Method 1 – Using a Logical Operator to Test the If Greater Than Condition
Here’s a dataset of the marks obtained by several students. We want to find who got a score higher than 80.
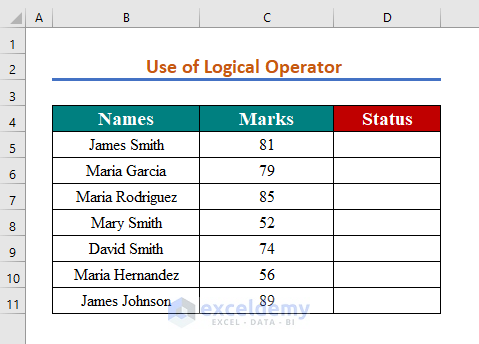
Steps:
- Insert the following formula in cell D5
=C5>80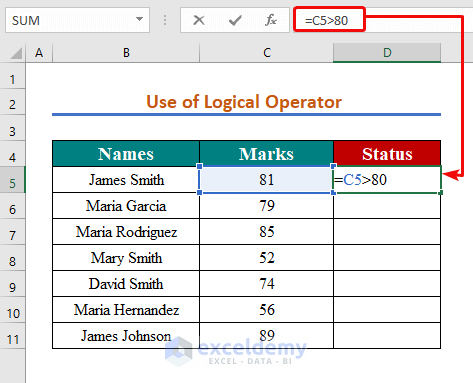
- Hit Enter.
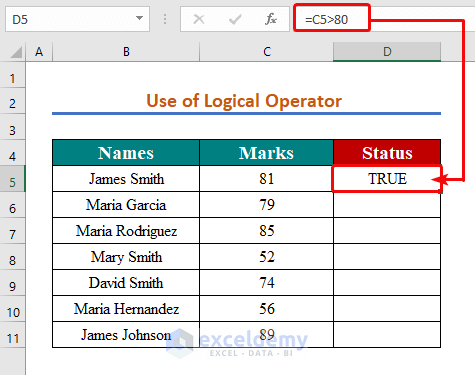
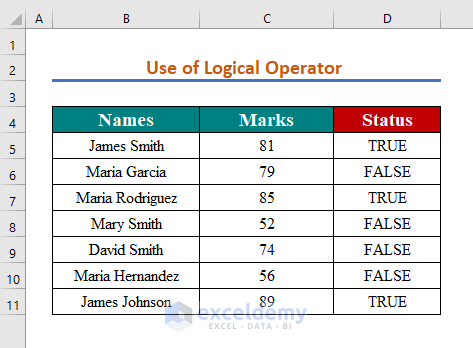
- Repeat the formula while changing the cell reference or use the AutoFill Handle Tool.
Read More: How to Use Comparison Operators in Excel
Method 2 – Using the OR Function with an If Greater Than Operator
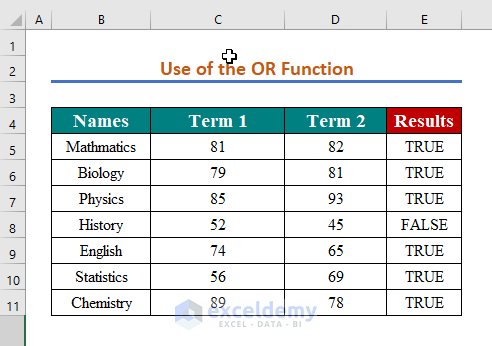
We have a dataset of obtained marks in two consecutive months. We want to know if the score is higher than 60 in either of the two terms.
Steps:
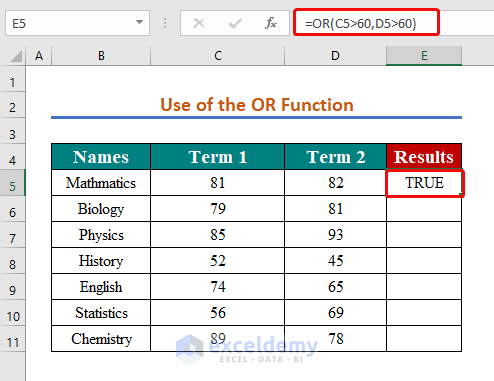
- In cell E5, use the following formula:
=OR(C5>60,D5>60)- Press Enter to the result.
- Repeat the formula for other cells or use AutoFill.
Read More: How to Perform Greater than and Less than in Excel
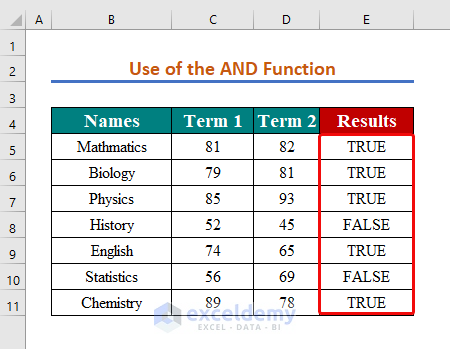
Method 3 – Combining the AND Function with the If Greater Than Operator
We’re looking for the subjects where the student acquired more than 60 marks in both terms.
Steps:
- Use the formula below to apply the AND Function:
=AND(C5>60,D5>60)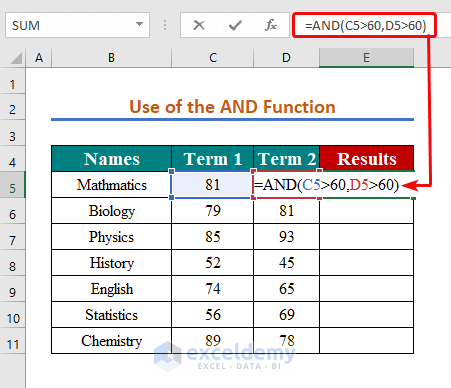
- Click Enter.
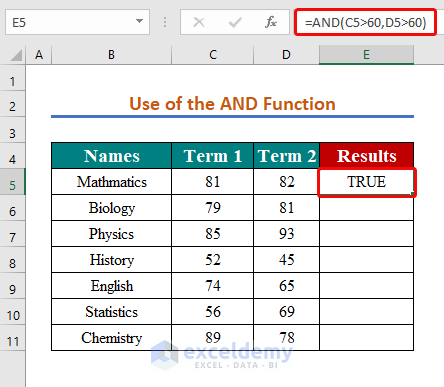
- Use AutoFill.
Read More: How to Use Greater Than or Equal to Operator in Excel Formula
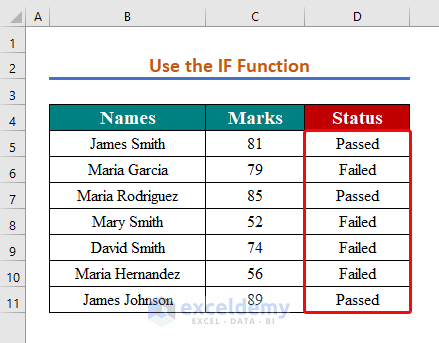
Method 4 – Using the IF Function to Apply the If Greater Than Condition
We want to return ‘Passed’ for numbers more than 80 and ‘Failed’ for numbers equal to or less than 80.
Steps:
- In cell D5, enter the formula below to apply the IF function:
=IF(C5>80,"Passed","Failed")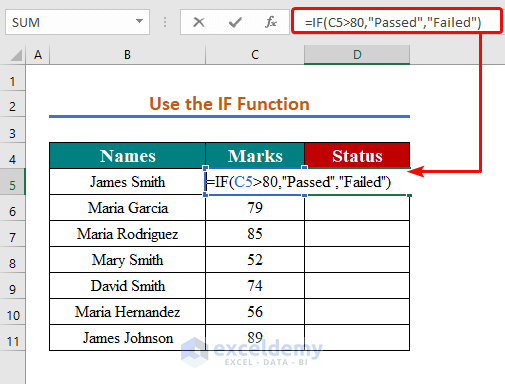
- Hit the Enter button to see the result.
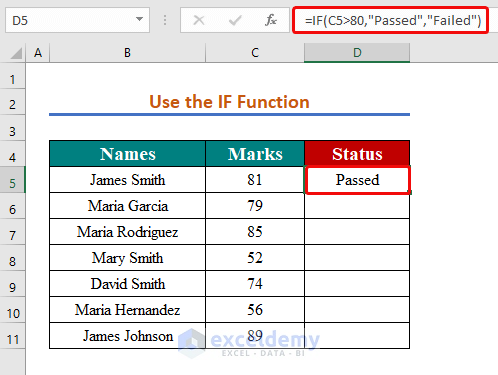
- Use AutoFill to copy the formula throughout the column.
Read More: How to Use Less Than Or Equal to Operator in Excel
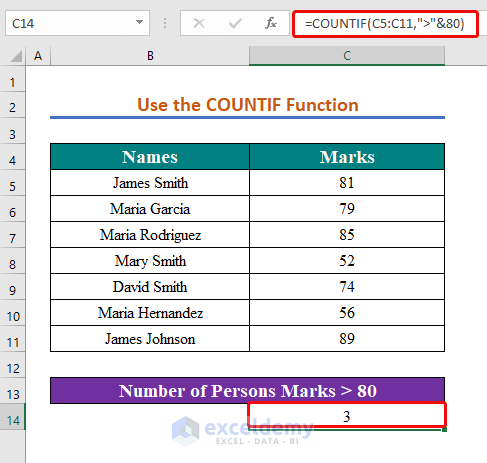
Method 5 – Using the COUNTIF Function with the If Greater Than Operator
We want to calculate the number of people who got more than 80.
Steps:
- Enter the following formula in cell C14.
=COUNTIF(C5:C11,">"&80)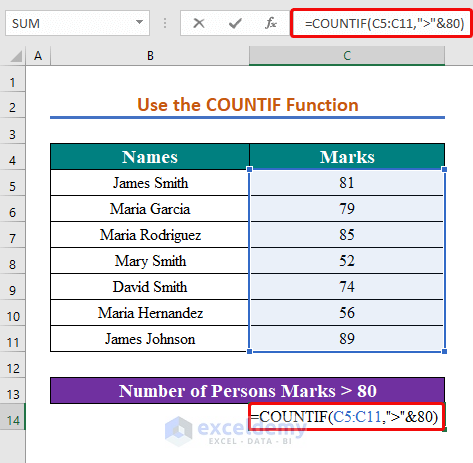
- Press Enter.
Method 6 – Applying the If Greater Than Operator with the SUMIF Function
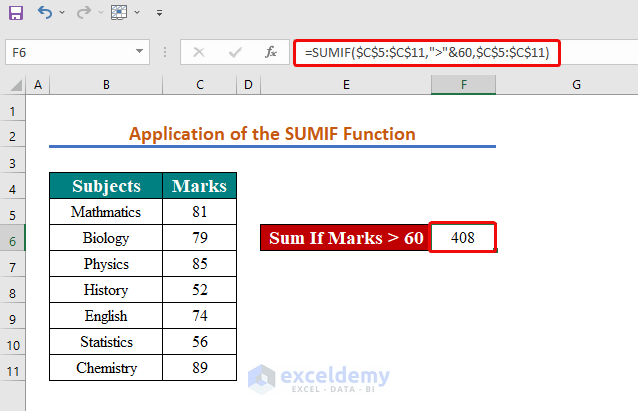
We want to sum scores that are greater than 60.
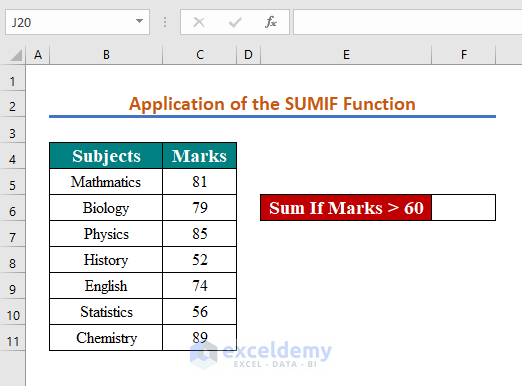
Steps:
- In cell F6, insert the formula below:
=SUMIF($C$5:$C$11,">"&60,$C$5:$C$11)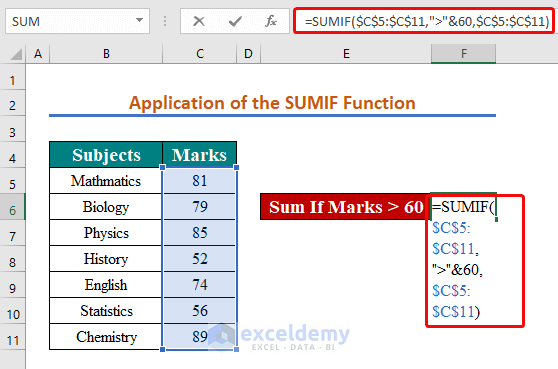
- Press Enter to find the total.
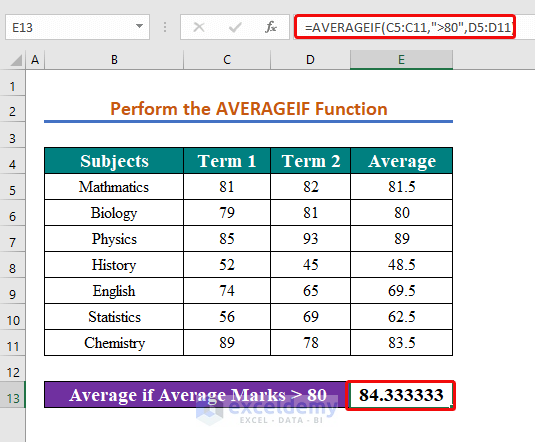
Method 7 – Using the AVERAGEIF Function with the If Greater Than Operator
We want to evaluate the average of those averages which are higher than 80.
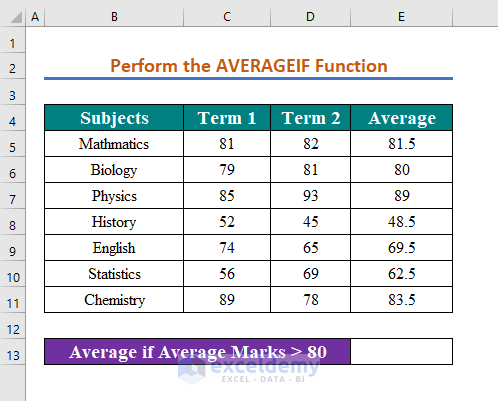
Steps:
- In cell E13, insert the following formula to find the conditional average.
=AVERAGEIF(C5:C11,">80",D5:D11)- Hit Enter to see the average.
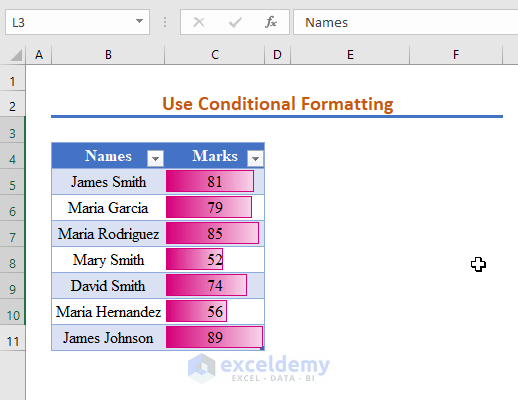
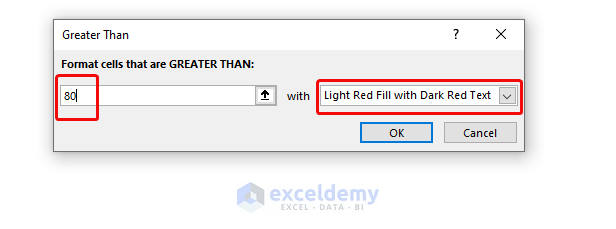
Method 8 – Using Conditional Formatting to Apply an If Greater Than Condition
We will highlight the cells with values greater than 80.
Steps:
- Select the entire dataset and press Ctrl + T to convert it into a table. Hit OK in the dialog box.
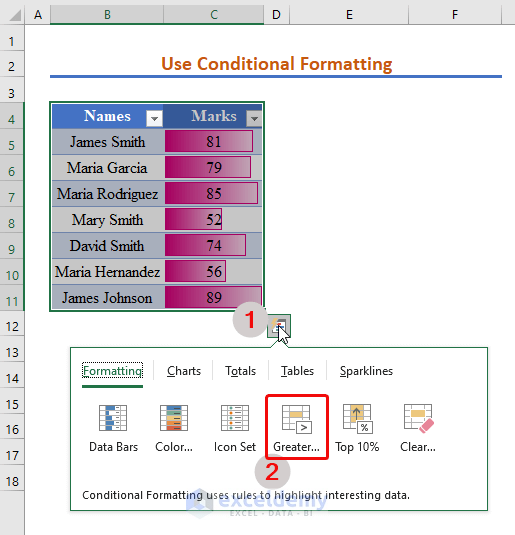
- Select the table and click the formatting sign on the right of the table.
- Select the Greater than option from Formatting.
- Input the range in the left box.
- Select the formatting color in the right box.
- Press Enter.
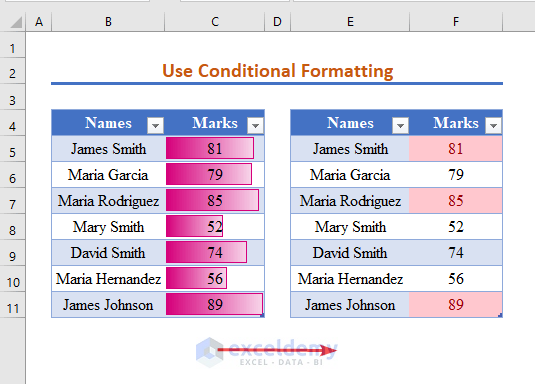
 You will get values greater than 80 in red.
You will get values greater than 80 in red.
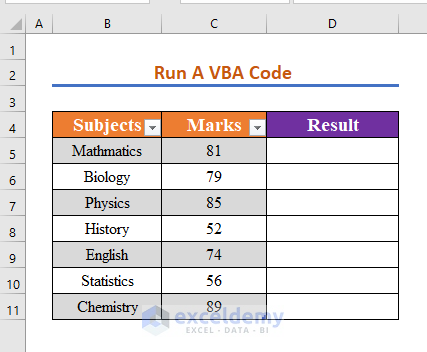
Method – Running VBA Code
We want to apply the VBA code to differentiate values greater than 80. Values greater than 80 will return passed.
Steps:
- Press Alt + F11 to open the Macro-Enabled Worksheet.
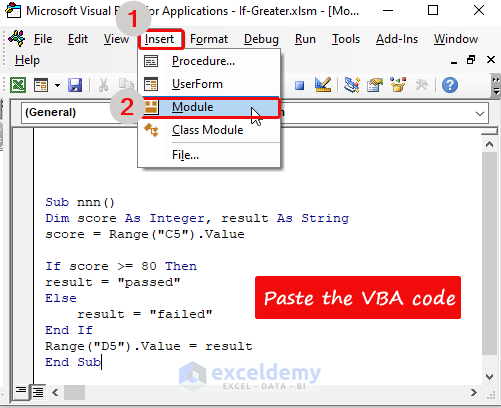
- Click Insert from the tab.
- Select Module.
- Paste the following VBA code into the module.
Sub nnn()
Dim score As Integer , result As String
score = Range("C5").Value
If score >= 80 Then
result = "passed"
Else
result = "failed"
End If
Range("D5").Value = result
End SubWhere,
score = Range(“reference cell”).Value
Range(“return cell”).Value = result
- Run the code by pressing F5.
- You will get the result in cell D5 as programmed.
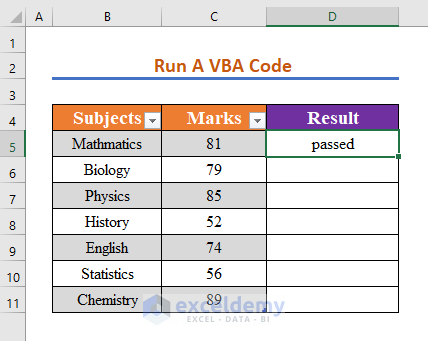
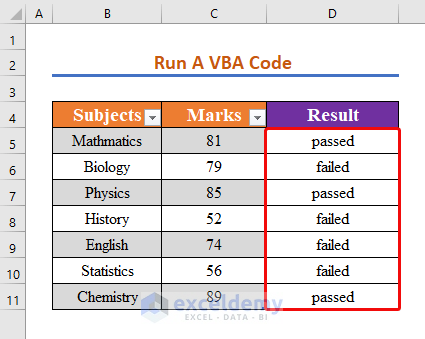
- Repeat the previous steps for all cells in the range C5:C11 and return the result in range D5:D11.
Download the Practice Workbook
Further Readings
- Excel Boolean Operators: How to Use Them?
- ‘Not Equal to’ Operator in Excel
- Reference Operator in Excel
- What is the Order of Operations in Excel
<< Go Back to Excel Operators | Excel Formulas | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

