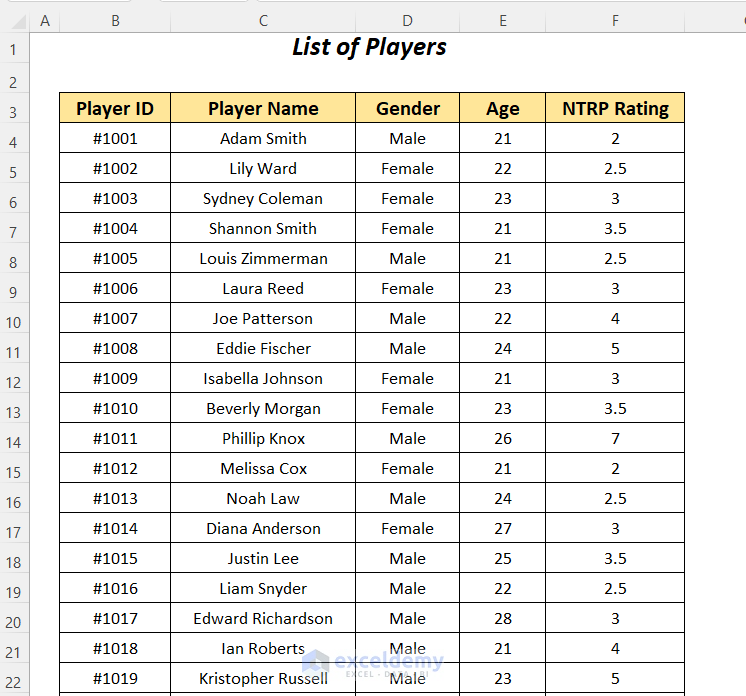
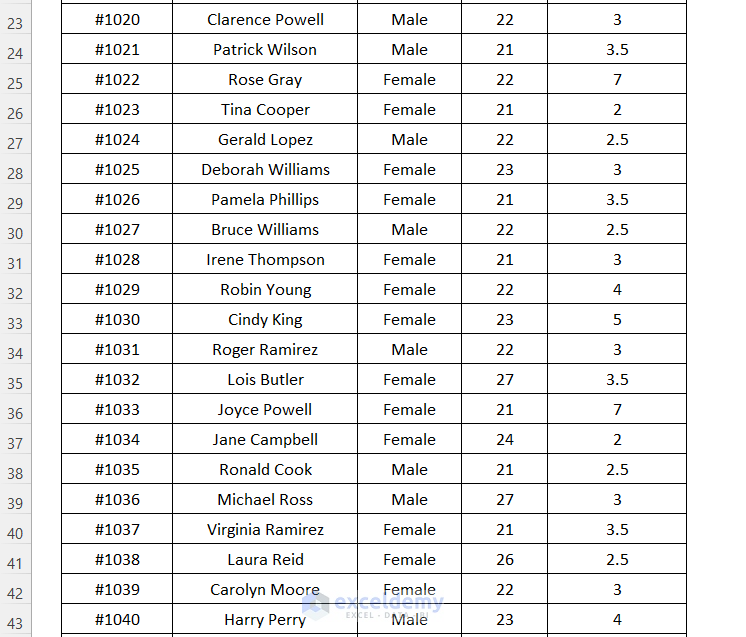
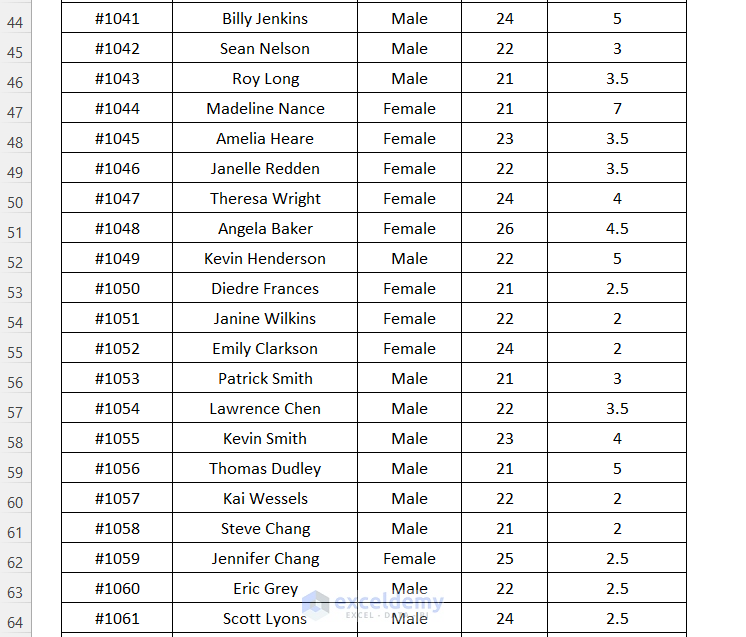
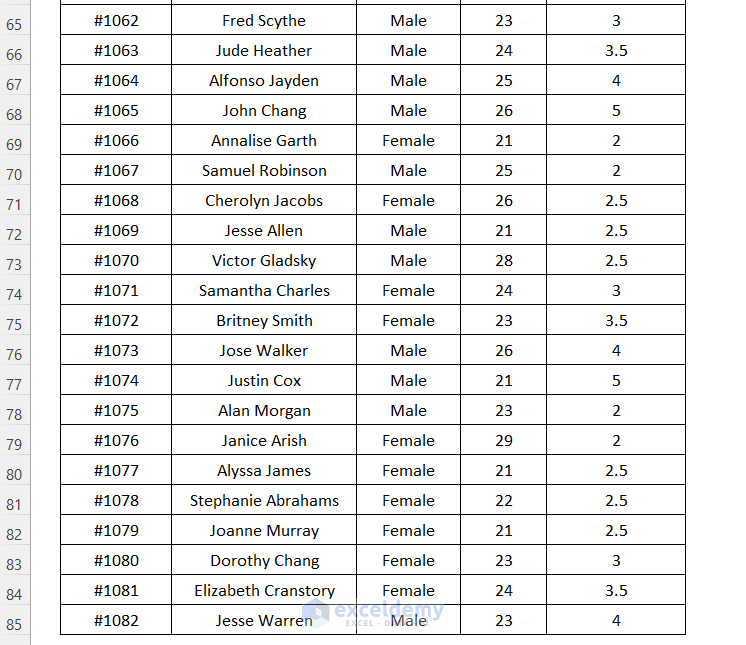
The following sample dataset will be used to illustrate the seven (7) key differences between DGET and VLOOKUP.
Difference 1 – Syntax of DGET vs VLOOKUP in Excel
1.1. DGET Function
The DGET function has the following three compulsory arguments. These arguments will return the value.
=DGET (database, field, criteria)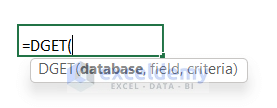
The database is the entire data set and the first row contains the labels or column headings, the field indicates the column that is used in the function and criteria are the group of cells that contains the conditions that we want to specify.
1.2. VLOOKUP Function
The VLOOKUP function has three mandatory arguments with an optional argument.
=VLOOKUP (lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, [range_lookup])
lookup_value is the value you want the function to use in order to find the matching output value, table_array is the range that contains all the columns of interest, the col_index_num specifies the number of the column containing the output value that we want to look up and [range_lookup] is a true or false value – where TRUE denotes an approximate match and FALSE is an EXACT match.
Difference 2 – Importance of Headers
2.1. DGET Function
Use the DGET function to find the NTRP Rating for the player named Beverly Morgan within the dataset.
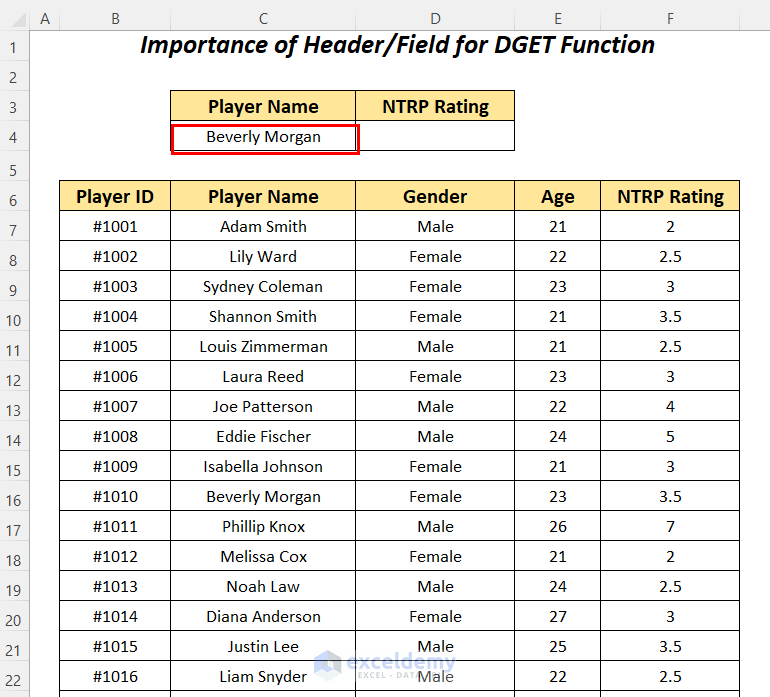
- Apply the following formula in cell D4.
=DGET(B6:F88,D3,C3:C4)B6:F88 is the dataset starting from the column header name, D3 is the cell reference for the Field name, and C3:C4 is the range of Criteria with the header name for which we are looking for the value.
It outputs the correct NTRP Rating of 3.5 for the player Beverly Morgan.
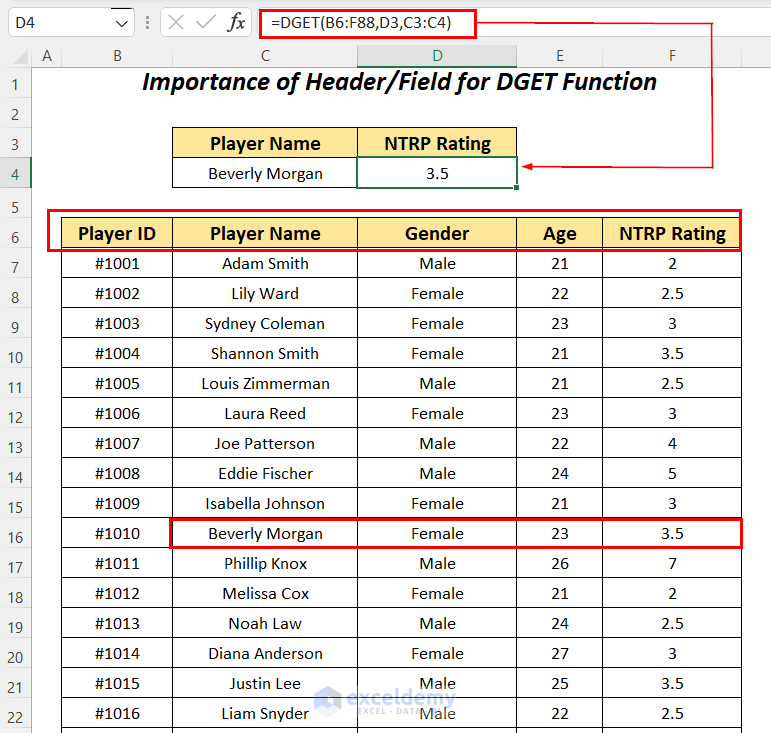
If we use the following formula instead,
=DGET(B7:F88,D3,C3:C4)where we have changed the dataset reference to B7:F88 by ignoring the column header names.
It outputs the #VALUE! error for ignoring the column headers’ names in the dataset argument position.
2.2. VLOOKUP Function
Use the VLOOKUP function to find the NTRP Rating for the player named Beverly Morgan within the dataset.
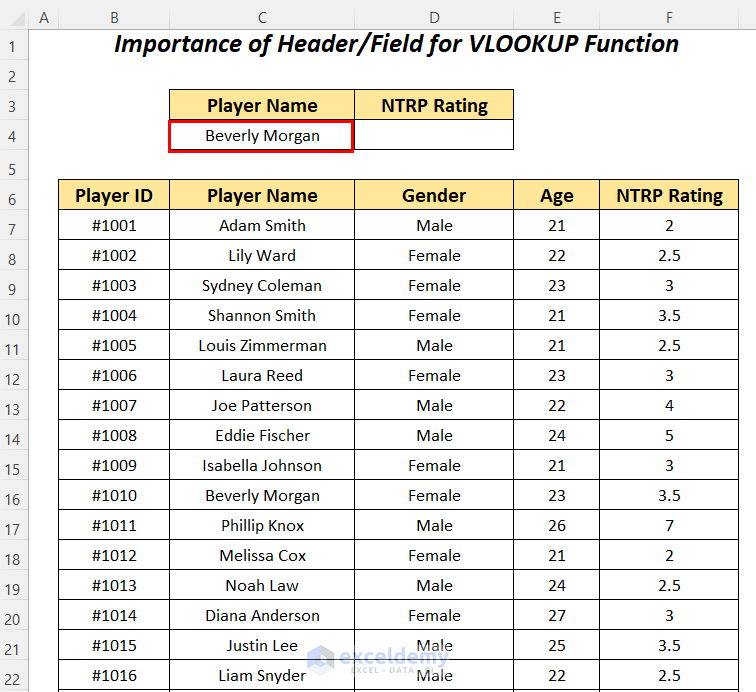
- Apply the following formula in cell D4.
=VLOOKUP(C4,C6:F88,4,FALSE)C4 is the lookup value, C6:F88 is the table_array starting from the column header name, 4 is the column index number, and FALSE is for an exact match.
It outputs the correct NTRP Rating of 3.5 for the player Beverly Morgan.
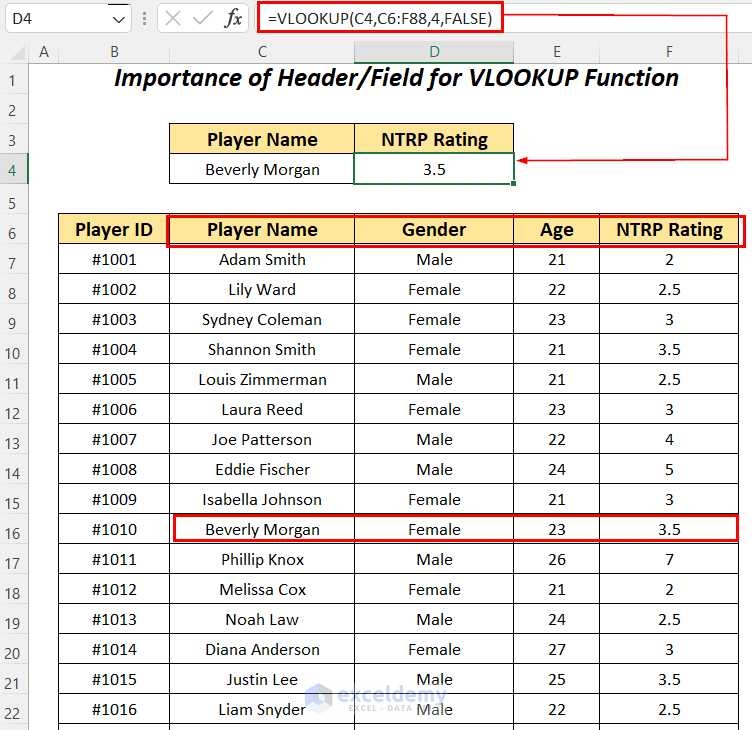
If we change the reference of the table_array argument,
=VLOOKUP(C4,C7:F88,4,FALSE)We have changed the table_array argument to C7:F88 excluding the column headers’ names and as a result, we are getting the same result as the previous one.
Difference 3 – Flexibility of Using Column Number or Header in DGET vs VLOOKUP Functions in Excel
3.1. DGET Function
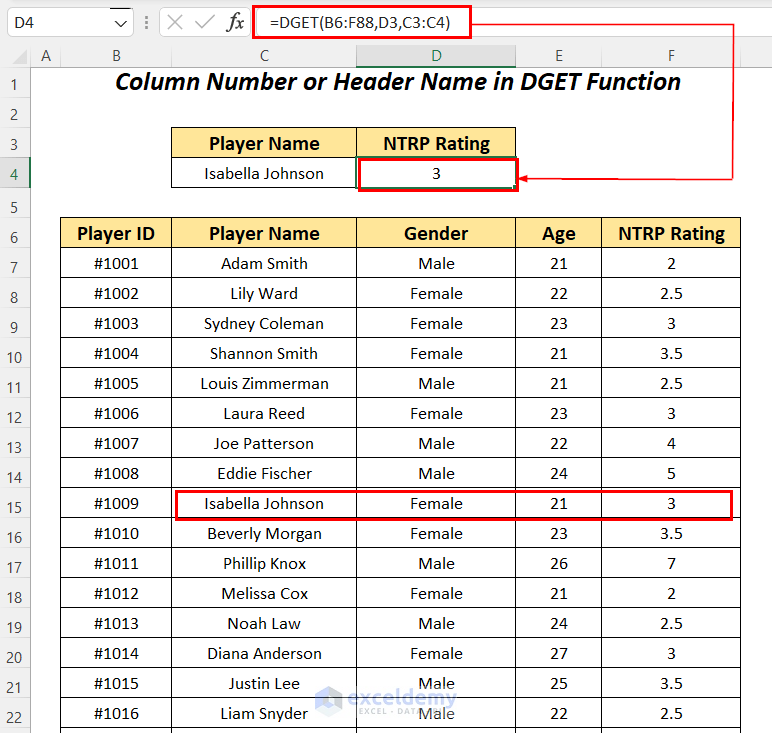
Use the DGET function to find the NTRP Rating for the player named Isabella Johnson within the dataset.
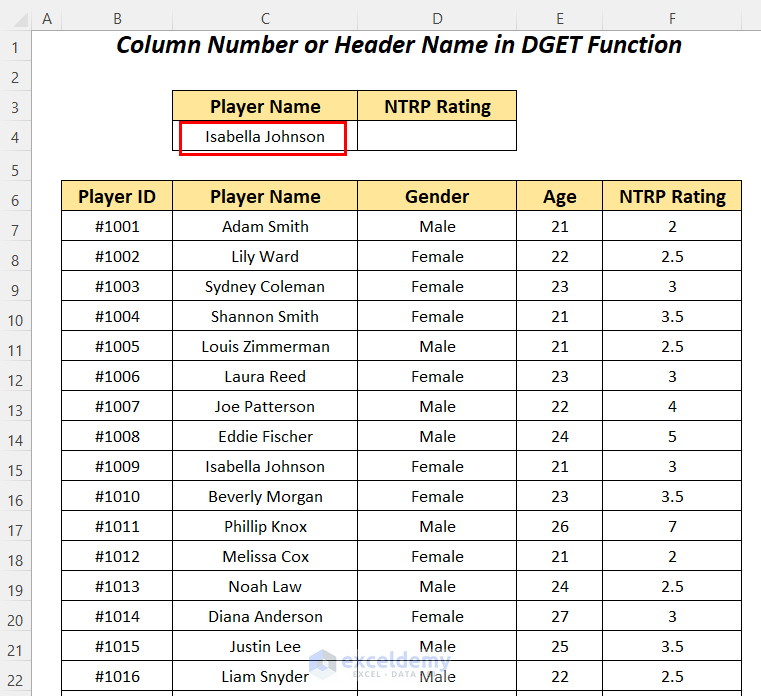
- Apply the following formula in cell D4.
=DGET(B6:F88,D3,C3:C4)B6:F88 is the dataset starting from the column header name, D3 is the cell reference for the Field name, and C3:C4 is the range of Criteria with the header name for which we are looking for the value.
It outputs the correct NTRP Rating of 3 for the player Isabella Johnson by using the Field name as the name of the column.
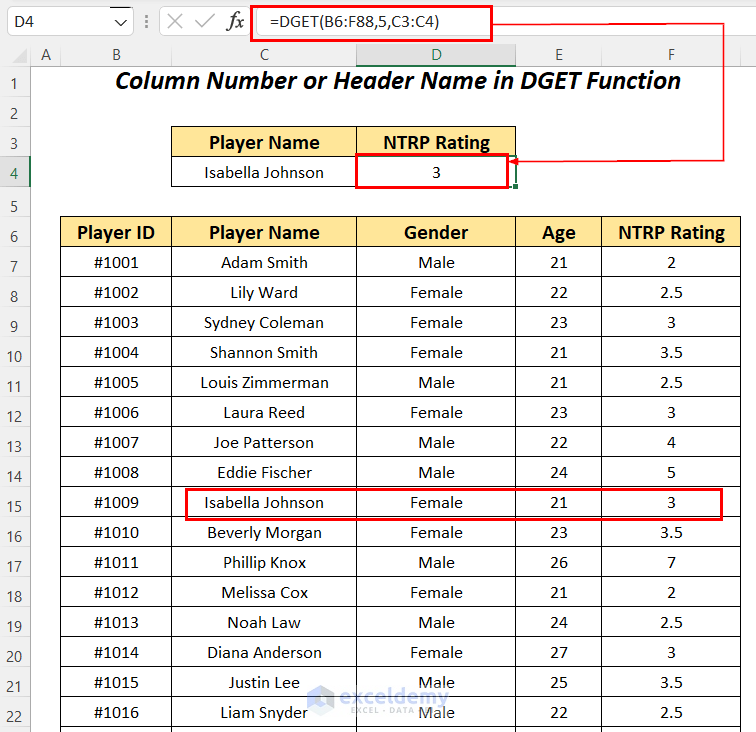
Instead of using the former formula if we use the following formula,
=DGET(B6:F88,5,C3:C4)where we have changed the Field argument to 5 and we have got a similar correct result.
3.2. VLOOKUP Function
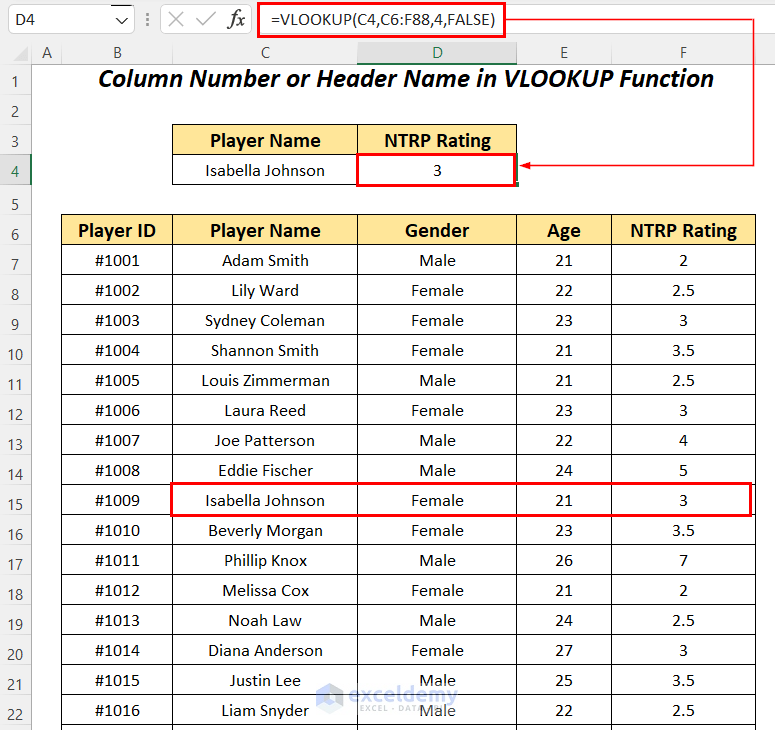
Use the VLOOKUP function to find the NTRP Rating for the player named Isabella Johnson within the dataset.

- Apply the following formula in cell D4.
=VLOOKUP(C4,C6:F88,4,FALSE)C4 is the lookup value, C6:F88 is the table_array starting from the column header name, 4 is the column index number, and FALSE is for an exact match.
It outputs the correct NTRP Rating of 3 for the player Isabella Johnson.
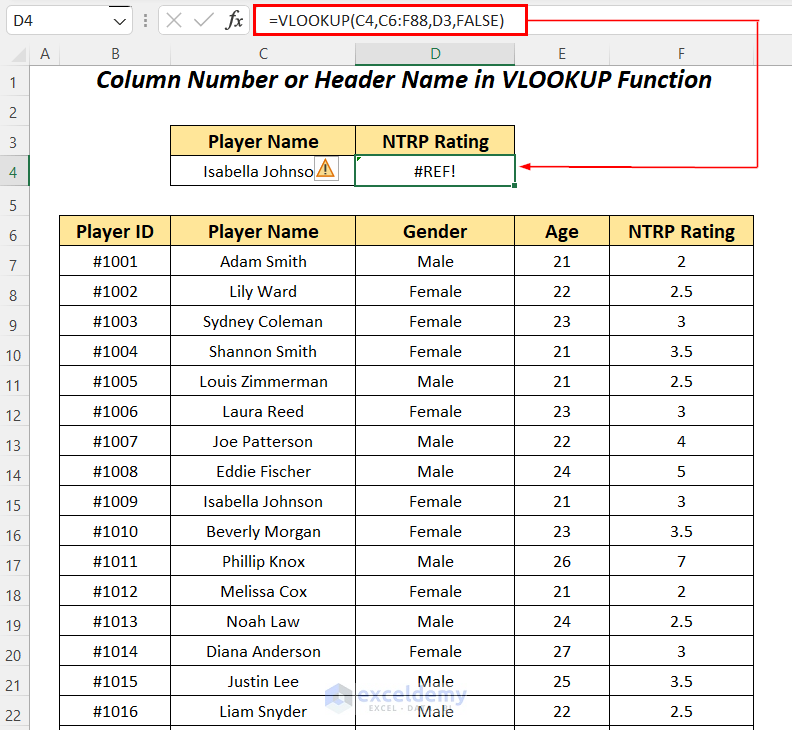
If we change the reference of the column index argument,
=VLOOKUP(C4,C6:F88,D3,FALSE)We have changed the column index argument to D3 to use the column name instead of the column number in the dataset.
As a result, we are getting the #REF! error.
Difference 4 – Column Direction for Look Up Values in DGET vs VLOOKUP Functions in Excel
The VLOOKUP function looks up the value in the right direction but you can use the DGET function to look up the value in both directions.
4.1. DGET Function
Using the DGET function, we will try to look up the NTRP Rating by moving to the right direction and for the Player ID, we will move to the left direction.
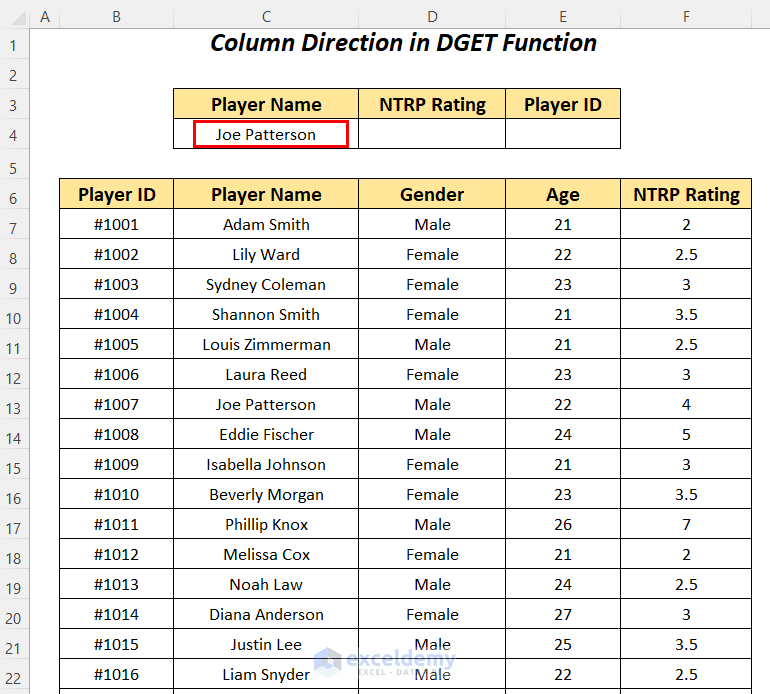
- Apply the following formula in cell D4.
=DGET(B6:F88,D3,C3:C4)B6:F88 is the dataset starting from the column header name, D3 is the cell reference for the Field name, and C3:C4 is the range of Criteria with the header name for which we are looking for the value.
It outputs the correct NTRP Rating of 4 for the player Joe Patterson by going from the column Player Name to the right to the column NTRP Rating.
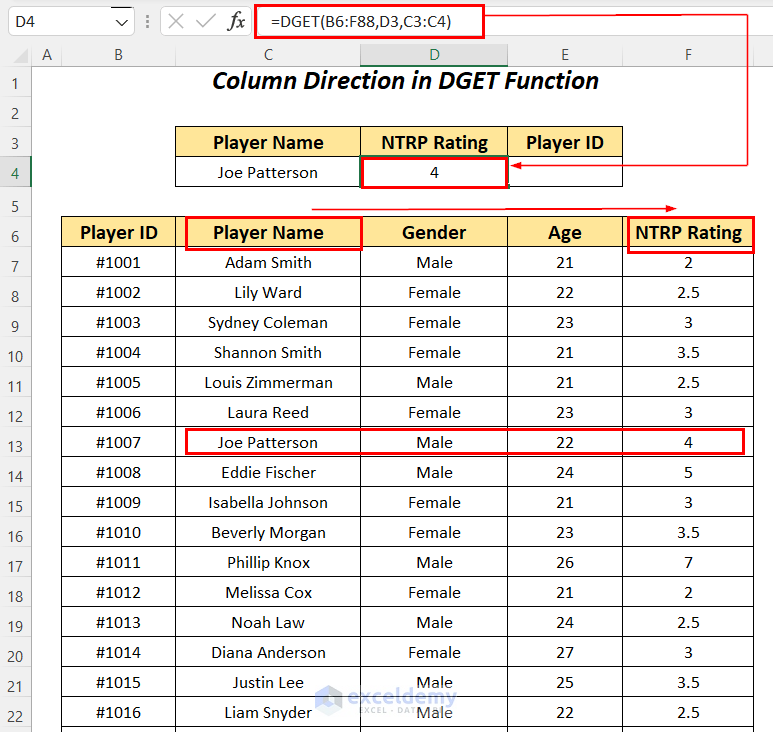
- Use the following formula in cell E4.
=DGET(B6:F88,E3,C3:C4)B6:F88 is the dataset starting from the column header name, E3 is the cell reference for the Field name, and C3:C4 is the range of Criteria with the header name for which we are looking for the value.
It outputs the correct Player ID of #1007 for the player Joe Patterson by going from the column Player Name to the left to the column Player ID.
4.2. VLOOKUP Function
Using the VLOOKUP function, we will try to look up the NTRP Rating by moving in the right direction and for the Player ID, we will move to the left direction.
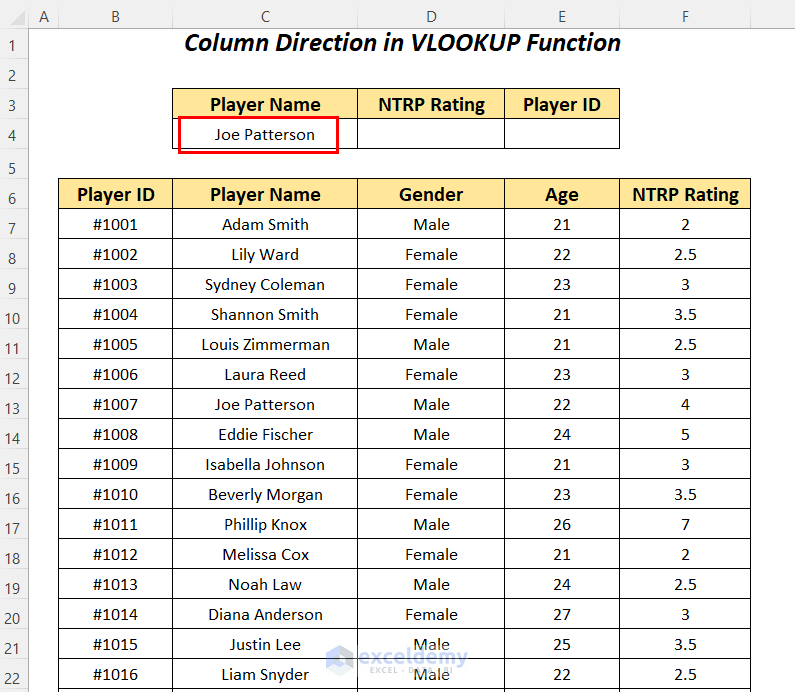
- Apply the following formula in cell D4.
=VLOOKUP(C4,C6:F88,4,FALSE)C4 is the lookup value, C6:F88 is the table_array starting from the column header name, 4 is the column index number, and FALSE is for an exact match.
It outputs the correct NTRP Rating of 4 for the player Joe Patterson by going from the column Player Name to the right to the column NTRP Rating.
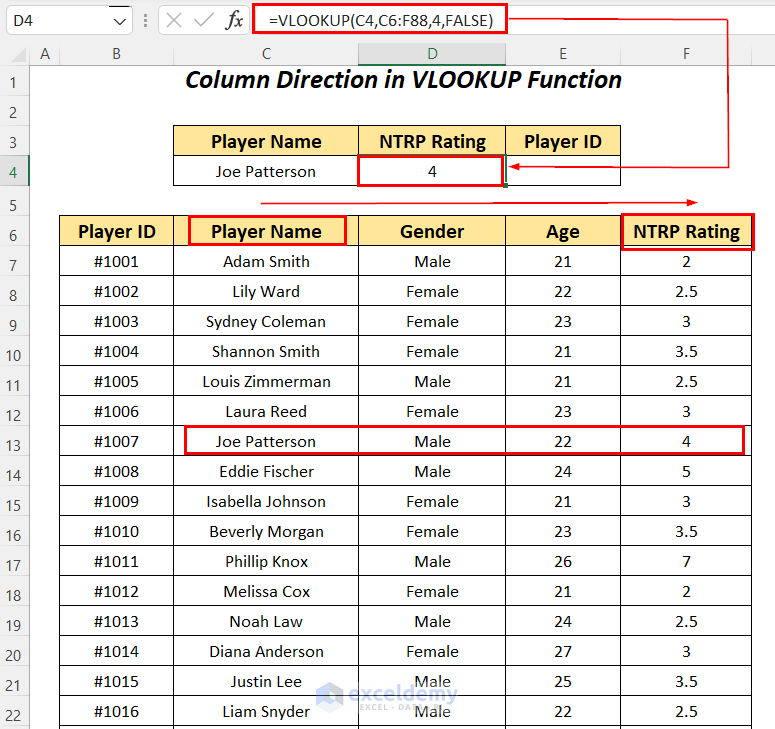
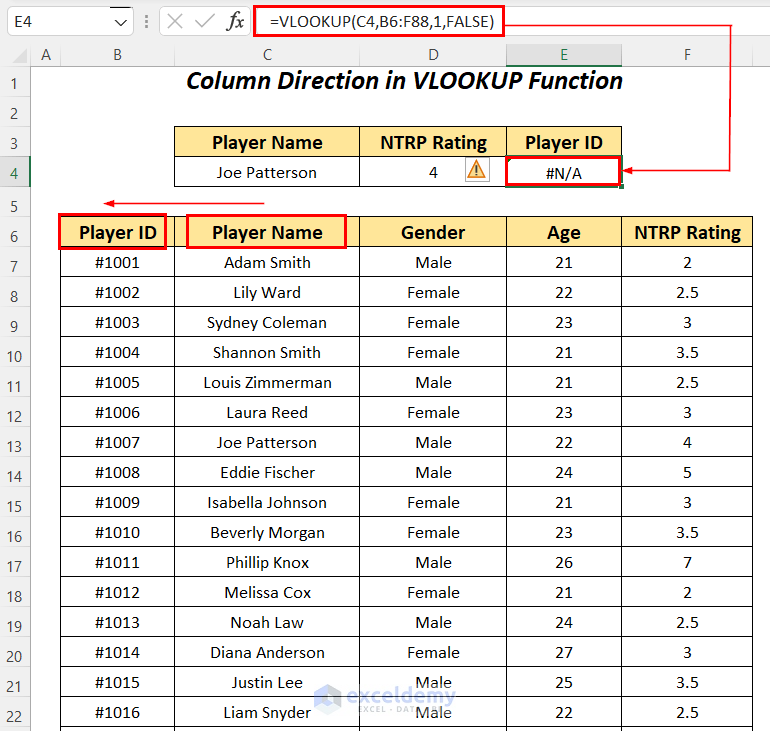
- Enter the following formula in cell E4.
=VLOOKUP(C4,B6:F88,1,FALSE)C4 is the lookup value, B6:F88 is the table_array starting from the column header name, 1 is the column index number, and FALSE is for an exact match.
It outputs the #N/A error for going from the column Player Name to the right to the column Player ID.
Difference 5 – Importance of Unique Values
5.1. DGET Function
Look up the NTRP Rating value for the player Isabella Johnson in the dataset using the DGET function. This name is listed twice in our main dataset.
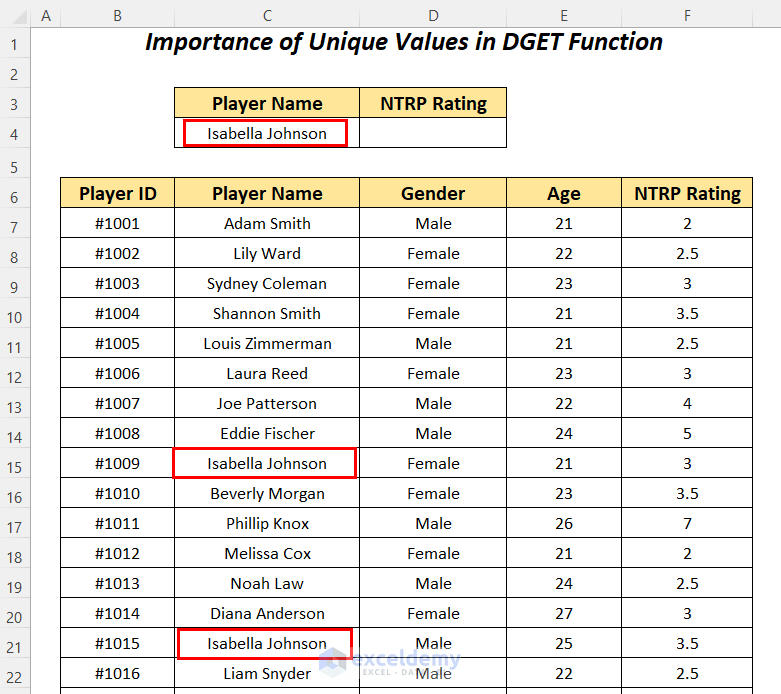
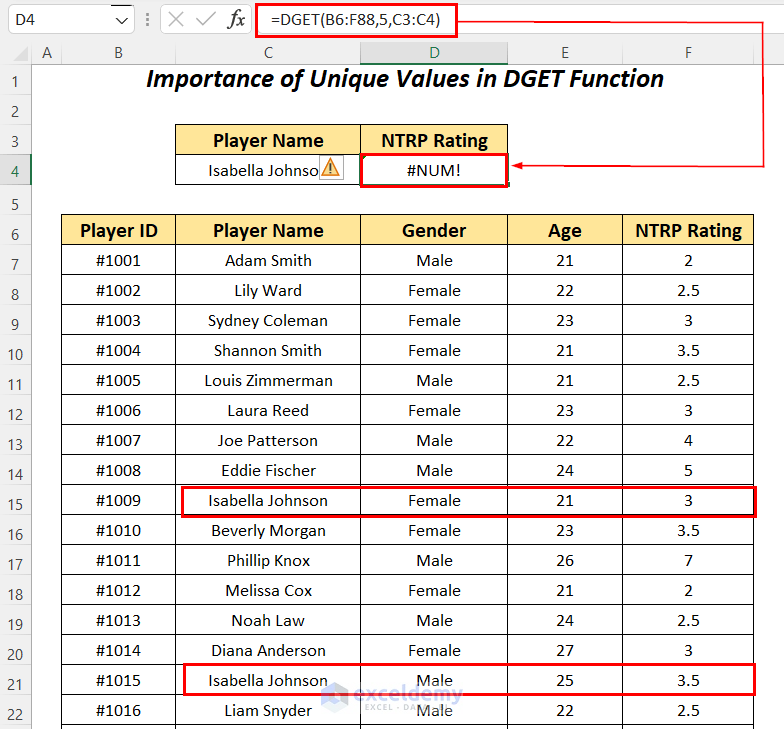
- Apply the following formula in cell D4.
=DGET(B6:F88,5,C3:C4)B6:F88 is the dataset starting from the column header name, 5 is the column number for the Field name, and C3:C4 is the range of Criteria with the header name for which we are looking for the value.
It gives the #NUM error because of the duplicate names in the dataset.
5.2. VLOOKUP Function
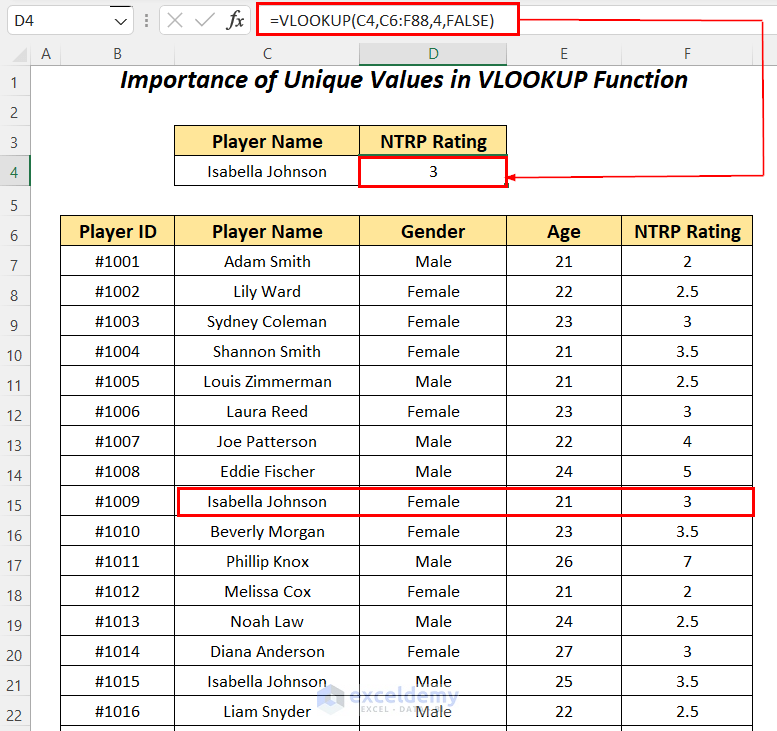
Look up the NTRP Rating value for the player Isabella Johnson in the dataset using the VLOOKUP function.
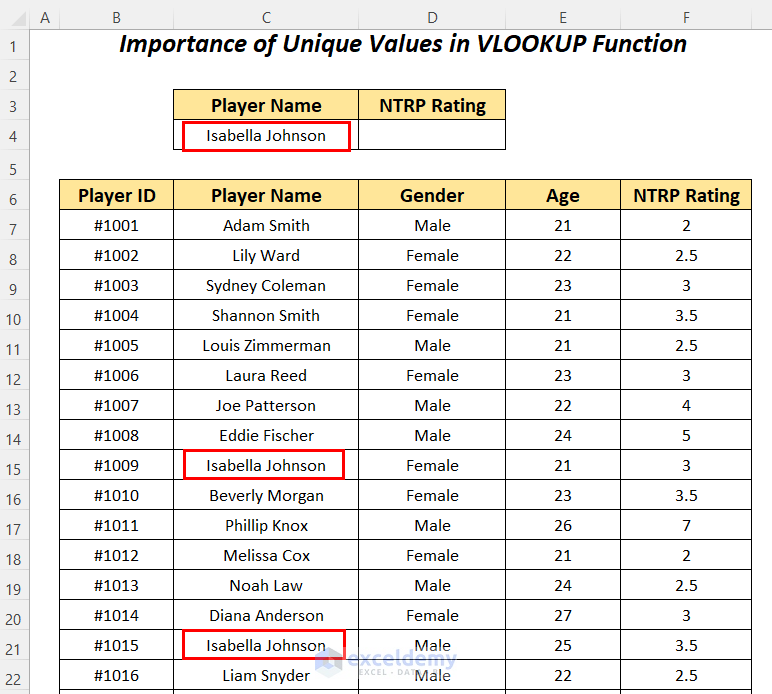
- Apply the following formula in cell D4.
=VLOOKUP(C4,C6:F88,4,FALSE)C4 is the lookup value, C6:F88 is the table_array starting from the column header name, 4 is the column index number, and FALSE is for an exact match.
It outputs the first NTRP Rating of 3 for the player Isabella Johnson.
Difference 6 – Getting Multiple Outputs in DGET vs VLOOKUP Functions in Excel
6.1. DGET Function
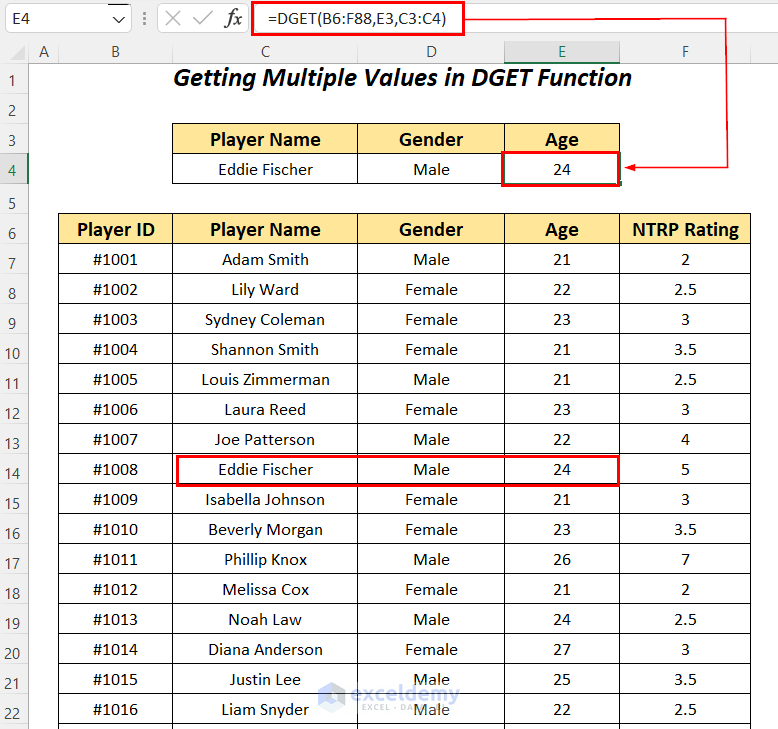
Look up the Gender and Age of the player Eddie Fischer in the dataset using the DGET function.
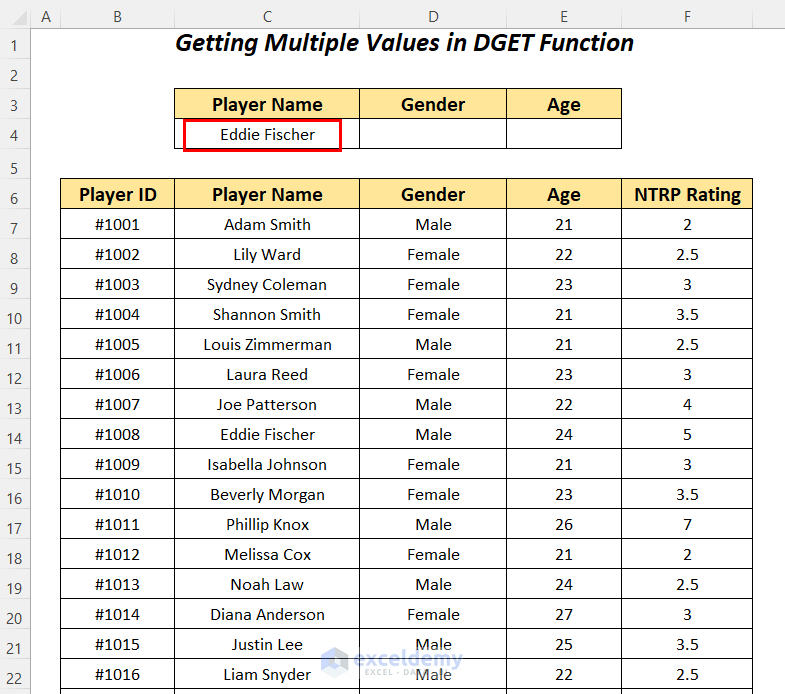
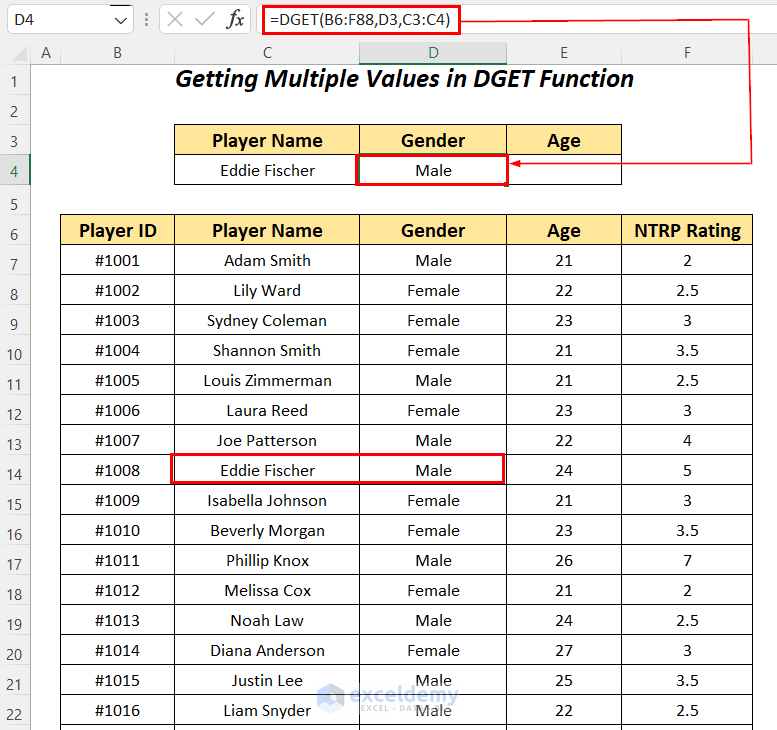
- Apply the following formula in cell D4.
=DGET(B6:F88,D3,C3:C4)B6:F88 is the dataset starting from the column header name, D3 is the reference of the column name for the Field name, and C3:C4 is the range of Criteria with the header name for which we are looking for the value.
It outputs Male as Gender for the player Eddie Fischer.
- To find the age enter the following formula in cell E4.
=DGET(B6:F88,E3,C3:C4)B6:F88 is the dataset, E3 is the reference of the column name for the Field name, and C3:C4 is the range of Criteria with the header name for which we are looking the value.
It outputs 24 as the Age for the player Eddie Fischer.
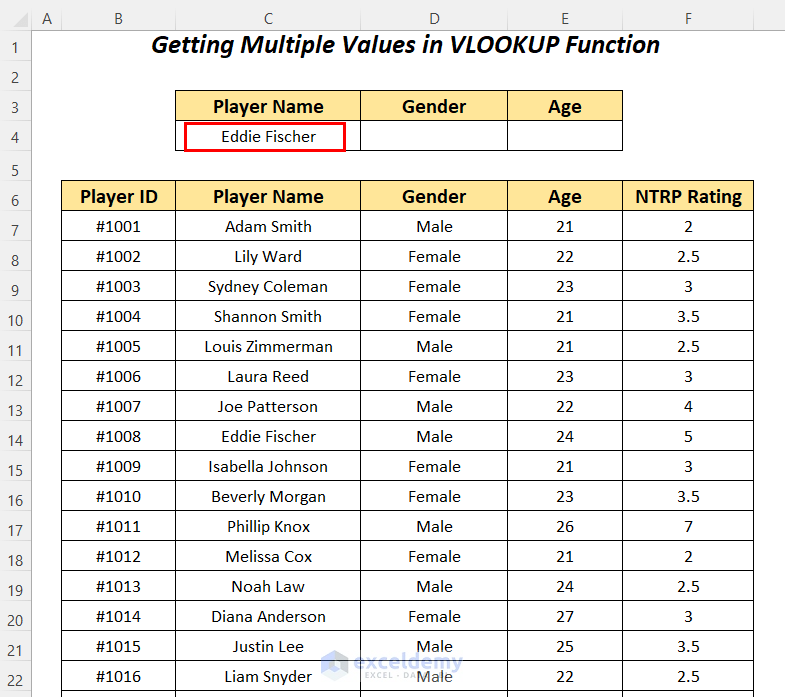
6.2. VLOOKUP Function
Look up the Gender and Age of the player Eddie Fischer in the dataset using the VLOOKUP function.
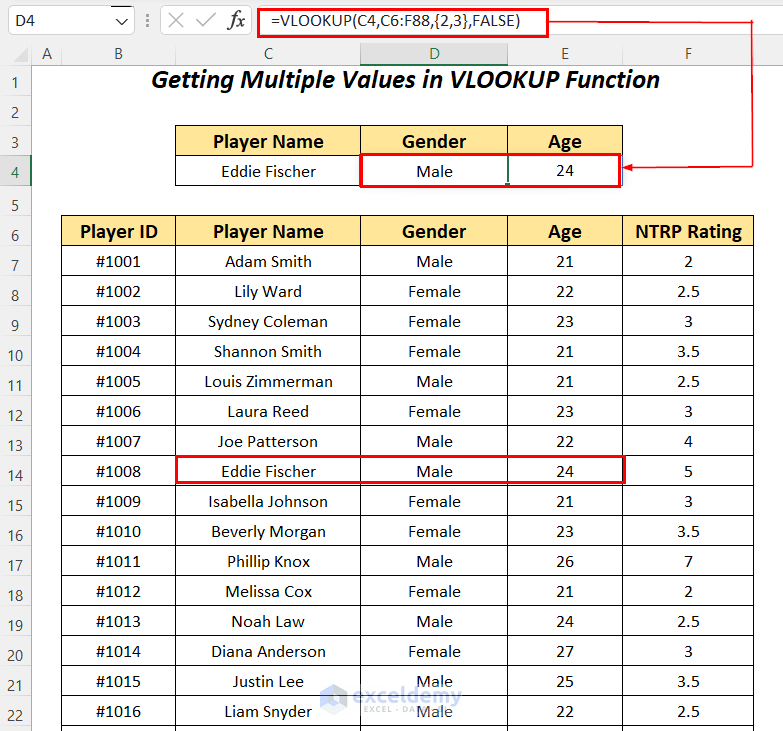
- Apply the following formula in cell D4.
=VLOOKUP(C4,C6:F88,{2,3},FALSE)C4 is the lookup value, C6:F88 is the table_array starting from the column header name, 4 is the column index number, and FALSE is for an exact match.
It outputs Male as the Gender and 24 as the Age for the player Eddie Fischer.
Note: For using any other versions except Microsoft Excel 365 you have to press CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER instead of pressing ENTER.
Difference 7 – Looking up Multiple Criteria in DGET vs VLOOKUP Functions in Excel
7.1. DGET Function
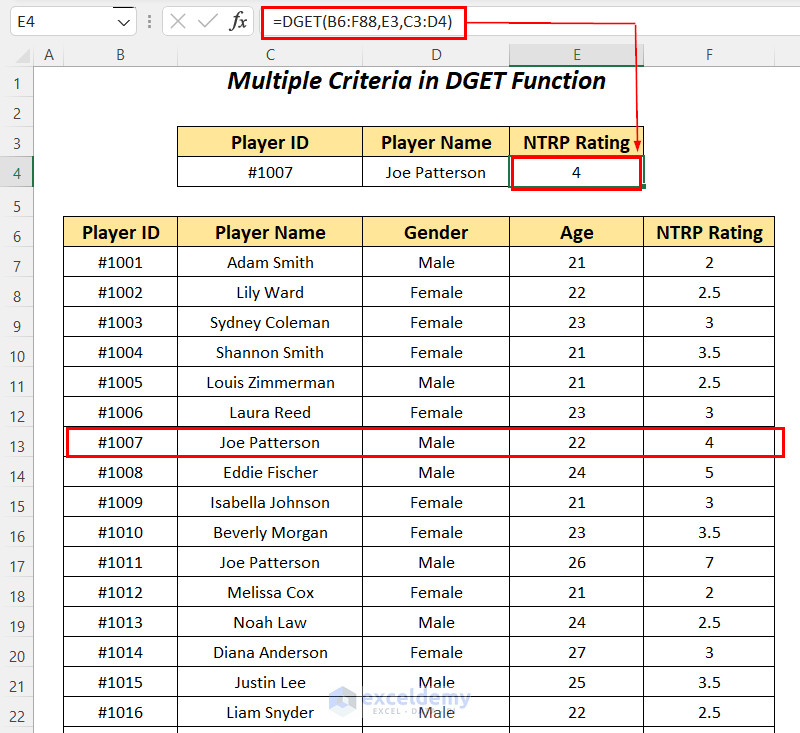
Check Player ID #1007 and Player Name, Joe Patterson using the DGET function to get the NTRP Rating. Using these two criteria you can avoid the error of duplicate values.
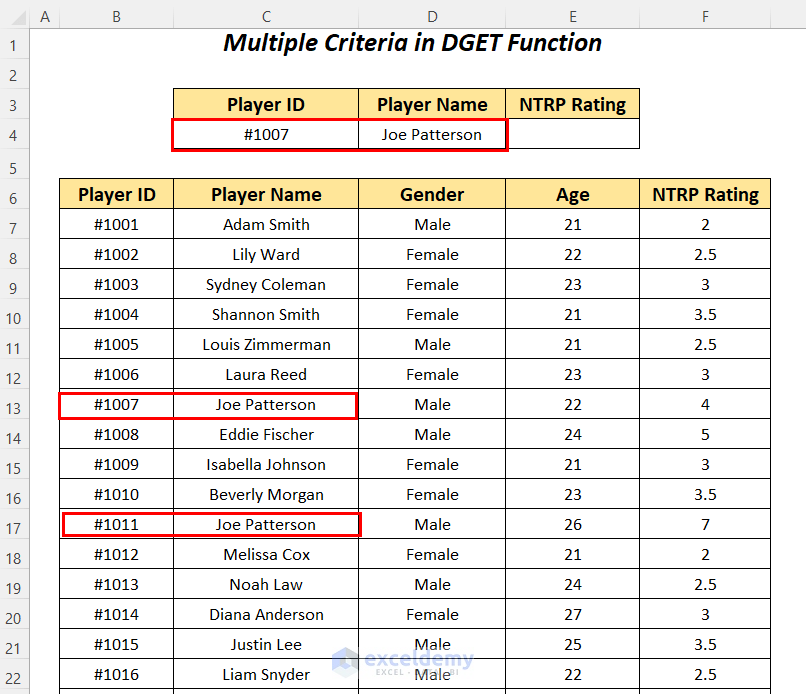
- Apply the following formula in cell E4.
=DGET(B6:F88,E3,C3:D4)B6:F88 is the dataset starting from the column header name, E3 is the reference of the column name for the Field name, and C3:D4 is the range of Criteria with the header name for which we are looking for the value.
It outputs the NTRP Rating of 4 for the player Joe Patterson with ID #1007.
7.2. VLOOKUP Function
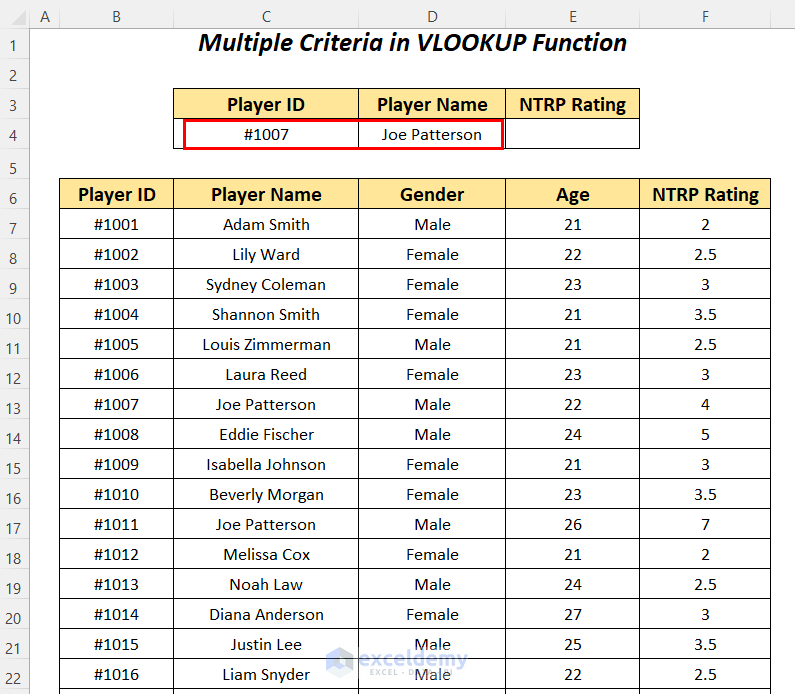
Check Player ID #1007 and Player Name Joe Patterson using the VLOOKUP function to get the NTRP Rating. You can avoid the error of duplicate values by using these two criteria.
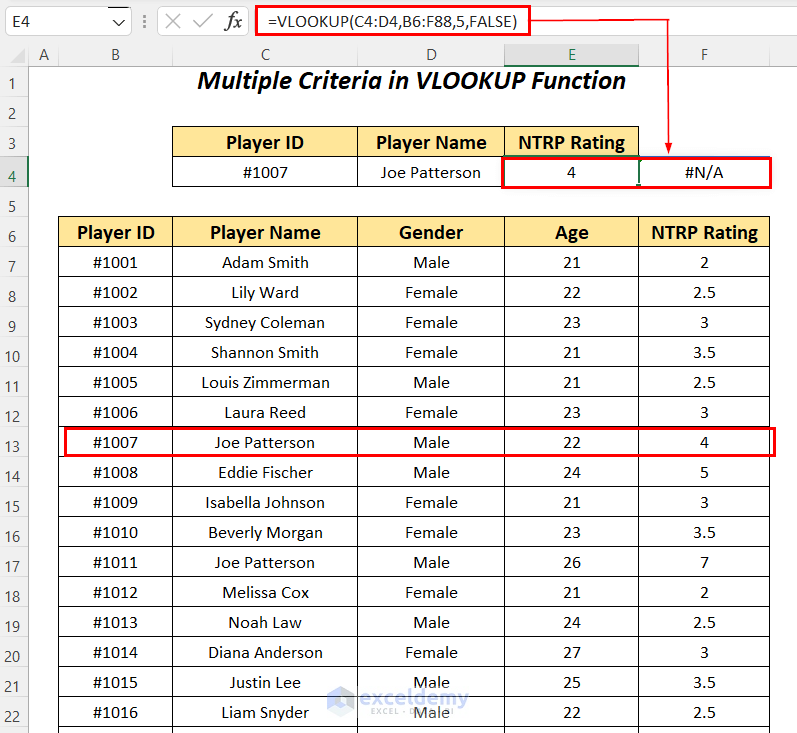
- Apply the following formula in cell E4.
=VLOOKUP(C4:D4,B6:F88,5,FALSE)C4:D4 is the lookup value, B6:F88 is the table_array starting from the column header name, 5 is the column index number, and FALSE is for an exact match.
It outputs the NTRP Rating of 4 for the player Joe Patterson with ID #1007 but besides this, the #N/A error is also shown.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of the DGET Function?
Advantages
- Doesn’t depend on the direction or position of columns.
- It can handle multiple criteria and larger data sets with ease.
Disadvantages
- For any formula that you have to pull down throughout the cells, this function is not good for this case.
- It automatically works on an approximate match.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of the VLOOKUP Function?
Advantages
- You can work with an exact match or an approximate match as per your requirement.
- This formula can be copied down easily.
- It is easy to learn.
Disadvantages
- It depends on the direction or position of the columns.
- The VLOOKUP function can be prone to errors in larger spreadsheets.
Download Practice Workbook
<< Go Back to Lookup | Formula List | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!


Thank you very much, it’s interinsting
You are very welcome. Thank you for reading and doing Excel with us 🙂
This was well written and easy to understand. I must admit I was not familiar with DGET but I will try using it. Thanks!
You are most welcome. I’m glad you found the tutorial useful and yes the database functions are very helpful when it comes to looking up data with criteria 🙂
Thank you for the easy to understand and useful tutorial. Always look forward to your tutorials posted on this website.
Main disadvantage with INDEX/MATCH is that you have to repeat the same range twice which makes maintenance more of an issue (unless you only used named ranges)
Main disadvantage of DGET is that you can’t fill the query down a column to get multiple answers.
Thanks for your valuable input.
Best regards
Kawser Ahmed