Quick View:
Download Practice Workbook
Overview of the CONCAT Function
Syntax:
=CONCAT(Text1, …)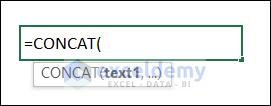
Arguments:
Text1 is a required argument. This is the first value to be joined. It can be a text, number, symbol, or cell reference. The rest of the arguments are optional and have similar characteristics.
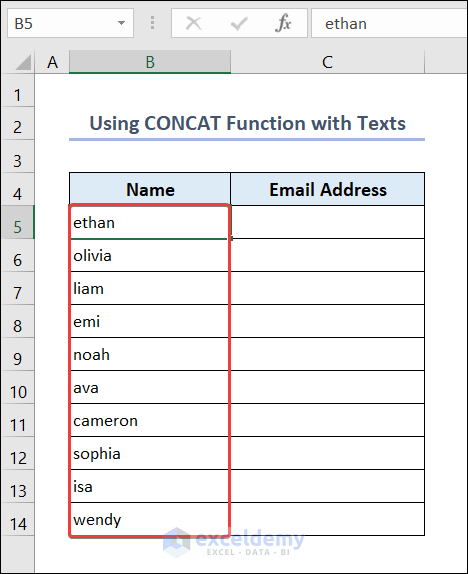
Example 1 – Use the CONCAT Function with Texts
There are different names in the dataset. Add the domain (@gmail.com) to these names to get the email addresses.
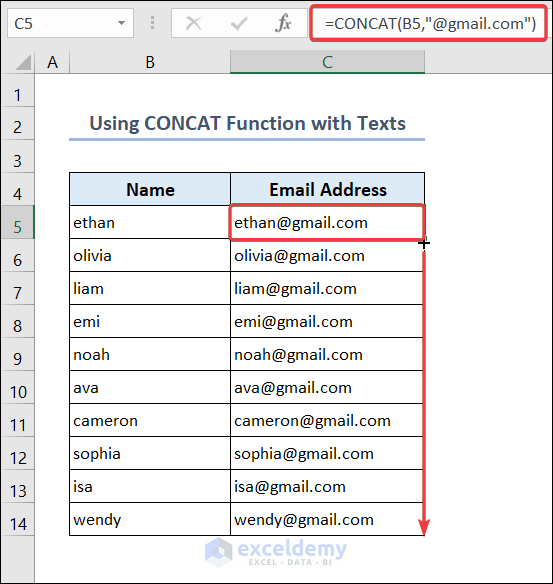
- Go to C5 and enter the following formula.
=CONCAT(B5,"@gmail.com")- Drag down the Fill Handle to see the result in the rest of the cells.
Example 2 – Use the CONCAT Function with Numbers
Add the country code (+1) before the phone numbers.
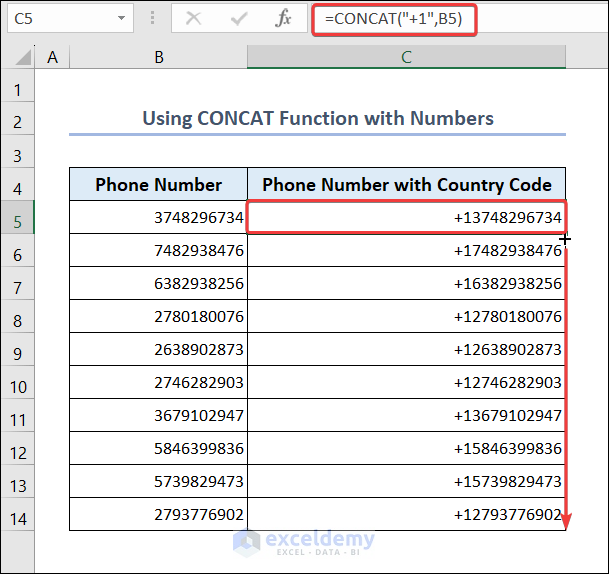
- Go to C5 and enter the following formula.
=CONCAT("+1",B5)- Drag down the Fill Handle to see the result in the rest of the cells.
Example 3 – Apply the CONCAT Function to a Range of Cells
To see the IDs along with the name of the students:
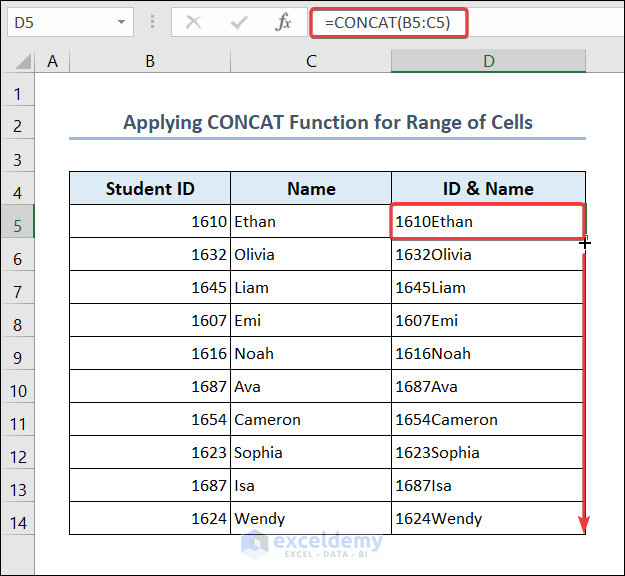
- Go to C5 and enter the following formula.
=CONCAT(B5:C5)- Drag down the Fill Handle to see the result in the rest of the cells.
Example 4 – Use the CONCAT Function for All Cells in a Column
Combine the cell values in column D.
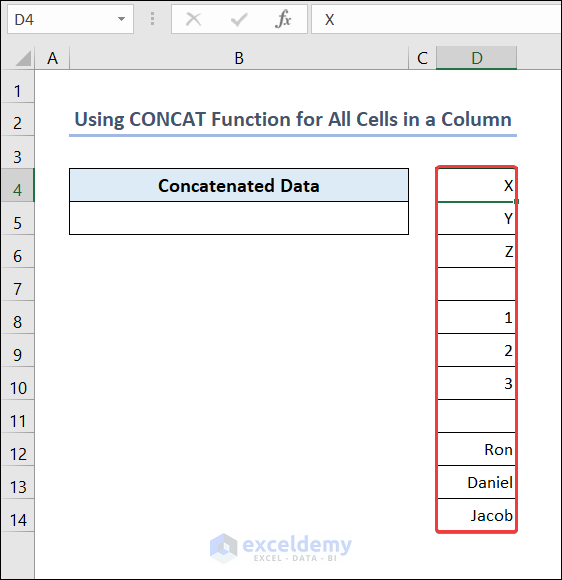
- Go to B5 and enter the following formula.
=CONCAT(D:D)You will get the concatenated value of all cells in column D.
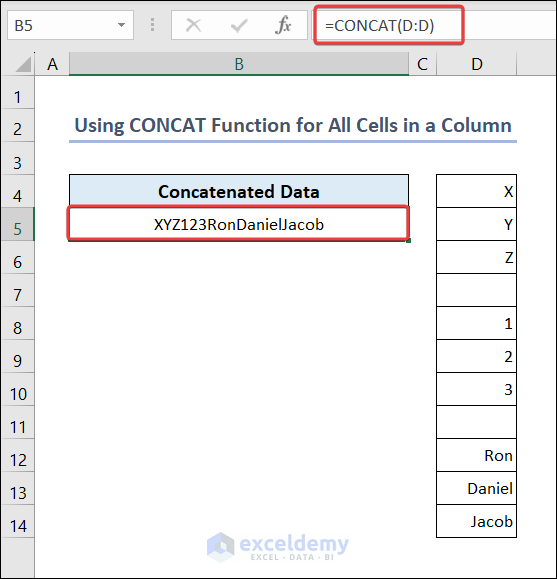
The CONCAT function skips empty cells. So, there will not be any gap in the resulting string of B5.
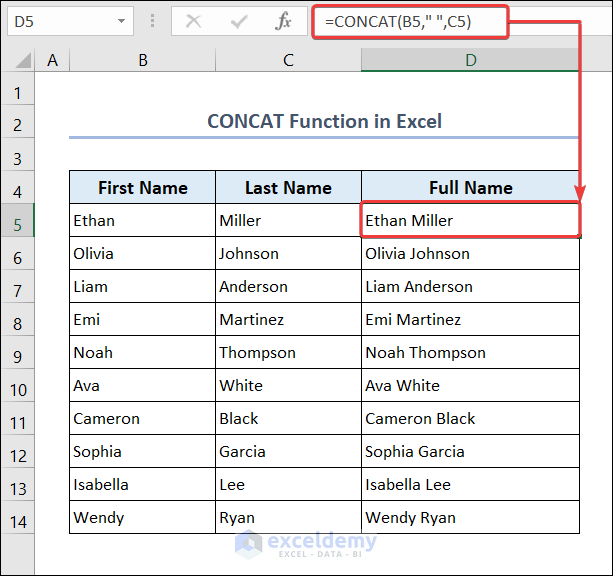
Example 5 – Using the CONCAT Function with a Separator
5.1. Space Separator
Find the full name:
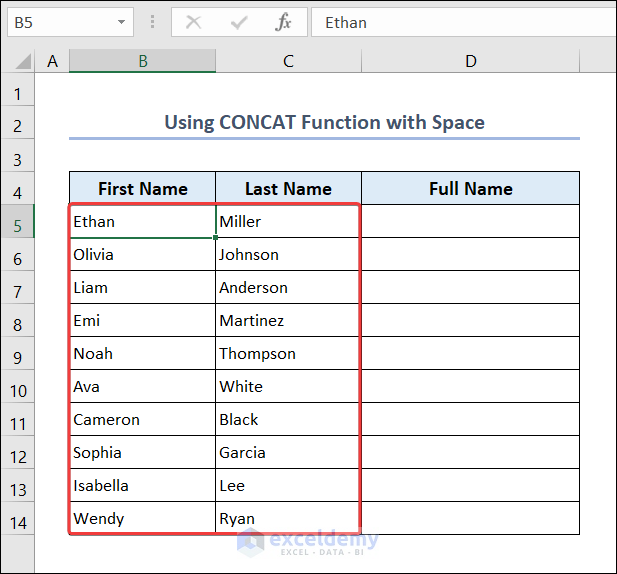
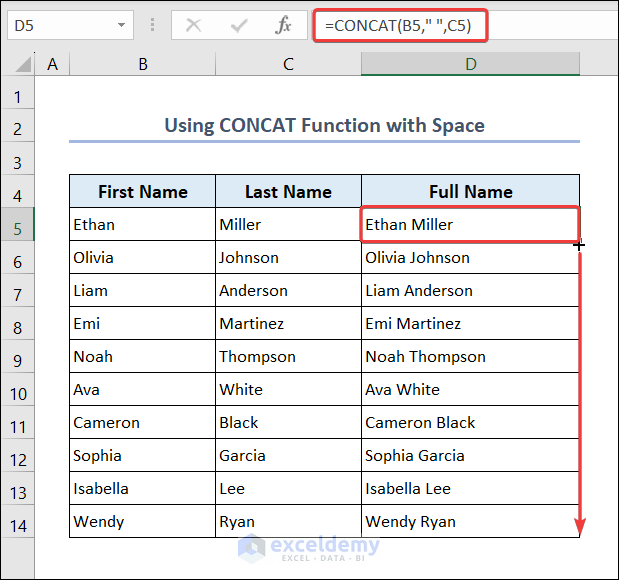
- Go to D5 and enter the following formula.
=CONCAT(B5," ",C5)- Drag down the Fill Handle to see the result in the rest of the cells.
5.2. Comma Separator
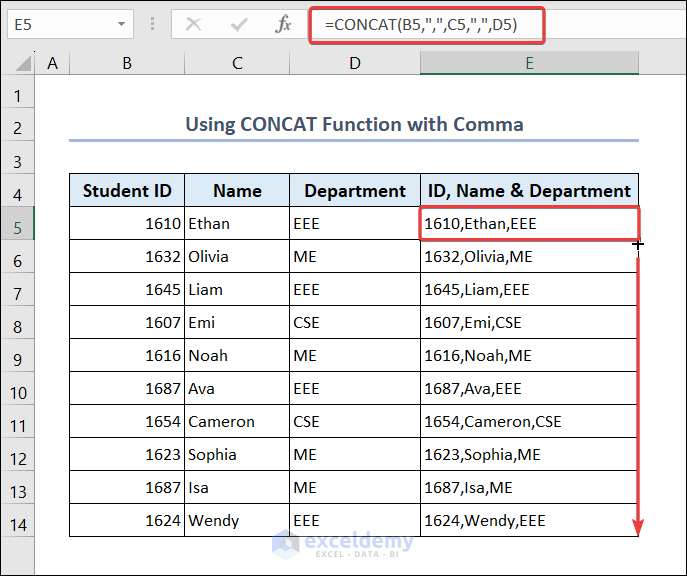
Combine students’ IDs, names, and departments:
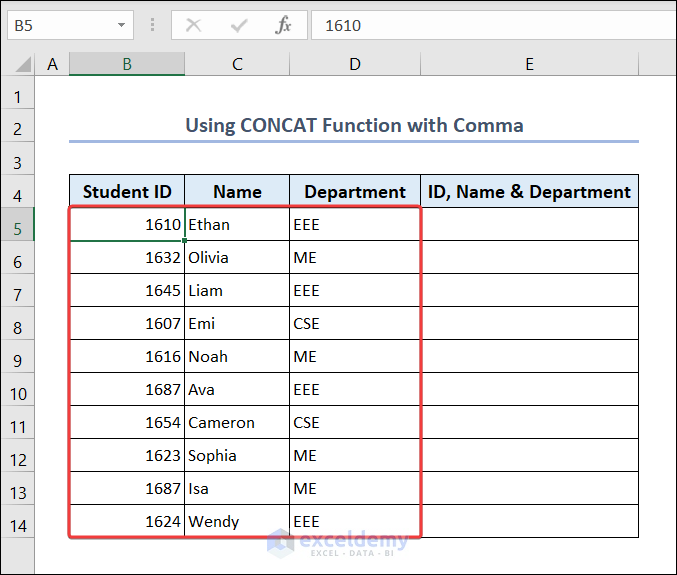
- Go to E5 and enter the following formula.
=CONCAT(B5,",",C5,",",D5)- Drag down the Fill Handle to see the result in the rest of the cells.
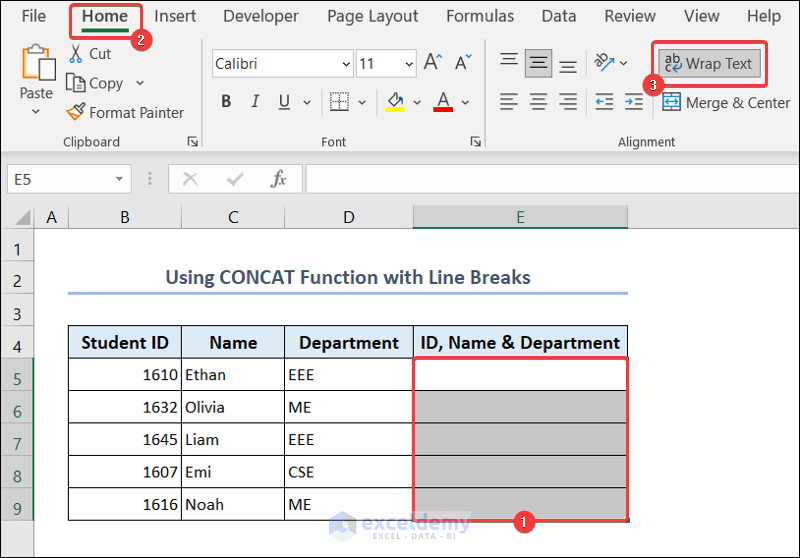
5.3. Line Breaks
To separate student ID, name, and department:
- Select E5:E9.
- Go to the Home tab >> Wrap Text in Alignment.
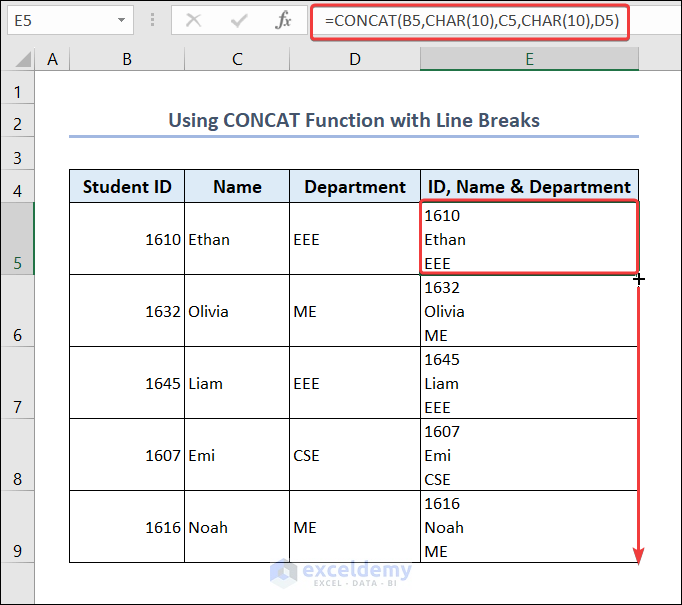
- Go to C5 and enter the following formula:
=CONCAT(B5,CHAR(10),C5,CHAR(10),D5)- Drag down the Fill Handle to see the result in the rest of the cells.
Do not set a fixed height for cells with the wrapped text. If you do so, the text may be invisible and you will need to adjust the row height. Use the default row height or autofit row height.
Example 6 – Using the CONCAT Function with Dates
Join departments and the date when they released the results.
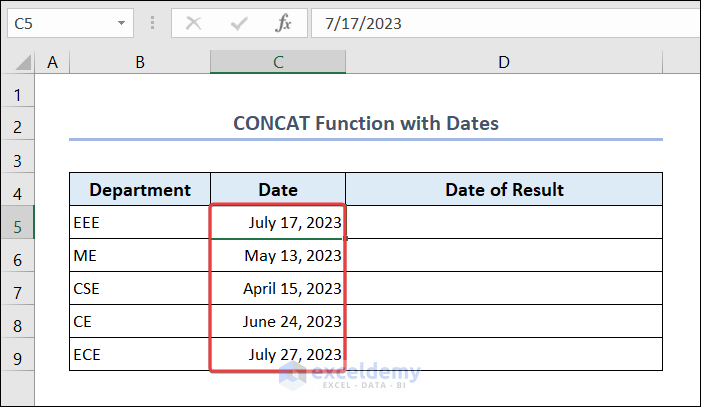
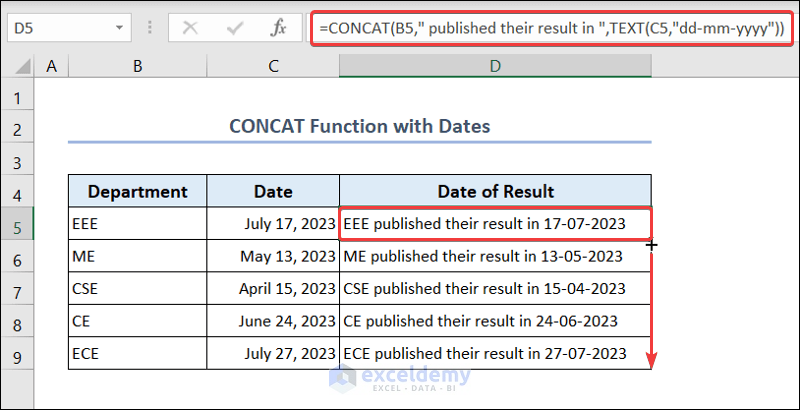
- Go to C5 and enter the following formula:
=CONCAT(B5," published their result in ",TEXT(C5,"dd-mm-yyyy"))- Drag down the Fill Handle to see the result in the rest of the cells.
Example 7 – Use the CONCAT Function in VBA
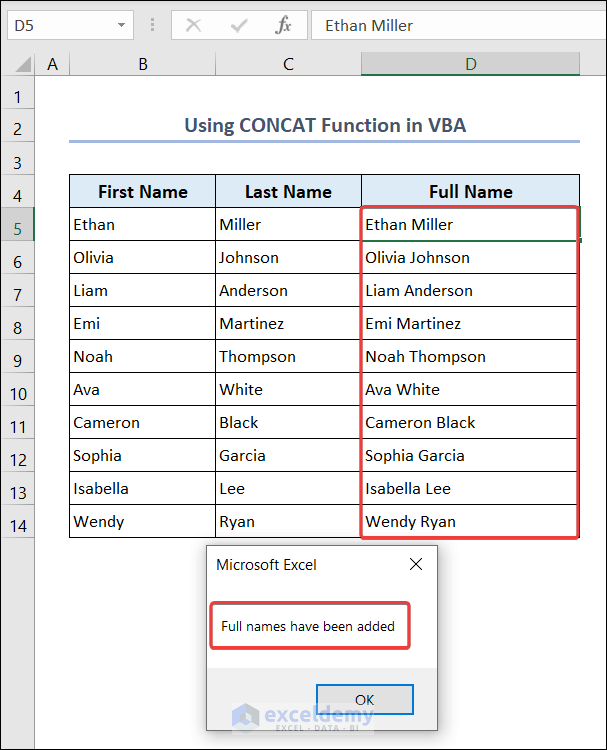
To get the full name of the students:
- Go to the Developer tab >> Visual Basic.
- Select Insert >> Module.
- Enter this code in the VBA Macro Editor.
- Click Run or press F5 to run the code.
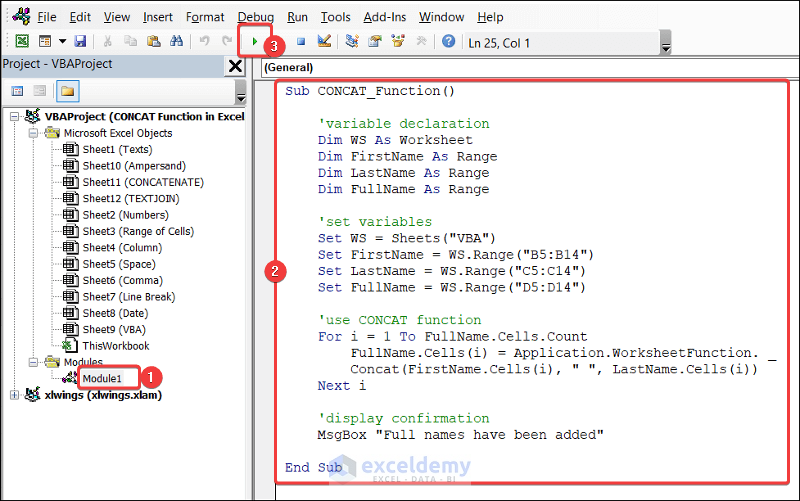
Sub CONCAT_Function()
'variable declaration
Dim WS As Worksheet
Dim FirstName As Range
Dim LastName As Range
Dim FullName As Range
'set variables
Set WS = Sheets("VBA")
Set FirstName = WS.Range("B5:B14")
Set LastName = WS.Range("C5:C14")
Set FullName = WS.Range("D5:D14")
'use CONCAT function
For i = 1 To FullName.Cells.Count
FullName.Cells(i) = Application.WorksheetFunction. _
Concat(FirstName.Cells(i), " ", LastName.Cells(i))
Next i
'display confirmation
MsgBox "Full names have been added"
End SubYou will see the full name of the students in D5:D14 of the VBA worksheet with a confirmation message.
Code Breakdown A loop is used to iterate through the cells in the FullName range and concatenate first name (FirstName), a space, and last name (LastName). The full name is stored in the FullName range. A MsgBox is displayed to indicate that full names were added to the worksheet.For i = 1 To FullName.Cells.Count
FullName.Cells(i) = Application.WorksheetFunction. _
Concat(FirstName.Cells(i), " ", LastName.Cells(i))
Next iMsgBox "Full names have been added"
Alternatives to the CONCAT Function in Excel
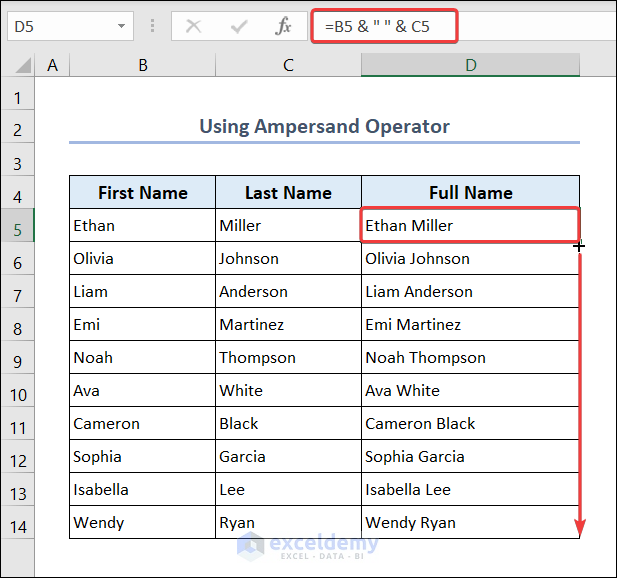
1. Ampersand Operator
To get full names from the first and last names.
- Go to D5 and enter the following formula.
=B5 & " " & C5- Drag down the Fill Handle to see the result in the rest of the cells.
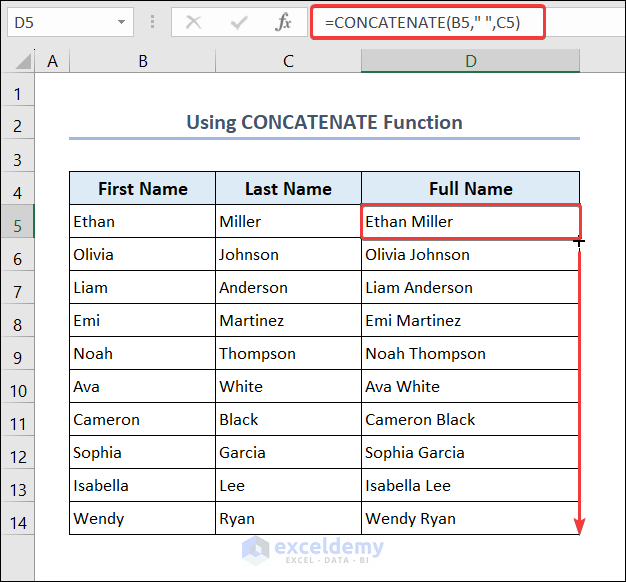
2. CONCATENATE Function
- Go to D5 and enter the following formula.
=CONCATENATE(B5," ",C5)- Drag down the Fill Handle to see the result in the rest of the cells.
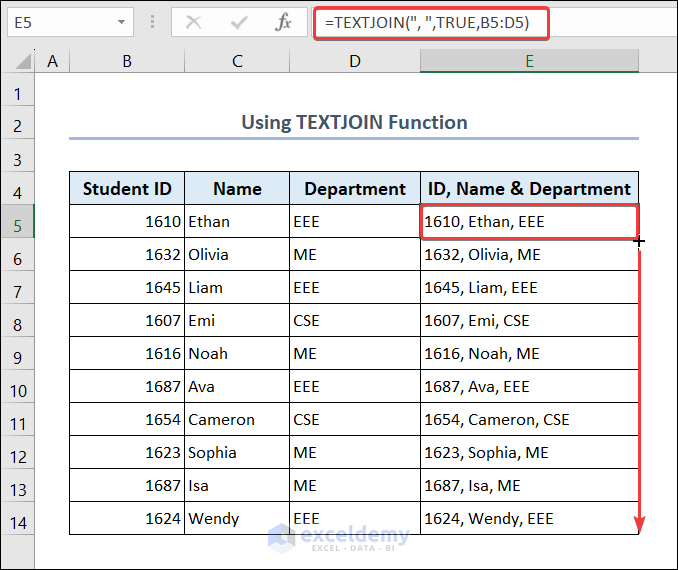
3. TEXTJOIN Function
Get student IDs, names and departments sequentially:
- Go to E5 and enter the following formula.
=TEXTJOIN(", ",TRUE,B5:D5)- Drag down the Fill Handle to see the result in the rest of the cells.
Things to Remember
The CONCAT function does not provide options for delimiters of empty values.
The quotation mark may be displayed in the output if a comma isn’t added between arguments.
The CONCAT function does not recognize arrays. Enter cell references separately.
You can use numbers with or without the quotation mark.
The numbers become text values in the output.
Double quotes, asterisk (*) or forward slash (/) can be used to separate the concatenated strings.
The #NAME? error occurs when you miss a quotation mark in the text arguments.
The #VALUE? error occurs when the output string exceeds the maximum cell character limit (32767).
Frequently Asked Question
1. What is the difference between the CONCATENATE and CONCAT functions?
These two functions have the same purpose and format. The CONCATENATE function is available in all versions, whereas the CONCAT function is available in Office 2016 and later versions. The CONCAT function is concise, and can take a range of cells as input and return a text with all the elements of the range of cells. The CONCATENATE function can take a range of cells as input but does not return a concatenated text. It returns an array of cells.
2. Can I use the CONCAT function to combine data from multiple sheets?
Yes, by referencing the cell ranges from different sheets within the function.
3. What happens if I try to concatenate too many characters?
The resulting string may exceed the character limit for a cell (32767) and will show a #VALUE? error.
<< Go Back to Excel Functions | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

