This is an overview.
.
Download Practice Workbook
Download the workbook here.
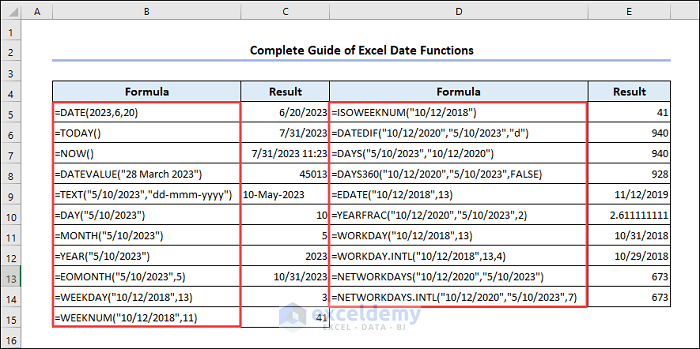
1 – Insert Dates Using the DATE Function
Syntax of DATE function:
- Use a value or cell reference to assign year, month and day in the arguments.
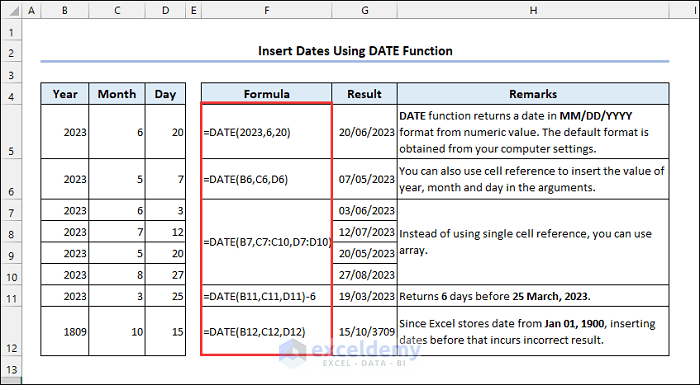
The result of the function will be the serial number for that date. Format your cell to display the date: Press Ctrl+1 to change format.
2 – Getting the Current Date
2.1 Using the TODAY Function
Syntax of TODAY function:
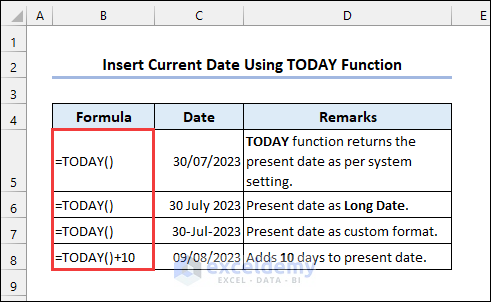
When you use the TODAY function in a cell, it will automatically update to the current date whenever you open or recalculate the Excel workbook. Format the date: press Ctrl+1 to access Format Cells.
2.2 Applying the NOW Function
Syntax of the NOW function:
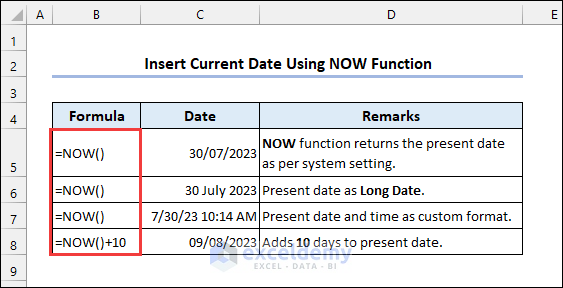
The NOW function automatically updates to the current date and time whenever you open or recalculate the Excel workbook. TODAY only returns the current date, whereas NOW returns both date and time.
3 – Change Dates from/to Text
3.1 Using the DATEVALUE Function
Syntax of the DATEVALUE function:
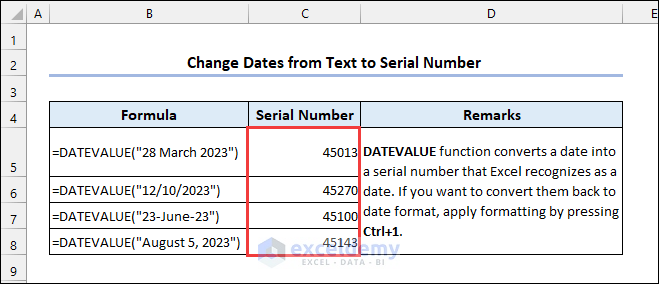
Dates are stored in Excel as consecutive integers. Only the formatting permits a number to be shown as a date. You can change the serial number back to date format by pressing Ctrl+1.
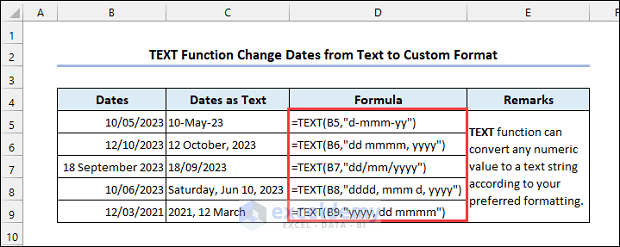
3.2 Applying TEXT Function
Syntax of the TEXT function:
In the format_text argument, choose your formatting.
4 – Get Dates
4.1 Using the DAY Function
Syntax of the DAY function:
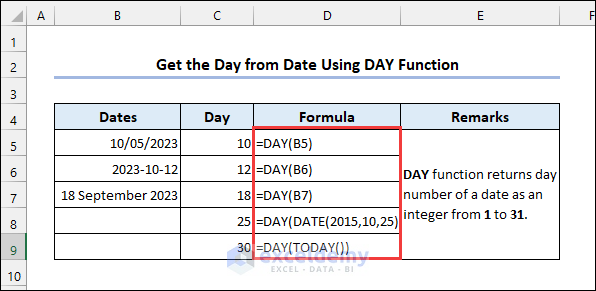
4.2 Using the MONTH Function
Syntax of the MONTH function:
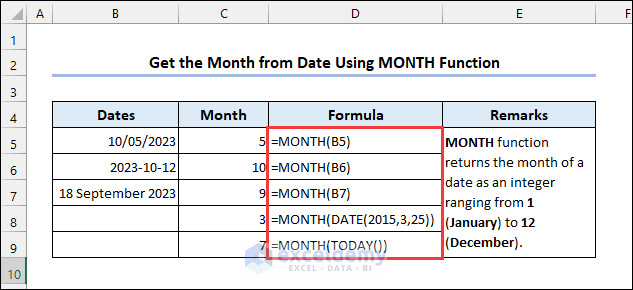
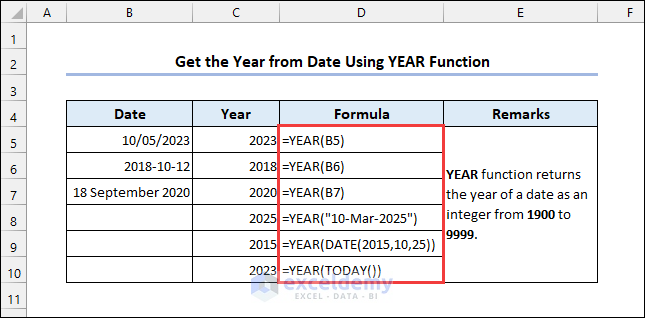
4.3 Applying the YEAR Funcion
Syntax of the YEAR function:
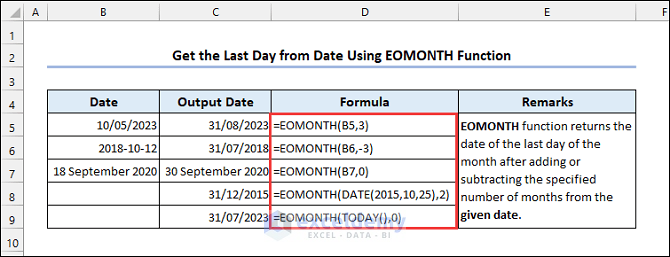
4.4 Utilizing the EOMONTH Function
Syntax of the EOMONTH function:
The start date is January 5, and you want to add 3 months. The function returns April 30.
4.5 Applying the WEEKDAY Function
Syntax of the WEEKDAY function:
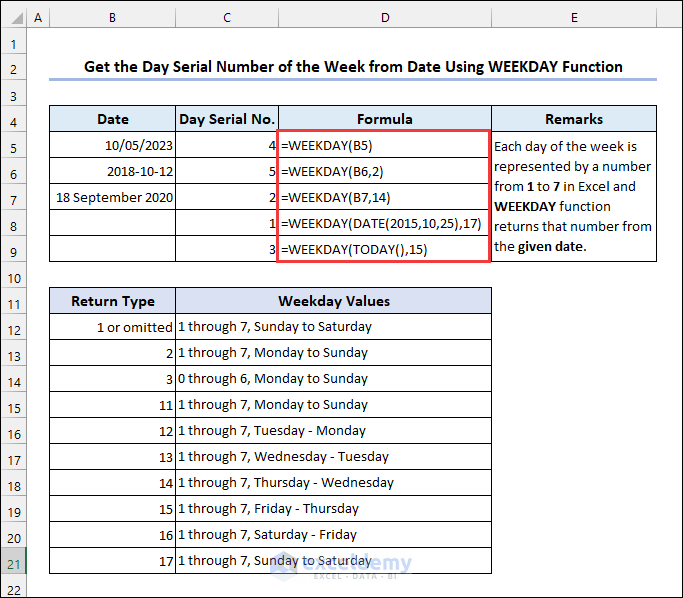
There is an optional argument to specify the numbering system for the days of the week. By default, it considers Sunday as the first day of the week, represented by 1, and Saturday as the last day of the week, represented by 7. The number you enter as the return_type will determine which date should be considered the first day of the week.
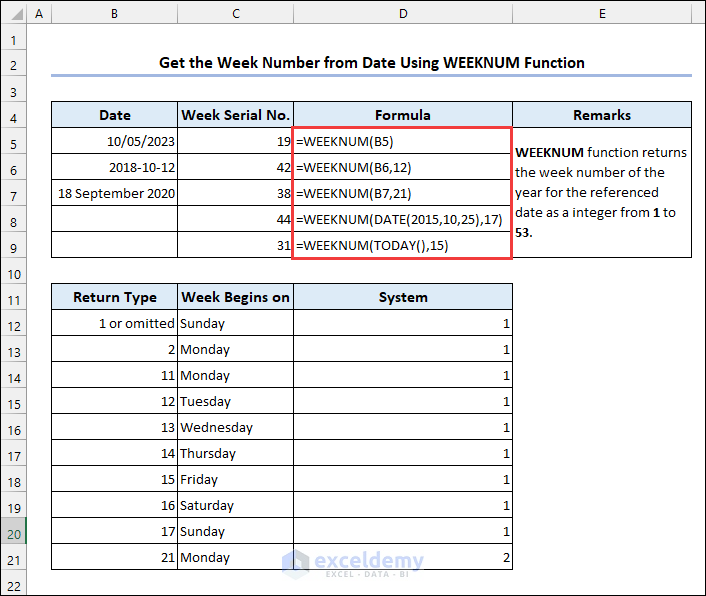
4.6 Using the WEEKNUM Function
Syntax of the WEEKNUM function:
The WEEKNUM function can return:
1: Week 1 specifies the week which contains January 1st;
2: Week 1 is the week that contains the first Thursday of the year.
4.7 Utilizing the ISOWEEKNUM Function
Syntax of the ISOWEEKNUM function:
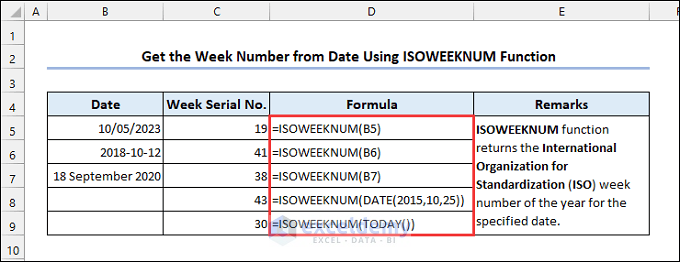
The ISO week numbering system considers the week containing the first Thursday of the year as the first week of the year. Each week starts on Monday. ISO week numbers can vary from 1 to 53.
5 – Calculate Date Difference
5.1 Using the DATEDIF Function
Syntax of the DATEDIF function:
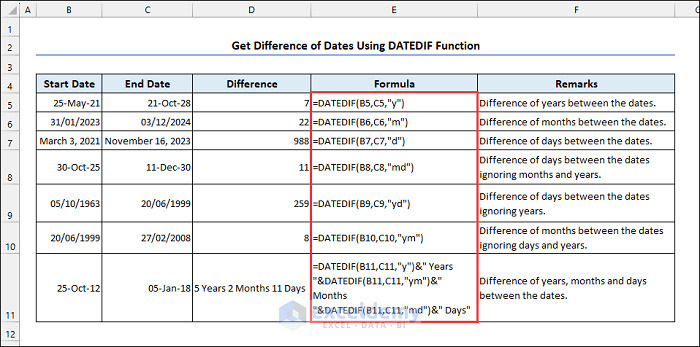
Units in this function are:
| Unit | Difference Type |
|---|---|
| D | Days between two dates. |
| M | Months between two dates. |
| Y | Years between two dates. |
| MD | Days between two dates ignoring months and years. |
| YM | Months between two dates ignoring years. |
| YD | Days between two dates ignoring years. |
5.2 Using the DAYS Function
Syntax of the DAYS function:
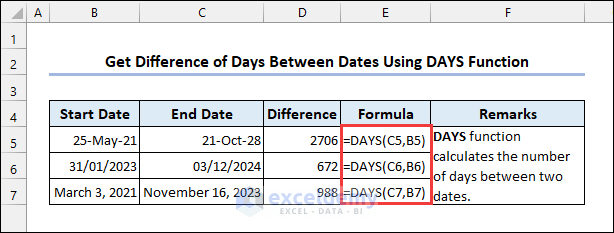
5.3 Applying the DAYS360 Function
Syntax of the DAYS360 function:
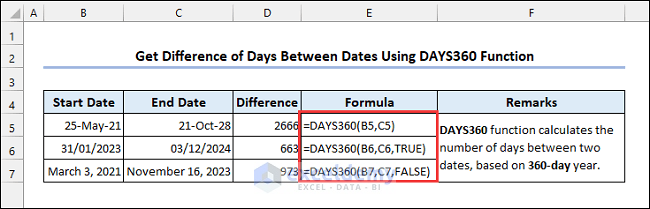
Method is an optional argument that specifies the day-count. TRUE is the European method and FALSE is the US method. Default is FALSE.
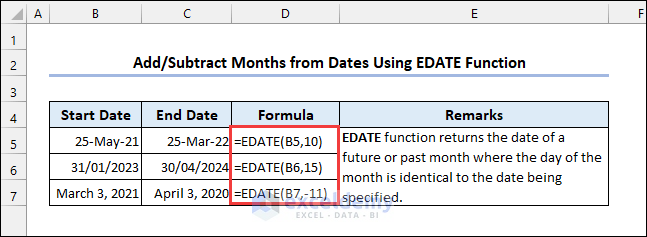
5.4 Applying the EDATE Function
Syntax of the EDATE function:
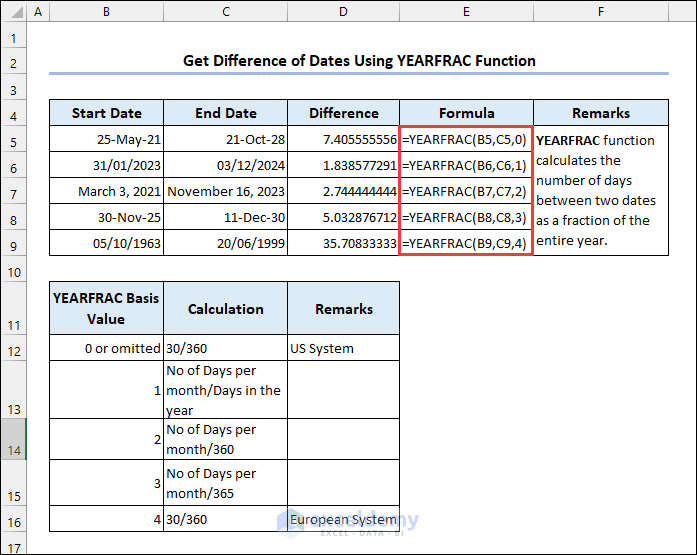
5.5 Utilizing the YEARFRAC Function
Syntax of the YEARFRAC function:
6 – Calculate Workdays
6.1 Using the WORKDAY Function
Syntax of the WORKDAY function:
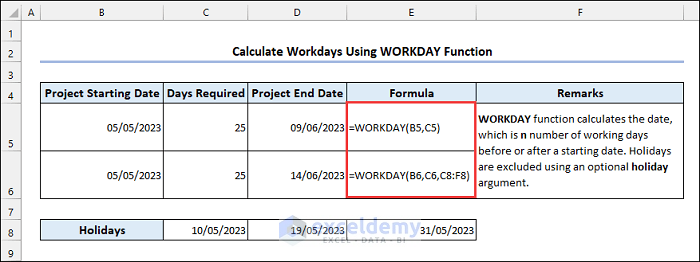
If there is a holiday in your time zone, you need to specify it in the holidays argument.
6.2 Applying the WORKDAY.INTL Function
Syntax of the WORKDAY.INTL function:
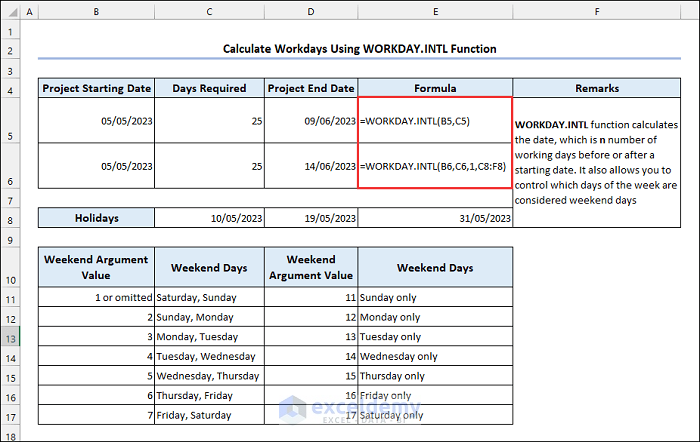
The WORKDAY.INTL function allows users to choose which days are considered as weekend.
6.3 Using the NETWORKDAYS Function
Syntax of the NETWORKDAYS function:
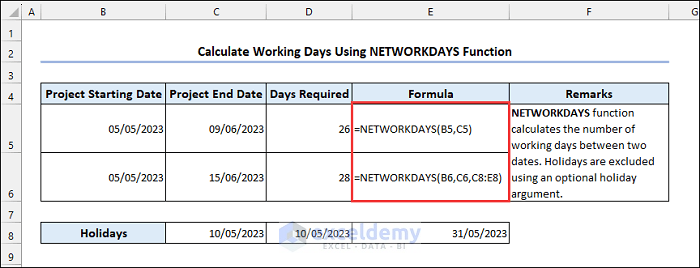
6.4 Using the NETWORKDAYS.INTL Function
Syntax of the NETWORKDAYS.INTL function:
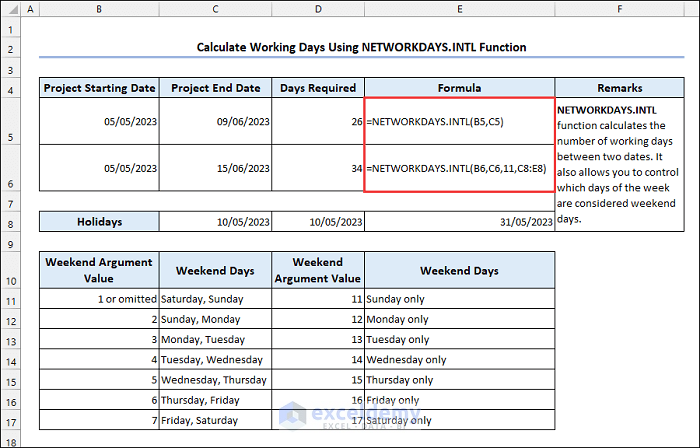
The NETWORKDAYS.INTL function allows users to choose which days are considered as weekend.
Excel Time Functions
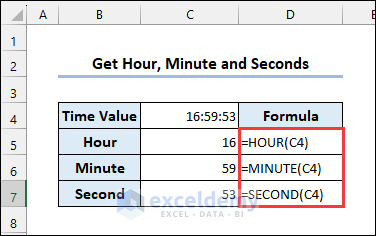
1 – HOUR, MINUTE & SECOND Functions
Syntax of the HOUR function:
Syntax of the MINUTE function:
Syntax of the SECOND function:
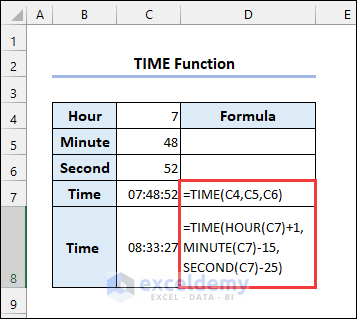
2 – TIME Function
Syntax of the TIME function:
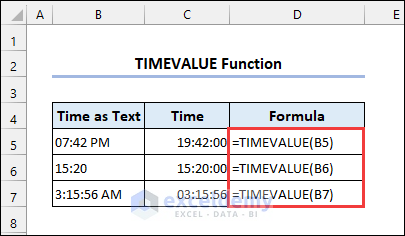
3. TIMEVALUE Function
Syntax of the TIMEVALUE function:
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do I calculate someone’s age based on their birthdate?
Ans: Use the DATEDIF function:
=DATEDIF(Birthdate, TODAY(), "y")Replace Birthdate with the cell reference containing the birth date. The formula will return the person’s current age in years.
2. How do I convert a date to a different date format?
Ans: To convert a date to a different date format:
- Select the cell with the date.
- Go to the Home tab, and click Number Format.
- Choose More Number Formats and select a date format or create a custom format.
3. How do I work with dates and time in different time zones?
Ans: Ensure your dates/times are in a standardized format (e.g., UTC). Use the CONVERT function to adjust the time zone offset:
=CONVERT(Date_Time, "UTC", "Time_Zone")Replace Date_Time with the cell reference containing the date and time, and Time_Zone with the time zone code (e.g., -07:00 for Pacific Time).
<< Go Back to Excel Function Categories | Excel Functions | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

