Here’s an overview of using the IF and ISERROR functions to check a car’s unit price depending on the amount of available stock.
What Is ISERROR in Excel?
The ISERROR function in Excel is a logical function that allows users to check if a cell contains an error value. It returns a Boolean value TRUE if the cell contains an error, such as #VALUE!, #REF!, #DIV/0!, #N/A, #NUM!, or #NAME?. If the cell does not contain an error, the function returns FALSE.
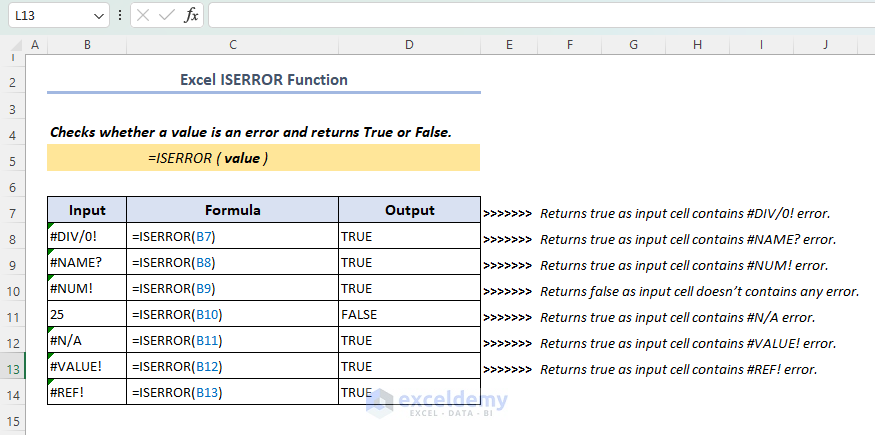
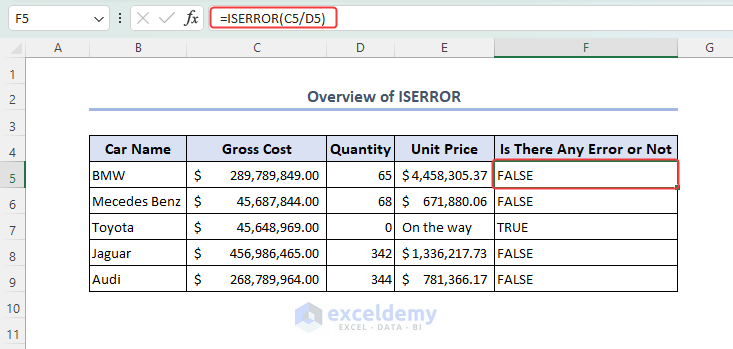
The ISERROR function is particularly useful when performing calculations or handling large datasets, as it helps identify and address potential formula errors.
IF with ISERROR Function in Excel: 4 Practical Examples
Example 1 – Combining IF with the ISERROR Function
Case 1.1 – Determining the Unit Price of Cars
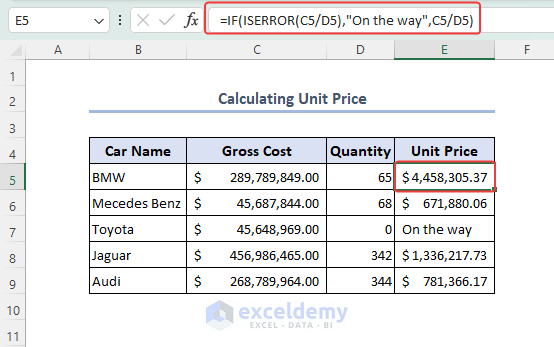
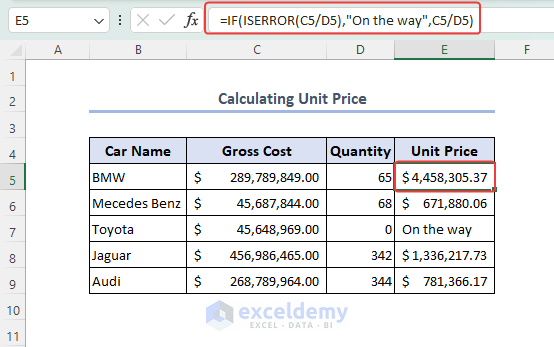
- Consider the formula below in the E5 cell to find the unit price. When there are no units left in the Quantity column for the model, the cell will show the message “On the way”.
=IF(ISERROR(C5/D5),"On the way",C5/D5)
Formula Explanation
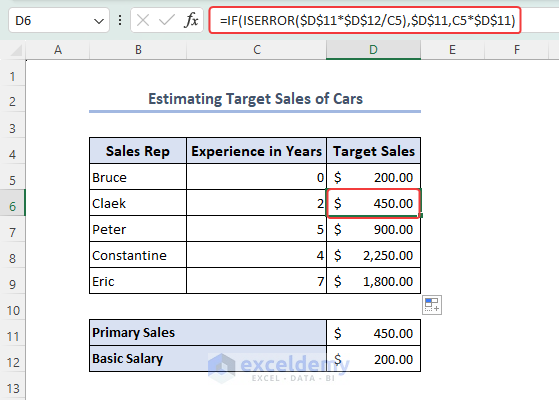
Case 1.2 – Estimating Target Sales of Cars
- We used a formula in the D5 cell below to find the estimated sales of cars of a representative. As Bruce has no experience, he will get only Basic Salary.
=IF(ISERROR($D$11*$D$12/C5),$D$11,C5*$D$11)
C5 represents Experience in Years. $D$11 and $D$12 are Primary Sales and Basic Salary respectively. We use the dollar sign ($) in D11 and D12 cells to make those references absolute. These won’t be changed if we use the Fill Handle tool.
Formula Explanation
Read More: Nested IF and ISERROR Formula in Excel
Example 2 – Using a Combination of Excel IF, ISERROR, MATCH Functions
- We have used the formula below in the C13 cell to find out whether a person has qualified for the job.
=IF(ISERROR(MATCH(B13, $C$5:$C$9, 0)), "No", "Yes" )
- If name is found, then the output is “Yes”. Otherwise, it’s “No”.
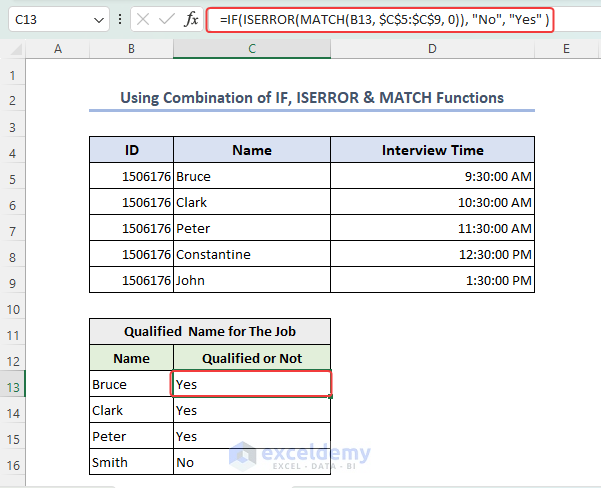
Formula Explanation Step 1 – MATCH(B13, $C$5:$C$9, 0) Step 2 – ISERROR(MATCH(B13, $C$5:$C$9, 0)) Step 3 – IF(ISERROR(MATCH(B13, $C$5:$C$9, 0)), “No”, “Yes”)
Example 3 – Using a Combination of IF, ISERROR, VLOOKUP Functions
- We’ll extract the schedule of qualified members’ names from a primary dataset by using the formula below in C13:
=IF(ISERROR(VLOOKUP(B13,$C$5:$D$9,2,FALSE)),"Not Exist",VLOOKUP(B13,$C$5:$D$9,2,FALSE))
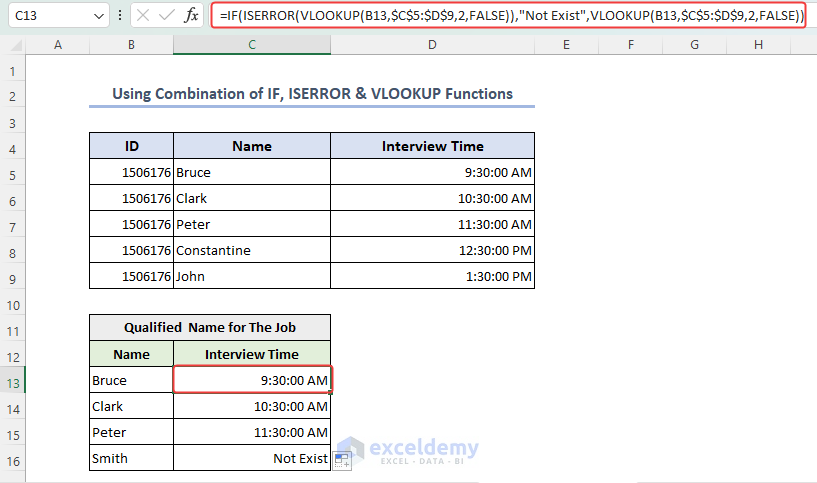
Formula Explanation Step 1 – VLOOKUP(B13,$C$5:$D$9,2,FALSE) Step 2 – ISERROR(VLOOKUP(B13,$C$5:$D$9,2,FALSE)) Step 3 – IF(ISERROR(VLOOKUP(B13,$C$5:$D$9,2,FALSE)),”Not Exist”,VLOOKUP(B13,$C$5:$D$9,2,FALSE))
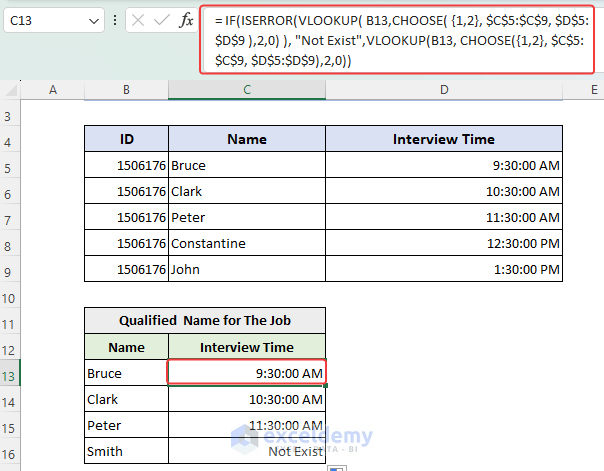
- You can use the CHOOSE function with the VLOOKUP function to get the similar output. Instead of entering the table_array argument manually, we can apply the CHOOSE function to make an array. The formula is given below:
= IF( ISERROR( VLOOKUP( B13, CHOOSE( {1,2}, $C$5:$C$9, $D$5:$D$9 ), 2, 0) ), “Not present”, VLOOKUP( B13, CHOOSE( {1,2}, $C$5:$C$9, $D$5:$D$9 ), 2, 0) )
The formula CHOOSE({1,2}, $C$5:$C$9, $D$5:$D$9) in Excel is used to select a value from a list based on an index number. In this case, the index numbers are {1,2}, and the lists are located in cells C5:C9 and D5:D9.
The CHOOSE function will return an array of values corresponding to the selected index numbers. In this case, it will return the value from C5:C9 when the index is 1 and the value from D5:D9 when the index is 2. The value will be from D5:D9 which is 9:30:00 AM.
Read More: How to Use ISERROR and VLOOKUP Functions in Excel
Example 4 – Applying IF and ISERROR Functions with an INDEX-MATCH Formula in Excel
- We’ll track the names based on the interview times. We have used this formula in C13.
=IF(ISERROR(INDEX($C$5:$C$9, MATCH(B13, $D$5:$D$9, 0))), "Not qualified", INDEX($C$5:$C$9, MATCH(B13, $D$5:$D$9, 0)))
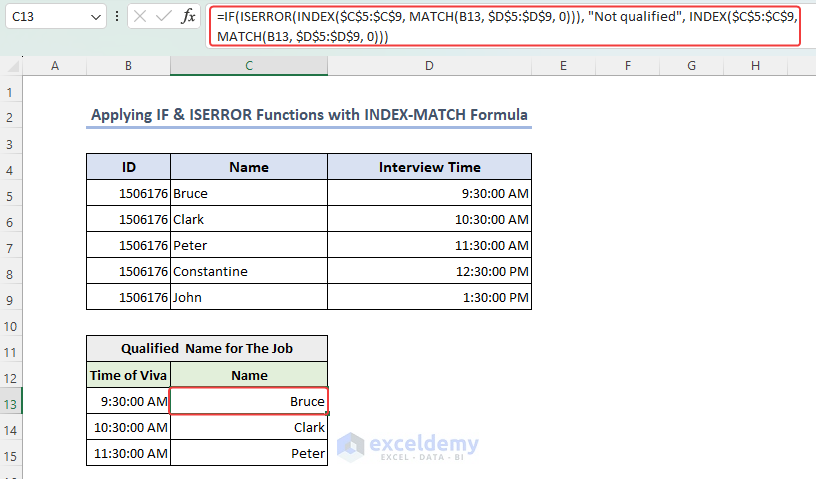
Formula Explanation Step 1 – MATCH(B13, $D$5:$D$9, 0) Step 2 – INDEX($C$5:$C$9, MATCH(B13, $D$5:$D$9, 0)) Step 3 – ISERROR(INDEX($C$5:$C$9, MATCH(B13, $D$5:$D$9, 0))) Step 4 – IF(ISERROR(INDEX($C$5:$C$9, MATCH(B13, $D$5:$D$9, 0))), “Not qualified”, INDEX($C$5:$C$9, MATCH(B13, $D$5:$D$9, 0)))
Things to Remember
- After using a formula, you may need to change the data type of the input or output cells.
- While using the VLOOKUP function, be careful when selecting the table_array and inputting the col_index_num argument.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I display a custom message when an error is detected using the nested IF and ISERROR functions?
To display a custom message when an error is detected, you can include a text value or message as the action_if_error parameter within the nested IF and ISERROR functions. For example, you can use =IF(ISERROR(A1), “Error: Invalid value”, A1) to display the custom message “Error: Invalid value” when cell A1 contains an error.
Can I use the nested IF and ISERROR functions to handle multiple error conditions?
Yes, you can use the nested IF and ISERROR functions to handle multiple error conditions by nesting multiple IF and ISERROR functions or combining them with other logical functions. By checking for different error types within separate nested IF and ISERROR functions or using logical operators like OR, AND, you can create complex conditions to handle various error scenarios.
Download the Practice Workbook
<< Go Back to Excel ISERROR Function | Excel Functions | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

