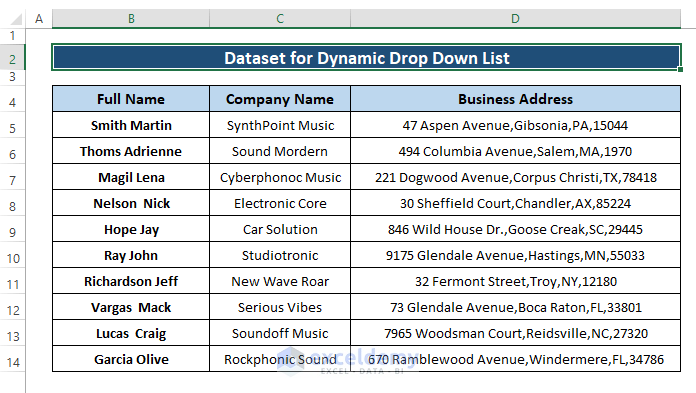
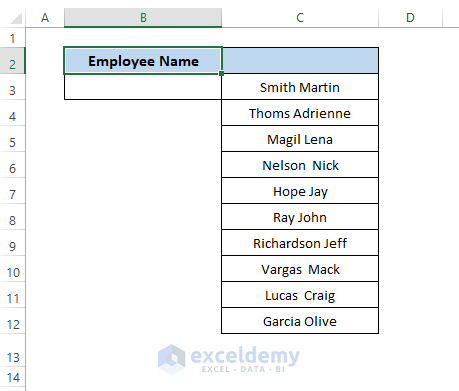
Let’s say we have a dataset where Employee Name, Company Name, and Business Addresses are displayed. We want a dynamic drop-down list where we can assign any employee name besides the Company Name and Business Addresses.
Opening Microsoft Visual Basic and Inserting Code in the Module
There are mainly 3 ways to open Microsoft Visual Basic window:
- Using Keyboard Shortcuts: Press Alt + F11 to open the Microsoft Visual Basic window.
- Using Developer Tab: In an Excel worksheet, go to Developer Tab and select Visual Basic.
- Using Worksheet Tab: Go to any worksheet, right-click on it, and choose View Code from the Context Menu.
Inserting a Module in Microsoft Visual Basic: There are 2 ways to insert a Module in Microsoft Visual Basic window:
- Select a Worksheet and Right-Click on it, then select Insert (from the Context Menu) and choose Module.
- Select Insert from the Toolbar and choose Module.
Dynamic Drop-Down List in Excel Using VBA: 2 Easy Ways to Create
Method 1 – Range to Create a Dynamic Drop-Down List in Excel
From the dataset, we know that our worksheet contains multiple employee names. We want to create a dynamic drop-down list using the range (i.e., C column).
Steps:
- Open Microsoft Visual Basic then insert a Module using the instruction section.
- Paste the following macro in any Module:
Sub Dynmc_DropDown_Range()
Dim wrk As Worksheet: Set wrk = Worksheets(2)
Dim nameText As String
Dim nameRng As Range
nameText = "DynamicList"
Set nameRng = wrk.Range("$C:C")
ThisWorkbook.Names.Add Name:=nameText, RefersTo:=nameRng
With Worksheets(2).Cells(3, "B").Validation
.Delete
.Add Type:=xlValidateList, AlertStyle:=xlValidAlertStop, _
Operator:=xlBetween, _
Formula1:="=" & nameRng.Address
End With
End Sub 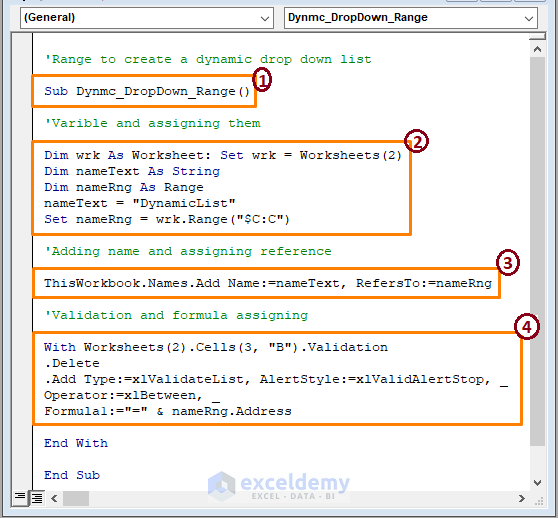
➤ in the code,
1 – start the macro procedure by declaring the Sub name. You can assign any name to the code.
2 – declare the variable then assign the variable to create a DynamicList in the Name Manager. Also assign the range (i.e., $C:C).
3 – assigns the names and range to the Worksheet2.
4 – data validation starts from row 3 in column B using the WITH statement and displays the nameRng (i.e., column C) entries in the validation.
- Press F5 to run the macro.
- After returning to the workbook, click on the drop-down icon.
- We see all the entries from column C are present in the drop down list as depicted below picture.
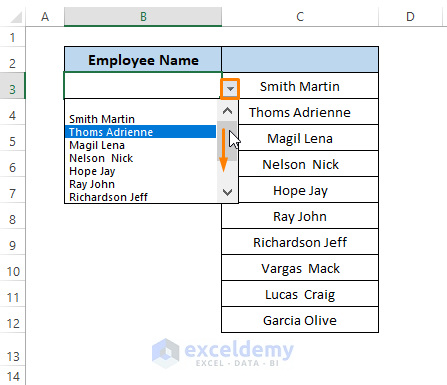
- Add another name (i.e., Jenny Anderson) to the column, then click on the drop-down icon in column B. You find out the last entry is added automatically to the list.

Read More: How to Make a Dynamic Data Validation List Using VBA in Excel
Method 2 – Dynamic Drop-Down List Using Name Manager
In Method 1, we created only one drop-down dynamic list box. In this method, we’ll create as many drop-down list boxes as the data requires. Our dataset is organized as shown in the below image. We want column F’s Name entries in column B (i.e., Employee Name) to assign the Company and Addresses.
Steps:
- Select the Range (i.e., C:C) to give it a Name.
- Go to the Formulas tab and click on Name Manager (from the Defined Names section).
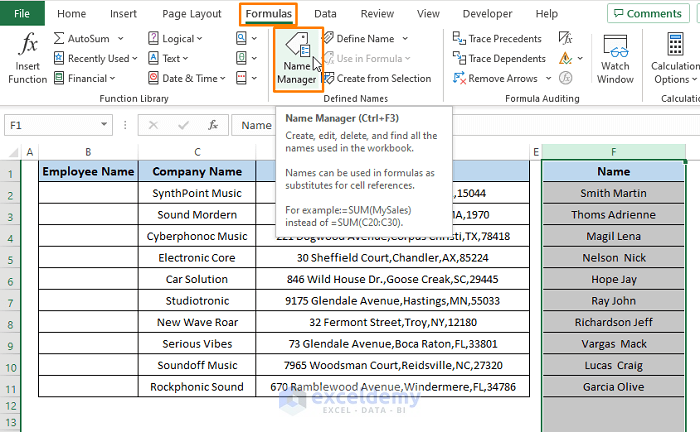
- The Name Manager window opens. Click on New.
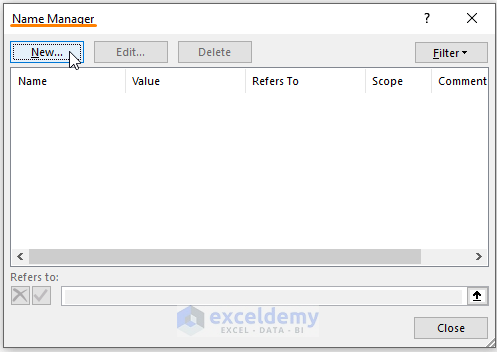
- In the New Name window, type a name in the Name dialog box.
- Paste the below formula in the Refers to command box:
=OFFSET(Name!$F$2, 0, 0, COUNTA(Name!$F:$F)-1)The OFFSET function takes Name!$F$2 as the reference, 0 and 0 as rows and columns. In the end, COUNTA (Name!$F:$F)-1 portion as the range height. 1 is subtracted from the count to ignore the column heading.
- Click on OK.
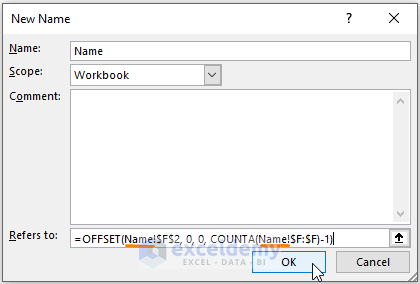
- Clicking OK assigns the range (C column) to the Name entity. Click on Close.
- Double-click on the Name sheet. The Name sheet’s macro window opens.
- Paste the following code there:
Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range)
Dim mrfrow As Single
Dim nameText As String
Dim Value As Variant
If Not Intersect(Target, Range("$C:$D")) Is Nothing _
Or Not Intersect(Target, Range("F:F")) Is Nothing Then
mrfrow = ActiveSheet.Range("C" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row
For Each Value In Range("Name")
nameText = nameText & "," & Value
Next Value
With ActiveSheet.Range("B2:B" & mrfrow).Validation
.Delete
.Add Type:=xlValidateList, AlertStyle:=xlValidAlertStop, Operator:= _
xlBetween, Formula1:=nameText
.IgnoreBlank = True
.InCellDropdown = True
.InputTitle = ""
.ErrorTitle = ""
.InputMessage = ""
.ErrorMessage = ""
.ShowInput = True
.ShowError = True
End With
End If
End Sub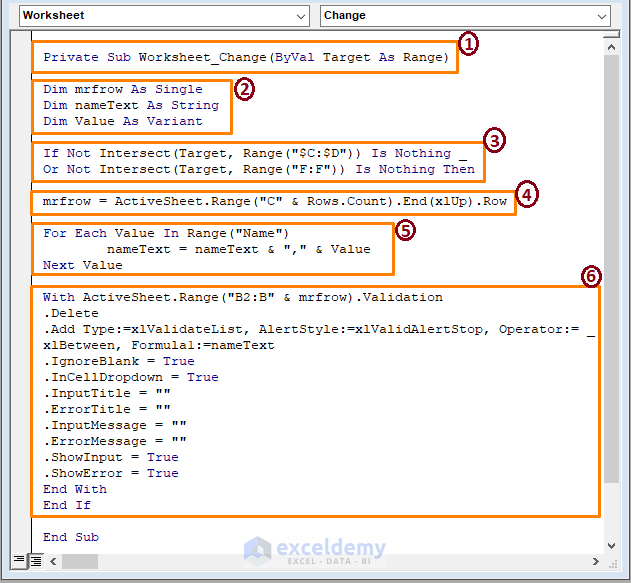
➤ From the above image, in the sections,
1 – begin the macro code declaring the VBA Macro Code’s Sub name.
2 – declare the variables as Single and String and Variant.
3 – impose a condition on targeted ranges using the VBA IF statement. Also, check whether the ranges intersect or not using the VBA Intersect Method.
4 – assign mrfrow to a range (i.e., column C) variable in case of no intersection.
5 – for each value in the range the macro assigns the nameText variable a formula.
6 – VBA With Statement applies data validation in column B ignoring blanks, error messages, etc.
- Return to the worksheet.
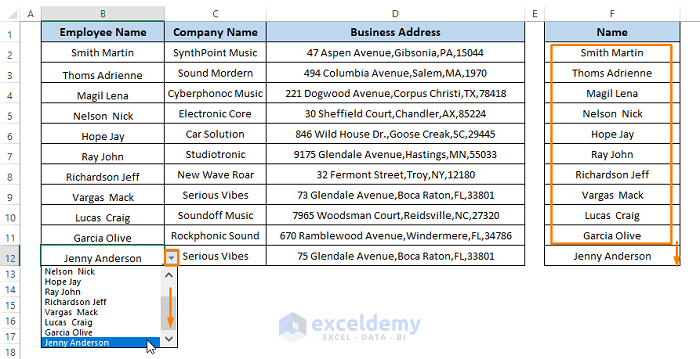
- Click on the Drop-Down List icon, where you can see all the names are available to get inserted in column B.

- You can assign all the employee names according to the Name column (i.e., F column) in column B. You can also type a new name, company, and business address in the respective rows, then click on the drop-down list icon.
- After scrolling you see the newly entered name present in the drop-down list.
Read More: How to Use Named Range for Data Validation List with VBA in Excel
Download Excel Workbook
Related Articles
- VBA to Select Value from Drop Down List in Excel
- Excel VBA to Create Data Validation List from Array
- Unique Values in a Drop Down List with VBA in Excel
- Data Validation Drop Down List with VBA in Excel
- How to Make Multiple Dependent Drop Down List with Excel VBA



Nice introduction, but I miss the combination of data validation and sheet protection.
Which of these methods work with an protected sheet (with UserInterfaceOnly = True)
unprotecting the sheet, doing the dynamic dropdown and protecting it, leaves the risk of an unprotected sheet (has already happened).
Hello Dennis,
Thank you for the feedback! To use dynamic dropdowns, using UserInterfaceOnly = True can indeed allow macros to run while keeping the sheet protected. The UserInterfaceOnly setting allows VBA to make changes, but it doesn’t allow certain actions like adding or modifying data validation directly on a protected sheet.
Here’s an updated VBA code that temporarily unprotects the sheet to apply the data validation and then reprotects it:
Regards
ExcelDemy