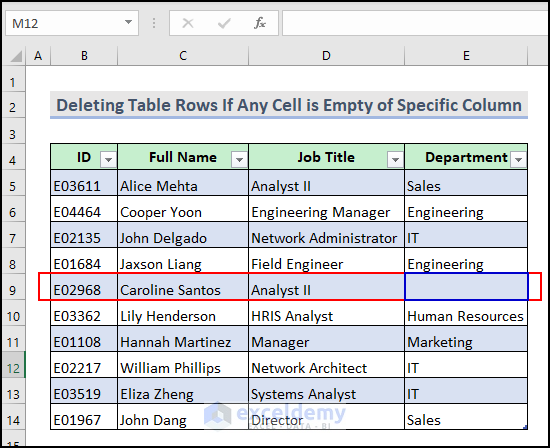
5.1 Delete If Any Cell in Excel Table is Empty of Specific Column
In our dataset, we have an empty cell in the Department column. We want to delete that row containing an empty cell in the Department Column.
You can understand better with the following step-by-step video.
- Enter a new module and copy and paste the following code:
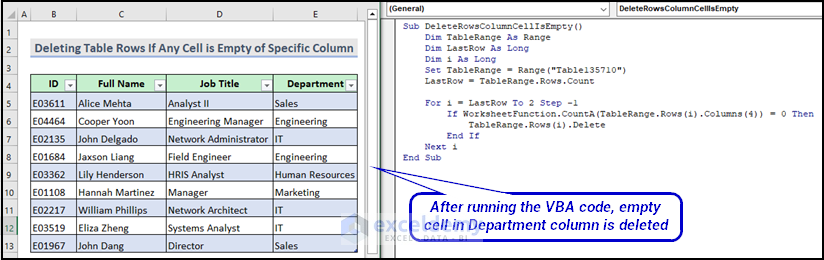
Sub DeleteRowsColumnCellIsEmpty()
Dim TableRange As Range
Dim LastRow As Long
Dim i As Long
Set TableRange = Range("Table135710")
LastRow = TableRange.Rows.Count
For i = LastRow To 2 Step -1
If WorksheetFunction.CountA(TableRange.Rows(i).Columns(4)) = 0 Then
TableRange.Rows(i).Delete
End If
Next i
End Sub- Select the Macro name DeleteRowsColumnCellIsEmpty and press Run.
Code Breakdown:
Here,
Dim TableRange As Range
Dim LastRow As Long
Dim i As LongThese three lines declare variables for the table range, last row, and counter.
Set TableRange = Range("Table135710")Assigning the table range to the TableRange variable.
LastRow = TableRange.Rows.Count We are determining the last row in the table range.
For i = LastRow To 2 Step -1
If WorksheetFunction.CountA(TableRange.Rows(i).Columns(4)) = 0 Then
TableRange.Rows(i).Delete
End If
Next iWe used a For Loop that loops through each row of the table range in reverse order. It checks if the fourth column of the current row is empty. If it is, it deletes the current row.
Here is the final output after running the VBA macro.
5.2 Delete If Any Row of Excel Table Is Completely Empty
You have a row in your dataset table that is completely empty. You want to delete that row.
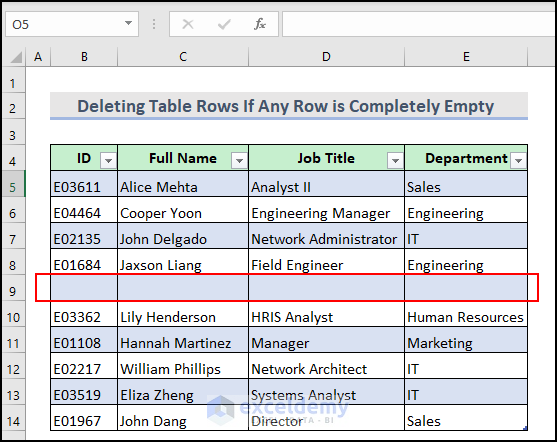
Take a look at the demonstrative video to gain a clear understanding.
- Enter the following code into a new module:
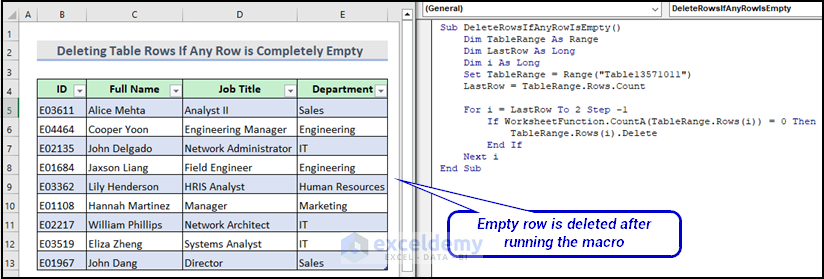
Sub DeleteRowsIfAnyRowIsEmpty()
Dim TableRange As Range
Dim LastRow As Long
Dim i As Long
Set TableRange = Range("Table13571011")
LastRow = TableRange.Rows.Count
For i = LastRow To 2 Step -1
If WorksheetFunction.CountA(TableRange.Rows(i)) = 0 Then
TableRange.Rows(i).Delete
End If
Next i
End Sub- Select the Macro name DeleteRowsIfAnyRowIsEmpty and press Run.
Code Breakdown:
Here,
Table13571011 is the data table name.
For i = LastRow To 2 Step -1
If WorksheetFunction.CountA(TableRange.Rows(i)) = 0 Then
TableRange.Rows(i).Delete
End If
Next iThis for loop goes through each row of the table range in reverse order and checks if any cell in the current row is empty. If it finds any cell in the current row is empty, then it deletes the current row.
Here is the final output after running the VBA macro.
Method 6 – Deleting Table Row Based on Specific Cell Value
You can delete rows with a specific cell value. We want to delete the row with ID E04464.
- Enter a new module and put the following code in that module.
Sub DeleteRowsBasedOnCellValue()
Dim TableRange As Range
Dim LastRow As Long
Dim i As Long
Set TableRange = Range("Table13578")
LastRow = TableRange.Rows.Count
For i = LastRow To 2 Step -1
If TableRange.Cells(i, 1).Value = "E04464" Then
TableRange.Rows(i).Delete
End If
Next i
End Sub- Select the Macro name DeleteRowsBasedOnCellValue and press Run.
Code Breakdown:
Dim TableRange As Range
Dim LastRow As Long
Dim i As LongThese three lines declare variables for the table range, last row, and counter.
Set TableRange = Range("Table13578")Assigning the table range to the TableRange variable. Here, Table13578 is the data table name.
LastRow = TableRange.Rows.CountThis line of code determines the last row of the table range.
For i = LastRow To 2 Step -1
If TableRange.Cells(i, 1).Value = "E04464" Then
TableRange.Rows(i).Delete
End If
Next iThis For Loop goes through each row of the table range in reverse order in order to check if the value in the first column of the current row is “E04464” or not. If the value in the first column is “E04464“, it deletes the current row.
Here is the final output after running the VBA macro.
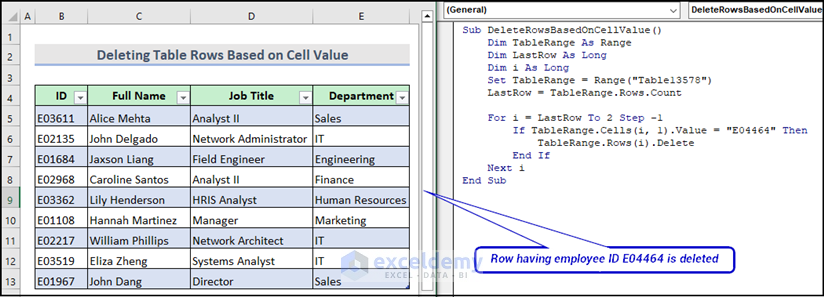
Read More: Excel VBA to Delete Row Based on Cell Value
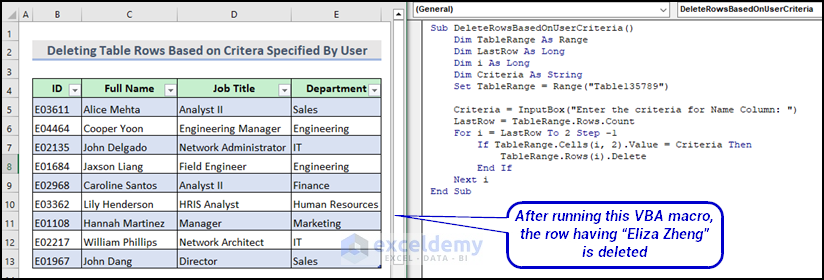
Method 7 – Deleting Table Row Based on Criteria Specified by User
- Enter another new module and copy and paste the following code:
Sub DeleteRowsBasedOnUserCriteria()
Dim TableRange As Range
Dim LastRow As Long
Dim i As Long
Dim Criteria As String
Set TableRange = Range("Table135789")
Criteria = InputBox("Enter the criteria for Name Column: ")
LastRow = TableRange.Rows.Count
For i = LastRow To 2 Step -1
If TableRange.Cells(i, 2).Value = Criteria Then
TableRange.Rows(i).Delete
End If
Next i
End Sub- Select the Macro name DeleteRowsBasedOnUserCriteria and press Run.
Code Breakdown:
Dim TableRange As Range
Dim LastRow As Long
Dim i As Long
Dim Criteria As StringThese lines declare four variables: TableRange as a Range data type, LastRow as a Long datatype, i as a Long data type and Criteria as a String data type.
Set TableRange = Range("Table135789")→ Assigning the table range to the TableRange variable. Here, Table135789 is the data table name.
Criteria = InputBox("Enter the criteria for Name Column: ")
→ Prompt the user to enter the criteria for the Name column.
LastRow = TableRange.Rows.Count→ Determines the index of the last row in the table.
For i = LastRow To 2 Step -1
If TableRange.Cells(i, 2).Value = Criteria Then
TableRange.Rows(i).Delete
End If
Next iThis For Loop goes through the rows in the table, starting from the last row and moving up. It checks if the value in the Full Name column for the current row matches the user criteria. If the value matches, then it deletes the entire row.
After running the VBA macro, an input box will appear where users must put the criteria. Suppose, the criteria on which deletion operation will be done is “Eliza Zheng”. Enter the criteria “Eliza Zheng” and click OK.
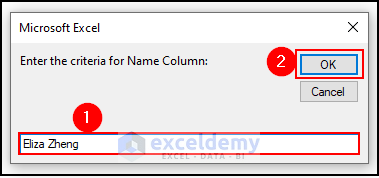
The row is deleted based on user-entered criteria. Here is the final output result.
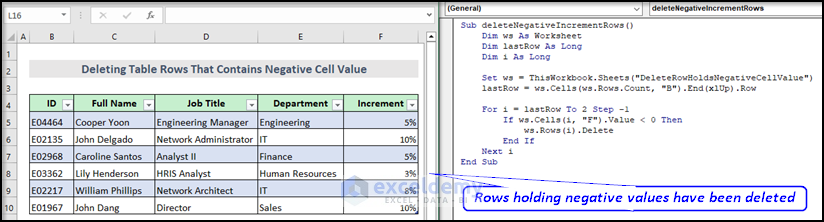
Method 8 – VBA Macro to Delete Entire Table Rows That Contain Negative Cell Value
To show this, we have added a new column named Increment to the dataset table. We have shown the increment or decrement of the employees.
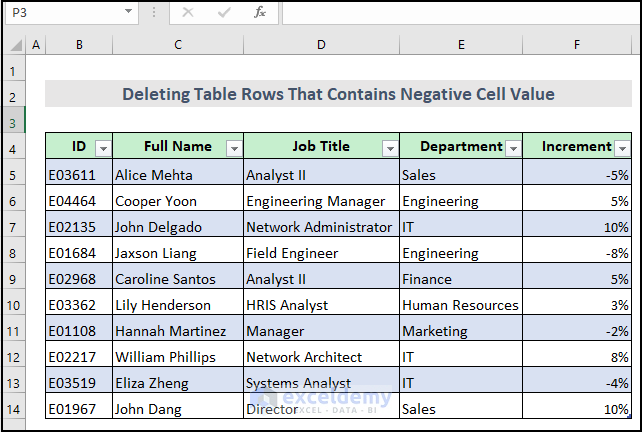
For a clear understanding, here’s a demonstrative video.
- Enter a new module and copy and paste the following code:
Sub deleteNegativeIncrementRows()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim lastRow As Long
Dim i As Long
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("DeleteRowHoldsNegativeCellValue")
lastRow = ws.Cells(ws.Rows.Count, "B").End(xlUp).Row
For i = lastRow To 2 Step -1
If ws.Cells(i, "F").Value < 0 Then
ws.Rows(i).Delete
End If
Next i
End Sub- Press F5 to run the entire code.
Code Breakdown:
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim lastRow As Long
Dim i As LongThese lines declare three variables.
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("DeleteRowHoldsNegativeCellValue")→ Setting the worksheet name. You can put your Excel worksheet name.
lastRow = ws.Cells(ws.Rows.Count, "B").End(xlUp).Row→ getting the last row number with data in column B.
For i = lastRow To 2 Step -1
If ws.Cells(i, "F").Value < 0 Then
ws.Rows(i).Delete
End If
Next iThis For Loop goes through each row in reverse order, starting from the last row. It checks if the value in column F is less than 0 (negative). If the value is negative, then it deletes the entire table row and moves on to the next row.
Here is the final output image after running the VBA macro.
Read More: How to Delete Row If Cell Contains Value Using Macro in Excel
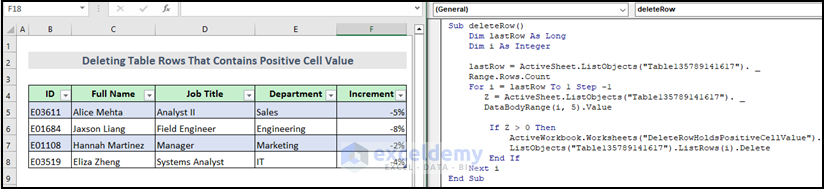
Method 9 – Delete the Entire Table Row That Contains Positive Cell Value Using VBA Macro
- Enter a new module and insert the following code:
Sub deleteRow()
Dim lastRow As Long
Dim i As Integer
lastRow = ActiveSheet.ListObjects("Table135789141617"). _
Range.Rows.Count
For i = lastRow To 1 Step -1
Z = ActiveSheet.ListObjects("Table135789141617"). _
DataBodyRange(i, 5).Value
If Z > 0 Then
ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("DeleteRowHoldsPositiveCellValue"). _
ListObjects("Table135789141617").ListRows(i).Delete
End If
Next i
End Sub- Press F5 to run the entire code.
Code Breakdown:
Dim lastRow As Long
Dim i As IntegerThese lines declare two variables: lastRow as Long and i as Integer.
lastRow = ActiveSheet.ListObjects("Table135789141617"). Range.Rows.Count→ Getting the last row number of the table. Here, Table135789141617 is the table name.
For i = lastRow To 1 Step -1
Z = ActiveSheet.ListObjects("Table135789141617"). DataBodyRange(i, 5).Value
If Z > 0 Then
ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("DeleteRowHoldsPositiveCellValue"). _
ListObjects("Table135789141617").ListRows(i).Delete
End If
Next iThis For Loop goes through each row in the table, starting from the last row and moving upwards.
Z = ActiveSheet.ListObjects("Table135789141617"). DataBodyRange(i, 5).Value→ Getting the value of the cell in column 5 (Increment column) of the current row.
If Z > 0 Then
ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("DeleteRowHoldsPositiveCellValue"). _
ListObjects("Table135789141617").ListRows(i).Delete
End IfIf the cell value is greater than 0, then it deletes the entire row and moves on to the next row in the table.
Here is the final output image after running the VBA macro.
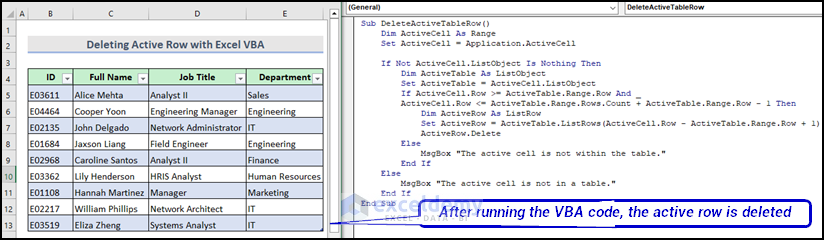
How to Delete Active Table Row with Excel VBA?
You can easily delete your current active row of the dataset table using the VBA code. Here are the steps that you need to follow.
Steps:
- Insert a new module and put the following code:
- Select the Macro name DeleteActiveTableRow and press Run.
Sub DeleteActiveTableRow()
Dim ActiveCell As Range
Set ActiveCell = Application.ActiveCell
If Not ActiveCell.ListObject Is Nothing Then
Dim ActiveTable As ListObject
Set ActiveTable = ActiveCell.ListObject
If ActiveCell.Row >= ActiveTable.Range.Row And _
ActiveCell.Row <= ActiveTable.Range.Rows.Count + ActiveTable.Range.Row - 1 Then
Dim ActiveRow As ListRow
Set ActiveRow = ActiveTable.ListRows(ActiveCell.Row - ActiveTable.Range.Row + 1)
ActiveRow.Delete
Else
MsgBox "The active cell is not within the table."
End If
Else
MsgBox "The active cell is not in a table."
End If
End SubCode Breakdown:
Dim ActiveCell As Range
Set ActiveCell = Application.ActiveCell→ Getting the active cell.
If Not ActiveCell.ListObject Is Nothing Then→ This article checks if the active cell is in a table or not.
Dim ActiveTable As ListObject
Set ActiveTable = ActiveCell.ListObject → Getting the active table.
If ActiveCell.Row >= ActiveTable.Range.Row And _
ActiveCell.Row <= ActiveTable.Range.Rows.Count + ActiveTable.Range.Row - 1 ThenHere, this If statement checks if the active cell is within the table or not.
Dim ActiveRow As ListRow
Set ActiveRow = ActiveTable.ListRows(ActiveCell.Row - ActiveTable.Range.Row + 1
ActiveRow.Delete→ Get the active row from the table and delete the active row.
Here is the final output image after running the VBA macro.
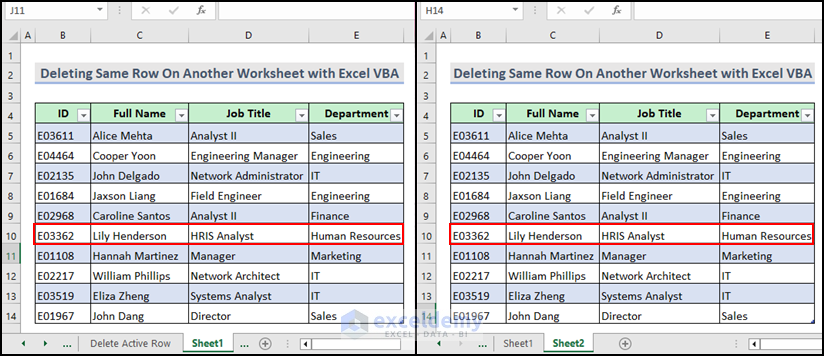
How to Delete the Same Row on Another Sheet Using Excel VBA
In our workbook, we have two worksheets named Sheet1 and Sheet2. You want to delete the row with ID E03362 from both worksheets simultaneously.
Steps:
- Insert a new module and insert the following code:
- Select the Macro name DeleteSameRowInSpecificWorksheets and press Run.
Sub DeleteSameRowInSpecificWorksheets()
Dim shtArr, i As Long, sameRow As Long
shtArr = Array("Sheet1", "Sheet2")
sameRow = Selection.Row
For i = LBound(shtArr) To UBound(shtArr)
Sheets(shtArr(i)).Rows(sameRow).EntireRow.Delete
Next i
End SubCode Breakdown:
Dim shtArr, i As Long, sameRow As LongThis line declares three variables: shtArr is an array to hold the worksheet names, i is a counter variable and sameRow is a variable to hold the row number of the selected cell.
shtArr = Array("Sheet1", "Sheet2")
→ Setting the worksheet names to be processed. Here, we have two worksheets to do the task.
sameRow = Selection.Row→ Getting the row number of the selected cell.
For i = LBound(shtArr) To UBound(shtArr)
Sheets(shtArr(i)).Rows(sameRow).EntireRow.Delete
Next iHere, this For Loop goes through the worksheet names in the shtArr array and deletes the entire row in each worksheet that matches the row number of the selected cell.
Here is the final output after running the VBA macro. The rows with ID E03362 from both worksheets are deleted simultaneously.
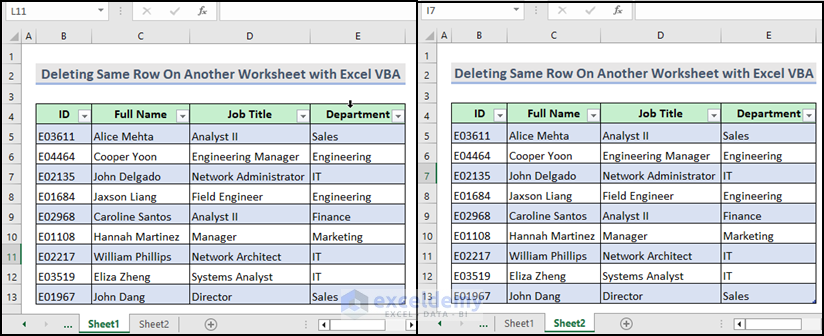
Read More: Excel VBA: Delete Row on Another Sheet
Key Takeaways
- I have shown how to launch VBA editor in Excel
- Chosen real-life dataset for better understanding.
- Focusing on how to delete table rows with VBA code in Excel.
- Explained different approaches with VBA code.
- Showed how to delete rows on another sheet using VBA code.
- Provide solutions to frequently asked questions of readers.
- Overall focused on using VBA code to delete table rows in Excel.
Download the Practice Workbook
You can download the practice workbook from here:
Related Articles
- How to Delete Selected Rows with Excel VBA
- VBA Delete Rows
- Delete Row with VBA and Shift Up Cells in Excel
- How to Delete Rows in a Range with VBA in Excel


