When working with large databases, dealing with ranges and cells is a common task. Sometimes, you need to perform the same action across a large range or a significant number of cells. Manually repeating this process can be time-consuming and inefficient. However, you can create a VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) code that runs through each cell in a specified range and performs the desired action. In this article, we’ll explore three methods for achieving this in Excel.
Method 1 – Applying VBA for Each Cell in a Range
Let’s consider a scenario where you want to apply the same VBA code to each cell in a given range (e.g., B4:F13). Follow these steps:
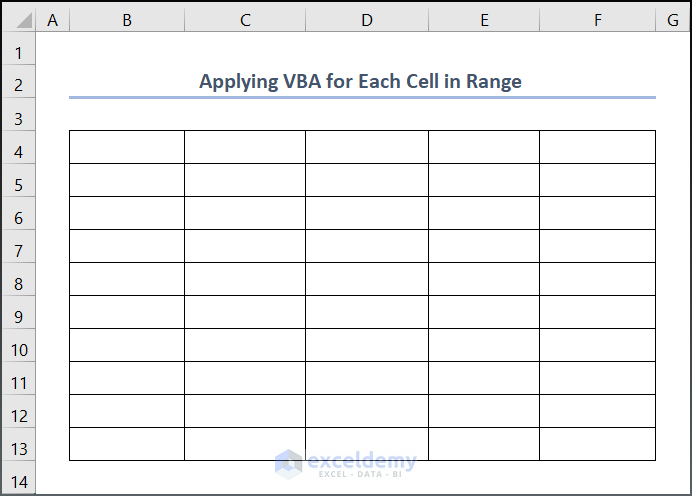
- Go to the Developer tab.
- Select Insert and choose the command button to add it to your worksheet.
The command button has been added.
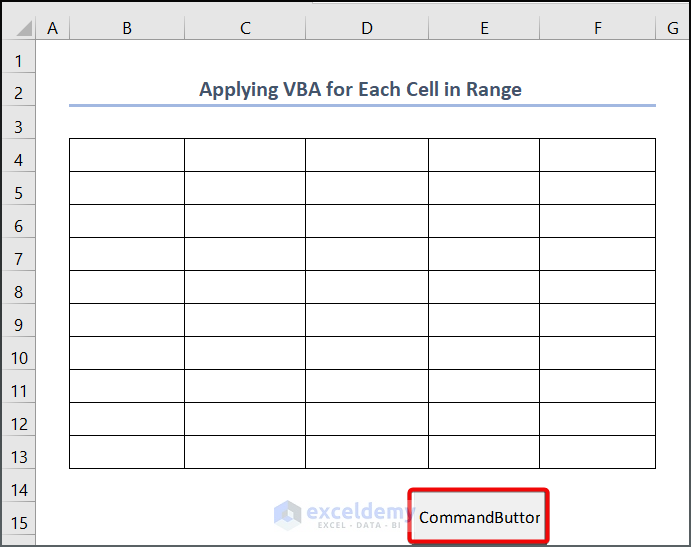
- Right-click on the command button and select Properties.
- Change the caption (name) of the button (e.g., Click Here).
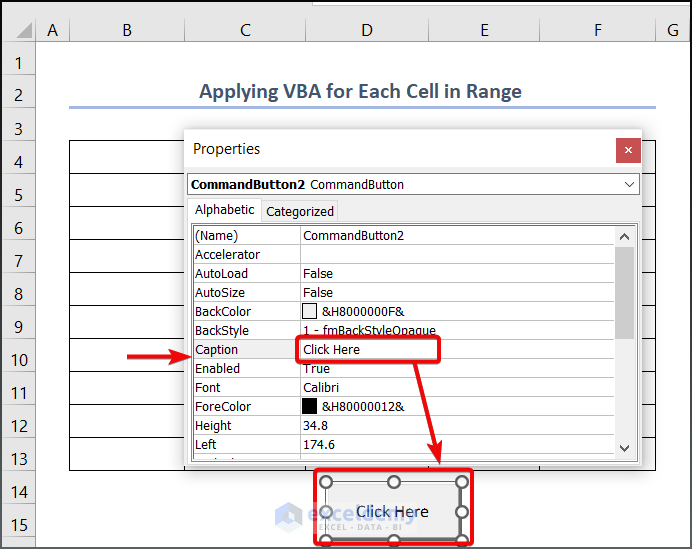
- Double-click the command button to open the VBA Module.
- Declare two variables for the range:
Dim CL As Range
Dim Rng As Range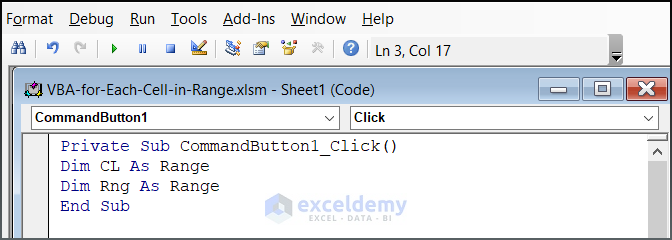
- Assign the specific range you want to work with:
Set Rng = Worksheets("Each Cell in Range").Range("B4:F13")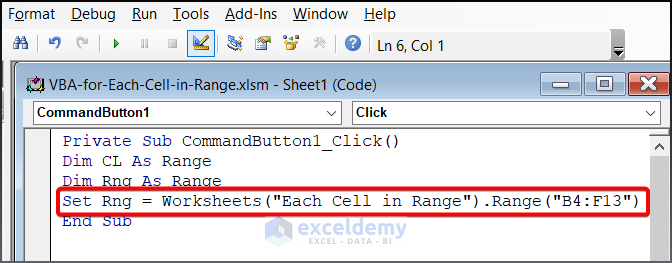
- Use a loop to perform an action on each cell in the range:
For Each CL In Rng
CL.Value = 100
Next CL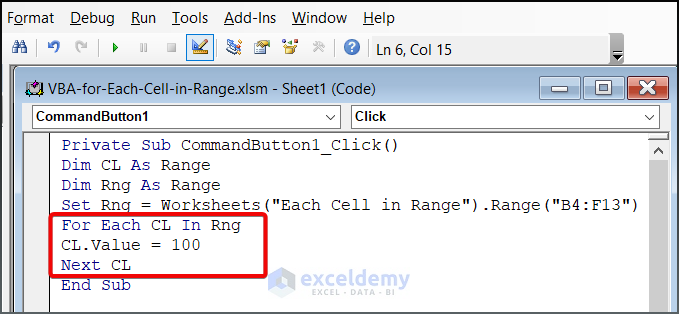
The final code is:
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Dim CL As Range
Dim Rng As Range
Set Rng = Worksheets("Each Cell in Range").Range("B4:F13")
For Each CL In Rng
CL.Value = 100
Next CL
End Sub- Return to your main worksheet.
- Click the Click Here command button to execute the VBA code.
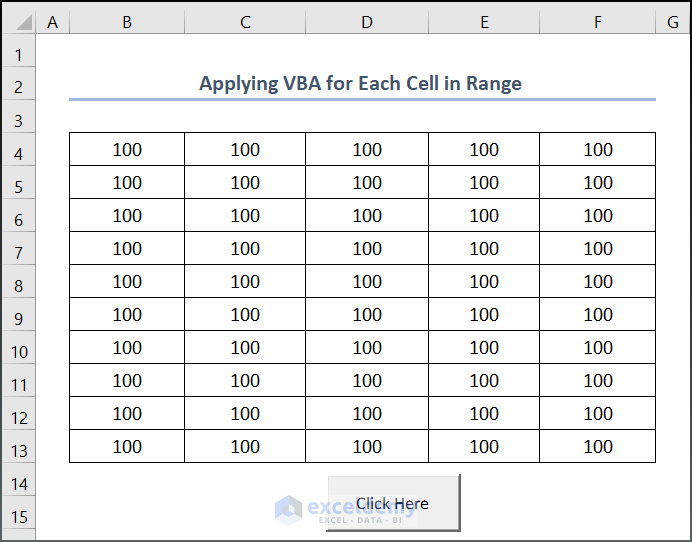
- You can also apply text values to each cell in the range. Instead of CL.Value = 100, use your desired text value (e.g., “ExcelDemy”).
CL.Value = “ExcelDemy”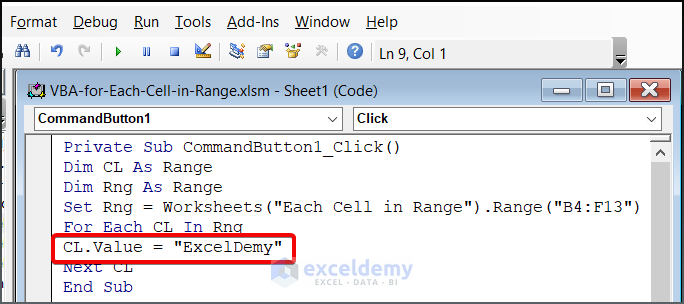
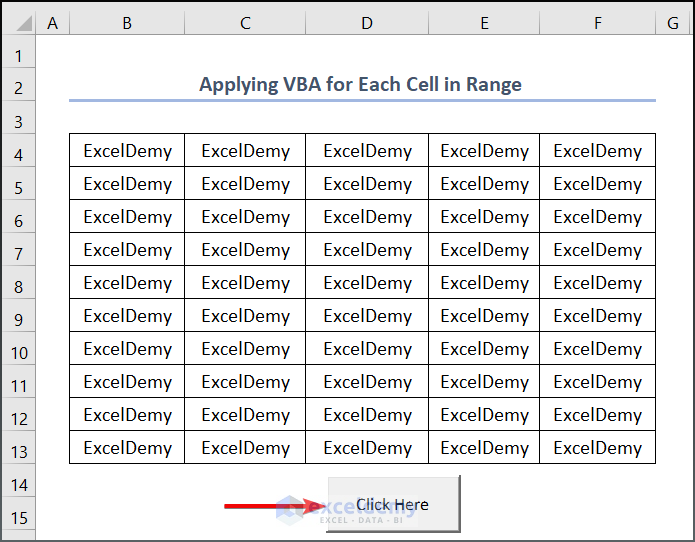
- Click on the command button and the VBA code will return this text value for each cell in the range.
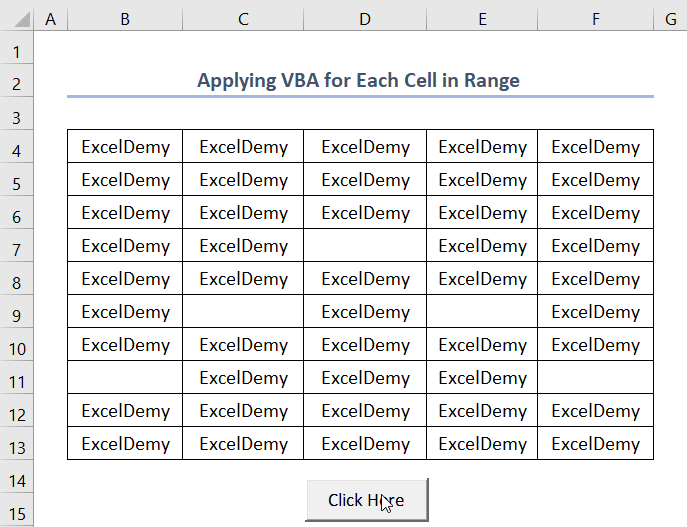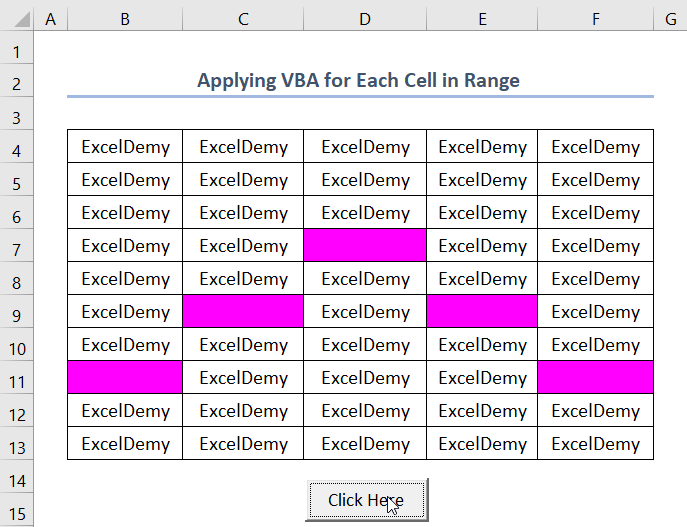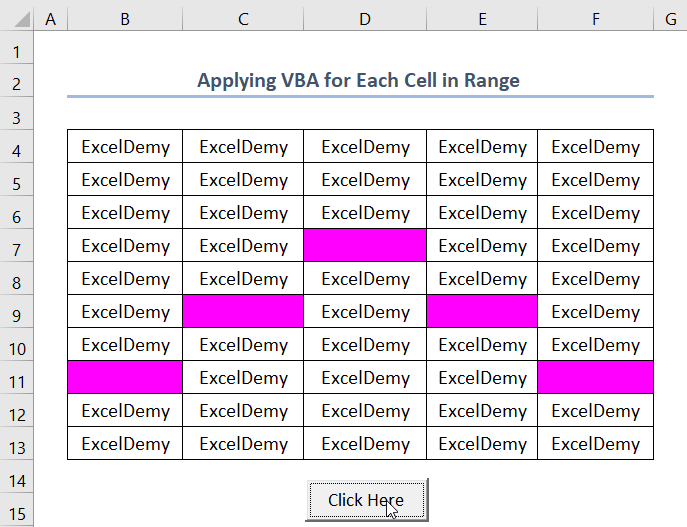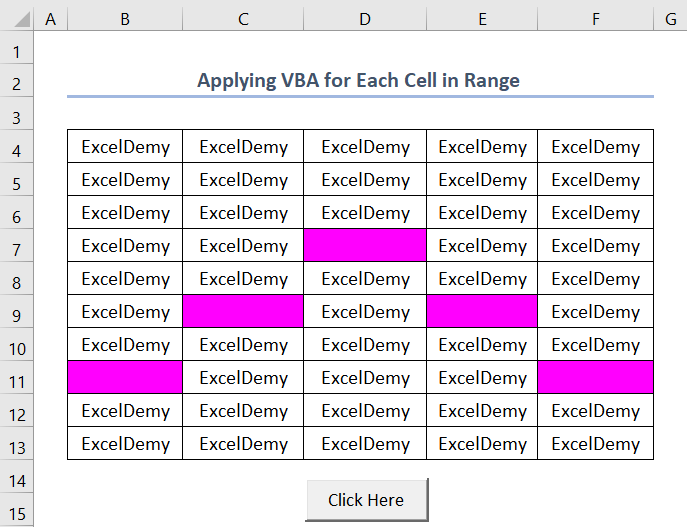
- To highlight blank cells within the range, add the following condition to your existing code:
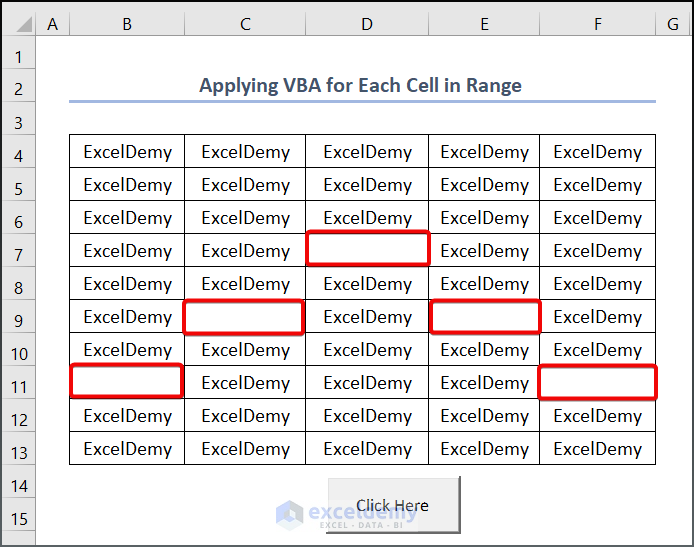
If CL.Value = "" Then
CL.Interior.ColorIndex = 7
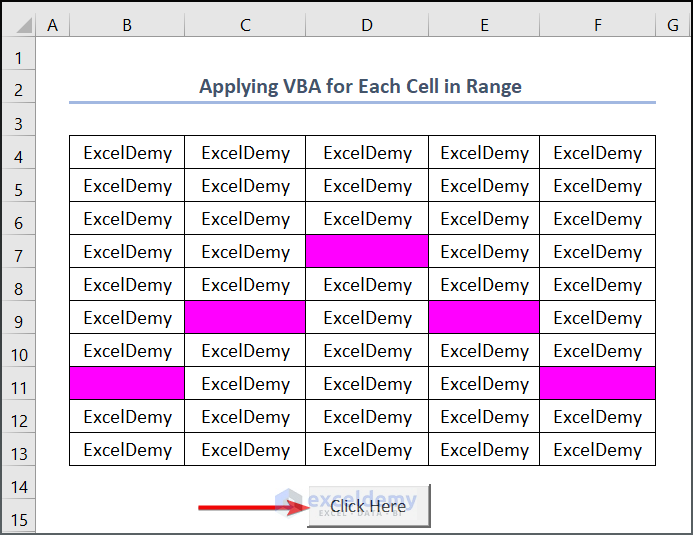
End If- In addition, the new code will highlight the blank cell with red color. So, the full code is,
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Dim CL As Range
Dim Rng As Range
Set Rng = Worksheets("Each Cell in Range").Range("B4:F13")
For Each CL In Rng
If CL.Value = "" Then
CL.Interior.ColorIndex = 7
End If
Next CL
End Sub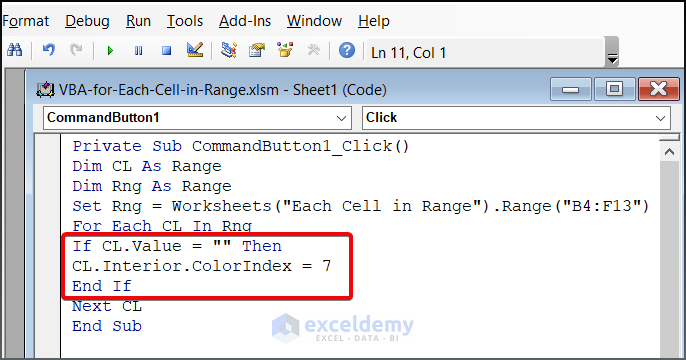
- Click the command button to see the results.
Method 2 – Inserting VBA Code for Each Cell in a Column
You can also run VBA code for each cell in a column. Let’s say you have a column containing numbers, and you want to color values that are lower than 10. Follow these steps:

- Follow the instructions we discussed earlier to insert a command button.
- Double-click the command button to open the VBA window.
- Enter the following code in your VBA window:
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Dim c As Long
Columns(2).Font.Color = vbBlack
For c = 1 To Rows.Count
If Cells(c, 2).Value < Range("D5").Value _
And Not IsEmpty(Cells(c, 2).Value) Then
Cells(c, 2).Font.Color = vbRed
End If
Next c
End Sub⚡Code Breakdown
The code is divided into 2 steps.
- In the first part, we set c as a Long variable, and the font color is black.
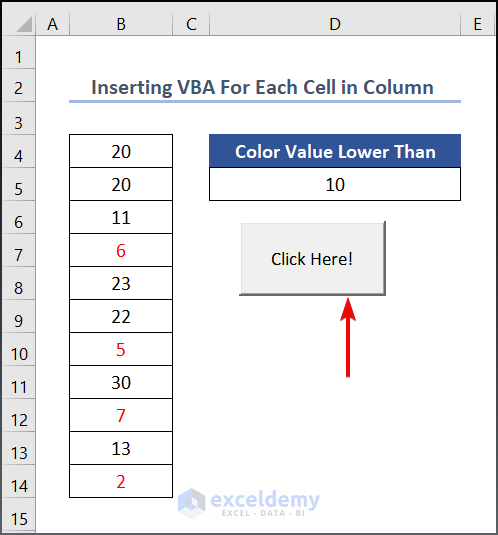
- The For loop checks each row to see if the value exceeds that of cell D5. If not, the font color is set to Red.
- Click the command button to execute the VBA code.
Read More: How to Use VBA for Each Row in a Range in Excel
Method 3 – Employing VBA for Each Cell in a Row
You can also run a VBA code for each cell in a row. Follow these steps:
- Add a command button and change its name to Click Here!
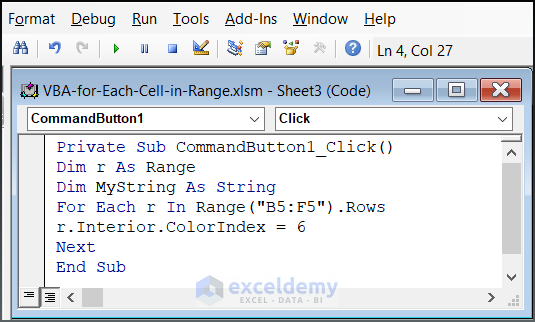
- Double-click on the command button to open the VBA window and enter the code below:
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click ()
Dim r As Range
Dim MyString As String
'For Each cell in a row, and apply a yellow color fill
For Each r In Range("B3:F3").Rows
r.Interior.ColorIndex = 6
Next
End Sub⚡Code Breakdown
The code is divided into 2 steps.
- In the first part, r is taken as Range and Mystring as String variable.
- In the second part, the For loop fills the cells in a specific row with yellow color (Interior.ColorIndex = 6).
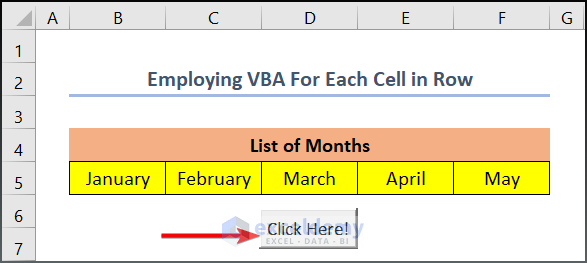
- Click the command button to see the results.
How to Use Excel VBA to Loop Through a Range Until a Single Empty Cell
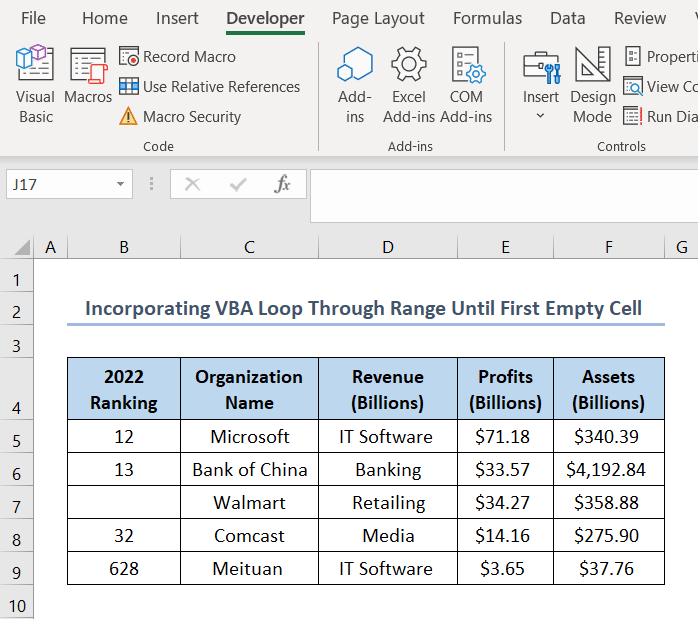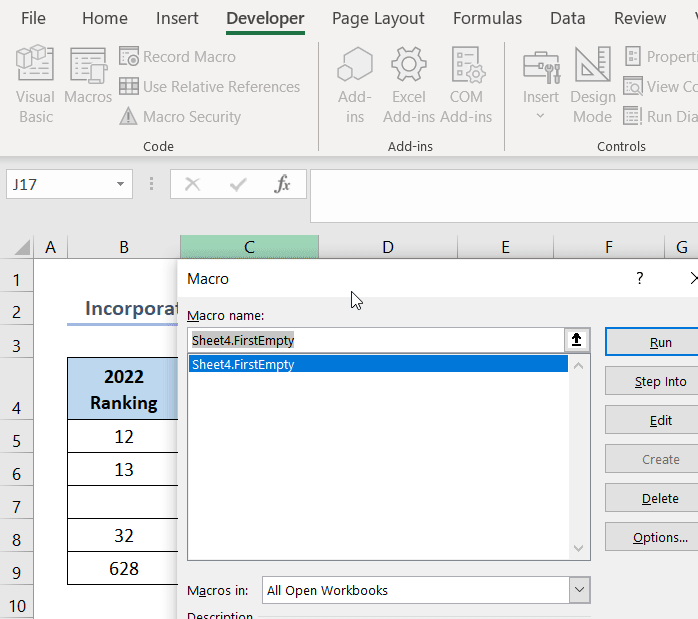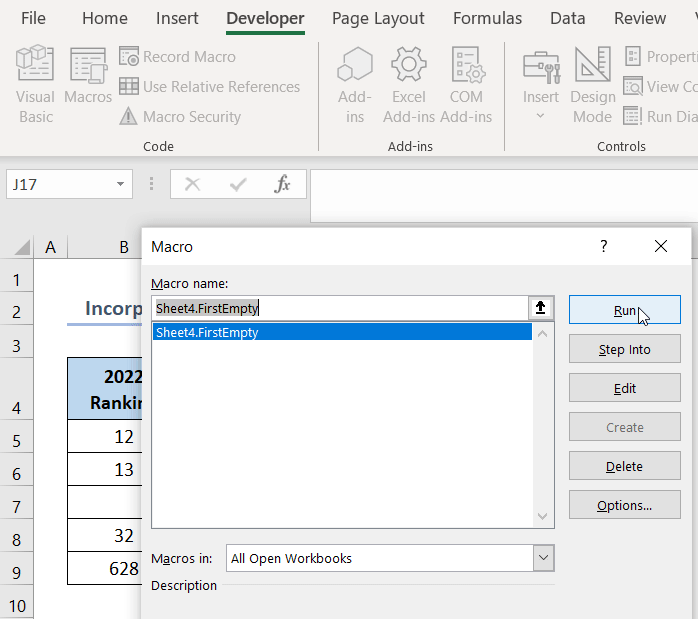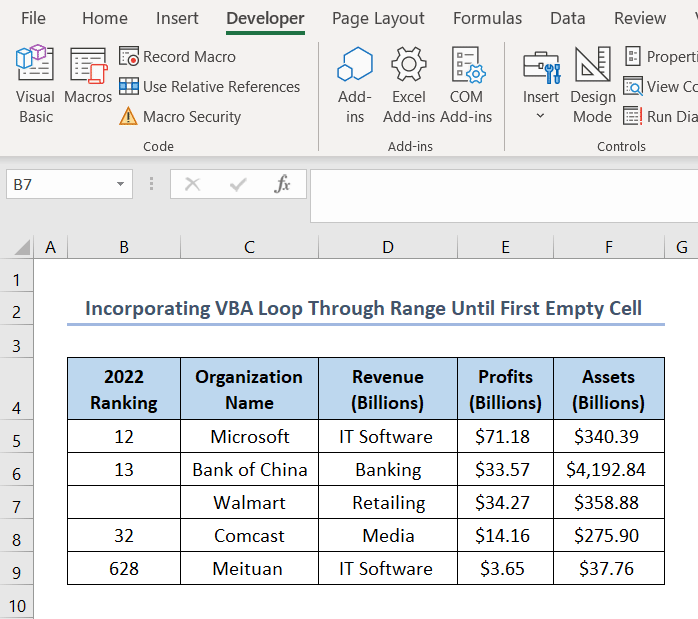
View the dataset given below, where you will see B7 cell is empty. Let’s develop a VBA code to find the empty cell.
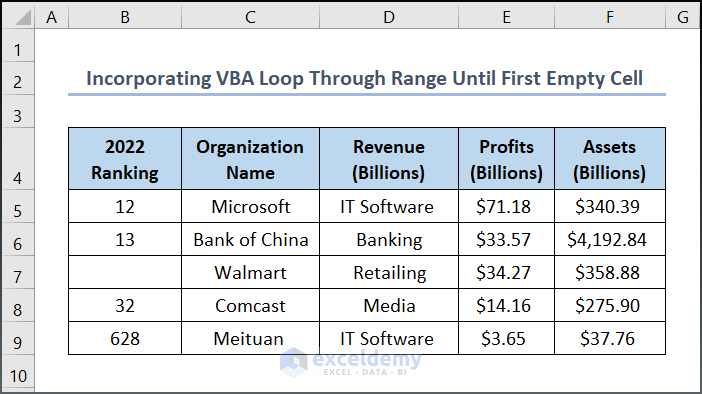
If you’re dealing with a large dataset and need to find an empty cell, enter the following VBA code:
- Press Alt + F11 to open Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications.
- Enter the following VBA code in Sheet4:
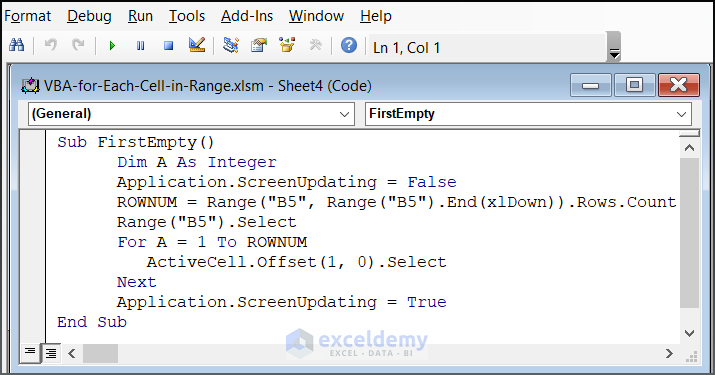
Sub FirstEmpty()
Dim A As Integer
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
ROWNUM = Range("B5", Range("B5").End(xlDown)).Rows.Count
Range("B5").Select
For A = 1 To ROWNUM
ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select
Next
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End Sub
- This code finds the first empty cell in column B starting from B5.
The output is given below:
Read More: Loop through a Range for Each Cell with Excel VBA
Things to Remember
If your developer tab isn’t visible, activate it via: Customized Quick Access Toolbar → More Commands → Customize Ribbon → Developer → OK
Download Practice Workbook
You can download the practice workbook from here:
Similar Articles to Explore
- How to Use For Each Loop in Excel VBA
- Excel VBA to Exit For Each Loop
- How to Use For Next Loop in Excel VBA



Great post! I really appreciated the clarity of the explanations for each method. The step-by-step approach makes it easy to follow along, even for beginners. I can’t wait to implement these techniques in my own Excel projects!
Hello,
Thanks for your appreciation. Glad to hear that our explanations is helpful to you. Keep learning Excel with ExcelDemy!
Regards
ExcelDemy