Method 1 – Use VBA Macro to Count Filled Cells from a Range
Step 1: Open Microsoft Visual Basic, insert a Module using the instruction section. Paste the following macro in any Module.
Sub Count_cells_fromRange()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets("NewYork")
ws.Range("H5") = Application.WorksheetFunction.CountA(ws.Range("B4:F14"))
End Sub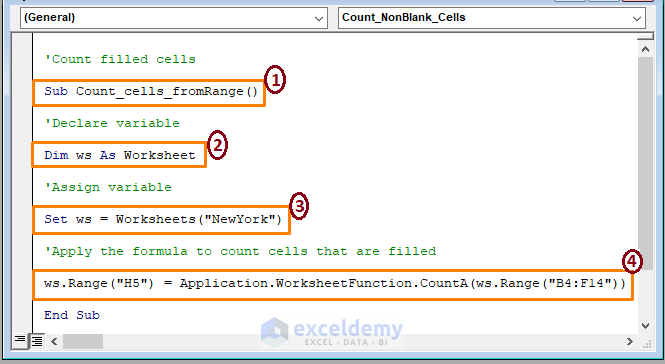
➤ In the code,
1 – Start the macro procedure by declaring the Sub name. You can assign any name to the code.
2 – Declare the variable as Worksheet.
3 – Assign the variable to a specific worksheet.
4 – Apply the COUNTA function to count filled cells from range B4:F14 and display it in the H5 cell.
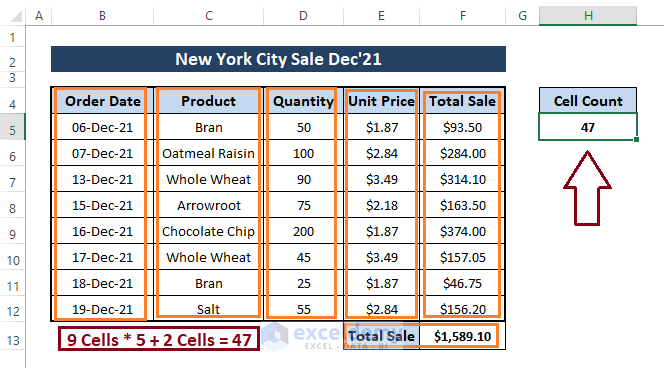
Step 2: Press F5 to run the macro. After returning to the workbook, you will see the total filled cell number, as depicted in the screenshot below.
Method 2 – Count Cells Filled with Values Using VBA
Step 1: Repeat the instruction section to open and insert a Module in Microsoft Visual Basic.
Sub Count_Cells_withValues
Range("H5") = Application.WorksheetFunction.Count(Range("B4:F14"))
End Sub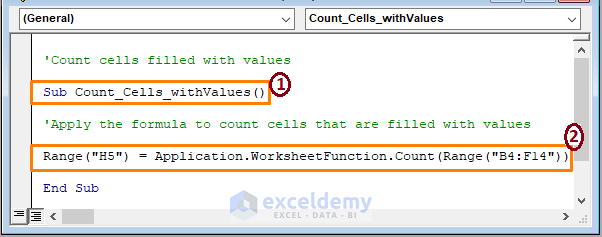
➤ From the above image, in the sections,
1 – Begin the macro code declaring the VBA Macro Code’s Sub name.
2 – The COUNT function counts cells that contain values in the range B4:F14 and afterward displays it in cell H5.
Step 2: Hit F5 to run the macro, and it inserts the total cell count containing values.
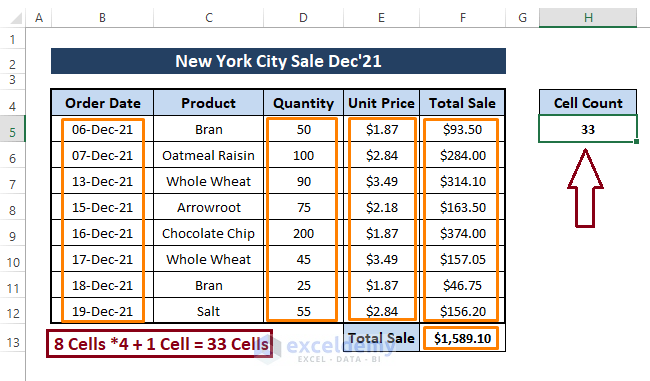
One revealing thing is that the range B4:F14 contains text cells (i.e., B4:F4, C5:C12, and E13), blank cells (i.e., B13:D13 and B14:F14), and the macro ignores it.
Method 3 – Count Specific Filled Column Cells in Excel Using VBA
Step 1: Type the below macro code in the Module (inserted by following the instruction section).
Sub Count_FilledCells_inColumn()
Dim N As Integer
N = Worksheets("NewYork").Range("B:B").Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeConstants).Count
MsgBox "There total number of filled cells in the column:" & N
End Sub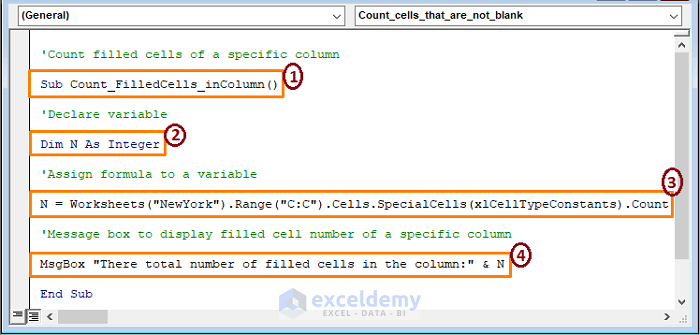
➤ The code’s sections,
1 – Initiate the macro procedure declaring the Sub name.
2 – Declare the N variable as an Integer.
3 – Assign the variable to a formula. The formula takes a worksheet (i.e., NewYork) and a column (i.e., C column). The COUNT function counts all the filled cells in the column.
4 – A message box displays the count.
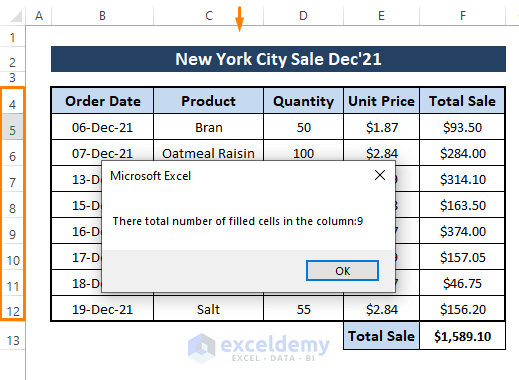
Step 2: Press F5 to run the macro. The macro will display a message box shortly, and the filled cell count will appear in it.
Method 4 – Formula to Count Cells Filled with Values
Step 1: Write the subsequent macro in the Microsoft Visual Basic Module.
Option Explicit
Sub Formula_Count_ValueCells
Range("H14").Formula = "=Count(H2:H12)"
End Sub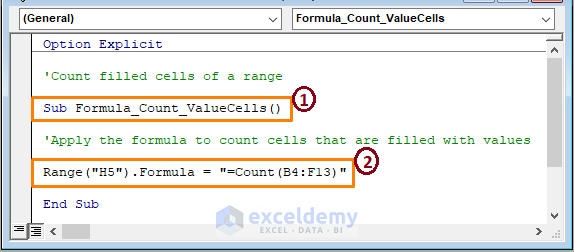
➤ From the above image, the code’s sections,
1 – Take forward the macro by setting the Sub name.
2 – Use the COUNT formula to count numeric cells from the B4:F13 range. Then, the macro displays the count in cell H5.
Step 2: Run the macro and press F5. The macro displays the count in cell H5.
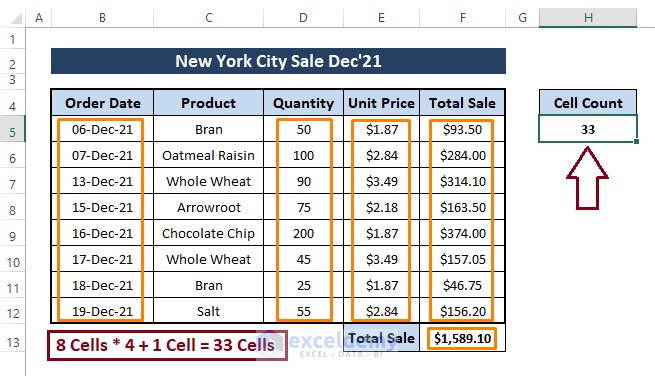
➤ To cross-check our findings, we can modify the dataset. For instance, we can insert 2 or 3 blank cells in the range and see what the macro returns.
We modify the dataset as depicted in the below picture.
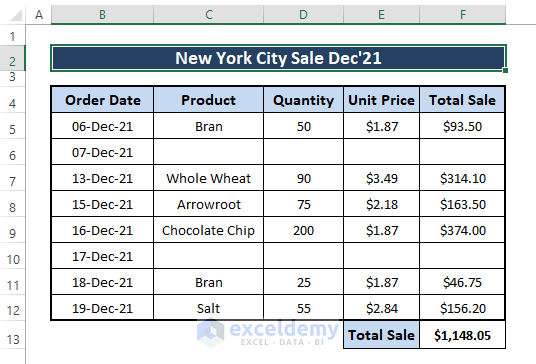
➤ After executing the same macro, the macro returns 27 as the numeric value containing cells in the range.
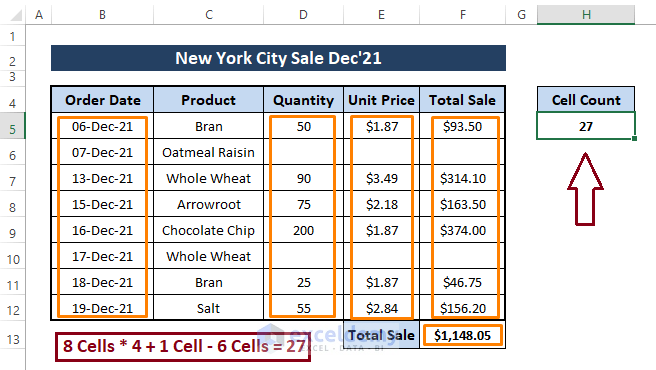
After inspecting the above depiction, the macro returns the correct counting. So, existing blank cells are not an issue when we count filled cells with macros. Macros that count filled cells ignore blank or empty cells.
Method 5 – Count Filled Cells from a Selection Using VBA
Step 1: Use the following macro code in any Module of any Microsoft Visual Basic window.
Sub Count_FilledCells_Selection()
Dim Rng As Range
Dim ActiveRng As Range
Dim Total As Long
On Error Resume Next
Text = "Select the range"
Set ActiveRng = Application.Selection
Set ActiveRng = Application.InputBox("Range", Text, ActiveRng.Address, Type:=8)
For Each Rng In ActiveRng
If Not IsEmpty(Rng.Value) Then
Total = Total + 1
End If
Next
MsgBox "The total filled cells number in the range:" &Total
End Sub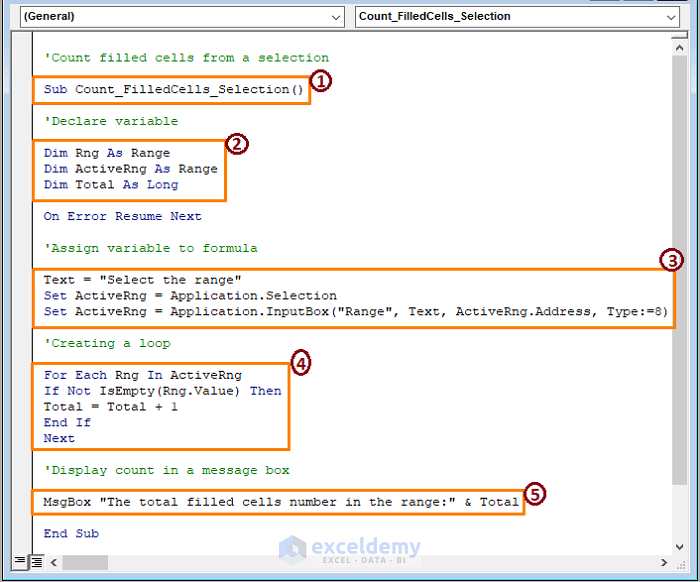
➤ The above image has code sections,
1 – Take forward the macro by setting the Sub name.
2 – Declare the variables as Range and Long.
3 – Assign the variables to the text and Input box function that requires range insertion through a message box command.
4 – Create a loop to pass each cell within the range and add the non-empty cells.
5 – Display the count through a message box.
Step 2: To run the macro, press F5. A dialog box named Select the range will appear. Click OK.
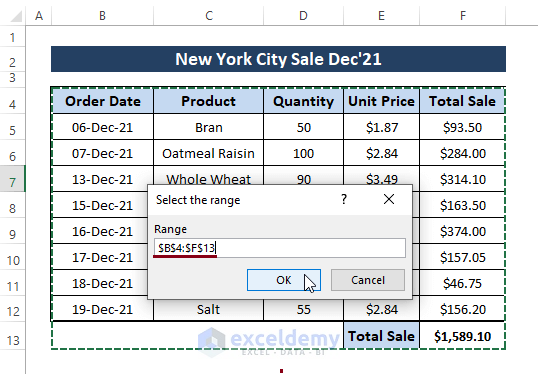
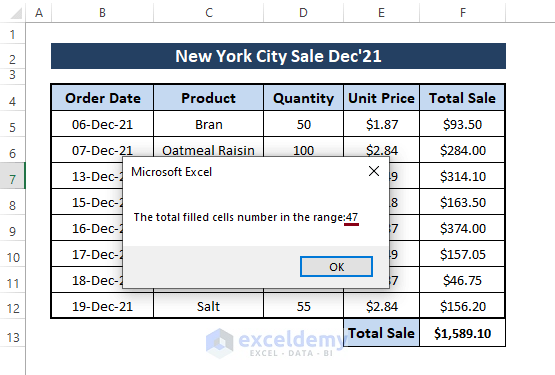
➤ Clicking OK displays the count number in a message box below.
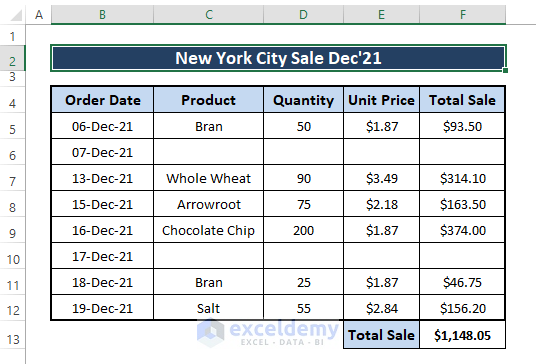
➤ To cross-check the resultant value we got in this method previously. Empty some of the cells, as depicted in the following picture.
➤ Insert and run the same macro for this modified dataset, and we get the result as follows.
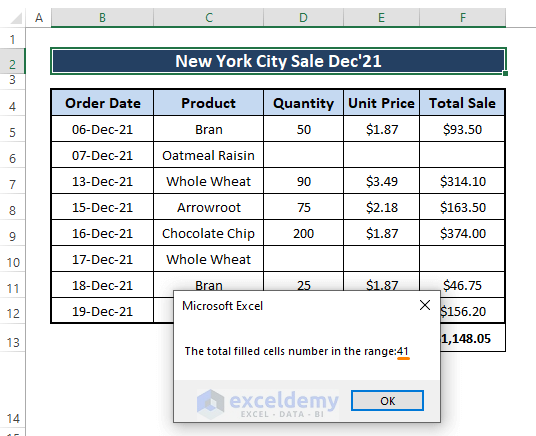
As you can see from the dataset, we empty 6 cells, and the macro returns 41 as a result. Before emptying the cell, the result was 47; now, it is (47-6) or 41. As a result, we can say the delivered count number is correct.
Method 6 – Using Excel VBA to Count Cells Filled with Text from a Selection
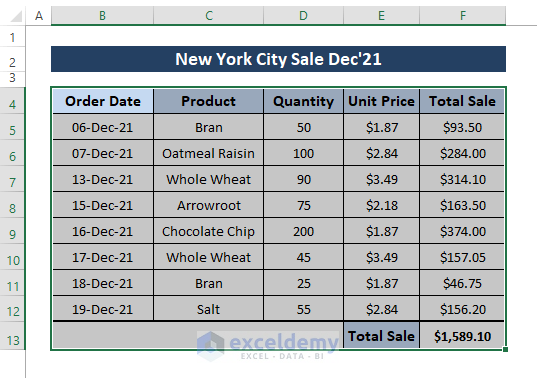
Step 1: Select the entire range from which you want to count the text cells similar to the picture below.
Step 2: To count the text paste the below macro in the Microsoft Visual Basic Module.
Sub Count_TextCells_Selection()
Dim Rng As Range
Dim i As Integer
For Each Rng In Selection
If Application.WorksheetFunction.IsText(Rng) Then
i = i + 1
End If
Next Rng
MsgBox "The total cells filled with text in the selection:" &i
End Sub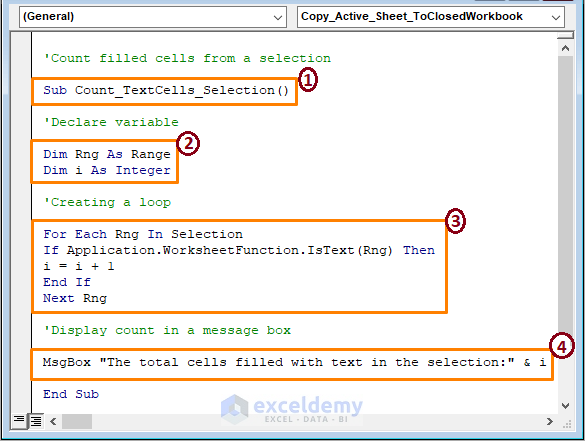
➤ The code is marked in parts,
1 – Begin the macro by setting the Sub name.
2 – Declaring the variables as Range and Integer.
3 – Create a loop. Each cell in the range is tested for being Text or not then add the count if returns TRUE.
4 – Display the count in a message box.
Step 2: Press the F5 key to run the macro. The cell number containing text will then appear in a message box.
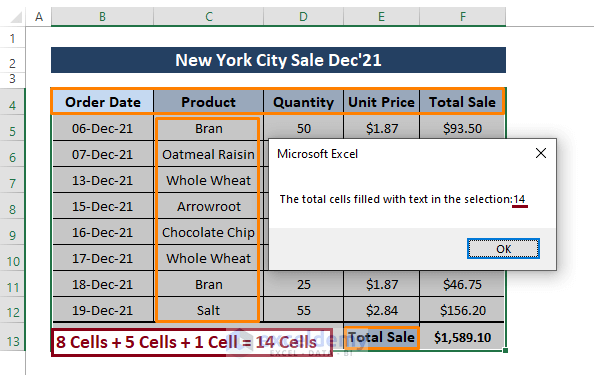
Method 7 – Custom Function to Count Cells Filled with Color Using VBA
Step 1: To create a custom function, use the following macro in any Module.
Function CountCellColored(Rng As Range, criteria As range) As Long
Dim data As range
Dim cell As Long
cell = criteria.Interior.ColorIndex
For Each data In Rng
If data.Interior.ColorIndex = cell Then
CountCellColorED = CountCellColored + 1
End If
Next data
End Function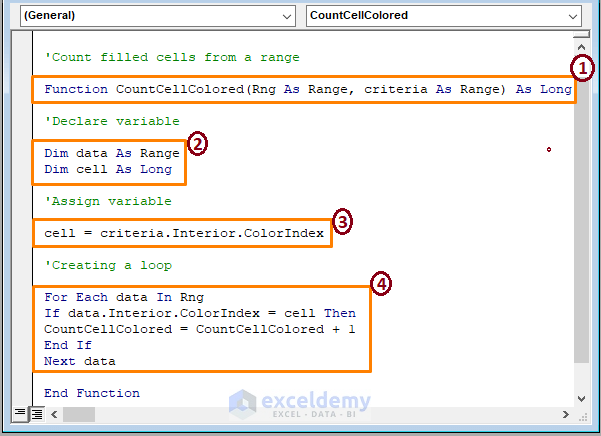
➤ The macro code is numbered in parts,
1 – Begin the macro by setting the Function name CountCellColored and function syntax (i.e., range, criteria).
2 – Declaring the variables as Range and Long.
3 – Assign the cell variable to a criteria ColorIndex function.
4 – Create a loop to test whether each cell is conditionally colored. Add cells in case the test returns TRUE.
Step 2: After inserting the macro, return to the worksheet. In the worksheet, type the following formula in cell I5.
=CountCellColored(B4:F13,H5)CountCellColored is the custom function. B4:F13 is the range, and H5 is the criteria.

Step 3: Hit ENTER to display the colored cell count.
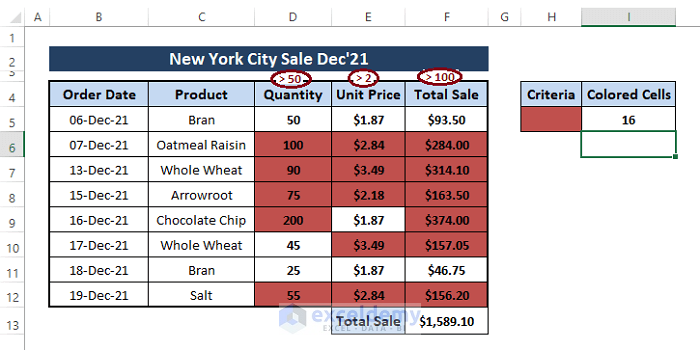
If you want to cross-check the count, just count the colored cells in the dataset. You’ll find that the formula’s returned values are correct.
Download Excel Workbook
<< Go Back to Count Cells | Formula List | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

