The Runtime Error 13 Type Mismatch in VBA is one of the most common types of errors while using VBA and occurs if the data type that is given does not match the data type that the system is expecting. However, this is not the case for every scenario. We’ll provide over a dozen of possible reasons behind the error and solutions.
How to Launch the VBA Macro Editor in Excel
In order to run any VBA code, we first need to write or edit the code in the VBA Macro Editor.
- Go to the Developer tab and then to Visual Basic. This will open the Visual Basic window.
- Select Insert and Module in the macro editor.
- An empty module will appear on the screen where you can write the code.
Runtime Error 13 Type Mismatch in VBA: 8 Possible Reasons with Solutions
If you press Debug in the VBA window, the portion with the error will be highlighted.
Reason 1 – Setting a String Value to a Number Type Variable
If you assign a string value to a numeric data type variable, VBA cannot convert it.
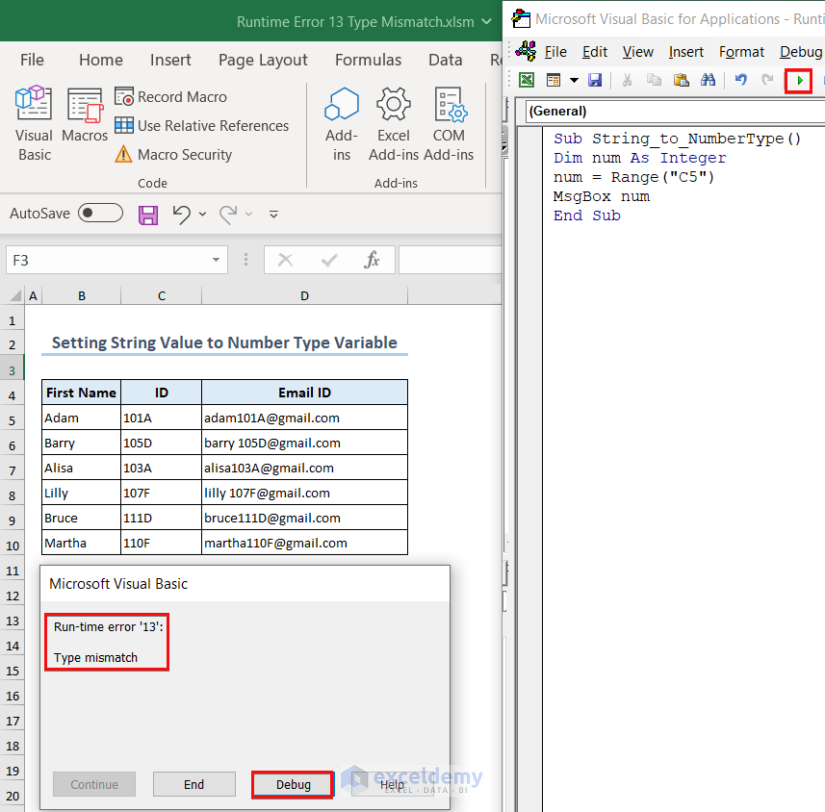
- The error prompt showing the data type mismatch error will appear on the screen.
- Press Debug to find the line where the error occurred.
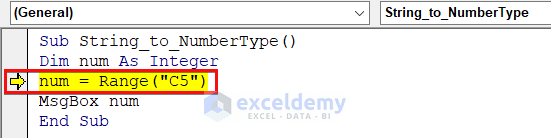
- The error occurred when we assign the num variable which is an Integer type variable to a string value present in the C5 cell of the worksheet.
Solution – Assigning a Numeric Value to Number Type Variable
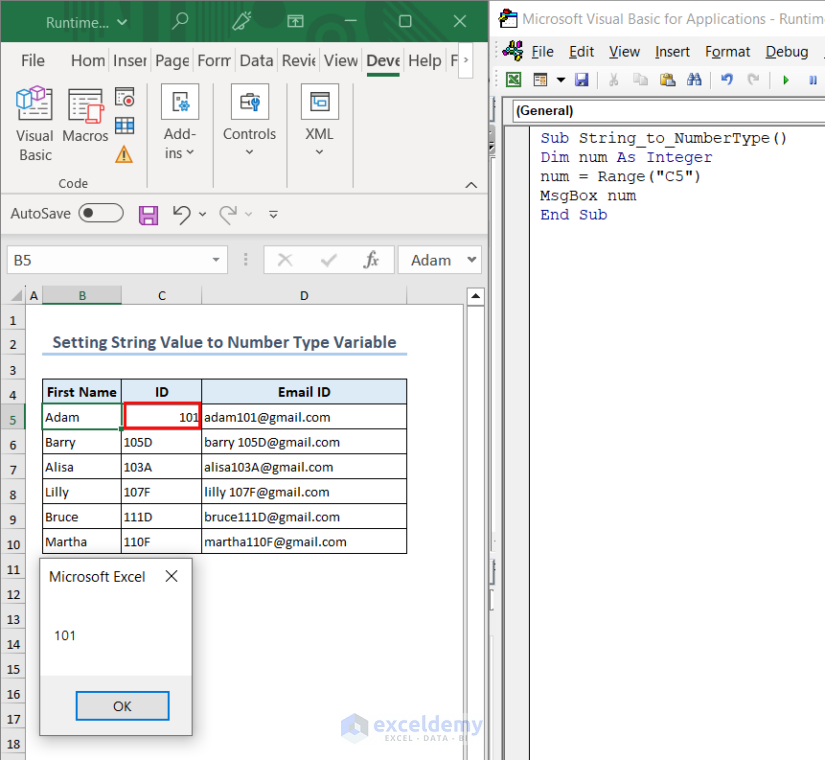
When we change the value in the C5 cell to a numeric value, as evident from the alignment of the data from the other values in that column, the code executes properly without any type mismatch error.
Reason 2 – Using Operators on Mismatching Data Types
The plus operator can’t concatenate a string and numeric value and results in a type mismatch error.
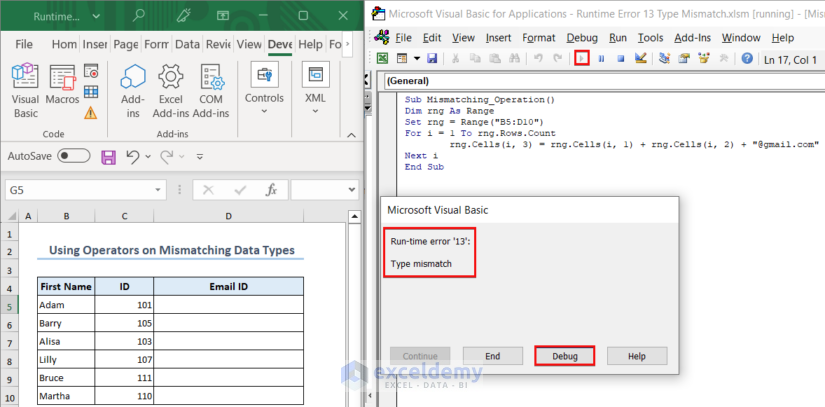
Here, we want to concatenate the First Name and ID of each employee with “@gmail.com” string with the addition operator. However, the code shows an error message. When you press the Debug option, you will get to the cause of the error.
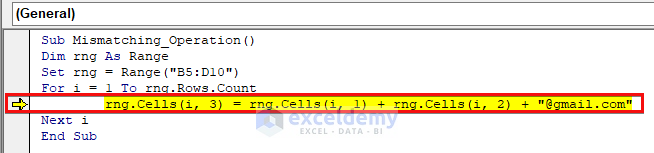
The code finds the line where it’s trying to concatenate the First Name and ID with a string as the source of the error, because the ID numbers are in numeric form.
Solution – Using Proper Data Types while Using Operators
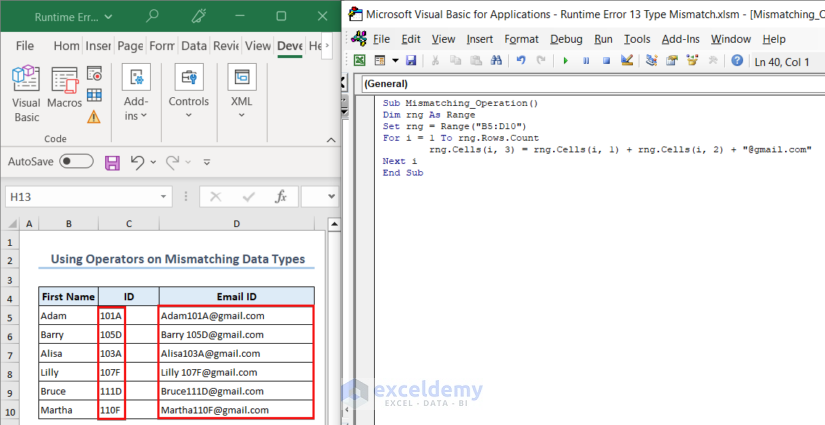
- Convert the ID numbers into string values.
- The easiest way to do that is to add non-numeric characters in the cells. In this way, VBA will assume them as strings.
- You can also convert the cell formatting.
- The code will concatenate the strings by using the addition operator and we will get the Email ID of the employees.
Reason 3 – Inserting the Wrong Data Type into a VBA Range
If the datasheet contains data types that the code is not expecting, it will show the Runtime Error 13: Type Mismatch error.
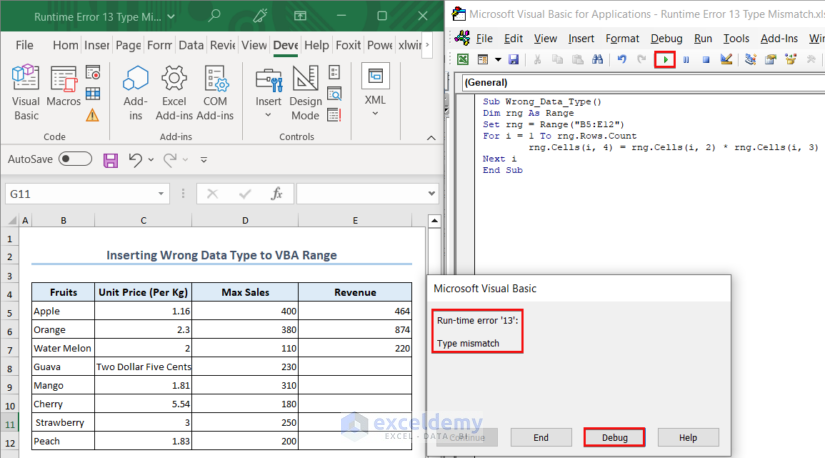
Here, we want to calculate the total revenue of each fruit by multiplying the unit price by the maximum sales of the fruit. However, as soon as we execute the code, the code shows an error message.
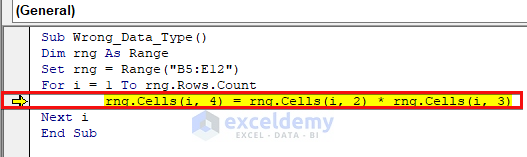
The line where we are multiplying each unit price with the sales is the source of error. In the C8 cell, the unit price is in text format and VBA cannot perform a multiplication operation between a string and a number.
Solution – Inserting Proper Data into the Dataset
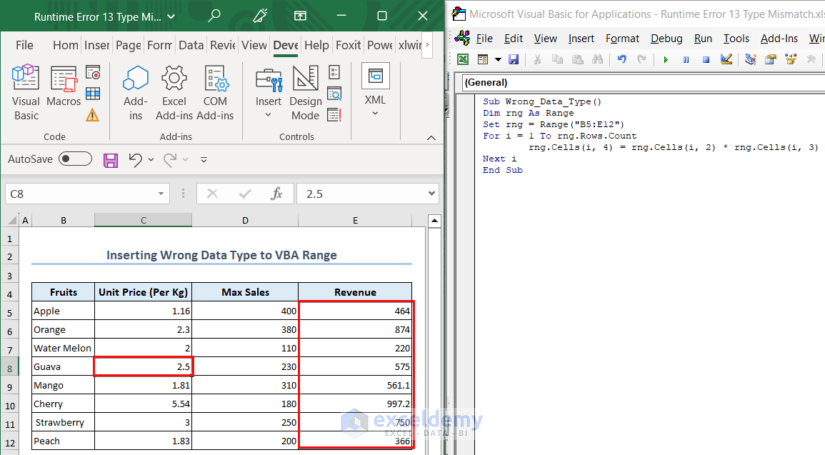
Change the value in the C8 cell to a numeric value and the code executes.
Read More: [Fixed!] Runtime Error 438 in Excel VBA
Reason 4 – Passing a Wrong Argument Type to a Function
In VBA we can build user-defined functions and ask users to pass arguments to those functions to get an output. In those functions, we can define the data types of the arguments. However, if someone passes an argument to that function that is other than the documented data type, then the function will show a mismatch error.

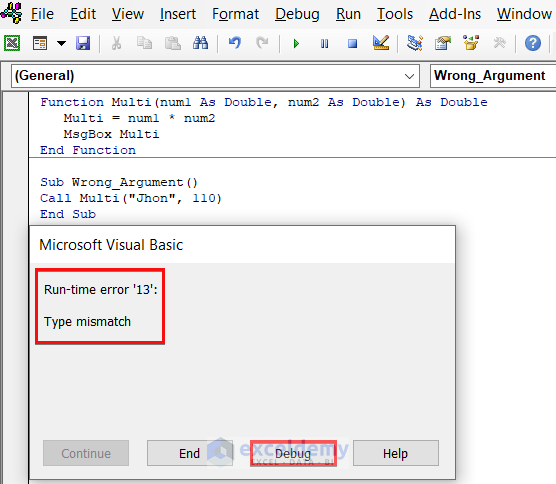
In this example, we have created a simple function Multi that takes in two Double type numbers as its argument and multiplies it to show in a MsgBox. However, when we call the function in the Wrong_Argument subroutine, an error message pops up. We will Debug the code next.
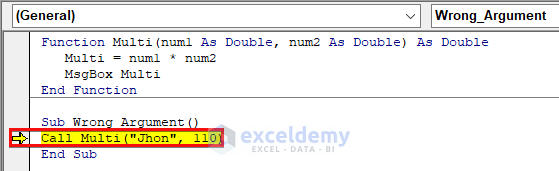
As seen from the image above, we passed “Jhon”, a string-type argument to that function which was expecting a numeric value.
Solution – Inserting Proper Arguments
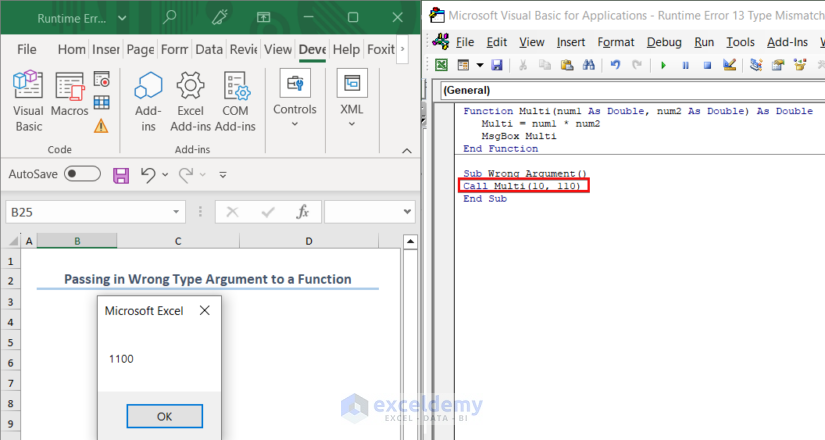
If we pass in two numeric values to that function, the function will work properly.
Reason 5 – Passing an Object Reference to a Procedure That Expects a Property or Value
The MsgBox property of VBA shows a value. So, it expects a value as its input. However, if someone passes an object as the input of a MsgBox, a Runtime Error 13: Type Mismatch message will show up on the screen.
Example 1 – Mismatch Error for Range Object
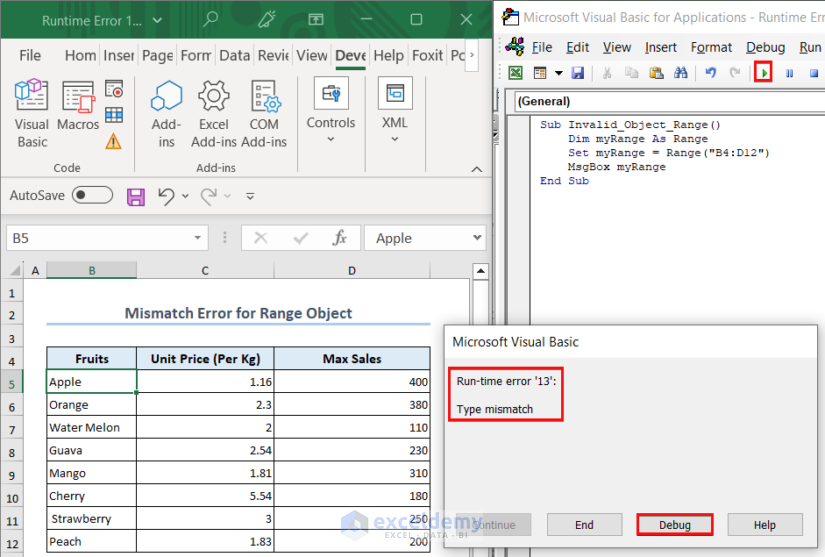
In this case, we set myRange as a Range type variable and assigned the range B4:D12 as its value. When we tried to output the range, an error message appeared on the screen.
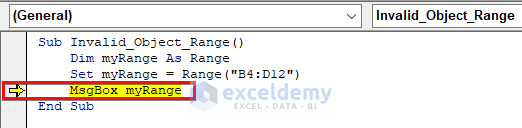
The MsgBox was expecting a value from that range instead we passed the entire range as the input of the MsgBox. So, we got a mismatch error.
Example 2 – Mismatch Error for Array Object
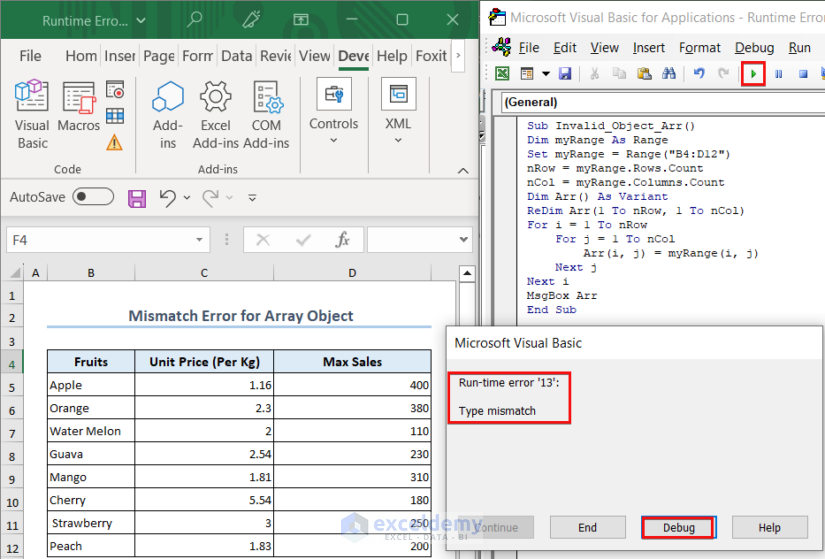
In this example, we took the B4:D12 range inside an array named Arr. When we tried to show the Arr array in a MsgBox, the Type Mismatch error occurred.
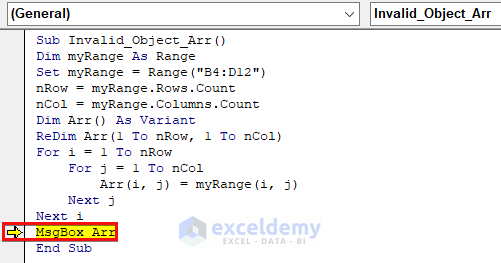
We passed the entire array object instead of one of the values from the array as the input of the MsgBox thus resulting in an error.
Solution – Passing in a Value or Property Instead of Object
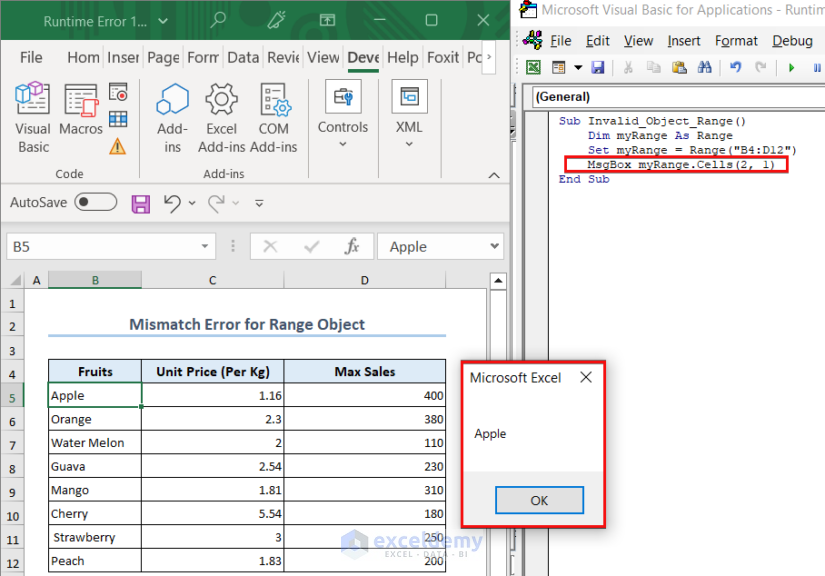
We wrote myRange.Cells(2,1) as the input of the MsgBox which indicates the value from the 2nd row and 1st column of the myRange variable. So, the MsgBox displays Apple as the output without showing any errors.
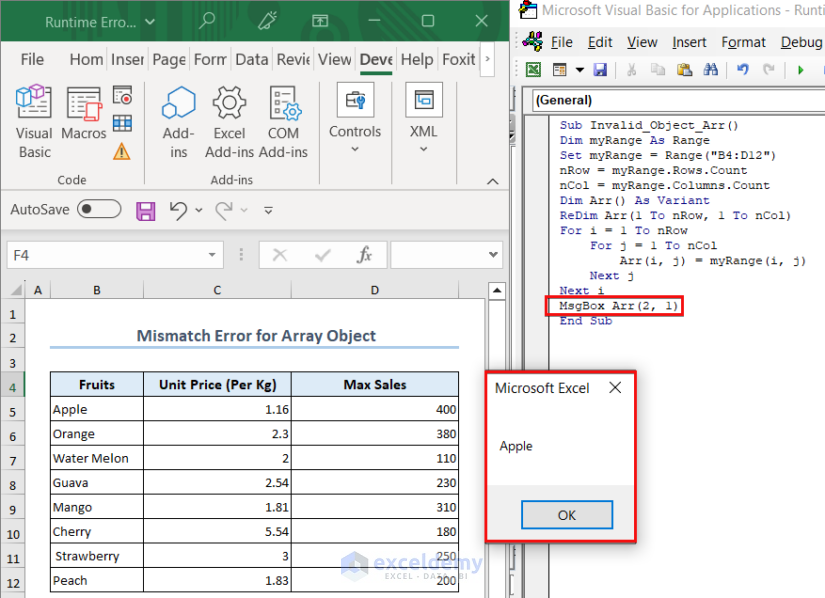
In the second case, we passed Arr(2,1) as the input of the MsgBox. This refers to the value from the 2nd row and 1st column of the Arr array which is Apple. Thus, we see it as the output message.
Reason 6 – Writing a Date in an Invalid Format
Writing dates in invalid formats that the VBA compiler can’t understand, or invalid dates that are formatted as text, results in Runtime error 13 type mismatch in VBA.
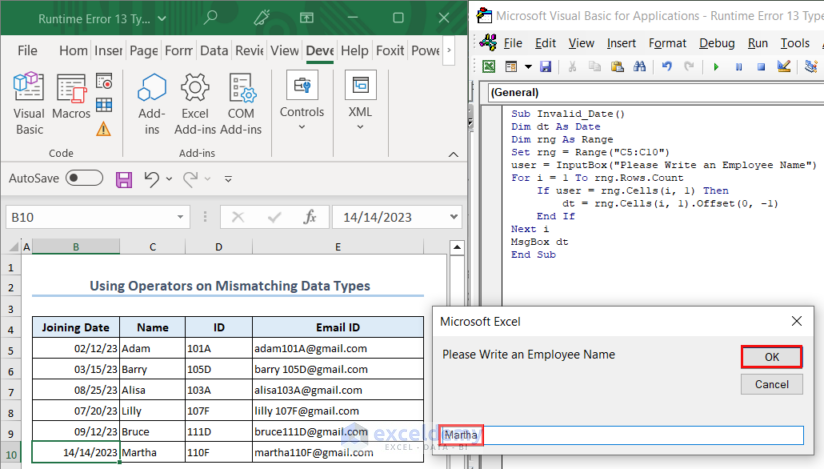
In this instance, the code prompts users to write an employee name from the dataset, and in return, it will show the joining date of the employee. So, we wrote Martha and pressed OK.
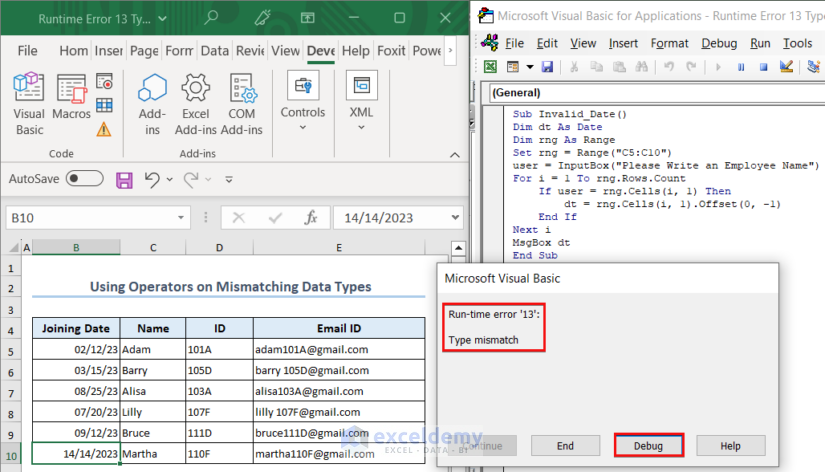
The code showed a Type Mismatch error. We clicked on Debug to know the error source.
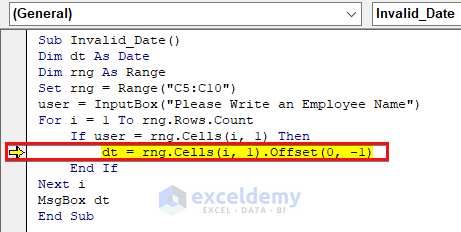
As seen from the image, the line where we assigned the joining date from the Joining Date column as the value of the dt variable is the source of the error. Because dt is a Date type variable and it expects a valid date as its value. However, the date pertaining to the employee Martha is 14/14/2023 which is an invalid date and creates the error.
Solution – Passing the Date in a Valid Format
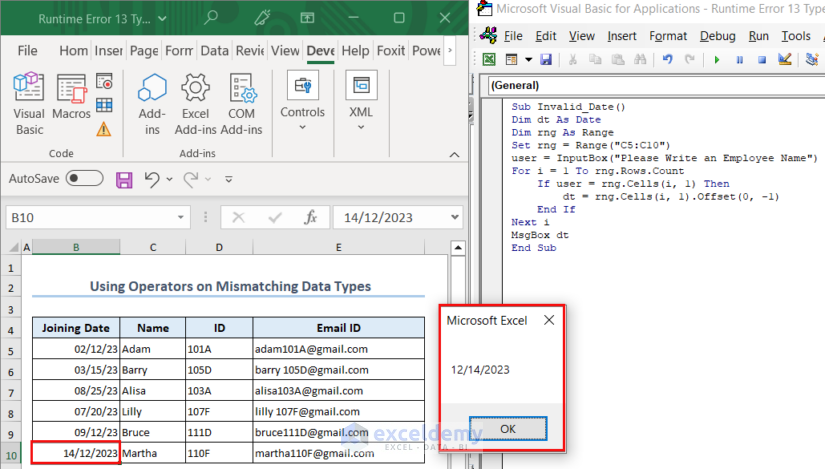
We fixed the date, and the code worked perfectly.
Reason 7 – Trying to Convert Incompatible Data Types
If we try to convert “Adam” to a numeric value, VBA will show the type mismatch error.
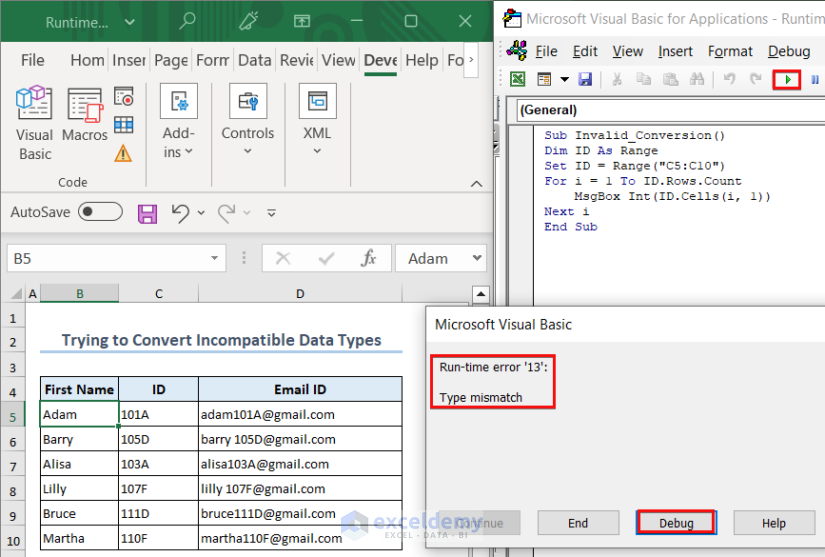
Here, we want to show the ID of each employee in a MsgBox. But when we ran the code, it showed an error.
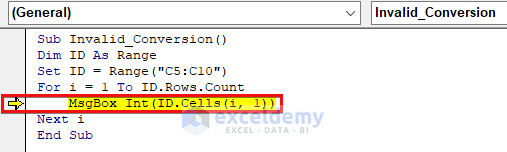
As the image suggests, the line inside the For Loop is the source of the error.
Solution – Converting Data Types That Are Compatible
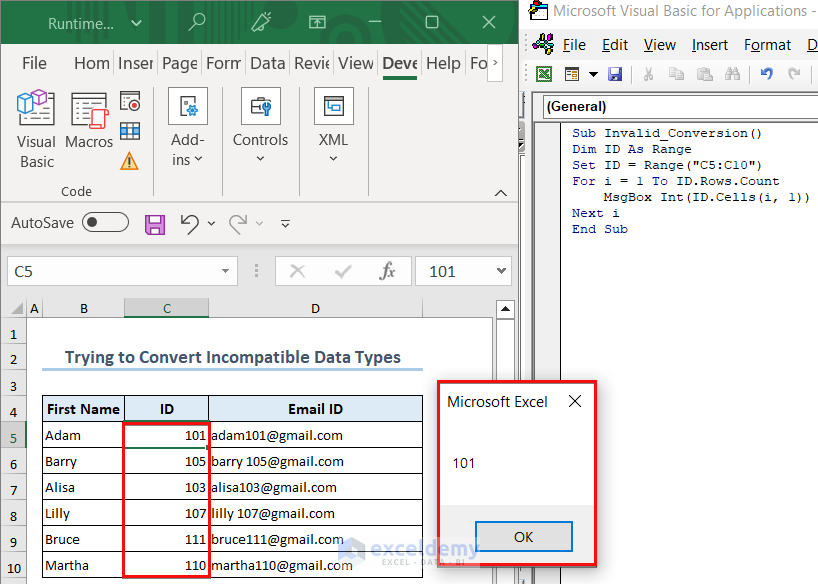
The ID of the employees was in string format. However, in the code inside the For Loop we tried to convert them into an integer with the Int(ID.Cells(i,1) command. Thus, we ran into an error. We changed the IDs to integers and the code ran just fine.
Read More: [Fixed!] Excel VBA Run Time Error 1004
Reason 8 – Invalid Array Conversion from a Range
In this instance, we will deal with another tricky Type Mismatch error. This happens when the conversion of a range into an array goes wrong.
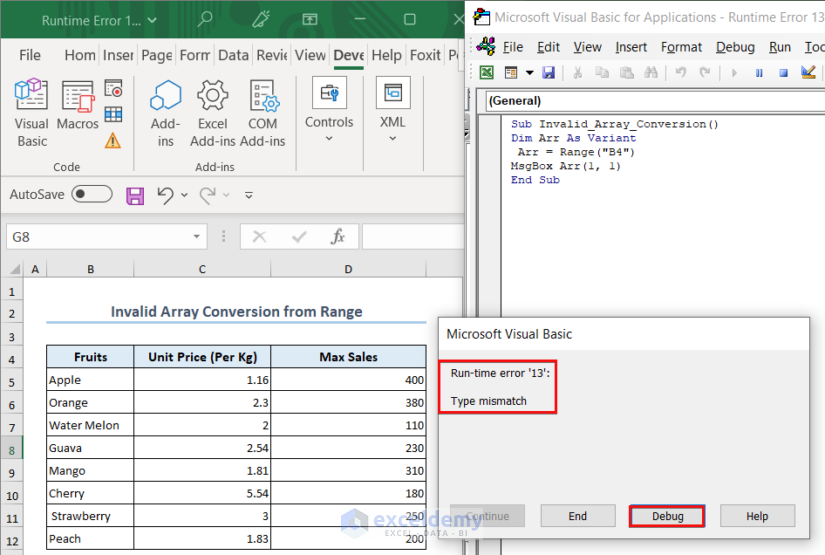
We assigned the Range(“B4”) to an array named Arr and tried to display the first element of the array in a MsgBox. As soon as we hit the run option, the error message popped up.
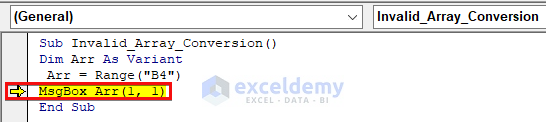
While debugging the code, we can see that the output code of the MsgBox is the source of the error. It is because the range has only one value B4 and so VBA assumed Arr as a single variable instead of an array. So, when we tried to display the first element of the array by writing Arr(1,1), the mismatch error occurred as Arr never became an array.
Solution – Creating a Proper Array from a Range
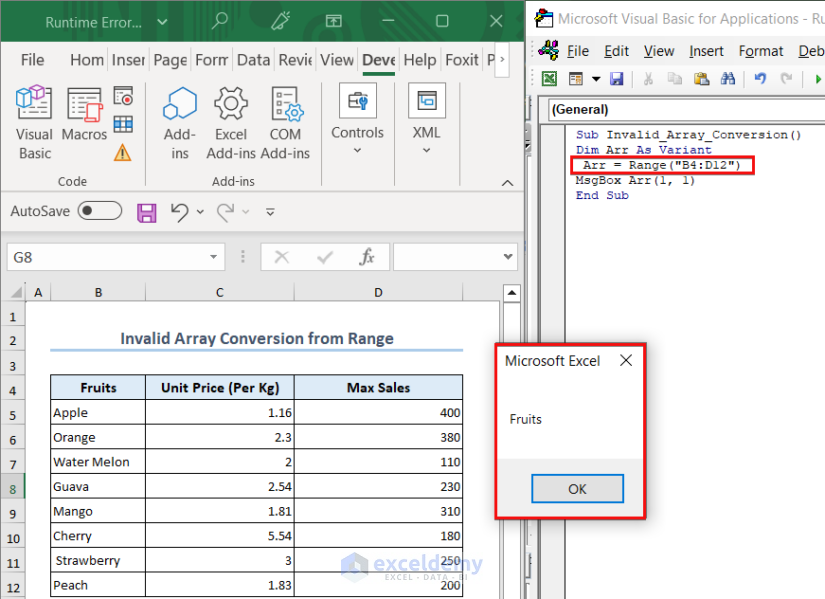
We fixed the code by adding a range of values to the Arr variable, making it an array. When we tried to show the first element of the array, the code displayed it without an error.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I fix macro errors in Excel?
To fix macro errors in Excel, follow these general steps:
- Determine the error message: When you receive an error message while running a macro, read the error message and try to understand what it’s telling you. Understanding the error message is the first step in fixing the problem.
- Debug your code: Use the debugging tools in the Visual Basic Editor to step through your code line-by-line to identify where the error occurs. You can use the “Debug” menu to run your macro in “Step Into” mode, which allows you to step through each line of code.
- Check your code for syntax errors: Review your code to check for syntax errors, such as missing or incorrect punctuation, or incorrect variable or function names. Fix any syntax errors that you find.
- Check for logical errors: If your code appears to be syntactically correct, but is still causing errors, check for logical errors. These are errors in the way your code is structured that may cause it to behave incorrectly. Review your code and make any necessary adjustments.
- Use error handling: You can use error handling to catch and handle errors that occur during the execution of your macro. This allows you to gracefully handle errors and provide useful feedback to the user.
- Test your code: Once you have fixed any errors in your code, test your macro to ensure that it works as expected.
Things to Remember
- In all the methods above, we could add Error Handling to get rid of the error. In VBA, you can use error handling to catch and handle errors that occur during the execution of your code. The syntax for error handling in VBA is as follows:
On Error GoTo [label]
OR
On Error Resume Next- The On Error statement sets the error trapping mode. There are two modes:
- GoTo [label]: This mode allows you to jump to a specified label in the code when an error occurs. The label should be defined using the “Label:” syntax.
- Resume Next: This mode tells VBA to continue executing the code from the next line when an error occurs.
Download the Practice Workbook


