Download the Practice Workbook
Overview of the EMI Calculation
The Equated Monthly Installment, or EMI, is payment for a traditional set monthly payment loan, where you’re paying a portion of the principal and the interest each month. You can use the following equation to determine the EMI payment:
EMI = (P * r * (1 + r)^n) / ((1 + r)^n - 1)EMI= Equated Monthly Installment
P = principal loan amount
r = monthly interest rate (annual interest rate divided by 12 and converted to decimals)
n = total number of monthly installments
How to Create a Loan EMI Calculator in Excel
Method 1 – Using the PMT Function to Create an EMI Calculator
We can see the Loan Amount (pv), Interest Rate (rate), and Number of EMIs (nper) in the following dataset.
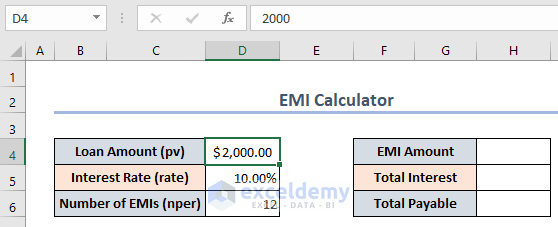
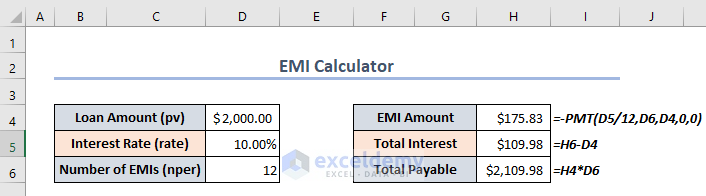
- Use the following formula in cell H4 to find the EMI Amount.
=-PMT(D5/12,D6,D4,0,0)To change the annual interest rate to a monthly interest rate, we divide the interest rate by 12 in the formula. PMT returns a negative value by default, so we put a – in front to change it to a positive one.
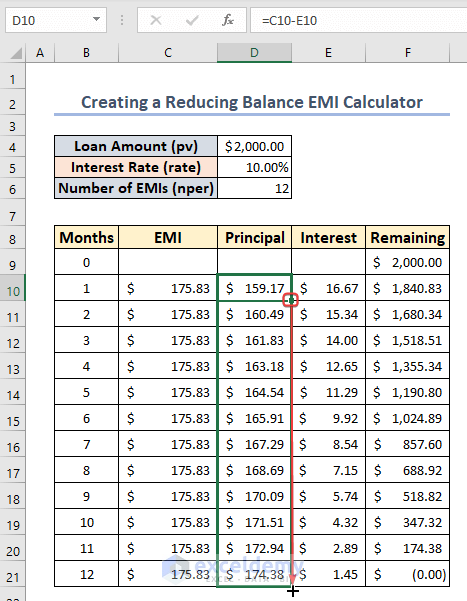
Method 2 – Creating a Reducing Balance EMI Calculator
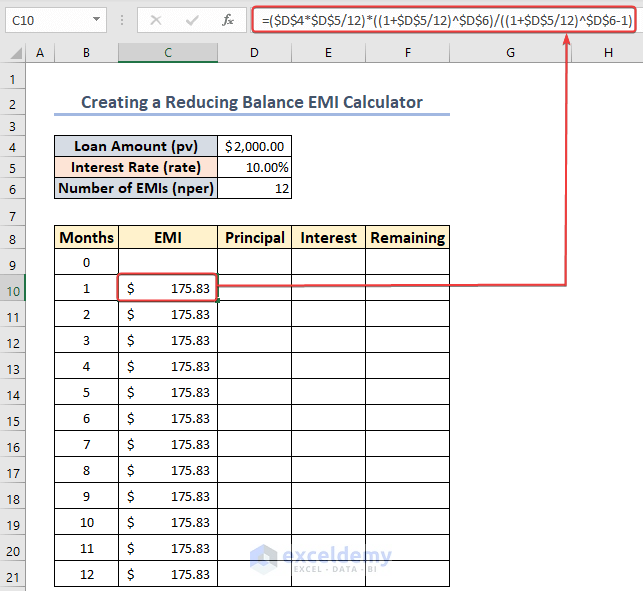
- Select the cell C10 and enter the following formula:
=($D$4*$D$5/12)*((1+$D$5/12)^$D$6)/((1+$D$5/12)^$D$6-1)- Drag the fill handle down to find the EMI for all months.
- Enter the value of your loan amount in cell F9.
- Choose cell E10 and enter the following formula to determine the portion of the interest paid each month:
=$D$5/12*F9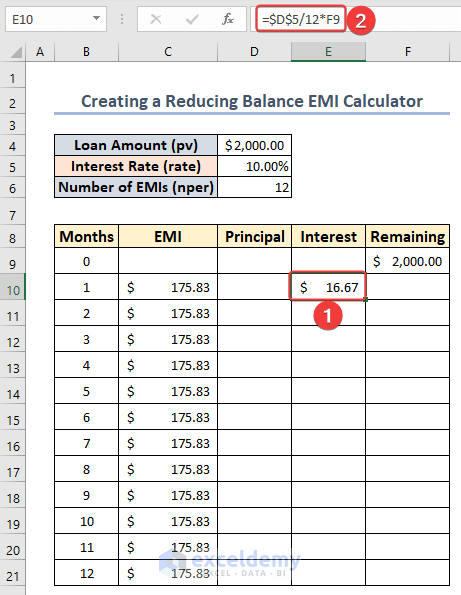
- Enter the following formula in cell D10 to calculate the portion of the principal paid each month:
=C10-E10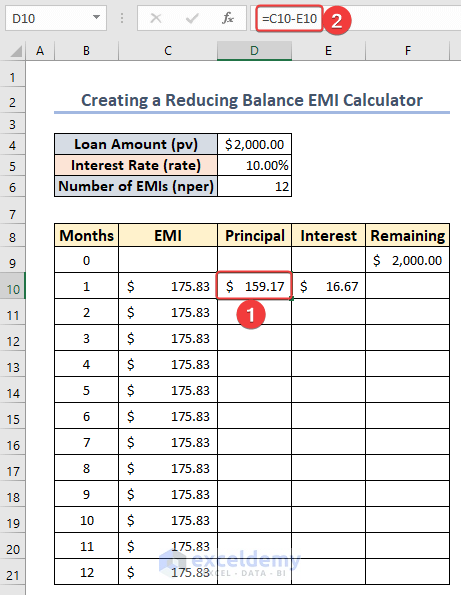
- Select cell F10 and insert the following to determine the leftover principal value:
=F9-D10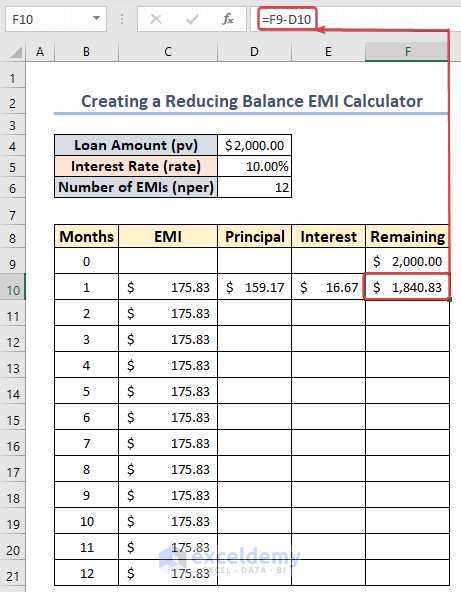
- Select F10 and drag down the fill handle to AutoFill the column.
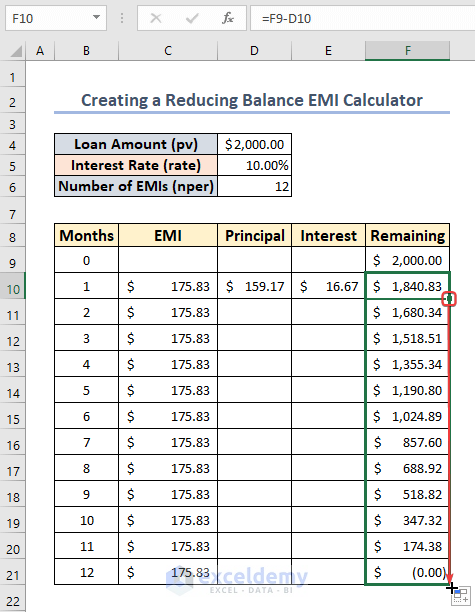
- Drag down the Fill Handle from E10.
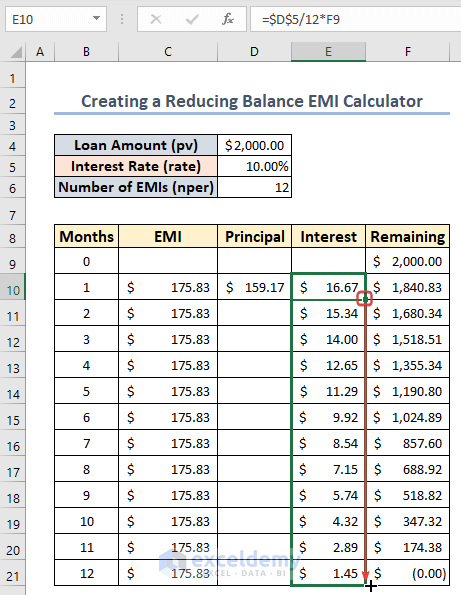
- Use AutoFill in column D as well.
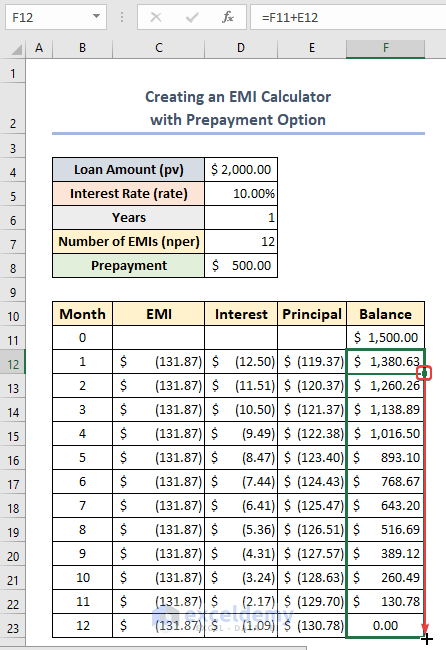
Method 3 – Creating an EMI Calculator with Prepayment
- Enter the following formula to find the current Balance in cell F11:
=D4-D8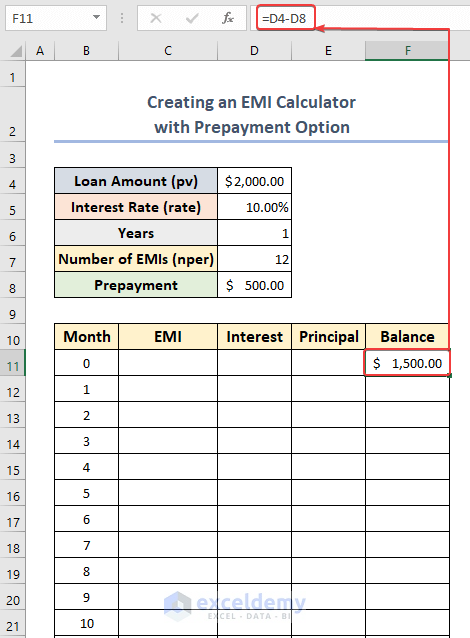
- Choose cell C12 and enter the following formula:
=PMT(D$5/D$7,$D$6*$D$7,F$11)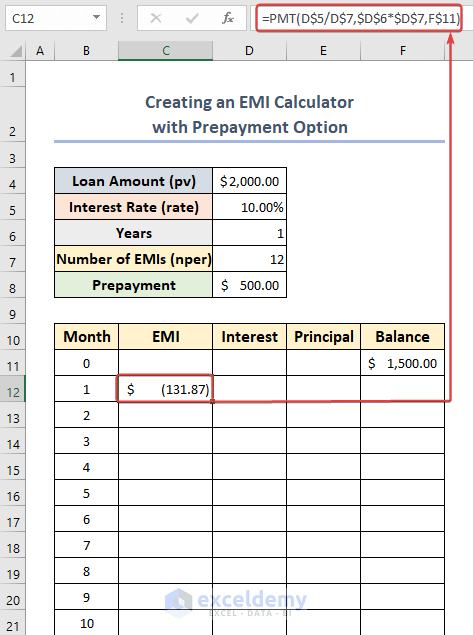
- AutoFill the column.
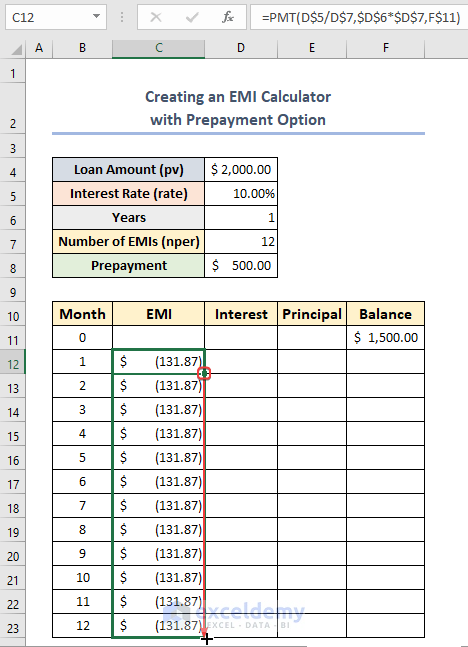
- Choose cell D12 and use the following formula:
=IPMT(D$5/D$7,B12,$D$6*$D$7,F$11)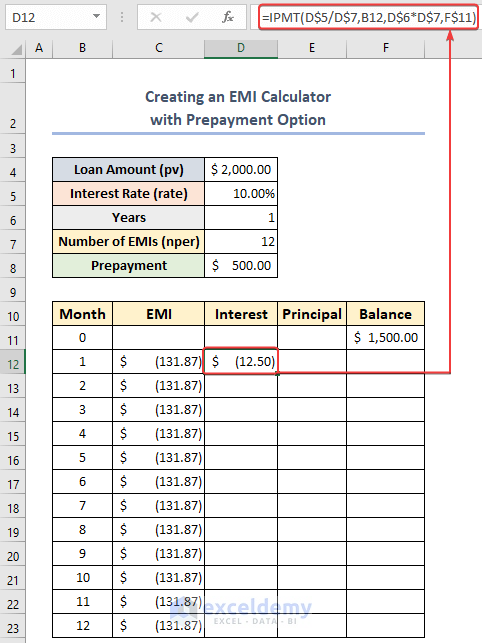
- Drag the fill handle to the remaining cells in column D.
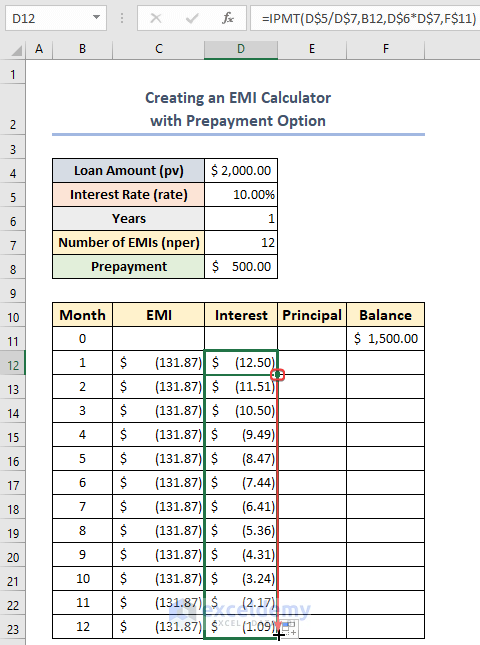
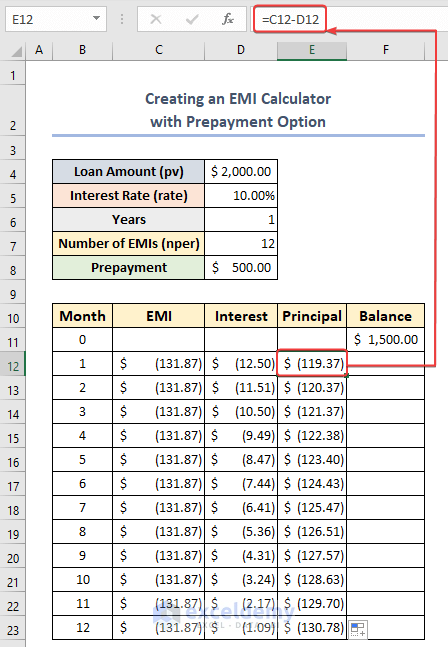
- Enter the following in E12:
=C12-D12- Drag the fill handle down to copy the formula for the rest of the cells.
- Insert the following in F12:
=F11+E12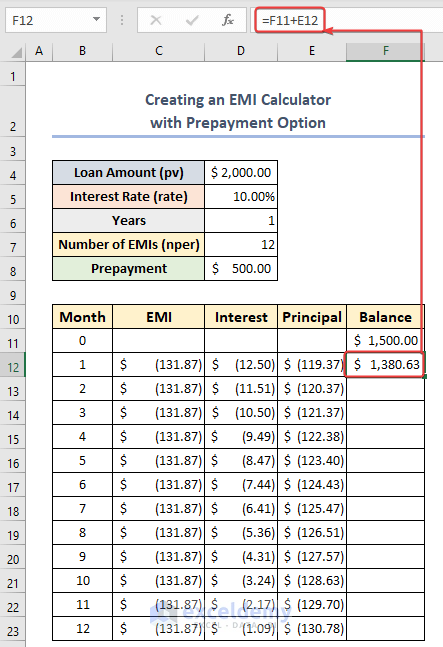
- Drag the fill handle down.
- You will get the month’s EMI, the interest paid, the principal paid, and the remaining principal in the table.
How to Create a Reverse EMI Calculator in Excel
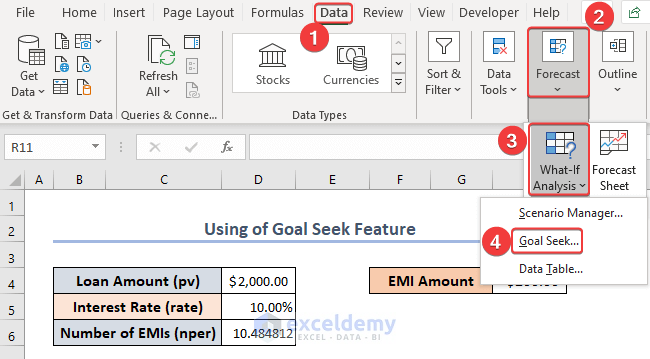
- Go to Data and select Forecast.
- Choose What If Analysis and select Goal Seek from the drop-down menu.
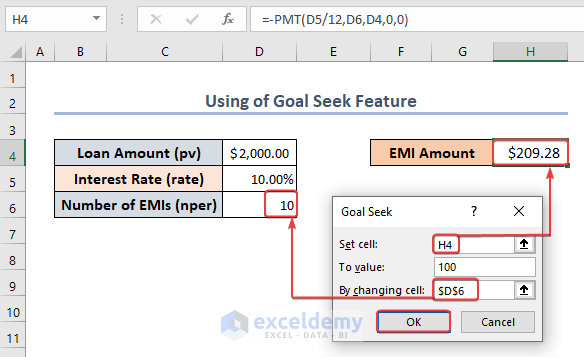
- In the Goal Seek box, put the EMI amount in cell H4 into the Set Cell field. In the To value box, enter the target EMI value (such as 100). Select the cell $D$6 containing the Number of EMIs for the By changing cell option.
- Click OK.
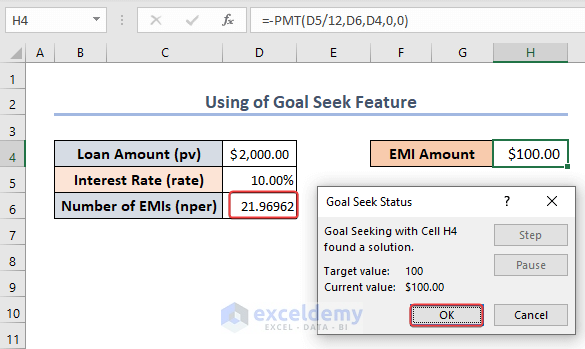
- The Number of EMIs changed to 22 for the fixed EMI Amount.
Things to Remember
Understanding EMI: Equated Monthly Installment, or EMI for short, is a set monthly payment made by a borrower to a lender on a particular date. EMIs are frequently used to pay back loans, including personal, auto, and home loans.
Input Data: You must collect the required input data before you can calculate the EMI in Excel. The sum of the loan, the interest rate, and the length of the loan (in months) are typically included. Depending on the loan terms, you might also need to take into account things like any down payment, processing costs, or prepayment options.
Loan Interest Rate: Make sure to enter the interest rate as the monthly rate rather than the annual rate when entering it. Divide the given annual interest rate by 12 to get the monthly interest rate.
Rounding the EMI: Use the ROUND function to make sure the EMI is rounded to the correct value. For instance, to round the calculated EMI in cell H4 to two decimal places, use the formula =ROUND(H4, 2).
Visualizing the EMI Schedule: To see the EMI payments over the loan term, you can create a repayment schedule. Calculate the principal and interest portions of each EMI payment using Excel’s functions. Make a table to show the schedule, which should include the due date, the principal, the interest, and the remaining loan balance.
Sensitivity Analysis: To perform a sensitivity analysis on the EMI calculation, use Excel’s data tables or the goal seek function. You can then see how different variables, like interest rates or loan amounts, affect the EMI amount. You can better understand the adaptability and affordability of various loan options with the aid of sensitivity analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What details do I need to use Excel’s EMI calculator?
To use the EMI calculator in Excel, you typically need to enter the loan amount, interest rate, and loan tenure. The calculator then calculates the monthly installment based on those specifications.
Is it possible to modify Excel’s EMI calculator?
You can modify the EMI calculator in Excel to meet your unique needs. Depending on your requirements and Excel skill level, you can change the formulas, format them, or add new features.
What is computed by the Excel’s EMI calculator?
The Equated Monthly Installment (EMI) calculator in Excel determines the amount of your fixed monthly loan payment. This is known as the Equated Monthly Installment (EMI). Additionally, a thorough breakdown of each payment’s principal and interest components is given.
EMI Calculator in Excel: Knowledge Hub
<< Go Back to Finance Template | Excel Templates
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

