The American System Code for Information Interchange, or ASCII, is a character encoding standard used in digital communications. A unique integer number is assigned to each character that can be entered in the CHAR function. The character can be a number, alphabet, punctuation marks, special characters, or control characters. For Example, the ASCII code for [comma], is 044. The lowercase alphabets a-z have ASCII values ranging from 097 to 122.
The CHAR Function
Objective
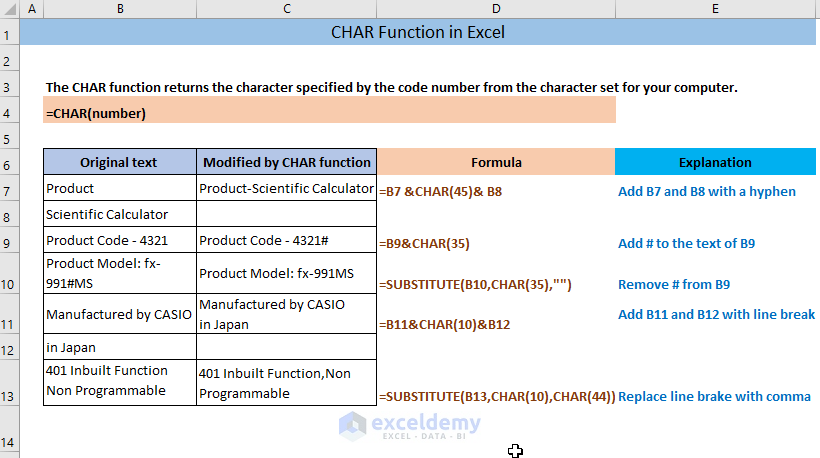
The CHAR function returns the character specified by its code number.
Syntax
CHAR(number)
Argument Explanation
| Argument | Required/Optional | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| number | Required | A number between 1 to 255 assigned to a specific character |
Output
The CHAR function returns a character based on the number given as argument.
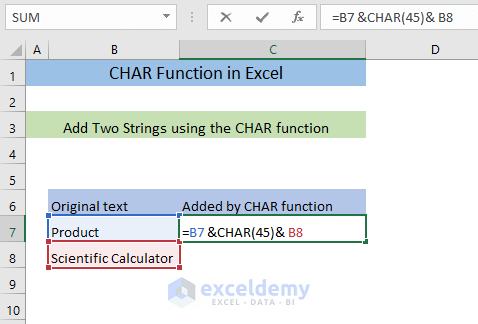
Example 1 – Add Two Strings Using The CHAR Function
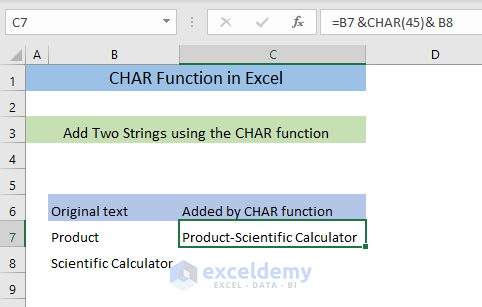
- Enter the following formula in an empty cell (C7),
=B7 &CHAR(45)& B8The formula will add the strings in B7 and B8 with a hyphen and return the output in C7. (to add other characters, insert a different code. For example, 44 for comma or 32 for a space).
- Press ENTER.
You’ll see the two strings joined by a hyphen in C7.
Example 2 – Add a Character to a String
To add a # to the product code:
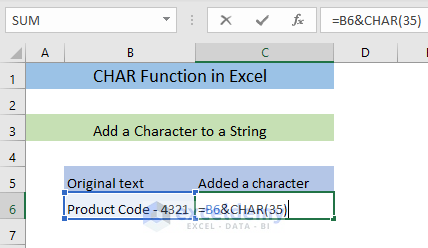
- Enter the following formula in an empty cell (C7).
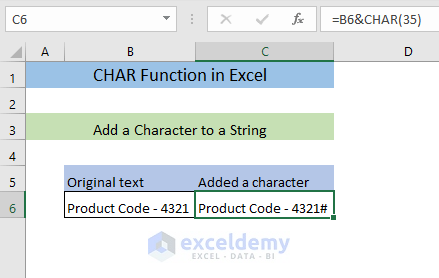
=B6&CHAR(35)The formula will add a # (code 35) to the text in B6 and return the output in C7.
- Press ENTER.
You’ll see a # added to the text in C7.
Read More: Character Codes for CHAR Function in Excel
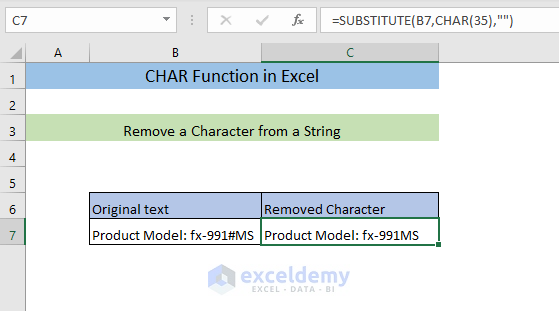
Example 3 – Remove a Character from a String
To remove the # from the string in B7:
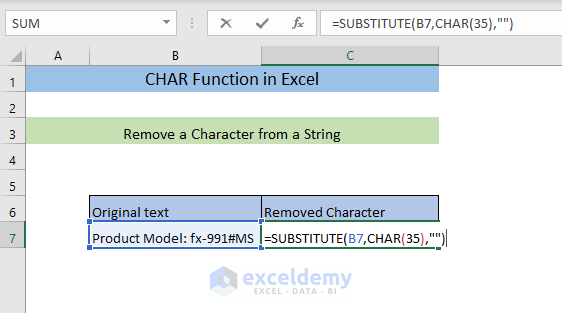
- Enter the following formula in C7.
=SUBSTITUTE(B7,CHAR(35),"")The CHAR function will return the character # for the code 35 and the SUBSTITUTE function will remove it from B7, replacing it with an empty string.
- Press ENTER.
The character was removed.
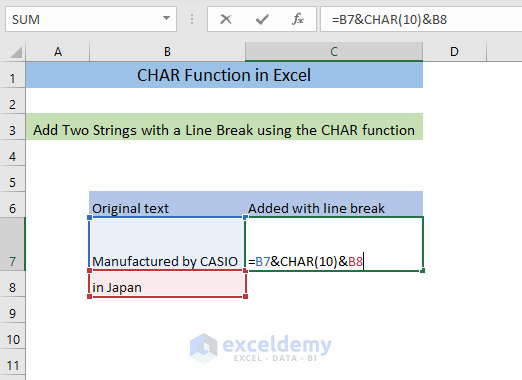
Example 4 – Add Two Strings with a Line Break Using the CHAR Function
- Enter the following formula in C7.
=B7&CHAR(10)&B8The formula will join the texts in B7 and B8 with a line break (character code 10).
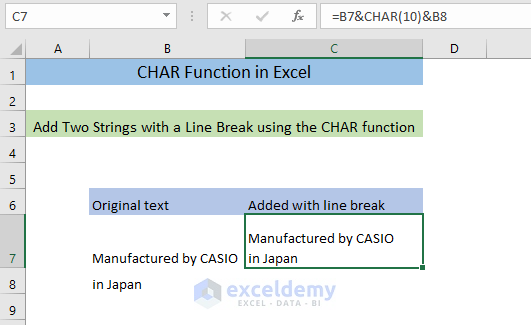
- Press ENTER.
This is the output.
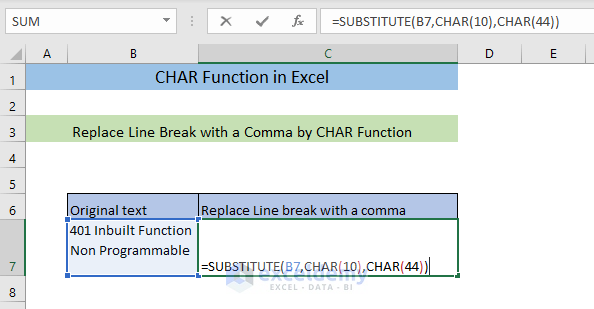
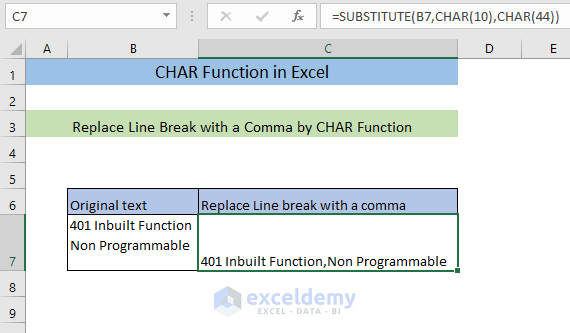
Example 5 – Replace a Line Break with a Comma using the CHAR Function
- Enter the following formula in C7.
=SUBSTITUTE(B7,CHAR(10),CHAR(44))CHAR(10) returns a line break and CHAR(44) returns a comma. The SUBSTITUTE function replaces the line break with a comma.
- Press ENTER.
This is the output.
Read More: How to Insert a New Line Using CHAR Function in Excel
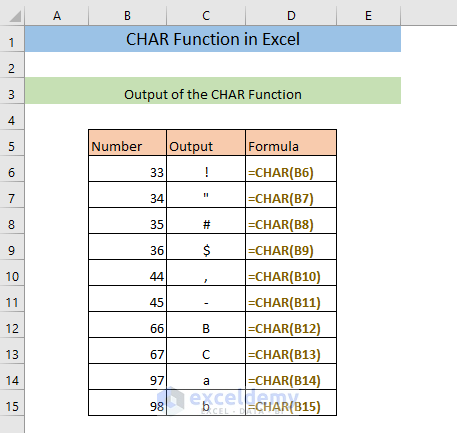
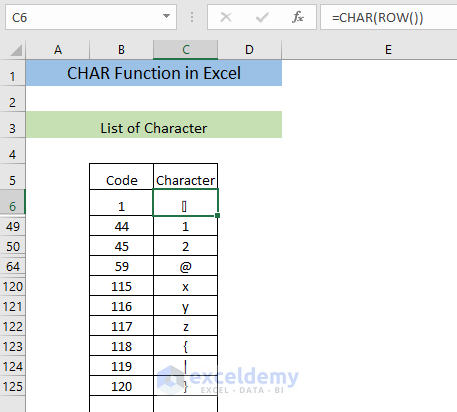
Example 6 – Using the CHAR Function to Create a List of Characters
- Enter the following formula.
=CHAR(ROW())The formula returns the first character.
- Press ENTER.
- Drag Fill Handle to the 255th cell.
You will get the complete list of the characters.
Read More: How to Use CHAR(32) Formula in Excel
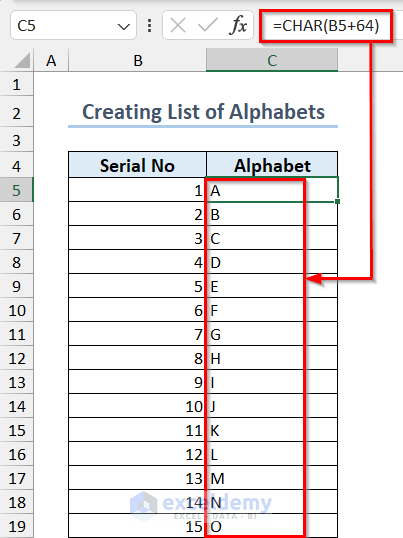
Example 7 – Create a List of Alphabets in Excel
- Create a list of numbers from 1 to 26 for each alphabet letter.
- Use the following formula.
=CHAR(B5+64)64 was added to each serial number as the alphabet code starts from 65.
Example 8 – Check If the ASCII Values Are Correct for a List of Characters
- Use the function:
=IF(CHAR(C5)=B5,"Correct","Incorrect")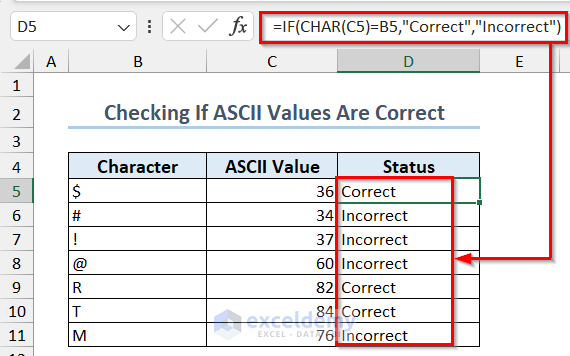
Read More: How to Convert Excel ASCII to Char
Things to Remember When Using The CHAR Function
- The CODE function can be used as a reverse CHAR function. For example, enter =CODE(“A”), it will return 65.
- The CHAR function can not return all characters. For advanced characters, use the UNICHAR function.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can I use the CHAR function to insert non-printable characters?
Yes, you need to specify their ASCII or Unicode codes.
Download Practice Workbook
Excel CHAR Function: Knowledge Hub
- How to Use CHAR(34) Formula in Excel
- How to Use Code 9 with Excel CHAR Function
- How to Use CHAR(10) Function in Excel
<< Go Back to Excel Functions | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

