Method 1 – Using Call Function
Using the Call Function we can call a sub and execute the task inside the sub directly. There are three methods of doing this, one is to call directly, with arguments, and finally without the arguments.
Call a Sub Directly
- Open the VBA code editor from the developer tab.
- Paste the below code in the code editor.
Sub call_sub_directly()
SortData_with_arguments sortOrder:="descending"
End Sub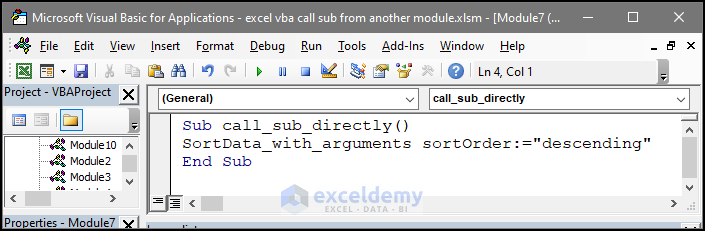
- The main code that is going to be executed is below. Data saved in a certain range will be sorted according to the Age column value.
Sub SortData()
Dim sortRange As Range
Set sortRange = Range("B5:G9")
sortRange.Sort key1:=Range("D5"), _
order1:=xlAscending, _
Header:=xlNo, _
Orientation:=xlSortColumns
End Sub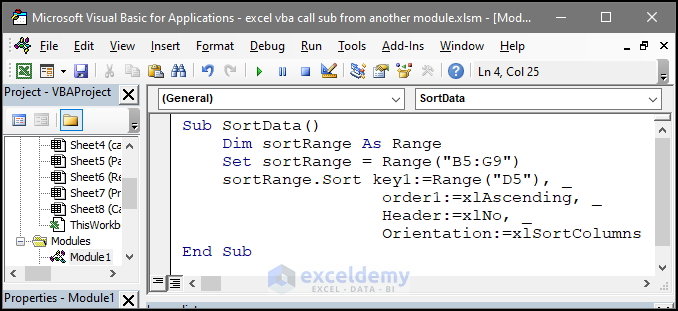
- The code includes a line that will execute the SortData_with_arguments sub stored in Module 3, which will sort the data stored in the range of B5:G9 in ascending order.
Call a Sub with Arguments
- Open the VBA code editor from the developer tab.
- Paste the below code in the code editor.
Sub SortData_with_arguments(ByVal sortOrder As String)
Dim sortRange As Range
Set sortRange = Range("B5:G9")
If sortOrder = "ascending" Then
sortRange.Sort key1:=Range("D5"), _
order1:=xlAscending, _
Header:=xlNo, _
Orientation:=xlSortColumns
ElseIf sortOrder = "descending" Then
sortRange.Sort key1:=Range("D5"), _
order1:=xlDescending, _
Header:=xlNo, _
Orientation:=xlSortColumns
Else
MsgBox "Invalid sort order. Please specify either 'ascending' or 'descending'."
End If
End Sub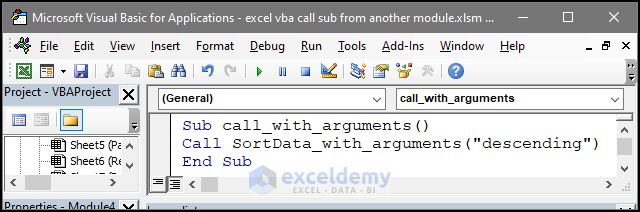
- This code is stored in Module 3.
- To call this sub from another module, paste the below code to another editor.
Sub call_with_arguments()
Call SortData_with_arguments("descending")
End Sub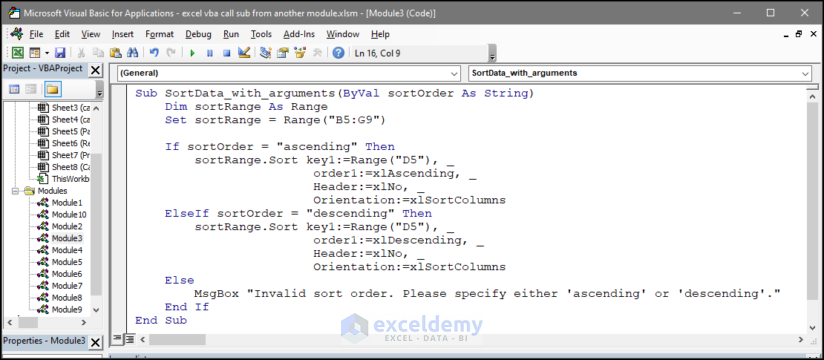
- This code is saved as Module 6. This will call the SortData_with_arguments sub, with descending argument input.
- The data in the B5:G9 range is now sorted according to the Age column.
Call a Sub without Arguments
- Open the VBA code editor from the developer tab.
- Paste the below code in the code editor.
Sub SortData()
Dim sortRange As Range
Set sortRange = Range("B5:G9")
sortRange.Sort key1:=Range("D5"), _
order1:=xlAscending, _
Header:=xlNo, _
Orientation:=xlSortColumns
End Sub
- The code is saved as Module 2. To run this code from another module, apply the code below.
Sub call_without_argument()
Call SortData
End Sub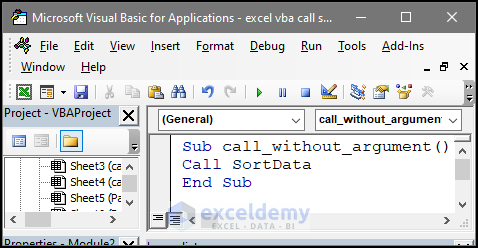
- The SortData sub is now called and the data stored in the B5:G9 range is now sorted in Descending order(as set in the code).
Read More: Excel VBA to Call Sub with Parameters
Method 2 – Call Sub from Another Module Using Parentheses
- Open the VBA code editor from the developer tab.
- Paste the code below in the code editor.
Sub SortData()
Dim sortRange As Range
Set sortRange = Range("B5:G9")
sortRange.Sort key1:=Range("D5"), _
order1:=xlAscending, _
Header:=xlNo, _
Orientation:=xlSortColumns
End Sub
- The code below will call this sub (Module1).
Sub Call_with_parentheses()
Call Module1.SortData
End Sub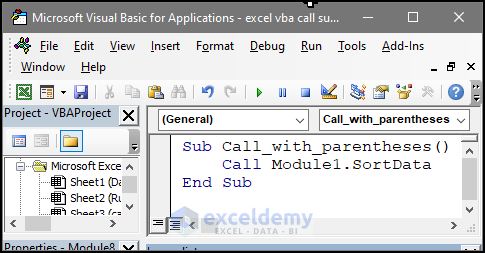
- The data in the B5:G9 range is now sorted according to the Age column values.
Method 3 – Using Run Command to Call Sub
- Open the VBA code editor from the developer tab.
- Create a Source code that will be called from another module by using the code below.
Sub SortData()
Dim sortRange As Range
Set sortRange = Range("B5:G9")
sortRange.Sort key1:=Range("D5"), _
order1:=xlAscending, _
Header:=xlNo, _
Orientation:=xlSortColumns
End Sub
- The final code that will call the source code to execute the source code is given below.
Sub call_with_Run()
Application.Run "Module1.SortData"
End Sub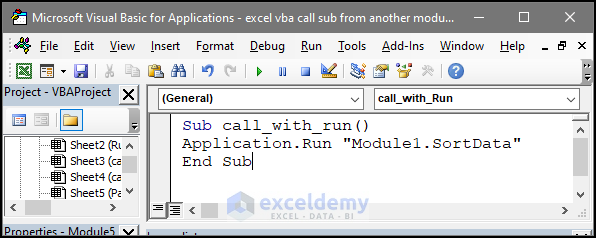
- The data in the B5:G9 range is now sorted according to the Age column.
Read More: How to Run a Private Sub in VBA
Method 4 – Call a Private Sub from Another Module in Excel VBA
- Open the VBA code editor from the developer tab.
- Paste the below code in the editor window.
Private Sub Call_sub_private()
Dim sortRange As Range
Set sortRange = Range("B5:G9")
sortRange.Sort key1:=Range("D5"), _
order1:=xlAscending, _
Header:=xlNo, _
Orientation:=xlSortColumns
End Sub
Public Sub Public_sub()
Call_sub_private
End Sub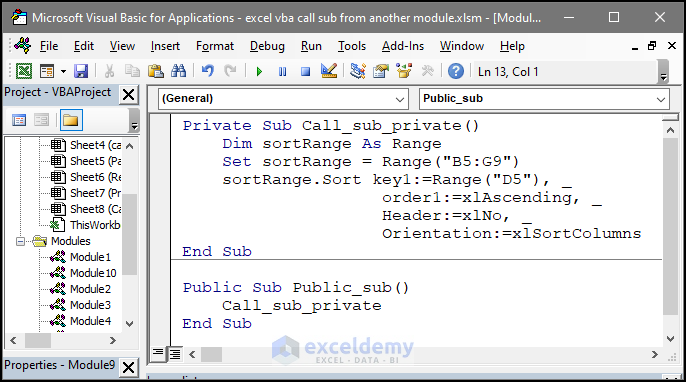
- The public module will connect the private module.
- The entire code must be run from another module.
- Open a new module and enter the following code in the code editor.
Sub call_public_sub()
Call Public_sub
End Sub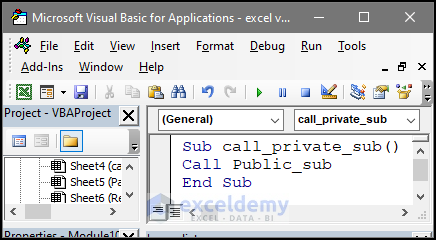
The data in the B5:G9 range is now sorted based on the Age column.
Read More: How to Call Private Sub in Excel VBA
Things to Remember
- Make sure that the module containing the Sub you want to call is referenced correctly. You can reference a module using the Call statement, the Application.Run method, or by creating a reference to the module using the Public keyword.
- If the Sub you want to call is Private, you will need to create a Public Sub or Function in the same module that calls the Private Sub or Function. This allows you to call the Private Sub or Function indirectly from another module.
- If the Sub you want to call requires arguments, make sure you provide the correct number and type of arguments in the correct order. If you’re not sure what arguments a Sub requires, check the Sub’s declaration in the module.
- If the Sub you want to call modifies data or objects, make sure that you fully understand the impact of the changes it makes. Make sure that the Sub doesn’t overwrite data or objects that other parts of your program rely on, and the correct changes are being made.
- If the Sub you want to call relies on data or objects from another module, make sure that the data or objects are accessible from the module where you have defined the Sub. If necessary, use references to pass data or objects between modules.
Frequently Asked Question
- How do you call a sub within a sub in Excel VBA?
You can call a sub from within a sub in an Excel VBA, using the call function below, or just including the macro name within the code.
Sub OuterSub()
InnerSub ' Call InnerSub
End Sub
Sub InnerSub()
' Code for InnerSub
End Sub
- Can you have a sub within function VBA?
Yes, you can call a sub from another function in Excel VBA. In the function below, the sub name is given inside the function.
Function MyFunction(arg1 As Integer, arg2 As Integer) As Integer
'Perform some calculations here
Dim result As Integer
result = arg1 + arg2
'Call a sub to perform additional steps
DoSomething arg1, arg2
'Return the result
MyFunction = result
End FunctionWhen the below function is called, the sub will also be called at the same time.
Sub DoSomething(arg1 As Integer, arg2 As Integer)
'Perform additional steps here
End Sub- Can a sub call itself in VBA?
Yes, a sub can call itself in VBA. This is called recursion, and it can be a useful technique for solving problems that involve repetitive calculations or iterations.
When a sub calls itself, it creates a new instance of the sub within the current instance. This new instance has its own set of variables and executes independently of the original instance. The new instance can call itself again, creating yet another instance, and so on, until it meets a specific condition and the recursion stops.
- Can I use a variable from another sub in VBA?
Yes, you can use a variable from another sub in VBA, but it depends on the scope of the variable.
In VBA, the scope of a variable determines where it can be accessed from. If you declare a variable within a sub, it has local scope and you can only access it within that sub. If you declare a variable outside of any sub, it has the module-level scope and you can access it from any sub or function within the same module. In the example given below, the variable is declared outside the sub, and then we defined the sub.
Dim myVar As Integer 'Declare the variable with module-level scope
Sub Sub1()
myVar = 1 'Set the value of myVar within Sub1
End SubThe sub given below.
Sub Sub2()
MsgBox "The value of myVar is " & myVar 'Access the value of myVar within Sub2
End SubWe can also declare a sub publicly that we can access with any sub from any module as below.
Public myPublicVar As IntegerIf you declare a sub like this, then you can access this variable from any module and any sub stored in the Excel workbook.
Related Articles
- Excel VBA Call Sub from Another Sheet
- VBA to Call Sub From Another Workbook in Excel
- How to Use Excel VBA to Call Private Sub from Userform


