In this tutorial, you will learn about the Not Equal To operator in Excel with examples and illustrations. Here’s an overview of the basic use of the operator.
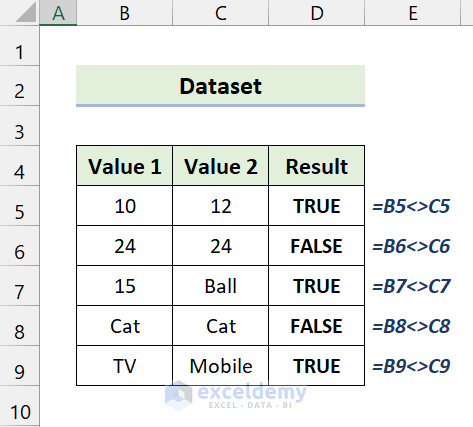
What Is ‘Not Equal to’ in Excel?
The Not Equal To is a logical operator that compares two values. It is opposite to the Equal To. To express this operator, we use the pair of angle brackets (<>) in Excel. It returns a Boolean value TRUE or FALSE.
- TRUE means the two values are not identical or equal.
- FALSE means the two values are the same or equivalent.
How to Use the ‘Not Equal to’ Operator in Excel?
The basic syntax of this operator is:
=value1 <> value2
The values can be cell references or constants. Here are some examples.

The ‘Not Equal to’ Operator with Other Functions: 5 Examples
Example 1 – ‘Not Equal to’ in the IF Function
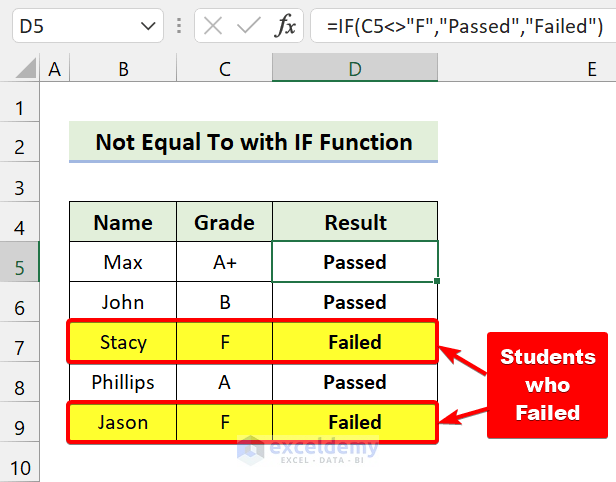
We have some student names and their grades. We’ll find the students who failed the exam. If anyone’s grade is not equal to “F”, they passed.
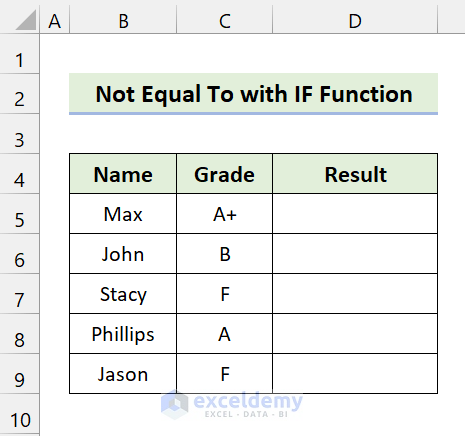
Steps
- Use the following formula in Cell D5:
=IF(C5<>"F","Passed","Failed")
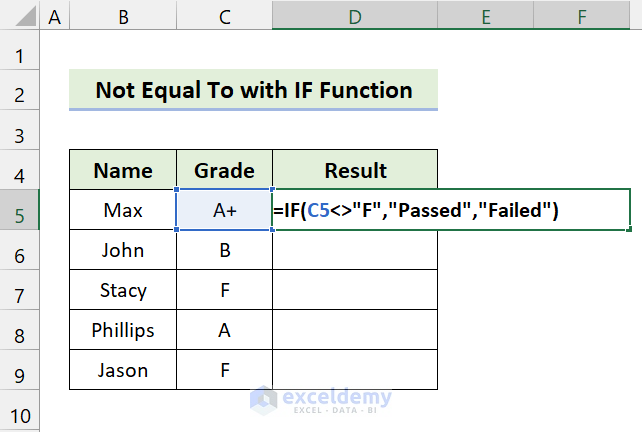
- Press Enter.
- Drag the Fill handle icon over the range of cells D6:D9.
Read More: How to Use Comparison Operators in Excel
Example 2 – ‘Not Equal To’ with the SUMIF Function
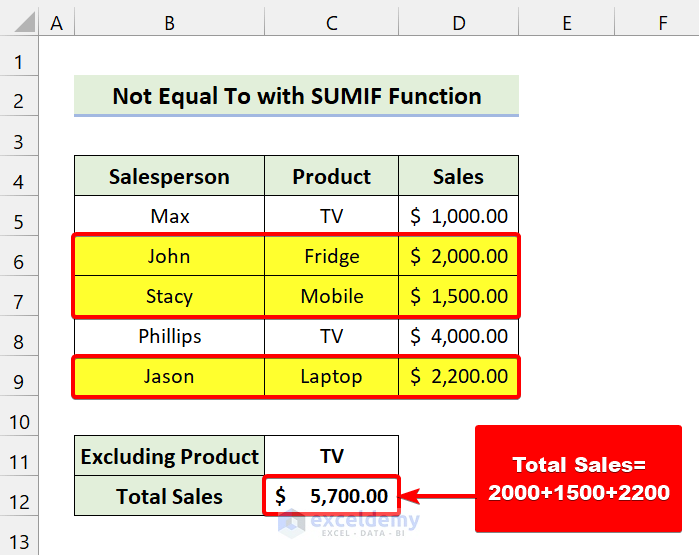
You can see some salesperson names, their selling products, and the sales amount. We’ll find the total sales without the product TV.
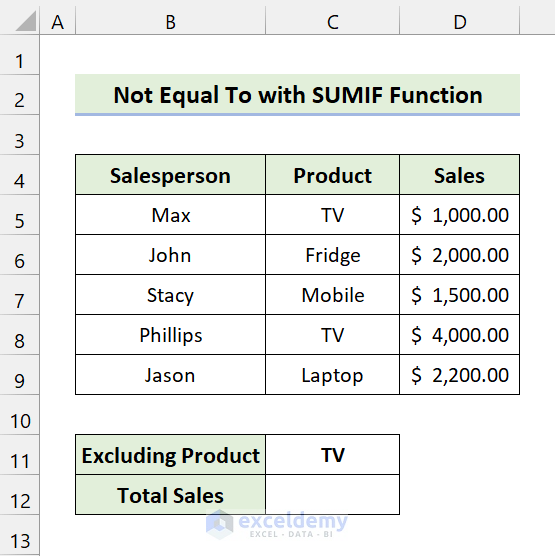
Steps
- Insert the following formula in Cell C12:
=SUMIF(C5:C9,"<>"&C11,D5:D9)
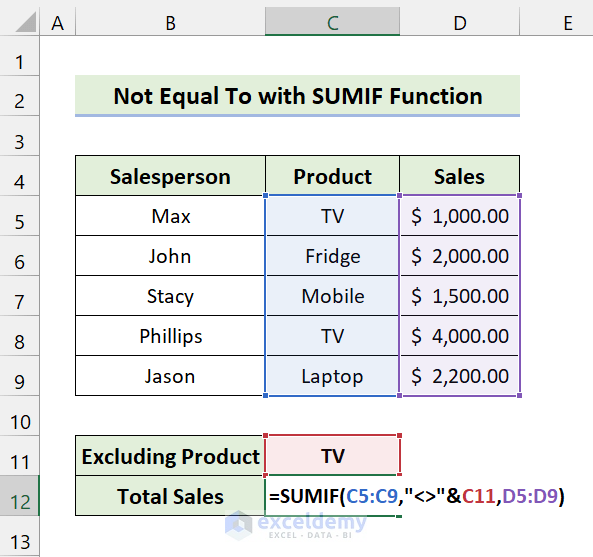
- Press Enter.
Example 3 – Excel COUNTIF Function with the ‘Not Equal To’ Operator
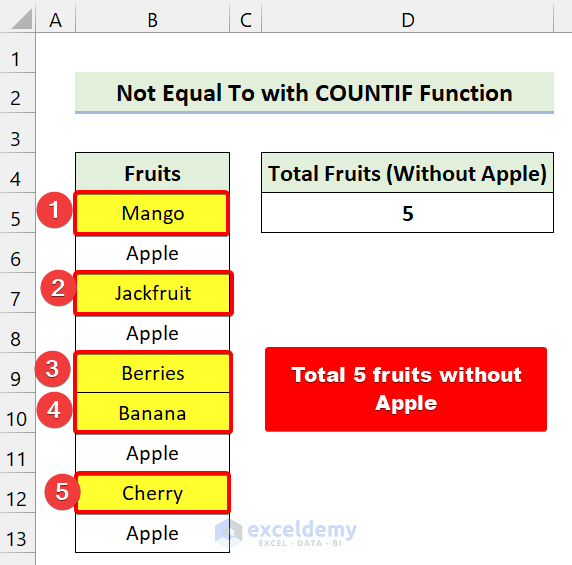
We have a dataset of some Fruits. We’ll count the number of total fruits without including “Apple”.
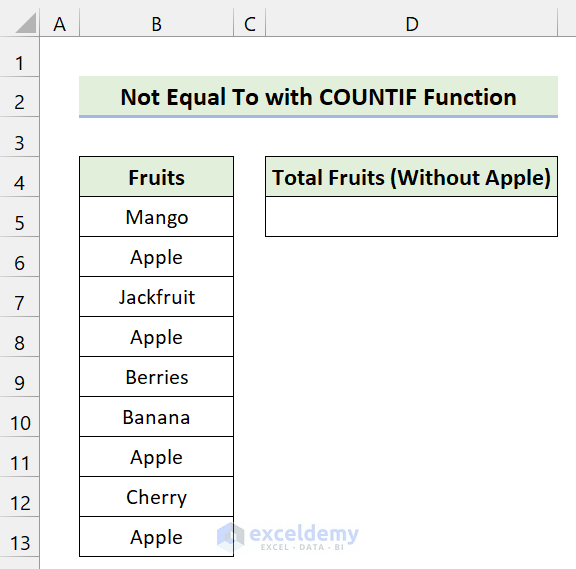
Steps
- Use the following formula in Cell D5:
=COUNTIF(B5:B13,"<>"&"Apple")
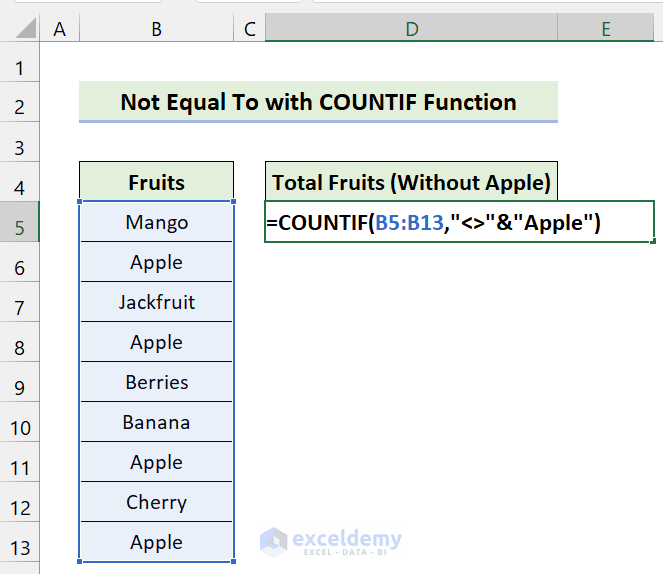
- Press Enter.
Read More: How to Use Less Than Or Equal to Operator in Excel
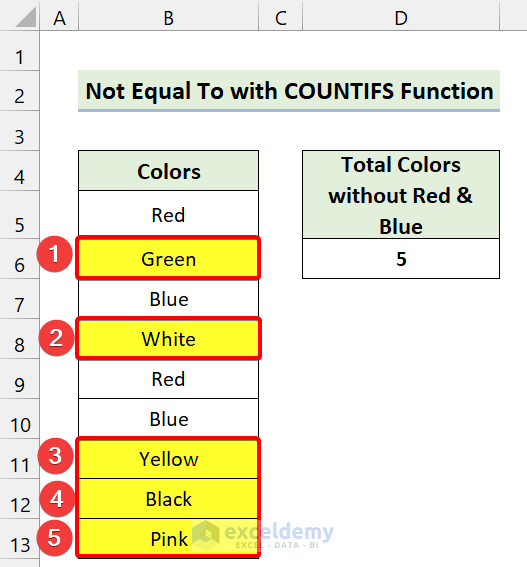
Example 4 – Combining ‘Not Equal To’ with the COUNTIFS Function
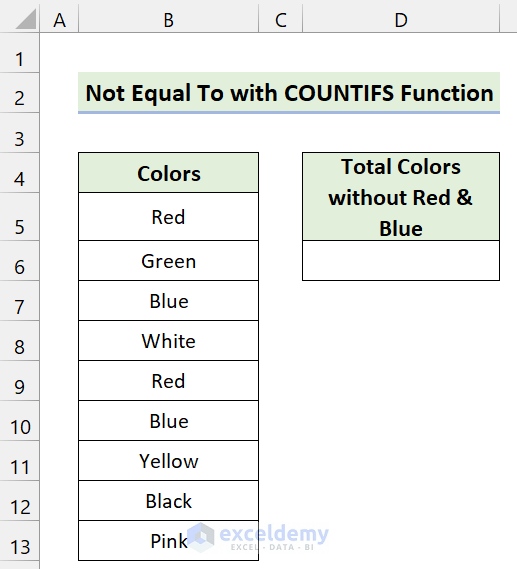
We have a dataset of some colors. We’ll use the Not Equal To operator to count the number of colors without “Red” and “Blue”.
Steps
- Use the following formula in Cell D5:
=COUNTIFS(B5:B13,"<>"&"Red",B5:B13,"<>"&"Blue")
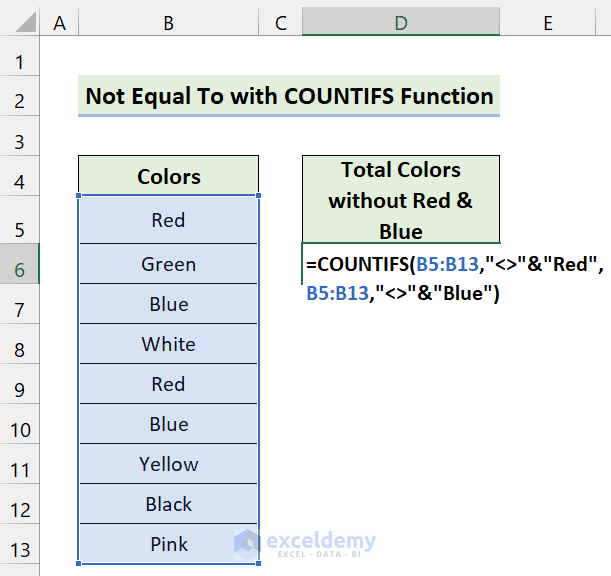
- Press Enter.
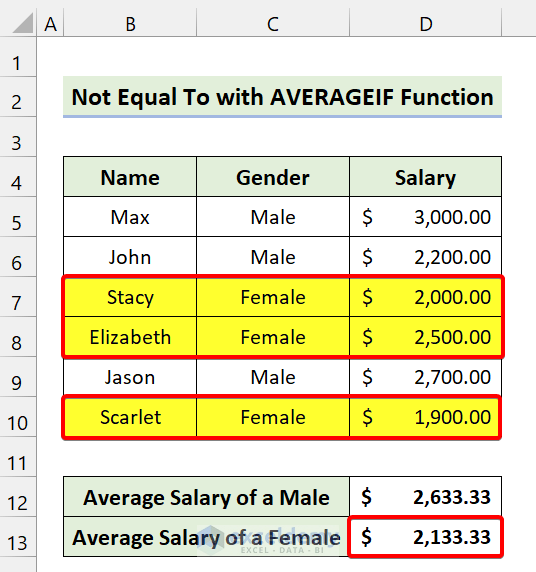
Method 5 – AVERAGEIF with ‘Not Equal to’ in Excel
We have some data on salaries. Let’s find the average salary for both male and female employees.
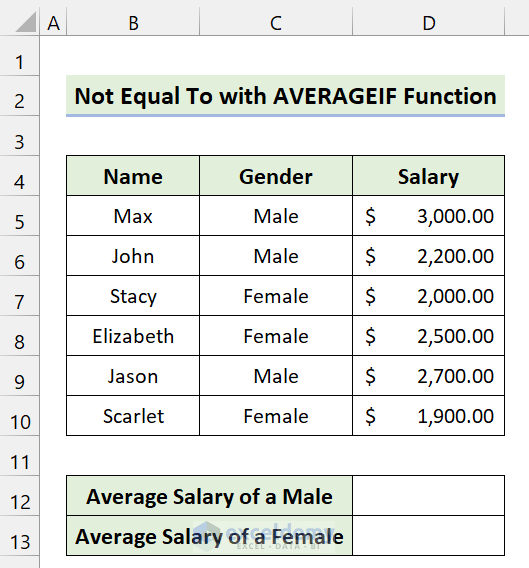
Steps
- Insert the following formula in Cell D12:
=AVERAGEIF(C5:C10,"<>"&"Female",D5:D10)
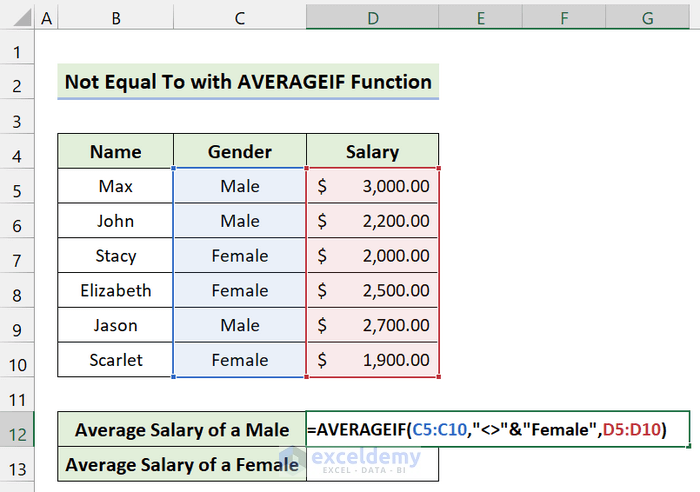
- Press Enter.
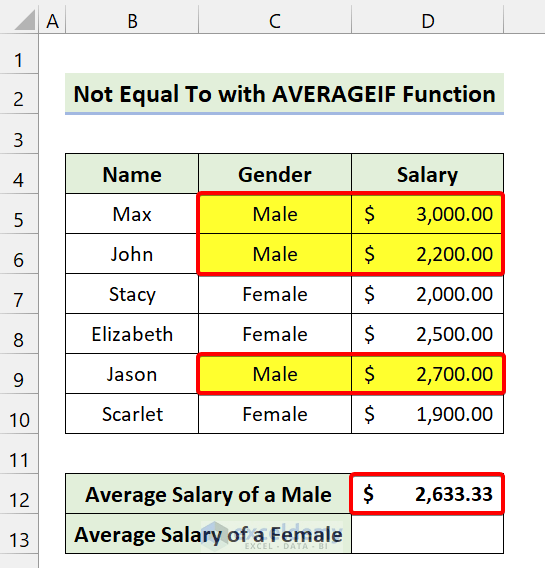
- Use the following formula in Cell D13:
=AVERAGEIF(C5:C10,"<>"&"Male",D5:D10)
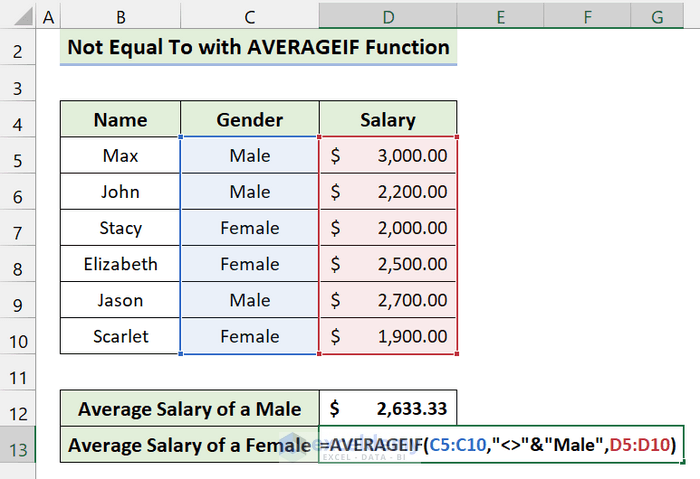
- Press Enter.
Things to Remember
✎ The Not Equal To operator requires at least two values to check. It won’t work until you give two values.
✎ The Not Equal To operator is case-insensitive. For instance, if you compare “ball” and “BALL” in, it will return FALSE.
Download the Practice Workbook
Further Readings
- Reference Operator in Excel
- How to Perform Greater than and Less than in Excel
- How to Use Greater Than or Equal to Operator in Excel Formula
- What is the Order of Operations in Excel
- Excel Boolean Operators: How to Use Them?
- How to Apply ‘If Greater Than’ Condition In Excel
<< Go Back to Excel Operators | Excel Formulas | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

