Download Practice Workbook
You can download the workbooks used to illustrate methods in this article from here.
How to Copy and Paste in Excel Using VBA: 12 Ways
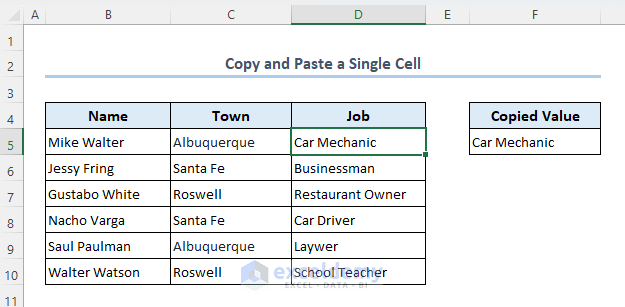
We will be using the following dataset as an example to elaborate methods in this article. The dataset is representing brief information for some people.
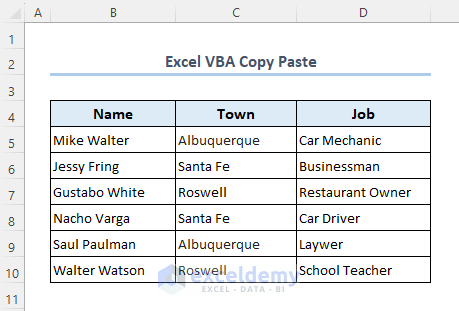
Method 1 – Copy and Paste the Value in a Single Cell
Let’s assume you want to copy the text in cell D5 to cell F5 using VBA.
- Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA window.
- Click on Insert and select Module.
- This will open a Module (Code) window.
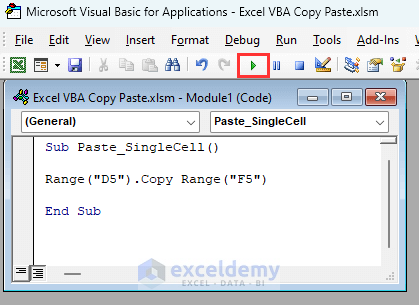
- Insert the following code in the window:
Sub Paste_SingleCell()
Range("D5").Copy Range("F5")
End SubThe code will copy the value in cell D5 and then will paste it in cell F5.
- Click on the Run icon in the VBA window and then close it.
VBA Breakdown
- Sub Paste_SingleCell()
Starts of the subroutine named Paste_SingleCell.
- Range(“D5”).Copy Range(“F5”)
The Range function copies the value in cell D5 to cell F5.
- End Sub
Ends the subroutine.
- You will see that the value in cell D5 is copied to cell F5.
Read More: Excel Formula to Copy Cell Value to Another Cell
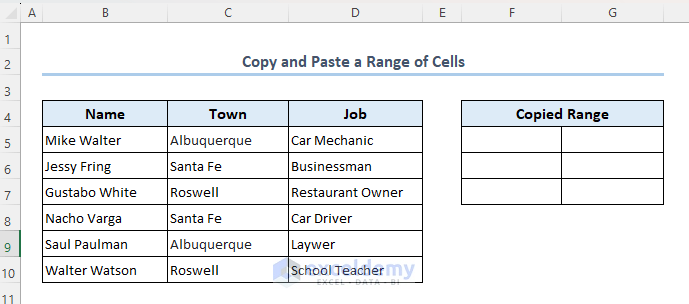
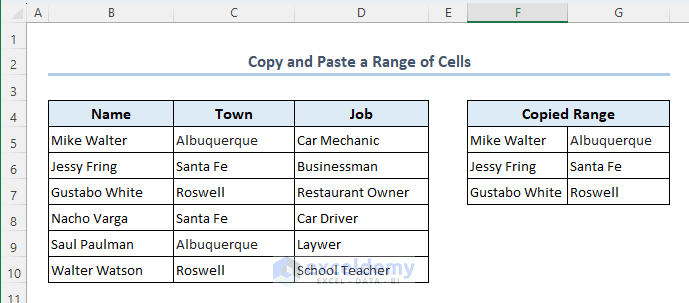
Method 2 – Copy and Paste Values in a Range of Cells
Suppose you want to copy the values in range B5:C7 to the empty range F5:G7.
- Create a new module just like the previous method.
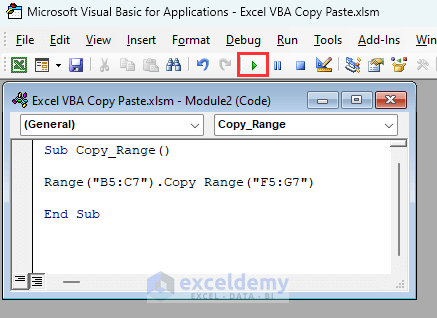
- Insert the following VBA code in the module and click on Run.
Sub Copy_Range()
Range("B5:C7").Copy Range("F5:G7")
End SubThe code will copy range B5:C7 and will paste it in range F5:G7.
VBA Breakdown
- Sub Copy_Range()
Starts the subroutine titled Copy_Range.
- Range(“B5:C7”).Copy Range(“F5:G7”)
Copies the values in range B5:C7 to range F5:G7.
- End Sub
Ends the subroutine.
- You can see that all the values in range B5:C7 are copied and pasted to range F5:G7.
Read More: How to Copy and Paste Multiple Cells in Excel (7 Quick Ways)
Method 3 – Copy and Paste an Entire Column
Let’s copy the entire column D and paste it to column F.
- Create a new VBA module.
- Copy and paste the following VBA code in the new module window.
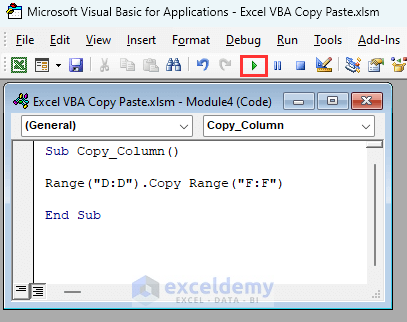
Sub Copy_column()
Range("D:D").Copy Range("F:F")
End SubThis will copy column D and will paste the column in column F.
VBA Breakdown
- Sub Copy_column()
This line initiates the subroutine titled Cppy_column.
- Range(“D:D”).Copy Range(“F:F”)
Then the Range function copies all values along column D to column F.
- End Sub
Ends the subroutine.
- Press the Run button in the VBA window and close it to see the results.
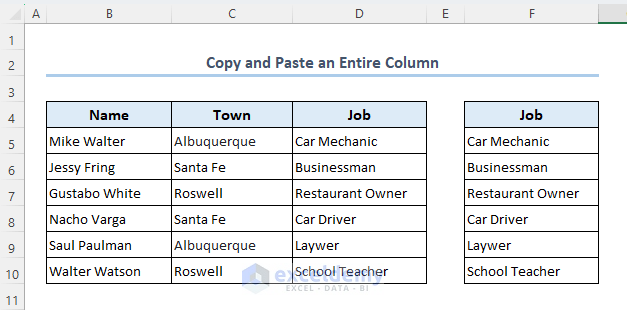
Read More: Macro to Copy Specific Columns from One Worksheet to Another in Excel
Similar Readings
- How to Copy and Paste in Excel Without Changing the Format
- How to Copy Merged and Filtered Cells in Excel (4 Methods)
- Run Time Error 1004: PasteSpecial Method of Range Class Failed
- How to Paste Link and Transpose in Excel (8 Quick Ways)
Method 4 – Copy and Paste an Entire Row
Let’s copy the entire row 10 into row 12.
- Create a new module.
- Copy and paste the following code into it.
Sub Copy_Row()
Range("10:10").Copy Range("12:12")
End SubThis will copy row 10 and will paste the row in row 12.
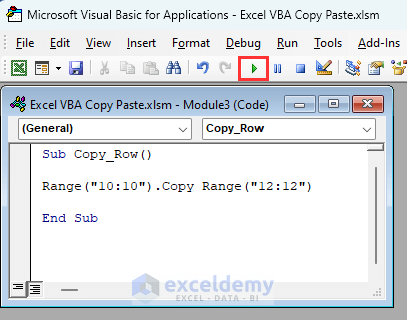
VBA Breakdown
- Sub Copy_Row()
Initiates the subroutine named Copy_Row.
- Range(“10:10”).Copy Range(“12:12”)
The Range function copies all values along row 10 to row 12.
- End Sub
Ends the subroutine.
- Click on the Run icon.
- Close the VBA window, and you will see that row 10 has been copied into row 12.
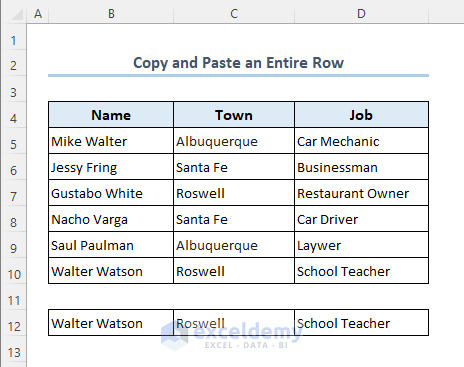
Read More: How to Copy Rows Automatically in Excel to Another Sheet (4 Methods)
Method 5 – Copy and Paste Multiple Ranges
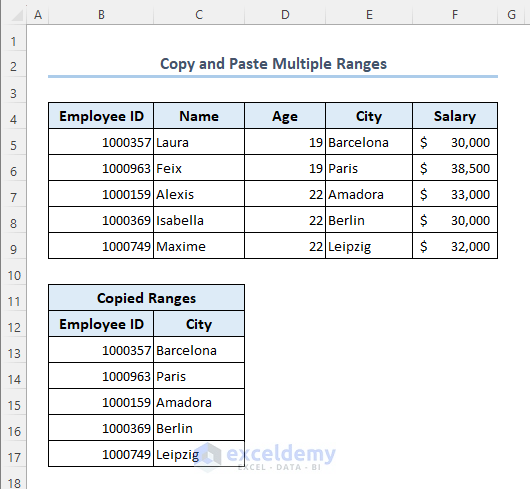
Let’s copy the Employee ID column and the City column from the existing dataset then create a new dataset out of those copied columns. The Employee ID column is within range B4:B19 and the City column is within range E4:E19.
- Create a new module as before.
- Copy and paste the following VBA code then click on Run.
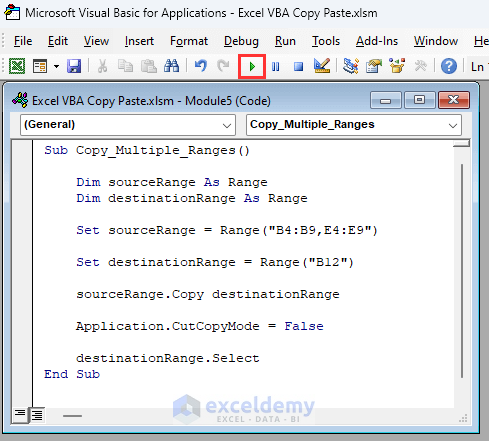
Sub Copy_Multiple_Ranges()
Dim sourceRange As Range
Dim destinationRange As Range
Set sourceRange = Range("B4:B9,E4:E9")
Set destinationRange = Range("B12")
sourceRange.Copy destinationRange
Application.CutCopyMode = False
destinationRange.Select
End Sub- This will copy range B4:B9 and range E4:E9 then paste these to range B12:C17.
VBA Breakdown
- Sub Copy_Multiple_Ranges()
Starts the subroutine named Copy_Multiple_Ranges.
- Dim sourceRange As Range
Dim destinationRange As Range
Here, two variables sourceRange and destinationRange are declared as Range type.
- Set sourceRange = Range(“B4:B9,E4:E9”)
The ranges from where the values will be copied are set here.
- Set destinationRange = Range(“B12”)
The ranges where the values will be pasted are set here.
- Copy destinationRange
This function copies the values in range B4:B9 and range E4:E9 to the destination range which’s first cell is cell B12.
- CutCopyMode = False
After the function completes, the copied data won’t be saved in the clipboard since this line clears the copy mode.
- Select
This function will select the destination cell B12 automatically after running the VBA macro.
- End Sub
Ends the subroutine.
- You will get your output as follows.
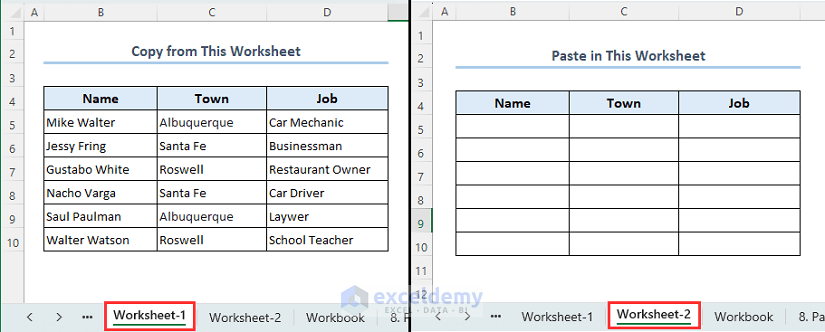
Method 6 – Copy and Paste from One Worksheet to Another
We will copy data from a worksheet named Worksheet 1 to a worksheet named Worksheet 2.
- Open a new VBA module.
- Copy the following code in the VBA Module.
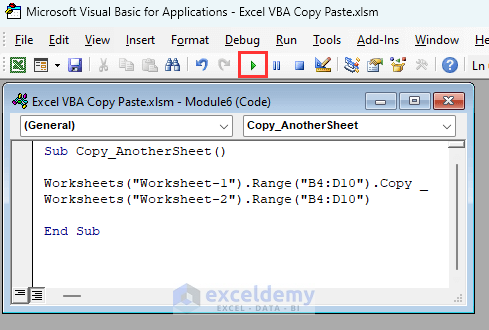
Sub Copy_AnotherSheet()
Worksheets("Worksheet-1").Range("B4:D10").Copy _
Worksheets("Worksheet-2").Range("B4:D10")
End SubThe code will copy the range B4:D10 from the Worksheet-1 sheet and paste it into range B4:D10 of the Worksheet-2 sheet.
- Click on the Run icon and then close the VBA window.
VBA Breakdown
- Sub Copy_AnotherSheet()
Initiates the start of the subroutine titled Copy_AnotherSheet.
- Worksheets(“Worksheet-1”).Range(“B4:D10”).Copy Worksheets(“Worksheet-2”).Range(“B4:D10”)
.Copy copies all the contents in range B4:D10 of sheet named Worksheet-1 then paste those contents to range B4:D10 of sheet Worksheet-2.
- End Sub
Ends the subroutine.
- If you open the Worksheet 2 sheet, you will see the range B4:D10 from the Worksheet 1 sheet.
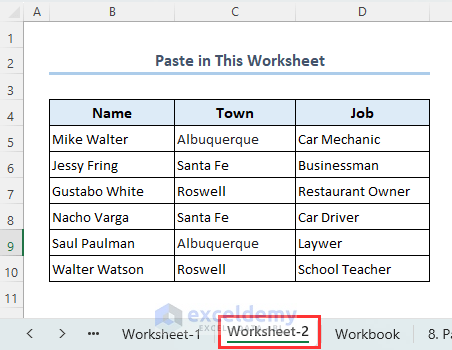
Read More: How to Copy a Worksheet in Excel (5 Smart Ways)
Similar Readings
- Use VBA to Paste Values Only with No Formatting in Excel
- How to Copy Only Visible Cells in Excel
- Copy and Paste is Not Working in Excel (9 Reasons & Solutions)
Method 7 – Copy and Paste from One Workbook to Another
Let’s say our existing workbook is Excel VBA Copy Paste and we want to copy values from it into the Workbook 2 file in the same folder.
Initially all the sheets in Workbook 2 are empty as follows.
Case 1 – Workbooks Are Open and Not Saved
- Open a Visual Basic window from the Developer tab from the workbook Excel VBA Copy Paste (the source workbook).
- Insert a new module window.
- Copy and paste the following VBA code in the newly created module window and run it.
Sub Copy_to_Another_Workbook_Open_Not_Saved()
Workbooks("Excel VBA Copy Paste").Worksheets("Workbook").Range("B4:D10").Copy _
Workbooks("Workbook 2").Worksheets("Sheet2").Range("B4:D10")
End Sub
VBA Breakdown
- Sub Copy_to_Another_Workbook_Open_Not_Saved()
Starts the subroutine Copy_to_Another_Workbook_Open_Not_Saved.
- Workbooks(“Excel VBA Copy Paste”).Worksheets(“Workbook”).Range(“B4:D10”).Copy Workbooks(“Workbook 2”).Worksheets(“Sheet2”).Range(“B4:D10”)
.Copy copies the range B4:D10 from the worksheet named Workbook within the workbook named Excel VBA Copy Paste and paste it into the same range on the worksheet named Sheet2 within another workbook named Workbook 2.
- End Sub
Ends the subroutine.
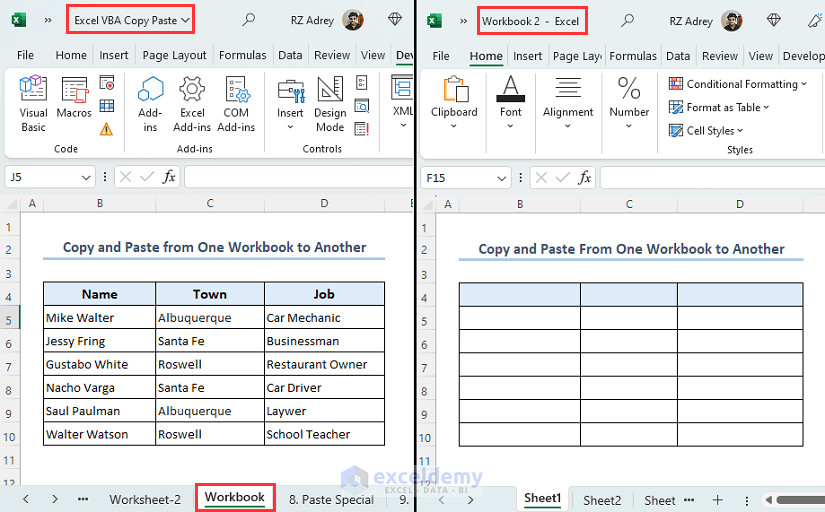
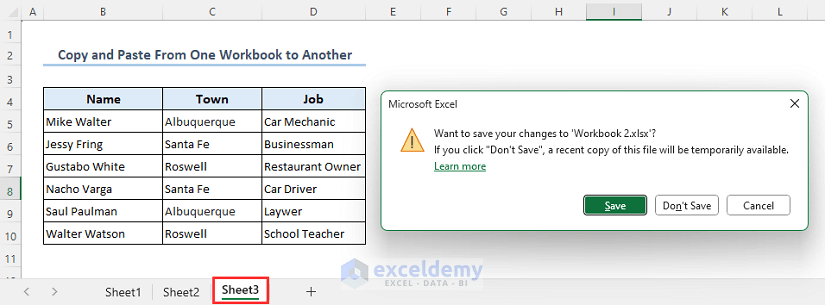
- You can see that the range B4:D10 from sheet Workbook of file Excel VBA Copy Paste has been copied to range B4:D10 of Sheet1 of file Workbook 2.
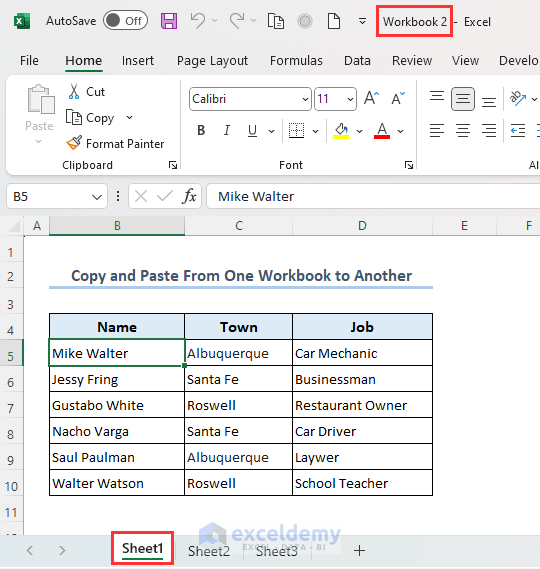
Case 2 – Workbooks Are Open and Saved
- Create a new VBA module in the source file Excel VBA Copy Paste.
- Copy and paste the following VBA code in the module section and click on Run:
Sub Copy_to_Another_Workbook_Open_Saved()
Workbooks("Excel VBA Copy Paste.xlsm").Worksheets("Workbook").Range("B4:D10").Copy _
Workbooks("Workbook 2.xlsx").Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("B4:D10")
End Sub
VBA Breakdown
- Sub Copy_to_Another_Workbook_Open_Saved()
Starts the subroutine Copy_to_Another_Workbook_Open_Saved.
- Workbooks(“Excel VBA Copy Paste.xlsm”).Worksheets(“Workbook”).Range(“B4:D10”).Copy Workbooks(“Workbook 2.xlsx”).Worksheets(“Sheet1”).Range(“B4:D10”)
.Copy copies the range B4:D10 from the worksheet named Workbook within the workbook named Excel VBA Copy Paste.xlsm and pastes it into the same range on the worksheet named Sheet1 within another workbook named Workbook 2.xlsx.
- End Sub
Ends the subroutine.
- The range B4:D10 from sheet Workbook of file Excel VBA Copy Paste will be copied to the range B4:D10 of Sheet2 of file Workbook 2 as shown below.
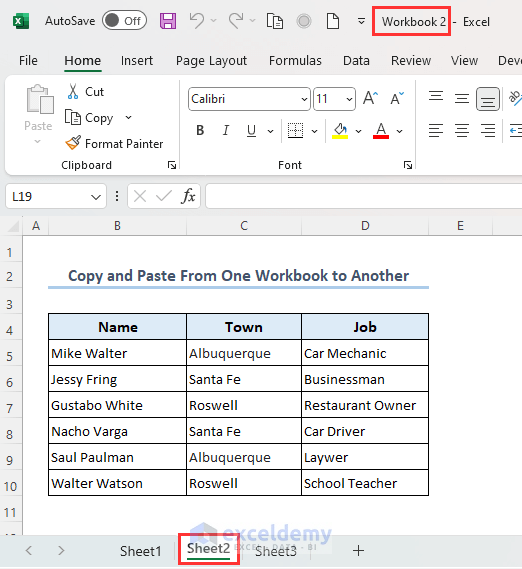
Case 3 – The Reference Workbook Is Closed
- Create a new module in the source file Excel VBA Copy Paste.
- Copy the following code in the module window and click on Run.
Sub Copy_to_Another_Workbook_Closed()
Workbooks.Open ("E:\Workbook 2.xlsx")
Workbooks("Excel VBA Copy Paste.xlsm").Worksheets("Workbook").Range("B4:D10").Copy _
Workbooks("Workbook 2.xlsx").Worksheets("Sheet3").Range("B4:D10")
Workbooks("Workbook 2.xlsx").Close
End Sub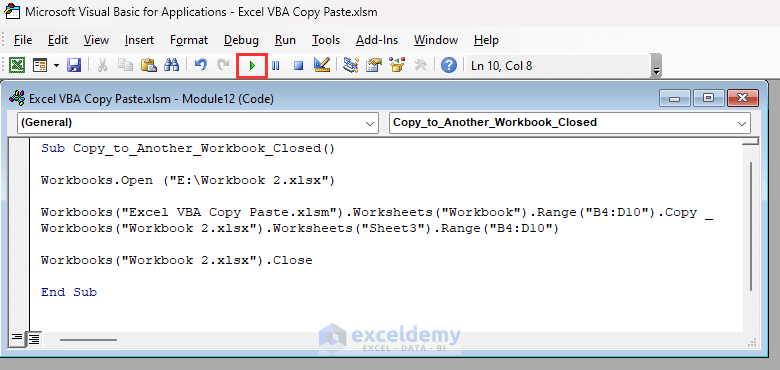
VBA Breakdown
- Sub Copy_to_Another_Workbook_Closed()
Initiates the subroutine named Copy_to_Another_Workbook_Closed.
- Open (“E:\Workbook 2.xlsx”)
The Workbooks.Open opens the workbook named Workbook 2.xlsx located at the specified file path E:\Workbook 2.xlsx.
- Workbooks(“Excel VBA Copy Paste.xlsm”).Worksheets(“Workbook”).Range(“B4:D10”).Copy Workbooks(“Workbook 2.xlsx”).Worksheets(“Sheet3”).Range(“B4:D10”)
.Copy copies the range B4:D10 from the worksheet named Workbook within the workbook named Excel VBA Copy Paste.xlsm and pastes it into the same range on the worksheet named Sheet1 within another workbook named Workbook 2.xlsx.
- Workbooks(“Workbook 2.xlsx”).Close
Asks for permission whether to save the workbook Workbook 2.xlsx, then closes the Workbook 2.xlsx.
- End Sub
Ends the subroutine.
- You will be asked whether you want to save the changes to the Workbook 2 file.
- If you press Save, the code will paste the values.
Method 8 – Copy and Paste Using Paste Special with VBA
You can copy and paste particular cell characteristics with Paste Special (examples: formats, values, column widths, etc.). You can also use it to execute custom paste operations such as skip blanks and transpose. We will copy the range B4:D10 to range F4:H10.
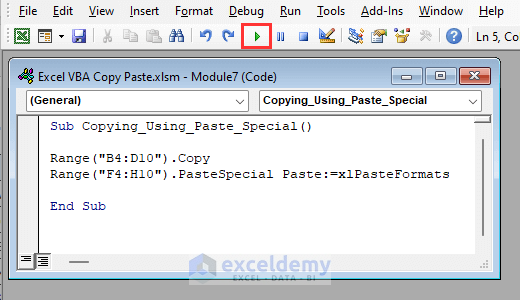
- Insert the following code in the VBA module window and click on Run:
Sub Paste_special()
Range("B4:D10").Copy
Range("F4:H10").PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteFormats
End Sub- The code will create a macro named Paste_special which will only copy the formats of cell range B4:D10 and will paste it in cell range F4:H10.
VBA Breakdown
- Sub Paste_special()
Starts the subroutine Paste_special.
- Range(“B4:D10”).Copy
.Copy copies the range B4:D10.
- Range(“F4:H10”).PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteFormats
The copied values will then be pasted in range F4:H10 with the special format specified by the argument Paste:=xlPasteFormats. The PasteSpecial method is used to paste the copied content in a specific way, specified by the argument.
- End Sub
Ends the subroutine.
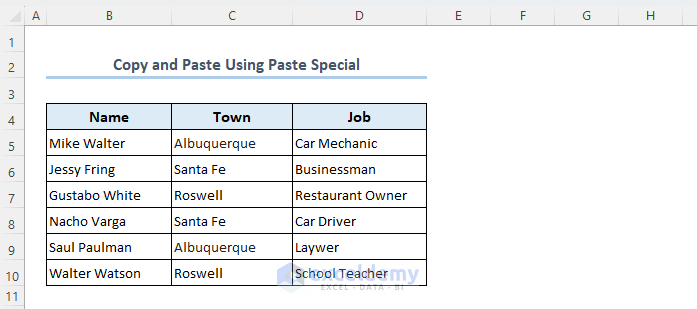
- After running the VBA code, you will see that the format of range B4:D10 is copied and pasted into range F4:H10.
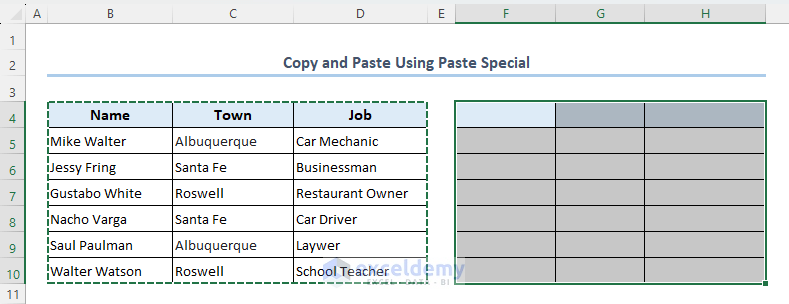
- Click on the first cell of the pasted dataset and press Enter.
- You can see that the data range is copied and pasted as follows.
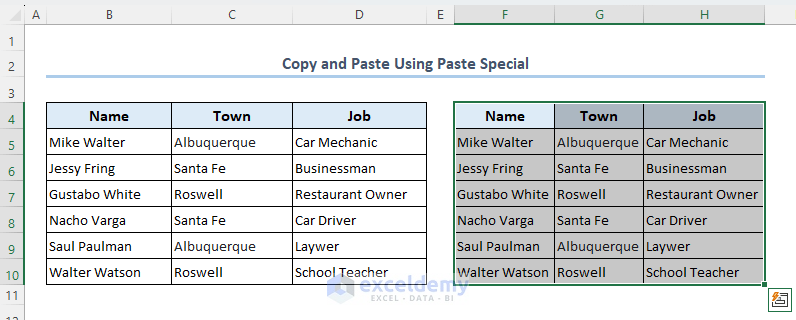
Read More: VBA Paste Special to Copy Values and Formats in Excel (9 Examples)
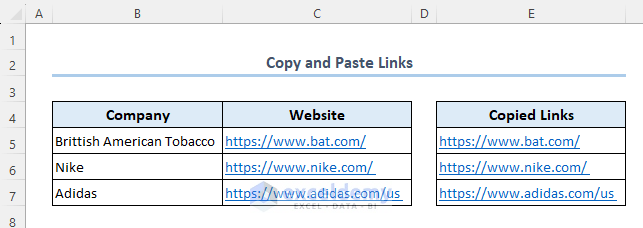
Method 9 – Copy and Paste Links
Let’s copy the links in C5:C7 and paste them in the range E5:E7.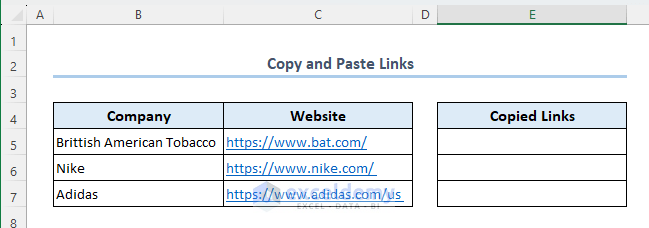
- Create a new module from the Visual Basic window:
- Copy and paste the following VBA code in the module section and run it.
Sub Copy_Links()
Dim sourceRange As Range
Dim destinationRange As Range
Dim cell As Range
Set sourceRange = Range("C5:C7")
Set destinationRange = Range("E1")
For Each cell In sourceRange
If cell.Hyperlinks.Count > 0 Then
destinationRange.Cells(cell.Row, 1).Hyperlinks.Add _
anchor:=destinationRange.Cells(cell.Row, 1), _
Address:=cell.Hyperlinks(1).Address, _
TextToDisplay:=cell.Hyperlinks(1).TextToDisplay
End If
Next cell
End Sub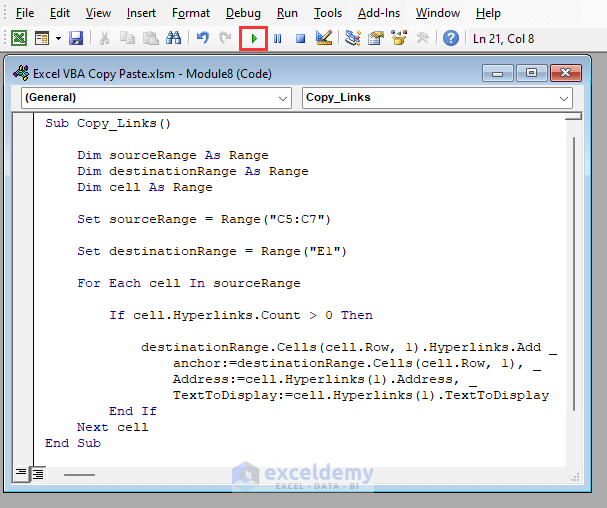
VBA Breakdown
- Sub Copy_Links()
Starts subroutine titled Copy_Links.
- Dim sourceRange As Range
Dim destinationRange As Range
Dim cell As Range
Declare variables sourceRange, destinationRange, and cell as Range type.
- Set sourceRange = Range(“C5:C7”)
Sets range of the variable sourceRange to range C5:C7.
- Set destinationRange = Range(“E1”)
Sets the range of the variable destinationRange to cell E1.
- For Each cell In sourceRange
If cell.Hyperlinks.Count > 0 Then
destinationRange.Cells(cell.Row, 1).Hyperlinks.Add _
anchor:=destinationRange.Cells(cell.Row, 1), _
Address:=cell.Hyperlinks(1).Address, _
TextToDisplay:=cell.Hyperlinks(1).TextToDisplay
End If
Next cell
The For Each loop is used to go through each cell in the sourceRange. The following operations are carried out by the code if a cell has one or more hyperlinks: It updates the destinationRange‘s relevant cell with a new URL. The cell in column 1 (column A) of the same row as the current cell in the loop is the cell that is referenced by the expression destinationRange.Cells(cell.Row, 1). The new hyperlink is identical to the first hyperlink discovered in the original cell in terms of URL and displayed text. Using the Next cell command, the code then advances to the following cell in the sourceRange. Until every cell in the sourceRange has been analyzed, this loop will keep running.
- End Sub
Ends the subroutine.
- You can see that the links are copied to the new range as follows.
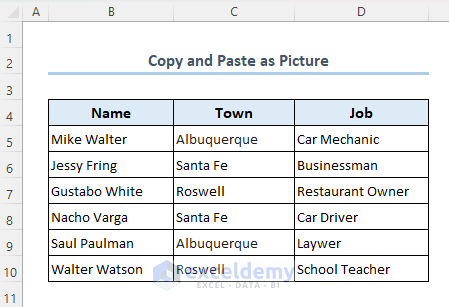
Method 10 – Copy and Paste as Picture
Let’s create an image out of the range B4:D10 from the following dataset then copy that image and paste it to your worksheet.
- Create a new module.
- Copy and paste the following code in the module and click on Run.
Sub Copy_As_Picture()
On Error Resume Next
Dim sourceRange As Range
Dim pictureRange As Range
Dim pictureShape As Shape
Set sourceRange = ActiveSheet.Range("B4:D10")
Set pictureRange = Application.InputBox("Select a cell where you want to put the picture", Type:=8)
pictureRange.Select
sourceRange.CopyPicture Appearance:=xlScreen, Format:=xlPicture
With pictureRange.Parent
Set pictureShape = .Pictures.Paste(Link:=False)
End With
With pictureShape
.Top = pictureRange.Top
.Left = pictureRange.Left
.Height = pictureRange.Height
.Width = pictureRange.Width
End With
End Sub
VBA Breakdown
- Sub Copy_As_Picture()
Starts the subroutine Copy_As_Picture.
- On Error Resume Next
Enables error handling and tells the programme to go on running in the event of an error.
- Dim sourceRange As Range
Dim pictureRange As Range
Dim pictureShape As Shape
The sourceRange, pictureRange variables are set as Range type and pictureShape is of Shape type variable.
- Set sourceRange = ActiveSheet.Range(“B4:D10”)
The sourceRange variable is representing the range B4:D10 on the active sheet.
- Set pictureRange = Application.InputBox(“Select a cell where you want to put the picture”, Type:=8)
The pictureRange variable receives the address of the selected cell as a range object.
With the Type:=8 parameter, which designates a cell reference as the input type, the Application.InputBox function is applied.
- Select
This function selects the cell set by the pictureRange variable.
- CopyPicture Appearance:=xlScreen, Format:=xlPicture
This function copies an image of the sourceRange . Then, that has copied the range as an image by the CopyPicture operator. The image should be duplicated exactly as it appears on the screen, according to the Appearance:=xlScreen parameter. The format of the copied photo is specified by the Format:=xlPicture parameter.
- With pictureRange.Parent
Set pictureShape = .Pictures.Paste(Link:=False)
End With
The With block defines the pictureShape object that starts here. pictureRange.Parent is a reference to the worksheet holding the picture, which is the pictureRange‘s parent object. The copied image is pasted onto the worksheet using this line.
The .Pictures.Paste(Link:=False) method is used to paste the picture without creating a link. With the With, it comes to an end here.
- With pictureShape
.Top = pictureRange.Top
.Left = pictureRange.Left
.Height = pictureRange.Height
.Width = pictureRange.Width
End With
Here the properties of the pictureShape object (such as top position, left position, height, and width) are set to match the corresponding properties of the pictureRange cell.
- End Sub
Ends the subroutine.
- After running the VBA macro and closing the VBA window, choose a cell where you want to paste the created picture. We have selected cell B12.
- Clicked on OK.
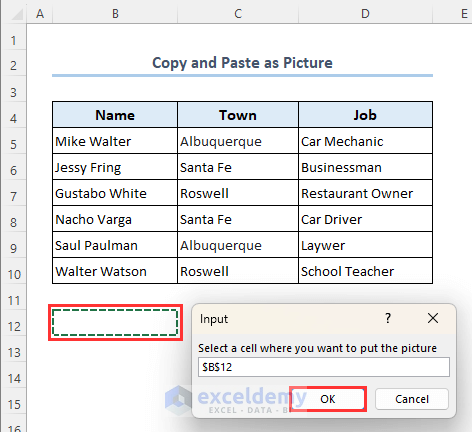
- The picture is copied and pasted as follows.

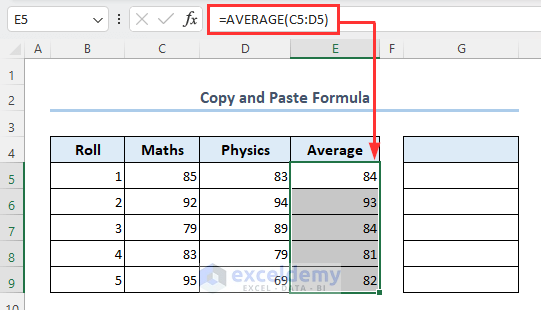
Method 11 – Copy and Paste Formula
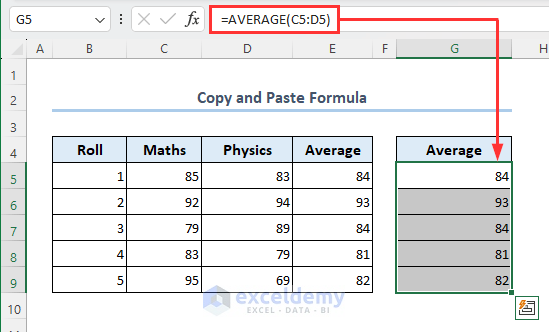
Consider a dataset as follows where range F5:F9 contains formulas. We’ll copy these values with the exact formulas used here to the range G5:G9.
- Create a new module then copy and paste the following VBA code there.
- Click on Run.
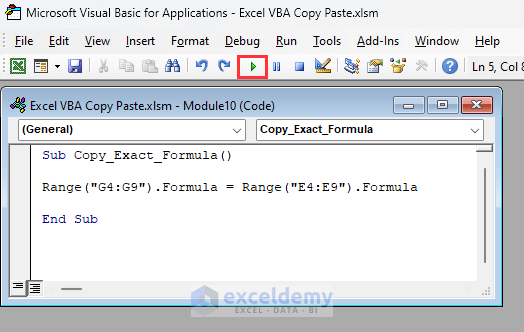
Sub Copy_Exact_Formula()
Range("G4:G9").Formula = Range("E4:E9").Formula
End Sub
VBA Breakdown
- Sub Copy_Exact_Formula()
Initiates the subroutine Copy_Exact_Formula.
- Range(“G4:G9”).Formula = Range(“E4:E9”).Formula
Copies the assigned formulas from the range E4:E9 to the range G4:G9.
- End Sub
Ends the subroutine.
- The range is copied with the exact formulas.
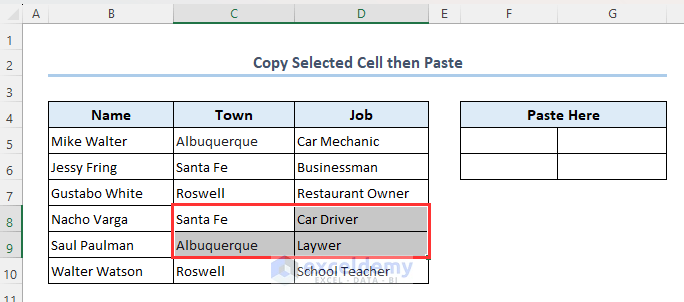
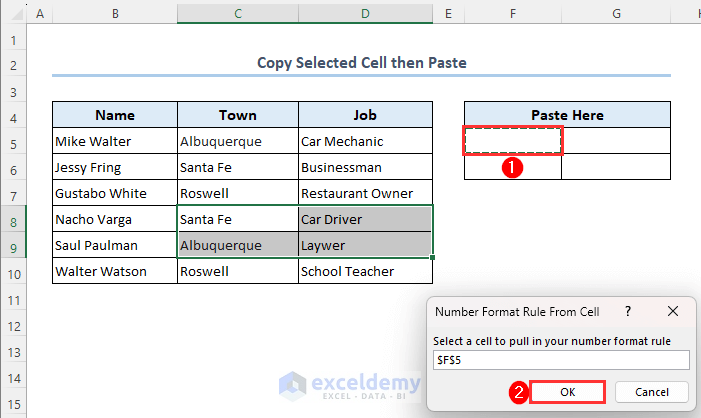
Method 12 – Copy and Paste Selected Cells
In this example, we have already selected range C8:D9. Let’s copy and paste this selection using VBA macro to range F5:G6.
- Create a new module.
- Enter the code below in the module section.
- Click on Run.
Sub Selection_Copy_Paste()
Dim location As Range
Set location = Application.InputBox( _
Title:="Number Format Rule From Cell", _
Prompt:="Select a cell to pull in your number format rule", _
Type:=8)
Selection.Copy location
End Sub
VBA Breakdown
- Sub Selection_Copy_Paste()
Starts the subroutine Selection_Copy_Paste.
- Dim location As Range
Declares a variable location as Range type.
- Set location = Application.InputBox( Title:=”Number Format Rule From Cell”, Prompt:=”Select a cell to pull in your number format rule”, Type:=8)
This initiates an input box using the Application object’s InputBox function. The user can choose a cell to pull in a number format rule by clicking on it in the input box. The location variable receives the address of the selected cell as a range object. We have set the title of the input box using the Title option. When the user uses the Prompt parameter, the input field shows a prompt message. The Type parameter represents the cell reference 8, which determines the type of input box.
- Copy location
This code copies the currently selected range (Selection) and pastes it into the specified destination range (location).
- End Sub
Ends the subroutine
- After running the code, choose the cell where you want to paste the copied values. We used cell F5.
- Click on OK.
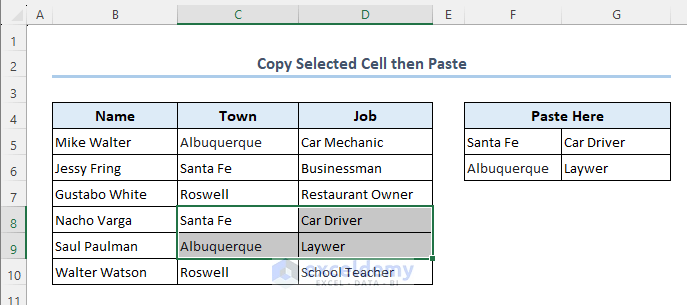
- The already selected range C8:D9 is copied and pasted to the range F5:G6 as follows.
Excel VBA Copy Paste: Knowledge Hub
- Copy Cell Value and Paste to Another Cell
- Copy and Paste From One Worksheet to Another
- Copy Range to Another Workbook
- Copy Specific Columns From One Worksheet to Another Worksheet
- Copy Data From Another Workbook Without Opening
- Copy Rows to Another Worksheet Based on Criteria
- Copy Paste Values Next Empty Row
- Copy Destination Values Only
- Paste Values Only No Formatting
- Copy Formula From Cell Above
- Copy Formula Relative Reference
- Paste From Clipboard to Excel
- Paste Range into Email Body
- Copy Visible Rows Using Autofilter
- Copy Visible Cells Only VBA Without Header
- Paste Special Values and Formats
- Paste Special Formulas And Formats
- Paste Special Keep Source Formatting
- PasteSpecial Method of Range Class Failed
- PasteSpecial Method of Worksheet Class Failed
- Copy Multiple Rows in Excel Using Macro
- Compare Two Excel Sheets and Copy Differences
Related Articles
- VBA Code to Compare Two Excel Sheets and Copy Differences
- [Fixed]: Right Click Copy and Paste Not Working in Excel (11 Solutions)
- PasteSpecial Method of Worksheet Class Failed (Reasons & Solutions)
- Excel Formula to Copy Cell Value from Another Sheet
- Copy Unique Values to Another Worksheet in Excel (5 Methods)
- Excel VBA: Copy Range to Another Workbook
- Macro to Copy and Paste from One Worksheet to Another (15 Methods)


