What Are Eigenvalues?
The Eigenvalues are a set of scalar values associated with a set of linear equations that has a non-zero absolute solution. They are also called Characteristic Roots. The process results in a set of Determinants that has this equation:
The scalar Lambda (λ) is the required eigenvalue that is associated with square k x k matrix A and Identity matrix I.
What Are Eigenvectors?
In a linear equation, along with calculating Eigenvalues, we also calculate the Eigenvector of a matrix. It is a vector generated through the scalar values. We can symbolize it with an X in the Determinant equation which results in this:
How to Calculate Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors in Excel: 2 Useful Methods
Let’s calculate them with the following 3X3 Matrix A.
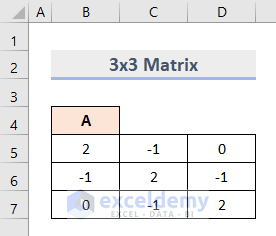
Method 1 – Calculate Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors with Goal Seek in Excel
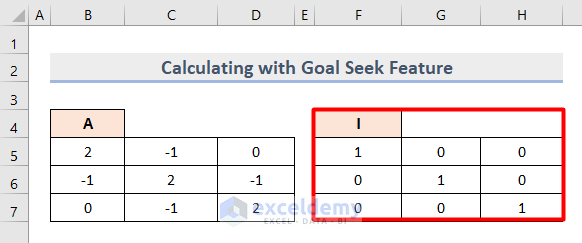
- Insert a general Identity Matrix in the Cell range F5:H7 where we have 1 in the diagonal cells.
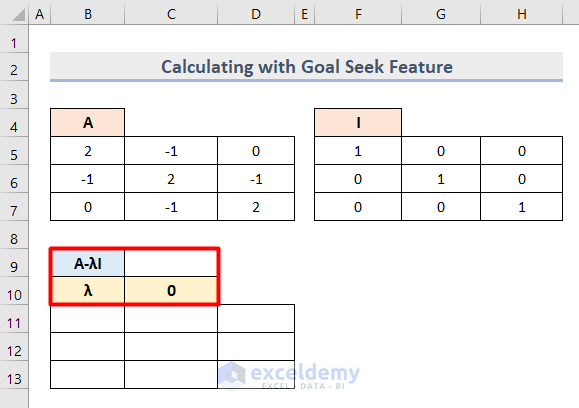
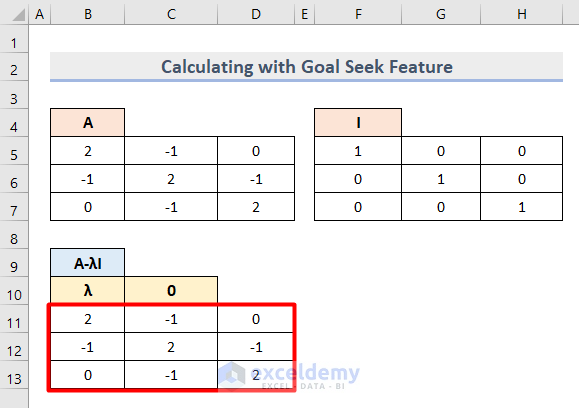
- Create a new column to find the Determinant where the initial scalar Lambda (λ) is 0.
- Insert this formula in Cell B11 to find the first value of the k x k matrix based on the determinant equation.
=B5-$C$10*F5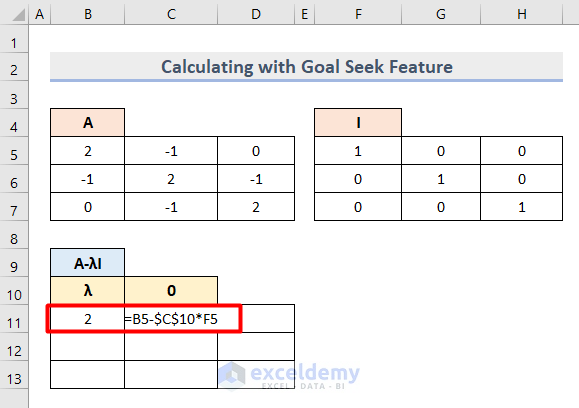
- Apply the same formula based on each cell of the A matrix.
- The output looks like this.
- Insert this formula into Cell C15 to find the Determinant value.
=MDETERM(B11:D13)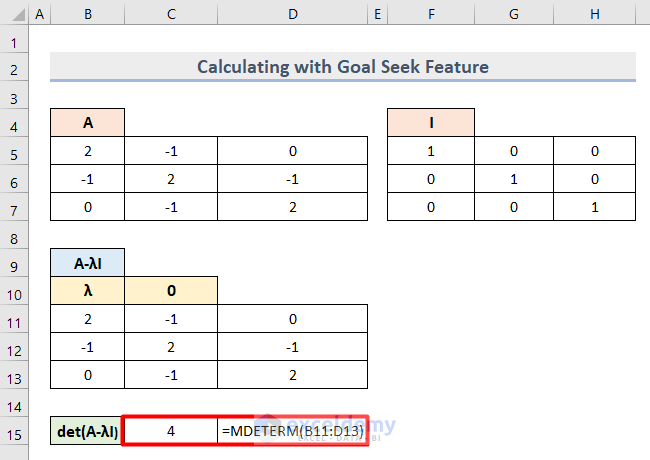
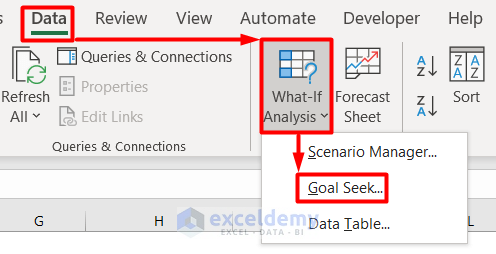
- Go to the Data tab and select Goal Seek from the What-If Analysis option.
- Refer to the Determinant value as the Set cell and the Lambda (λ) value in By changing cell.
- Put the To value as 0 as we want the Determinant value equal to zero.
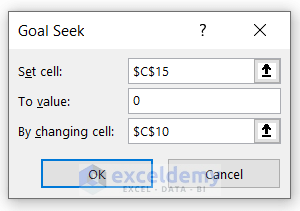
- Press OK and you will get the new Eigenvalue along with the Determinant value in Cells C10 and C15 respectively.
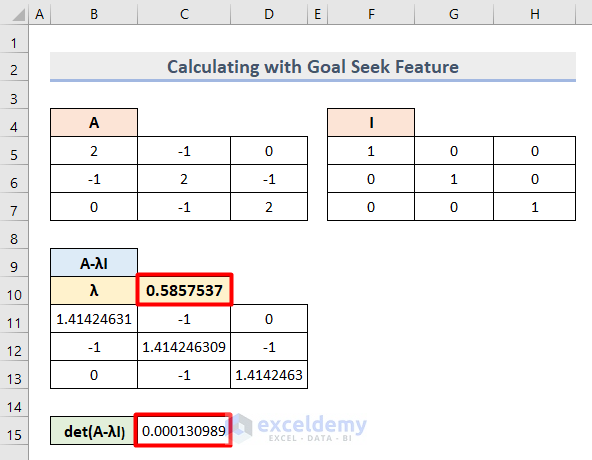
- Change the Lambda (λ) value to 1.5 and run the same process in Goal Seek to get another set of values as follows.
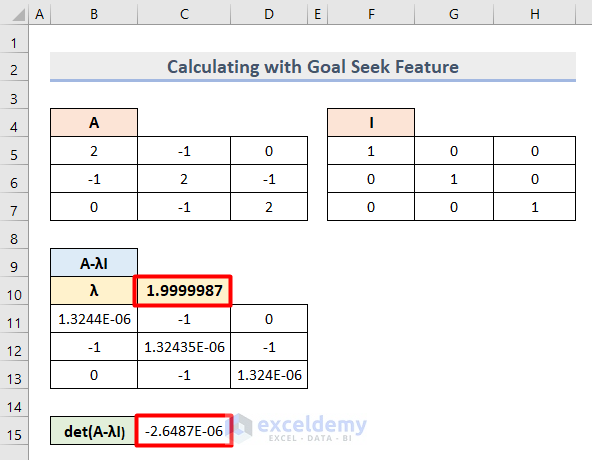
- Insert 3 as Lambda (λ) value and run the Goal Seek operation to get the following output.
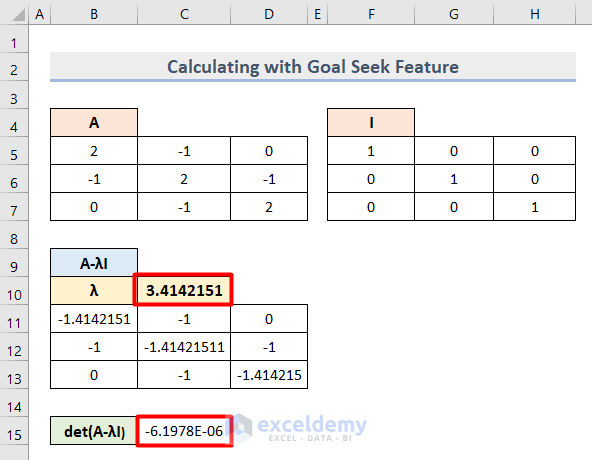
- We got 3 sets of eigenvalues as the Lambda (λ) value.
- Insert this formula for each set of eigenvalues and get the final eigenvectors like this.
=-MMULT(MINVERSE(C12:D13),B6:B7)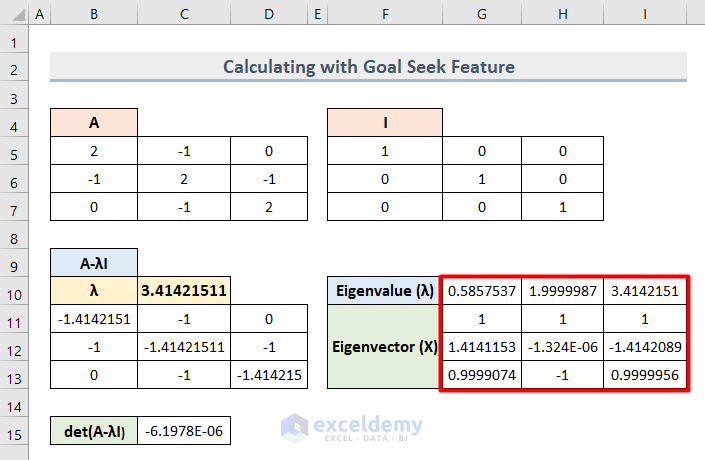
Method 2 – Apply the Power Method to Get Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
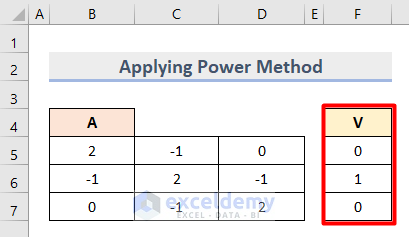
- Create an initial vector column with the following values in the Cell range F5:F7.
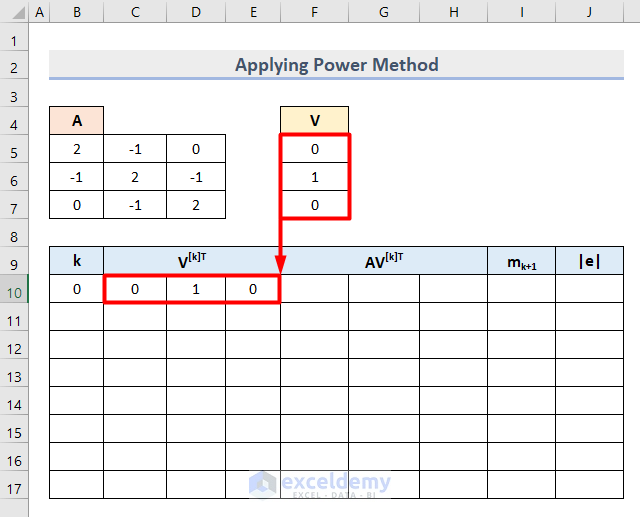
- Insert the values as a row vector in the Cell range C10:E10.
- Insert this formula in Cell F10 to transpose and return the absolute vector value.
=TRANSPOSE(ROUND(MMULT($B$5:$D$7,TRANSPOSE(C10:E10)),4))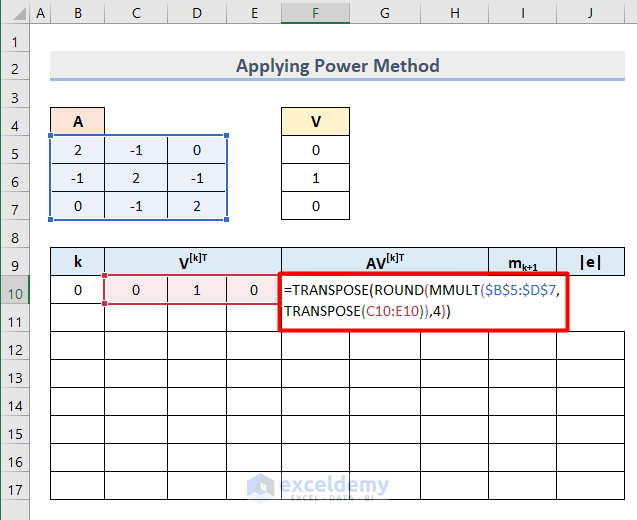
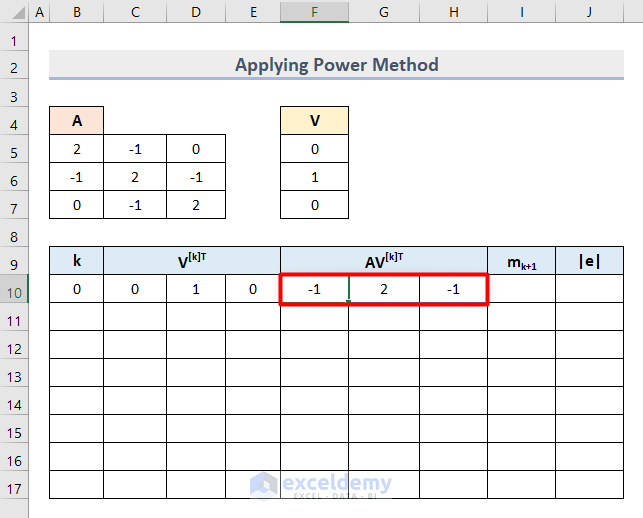
- Press Enter and you will get the following output where k=0.
- Insert this formula in Cell I10 to find the Maximum Absolute Eigenvalue.
=MAX(ABS(F10:H10))
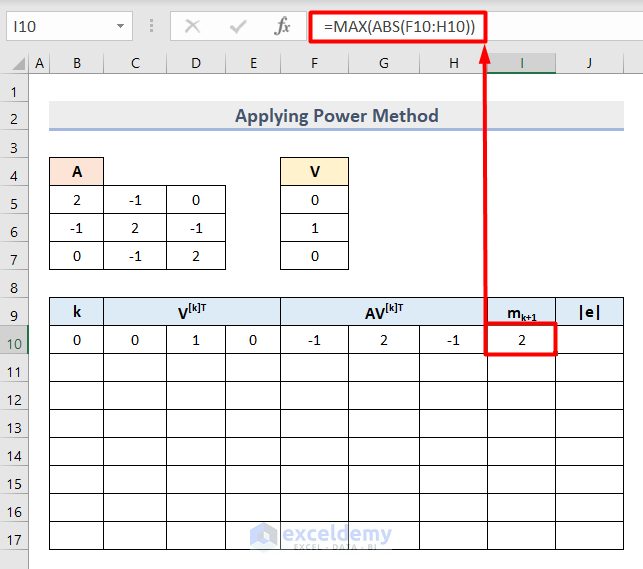
Here, the MAX function returns the maximum value from the Cell range F10:H10. Also, the ABS function returns an absolute value of this omitting negative values.
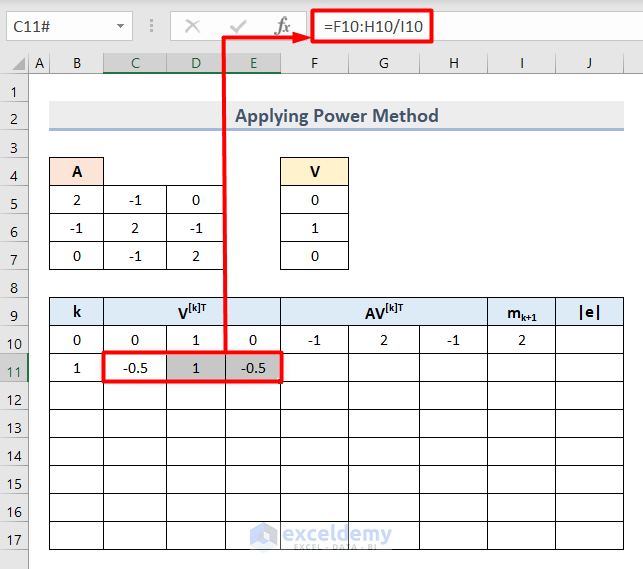
- Select the cell range C11:E11 and insert this formula to get the next horizontal vector value where k=1.
=F10:H10/I10
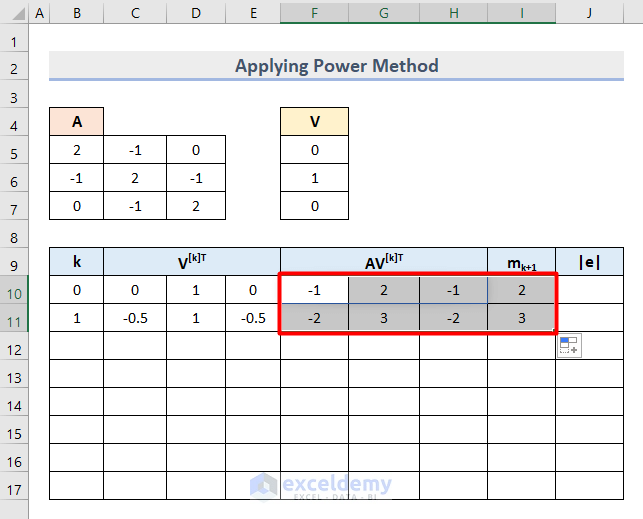
- Select the Cell range F10:I10 and drag its bottom corner downward.
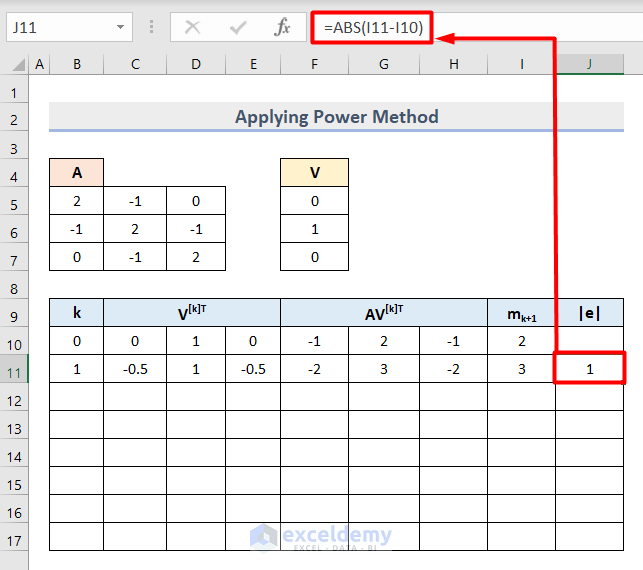
- Insert this formula in Cell J11 to get the absolute value of Epsilon (e) in the power method.
=ABS(I11-I10)
- Select the Cell range B11:J11 and drag the bottom corner of the last cell downward.
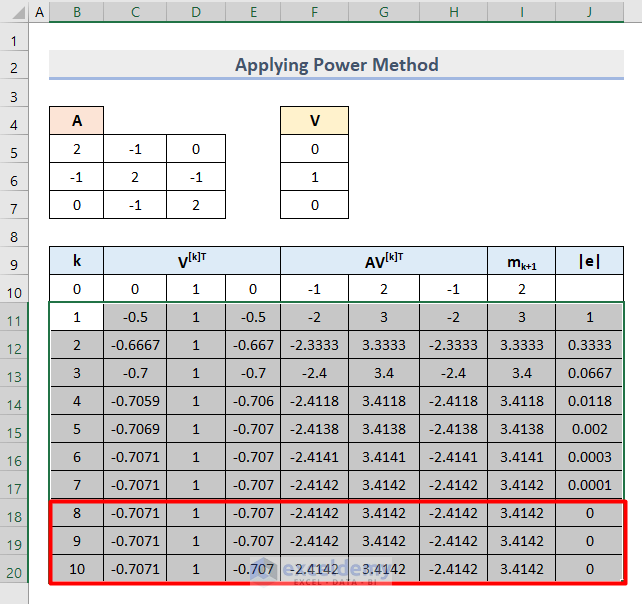
- We got the eigenvalues (mk+1) and eigenvectors (V[k]T) for each value of k.
- Delete the rows that have repetitive values.
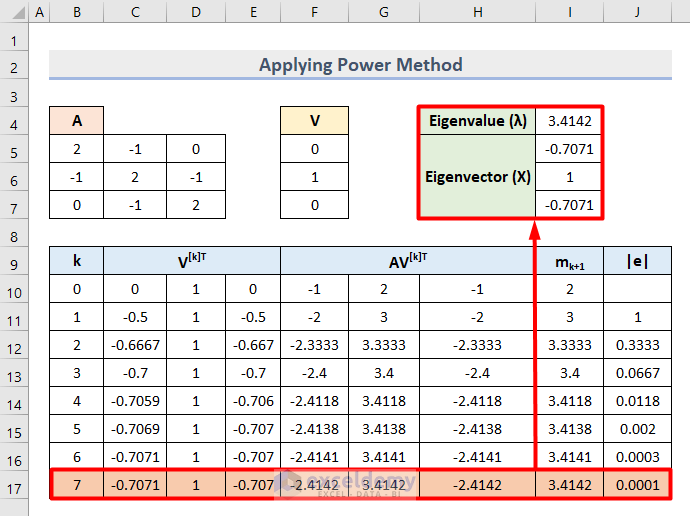
- Compare the last value of Epsilon (e) which is 0.0001 with the standard value 0.0005 to confirm that 0.0001 < 0.0005.
- We got the dominant eigenvalue and eigenvectors based on the adjacent cell values as shown below.
Download the Practice Workbook
<< Go Back to | Vectors in Excel | Excel for Math | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!


Hai, how do we know the standard value of Epsilon (e) = 0.0005? does the epsilon value is decided by us or does 0.0005 is the standard value?
Hi HANI,
Thanks for your query. The choice of epsilon depends on the desired accuracy of the eigenvalue estimate. It is typically a small positive value, and the algorithm terminates when the absolute difference between consecutive eigenvalue estimates falls below epsilon.
The specific value of epsilon will vary depending on the application and the desired level of accuracy. Using epsilon = 0.0005 indicates that the power method iterations will continue until the absolute difference between consecutive eigenvalue estimates falls below 0.0005. This level of tolerance can be suitable for many applications, especially when the eigenvalues of the matrix are relatively close in magnitude.
However, it’s important to note that the appropriate value of epsilon may vary depending on the specific problem and matrix being analyzed. If you find that the algorithm converges too quickly or does not reach the desired accuracy with epsilon = 0.0005, you may need to adjust the value accordingly.
Consider the scale and conditioning of the problem as well. If the matrix is ill-conditioned or has eigenvalues with large differences in magnitude, a smaller epsilon may be necessary to obtain accurate results.
So, it’s always important to assess the specific requirements of your problem and adjust the value of epsilon accordingly to achieve the desired accuracy.
Regards
Rafiul Hasan
Team ExcelDemy
Hi.Thx for your doc, I can try SVD in excel without programed library.
But I wonder, why do we must use “Round” function?
I tried to use without “round”, AV^kt was not calculated collectly.
Can you explain for me please?
Hi agian,
I solve the problem about “round” function, which is my just mistake…..
Now I wondering about ‘how can we find other Eigen Vector and Value.
In my case, I mus find eigen vectors of 10×10 matrix….
so, I practice with 3×3 matrix and try to find normalized method.
within 3×3 matrix, [5,4,-1; 4,5,1; -1,1,2],
starting with V = 0,1,0 give the eigen value = 9 but
starting with V = 0,0,1 give the eigen value = 3. how can we choose V?
Furthermore, in hand writing, eigen value = 0 is the another solution.
and I cannot find ‘V’ such as give back eigen value = 0
please help me…..
Dear MATHMAN,
We are glad that you have already got your answer related to the ROUND function.
Now let’s jump to the problem related to finding other EigenValue and EigenVector using the power method.
In the power method, it is a must to choose an initial vector V0. So, the tips for what to keep in mind while randomly choosing an initial vector V0:
If initial vector V0 =[0,1,1] and W is the given dominant Eigenvector, then V0 X W =0
The dominant Eigenvalue for the 3×3 matrix [5,4,-1; 4,5,1; -1,1,2] is approximately λ ≈ 9.
If you are getting Eignevalue λ≈0 for the initial EigenVector V0 = [0,0,1] most probably because the vector has no magnitude along the x and y axes and a magnitude of 1 along the z-axis. Therefore, the initial vector V0 does not converge to the dominant Eigenvalue for the given matrix. It is expected that different EigenVectors can lead to different EigenValues.
The dominant eigenvalue is typically the one with the largest magnitude. It is recommended to use multiple initial vectors in the power method so that you know which eigenvalue converges to the dominant eigenvalue.
I hope this solution resolves your issue. Feel free to email us at [email protected] if you have any further problems or inquiries.
Regards,
Qayem Ishrak Khan
Team ExcelDemy.