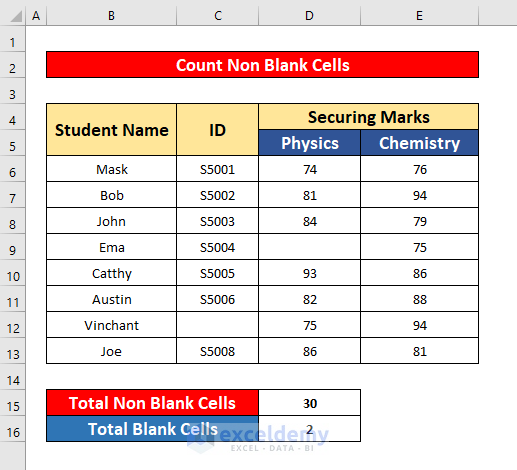
The dataset contains information about several students: student names, IDs, and marks secured in Physics and Chemistry.
Method 1 – Applying COUNTIF Function
1.1 Counting Non-Blank Cells If Cell Value is Greater Than Another Cell
Steps:
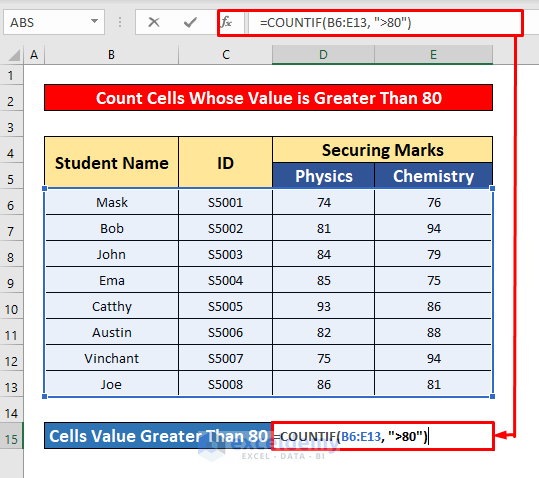
- Select cell D15 to count the cells with a value greater than 80.
- In the Formula Bar, enter the COUNTIF function:
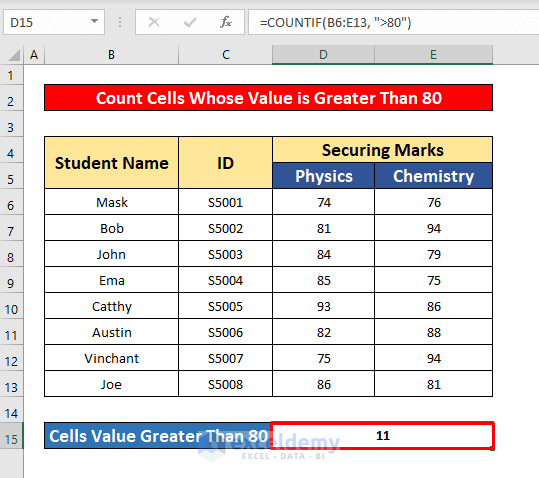
=COUNTIF(B6:E13, ">80")Where B6:E13 is the cell reference and >80 is the criterion, the cell’s value is greater than 80.
- Press Enter to get the return of the COUNTIF function. Here, the return is 11.
1.2 Counting Non-Blank Cells If Cell Value is Less Than Another Cell in Excel
Steps:
- Select cell D15 to count the cells with a value less than 80.
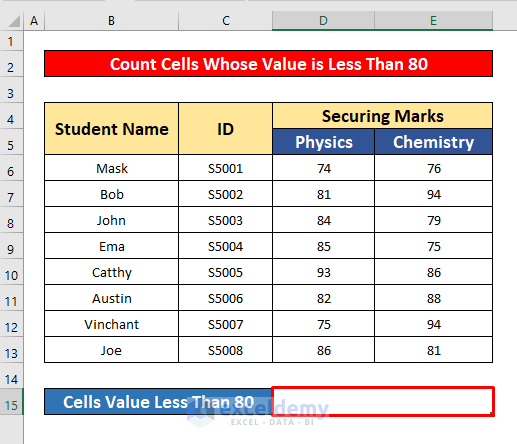
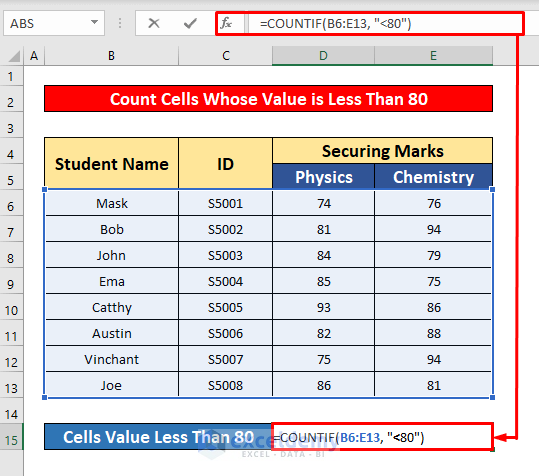
- In the COUNTIF function, enter the COUNTIF formula:
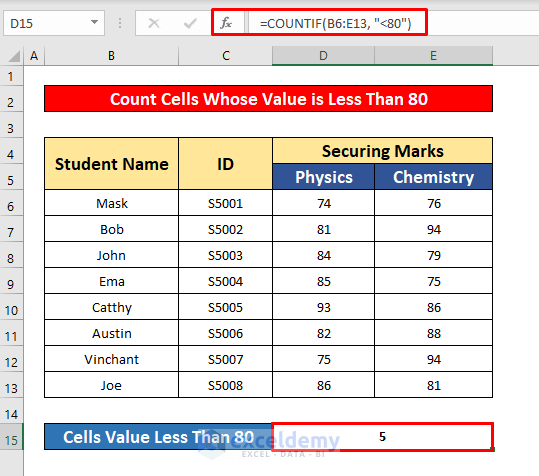
=COUNTIF(B6:E13, "<80")- Where B6:E13 is the cell reference and <80 is the criteria, the cell’s value is less than 80.
- Press Enter to get the return of the COUNTIF function. Here, the return is 5.
1.3 Counting Non-Blank Cells If Cell Value is Equal to Another Cell
Steps:
- Select cell D15 to count the cells with a value equal to 80.
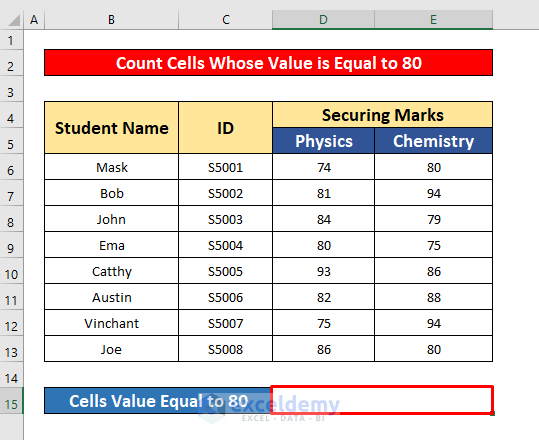
- In the Formula Bar, enter the COUNTIF function:
=COUNTIF(B6:E13, "=80")- Where B6:E13 is the cell reference and =80 is the criterion, the cell’s value is equal to 80.
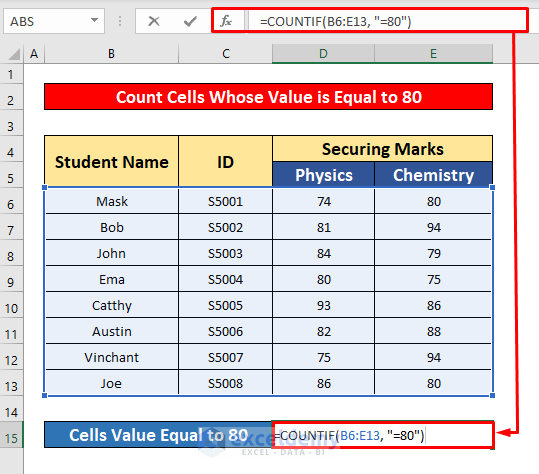
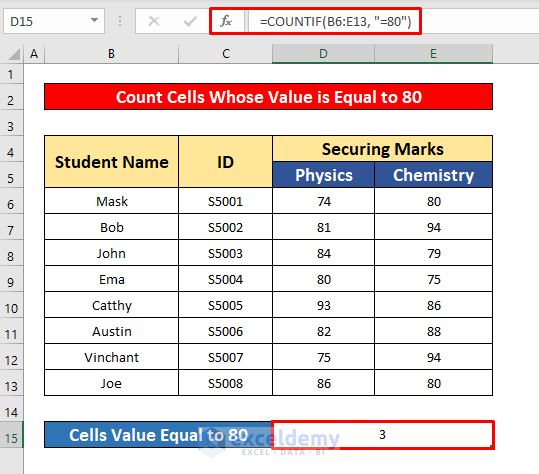
- Press Enter to get the return of the COUNTIF function. Here, the return is 3.
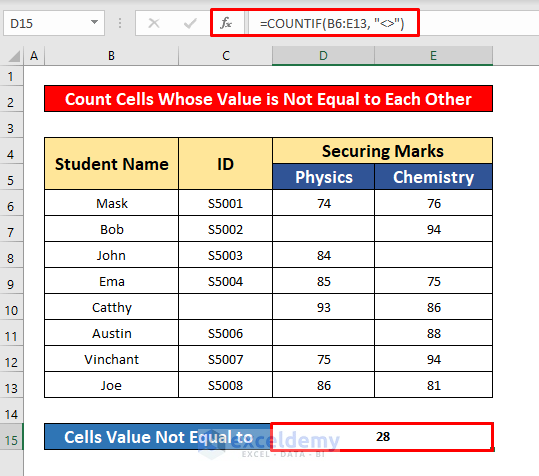
1.4 Counting Non-Blank Cells If Cells are not Equal to Each Other
Steps:
- Select cell D15 to count the cells with a value not equal to each other.
- In the Forumal Bar, enter the COUNTIF function:
=COUNTIF(B6:E13, "<>")- Where B6:E13 is the cell reference and <> is the criteria, the cells’ values are not equal to each other.
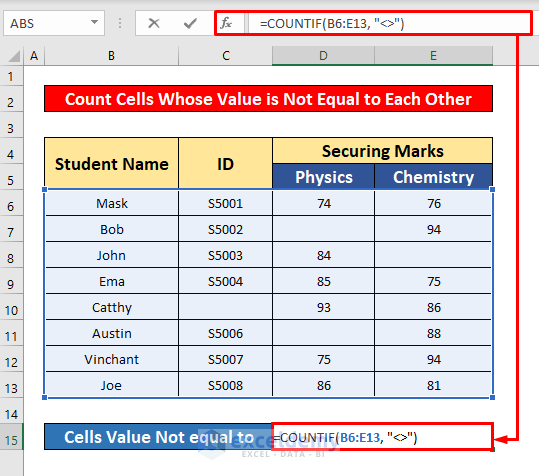
- Press Enter to get the return of the COUNTIF function. Here, the return is 28.
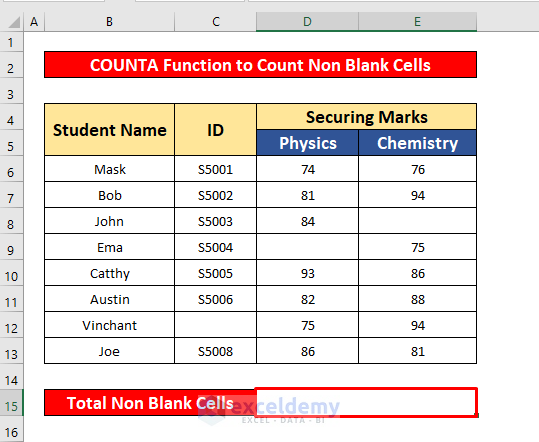
Method 2 – Using the Excel COUNTA Function
Steps:
- Select cell D15 to count non-blank cells.
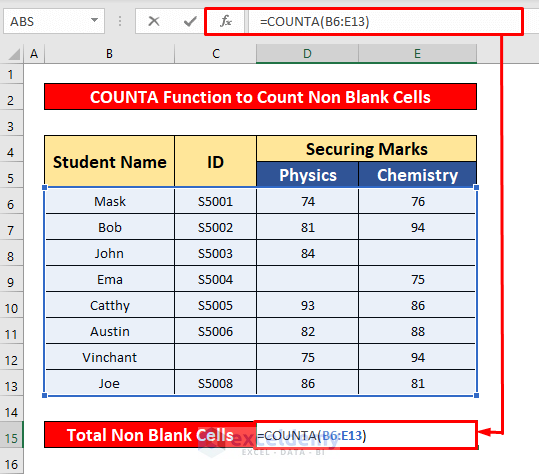
- In the Forumal Bar, enter the COUNTIF function:
=COUNTA(B6:E13)- B6:E13 is the cell reference.
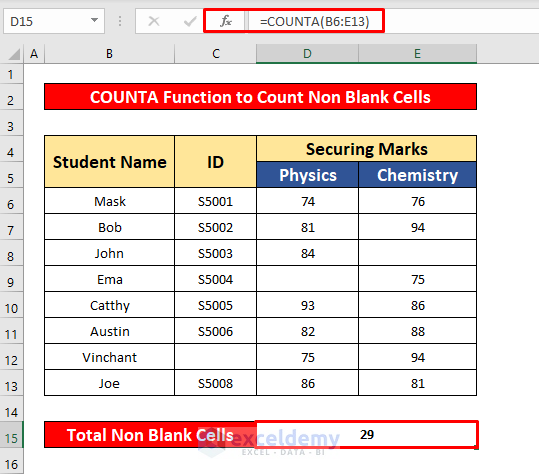
- Press Enter to get the return of the COUNTA function. Here, the return is 29.
Related Content: How to Count Blank Cells in Excel with Condition
Method 3 – Using the Excel SUMPRODUCT Function
Steps:
- Select cell D15.
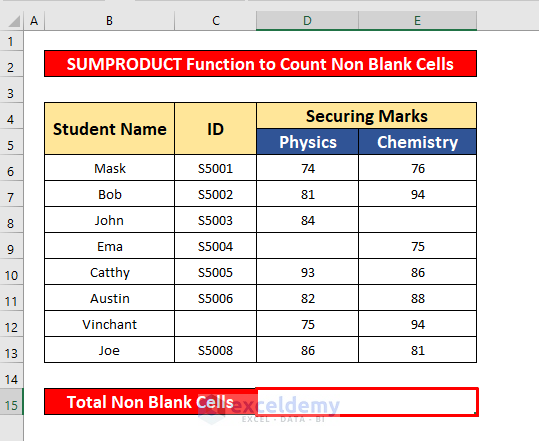
- In the Formula Bar, enter the SUMPRODUCT function:
=SUMPRODUCT((B6:E13<>"")*1)- B6:E13 is the cell reference.
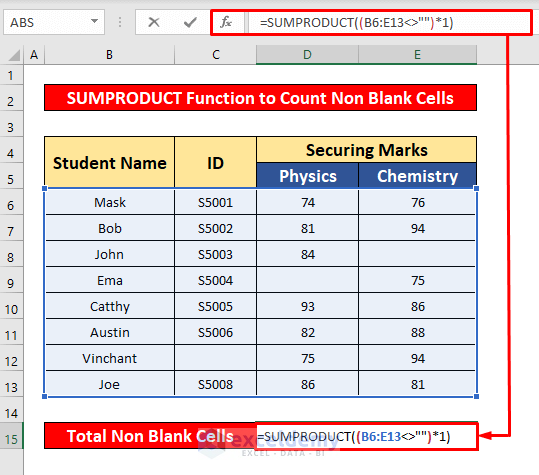
- Press Enter to get the return of the SUMPRODUCT function. Here, the return is 29.
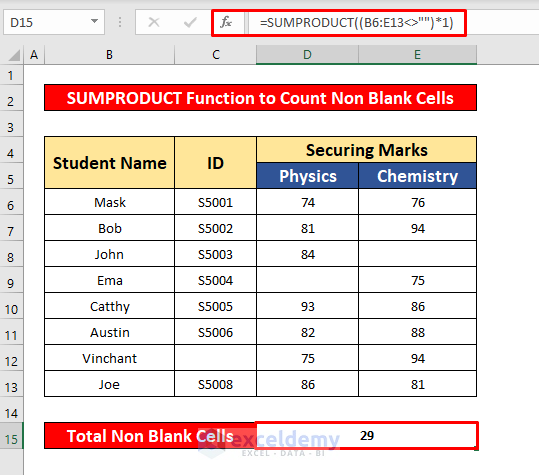
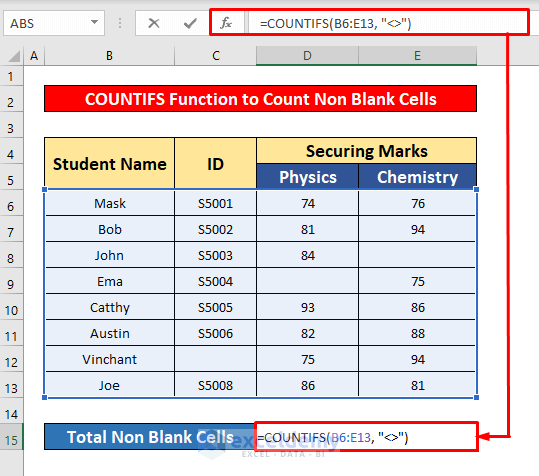
Method 4 – Inserting the Excel COUNTIFS Function
Steps:
- Select cell D15.
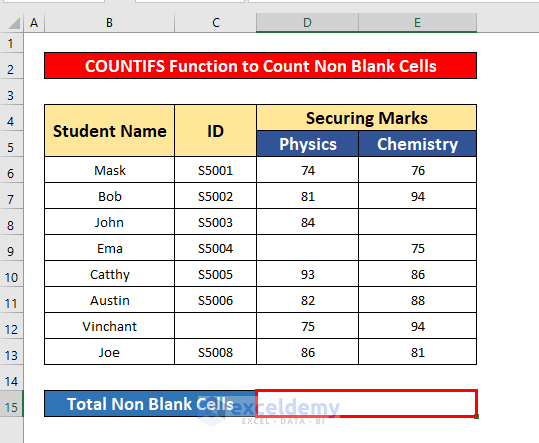
- In the Formula Bar, enter the COUNTIFS function:
=COUNTIFS(B6:E13, "<>")- Where B6:E13 is the cell reference and <> is the criteria, the cells’ values are not equal to each other.
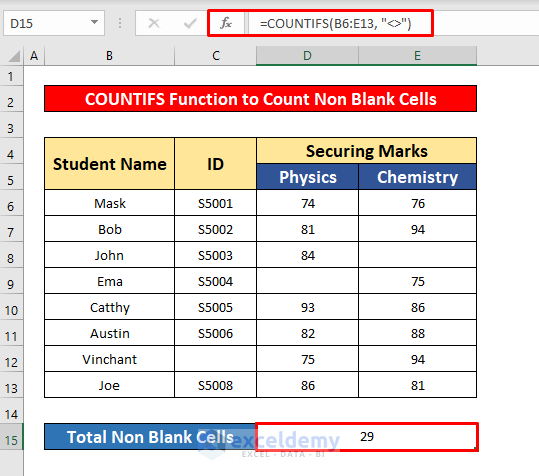
- Press Enter to get the return of the COUNTIFS function. Here, the return is 29.
Method 5 – Merging SUMPRODUCT and TRIM Functions
Steps:
- Select cell D15.
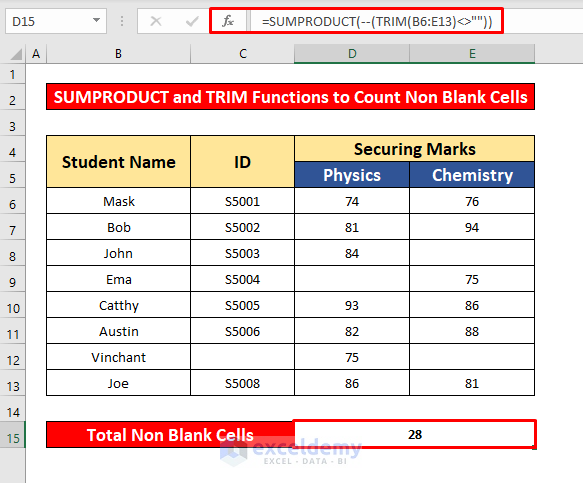
- In the Forumal Bar, enter the SUMPRODUCT and TRIM functions:
=SUMPRODUCT(--(TRIM(B6:E13)<>""))Formula Breakdown:
- Inside the TRIM function, B6:E13 is the cell’s reference, <> is the criteria, which means the cell’s values are not equal to each other, and “” is used to show that cells are not blank
- The SUMPRODUCT function counts the non-blank cells.

- Press Enter to get the return of the SUMPRODUCT and TRIM functions. Here, the return is 28.
Method 6 – Combining ROWS, COLUMNS, and COUNTBLANK Functions
Steps:
- Select cell D15.
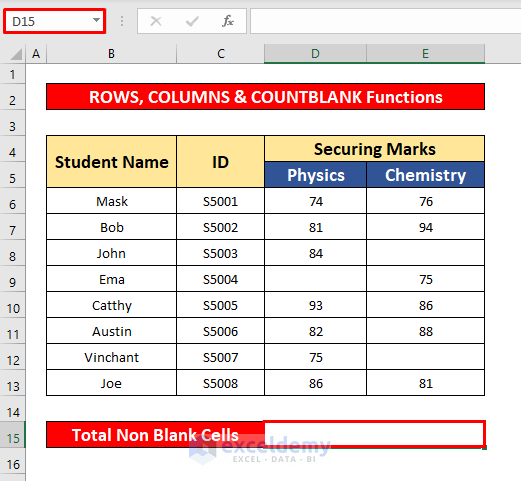
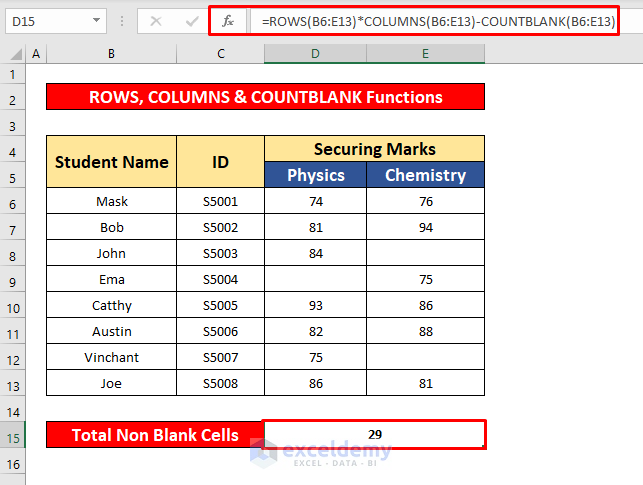
- In the Formula Bar, enter the ROWS, COLUMNS, and COUNTBLANK functions:
=ROWS(B6:E13)*COLUMNS(B6:E13)-COUNTBLANK(B6:E13)Formula Breakdown:
- The ROWS function counts the total rows, and the COLUMNS function counts the total columns. By multiplying these two functions we will be able to count the total cells with blank and non-blank cells.
- The COUNTBLANK function counts the total blank cells, and the minus(-) sign subtracts the blank cells from the total cells.
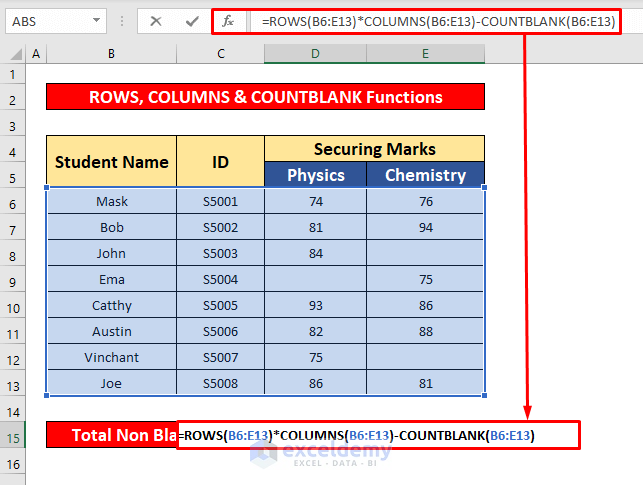
- Press Enter to get the return of the ROWS, COLUMNS, and COUNTBLANK functions. Here, the return is 29.
Things to Remember
#REF! error occurs when the cell reference is not valid.
Download the Practice Workbook
Download this workbook to practice.
<< Go Back to Count Cells | Formula List | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

