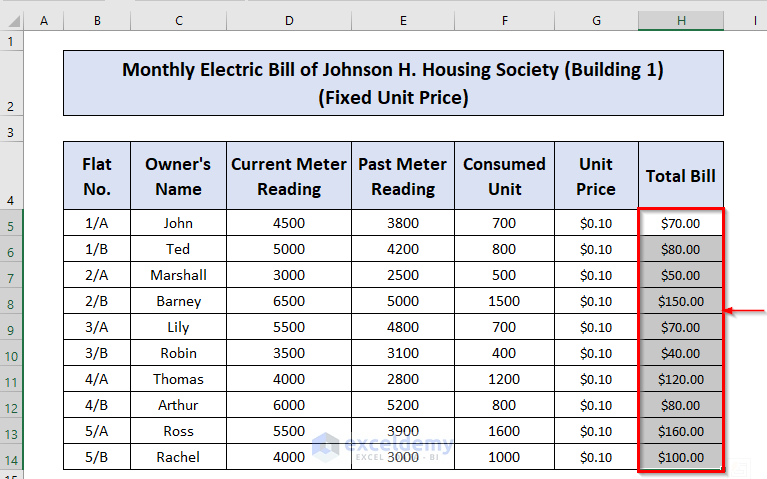
The dataset shown below contains the current meter reading, the past meter reading, and the consumed units of electricity of ten different households located inside a building. The cells on the right overview the final output you are going to get.
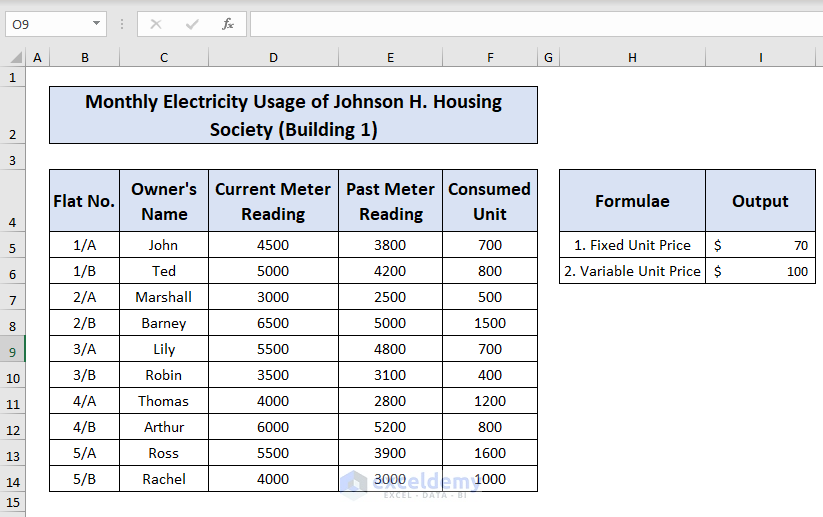
Consider the following dataset “Monthly electricity usage of Johnson H. housing society (Building 1)”.
Method 1 – Electricity Bill Calculation for Fixed Unit Price
Steps:
- Add the Unit Price and Total Bill columns (G and H) to the right.
- Fill in the column G with desired values.
- Go to cell H5 and type the following formula:
=F5*G5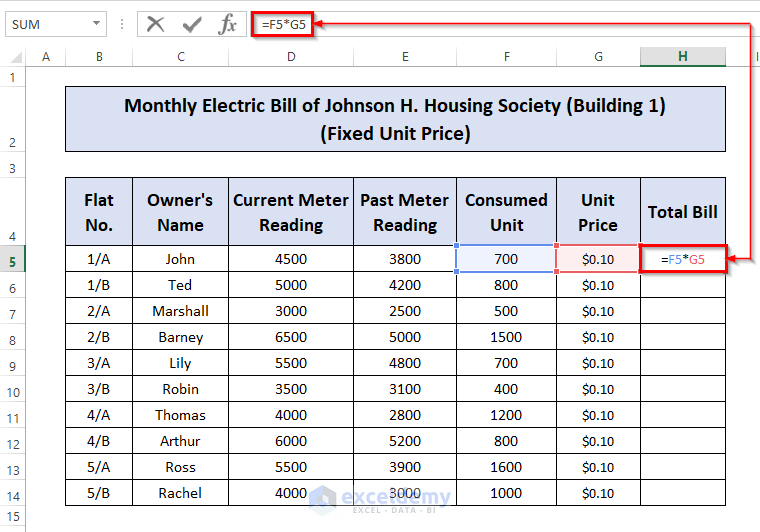
- Press ENTER to get the result.
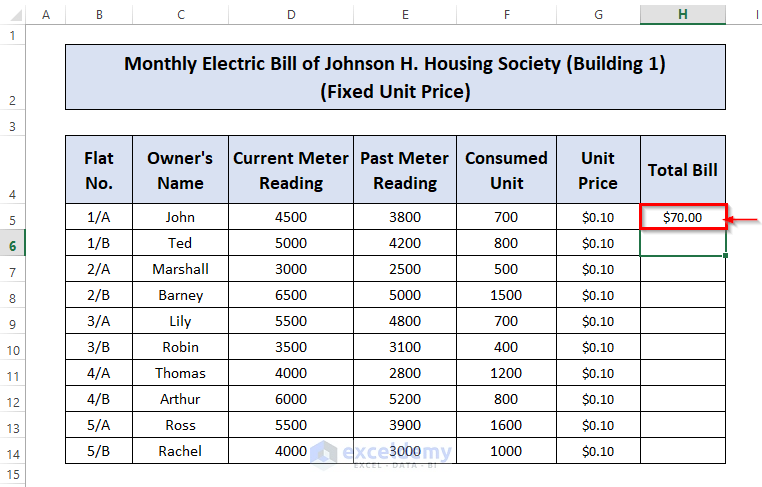
- Place the cursor at the bottom right corner of cell H5, left-click on it and drag the cursor down to cell H14.
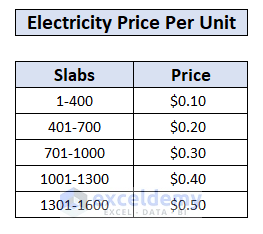
Method 2 – Electricity Bill Formula for Variable Unit Price (Slab)
Consider a table such as the one below, showing progressive prices in the electricity usage slabs.
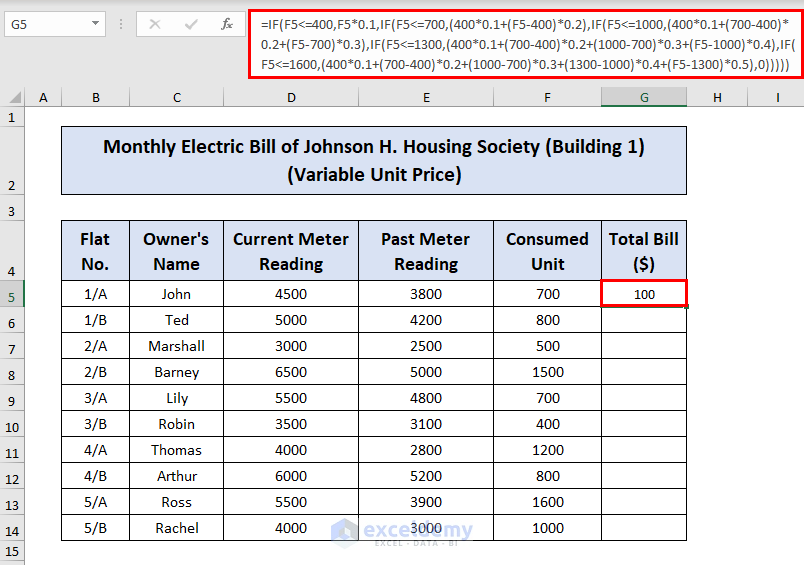
Steps:
- Make the column G as Total Bill.
- Select cell G5 and insert the following formula and press ENTER to get the expected result:
=IF(F5<=400,F5*0.1,IF(F5<=700,(400*0.1+(F5-400)*0.2),IF(F5<=1000,(400*0.1+(700-400)*0.2+(F5-700)*0.3),IF(F5<=1300,(400*0.1+(700-400)*0.2+(1000-700)*0.3+(F5-1000)*0.4),IF(F5<=1600,(400*0.1+(700-400)*0.2+(1000-700)*0.3+(1300-1000)*0.4+(F5-1300)*0.5),0)))))Formula Breakdown:
- =IF(F5<=400,F5*0.1, … ): This is the first condition. It checks if the value in cell F5 is less than or equal to 400. If it is, it returns the result of multiplying F5 by 0.1 (10% of F5). If F5 is greater than 400, it proceeds to the next condition.
- IF(F5<=700, … , … ): This is the second condition within the first condition. It checks if F5 is less than or equal to 700. If it is, it calculates a new result: 10% of the first 400 units plus 20% of the amount over 400 units. The expression (400*0.1 + (F5-400)*0.2) is used for this calculation. If F5 is greater than 700, it moves on to the next condition.
- IF(F5<=1000, … , … ): This is the third condition within the first condition. It checks if F5 is less than or equal to 1000. If it is, it calculates a new result: 10% of the first 400 units plus 20% of the next 300 units (400 to 700) plus 30% of the amount over 700 units. The expression (400*0.1 + (700-400)*0.2 + (F5-700)*0.3) is used for this calculation. If F5 is greater than 1000, it proceeds to the next condition.
- IF(F5<=1300, … , … ): This is the fourth condition within the first condition. It checks if F5 is less than or equal to 1300. If it is, it calculates a new result: 10% of the first 400 units plus 20% of the next 300 units plus 30% of the next 300 units (700 to 1000) plus 40% of the amount over 1000 units. The expression (400*0.1 + (700-400)*0.2 + (1000-700)*0.3 + (F5-1000)*0.4) is used for this calculation. If F5 is greater than 1300, it moves on to the next condition.
- IF(F5<=1600, … , 0): This is the fifth and final condition within the first condition. It checks if F5 is less than or equal to 1600. If it is, it calculates a new result: 10% of the first 400 units plus 20% of the next 300 units plus 30% of the next 300 units plus 40% of the next 300 units (1000 to 1300) plus 50% of the amount over 1300 units. The expression (400*0.1 + (700-400)*0.2 + (1000-700)*0.3 + (1300-1000)*0.4 + (F5-1300)*0.5) is used for this calculation. If F5 is greater than 1600, it returns 0.
- Drag the Fill Handle down to fill in the rest of the cells in the column.
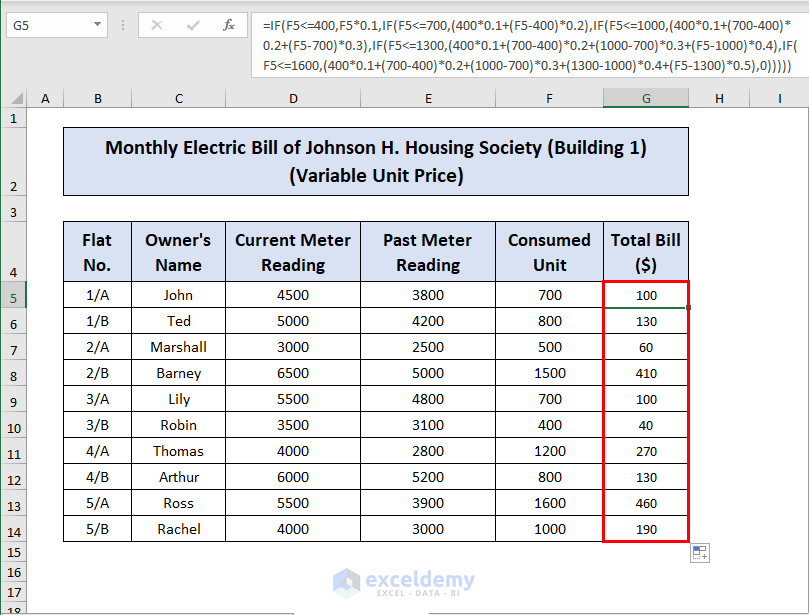
You can simplify the formula by manually calculating some of the constant values. Additionally, you can use dynamic information based on the table and use cell references and more advanced formulas to make it more efficient, allowing you to change the prices and automatically update the results.
Read More: Invoice Excel Formula
Things to Remember
- Careful use of parenthesis is very important while using multiple nested IF functions.
Download Practice Workbook
You can download and practice the dataset we used to prepare this article.
Related Articles
- Create Fully Automatic Invoice in Excel
- Create Invoice in Word from Excel Data
- How to Create Proforma Invoice in Excel
- Labour Contractor Bill Format in Excel
- Hotel Bill Format in Excel



Electricity Bill Formula for Variable Unit Price (Slab) Is totally wrong.
Hi MAHMUD,
Thank you for your valuable suggestion. I updated the formula for calculating electricity bill with Variable Unit Price (Slab). Hope you find this article useful.
Regards,
ExcelDemy
Great post! The step-by-step breakdown of the electricity bill calculation formula in Excel was super helpful. I especially appreciated the two different methods you provided. I’m looking forward to trying them out for my own bill calculations. Thanks for sharing!
Hello,
You are most welcome. Thanks for your appreciation. Glad to hear that the article’s step by step explanations is helpful to you. Keep learning Excel with ExcelDemy!
Regards
ExcelDemy