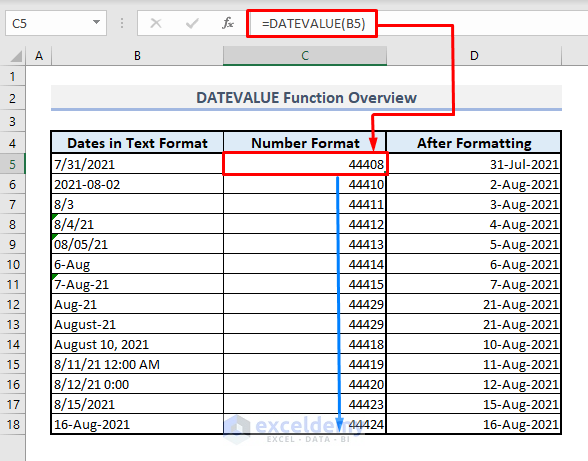
The screenshot below provides an overview of this article demonstrating the application of the DATEVALUE function in Excel.
Introduction to DATEVALUE Function
- Function Objective
The DATEVALUE function converts a date in text format into a numerical representation of the date using Microsoft Excel’s date-time code.
- Syntax
=DATEVALUE(date_text)
- Argument Explanation
| Argument | Compulsory/Optional | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| date_text | Compulsory | Representing the date in text format. |
- Return Parameter
The function returns a date-time code, which needs further formatting to convert it into a usable date value.
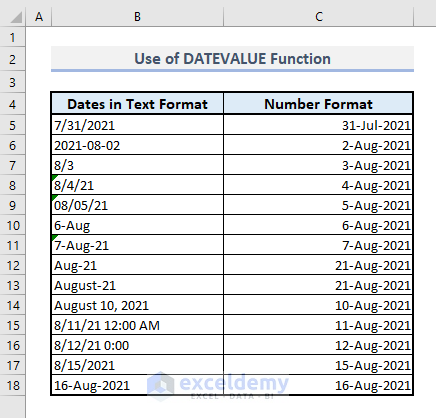
Method 1 – Converting Text Dates to Number Format
In Column B, we have several dates represented as text.
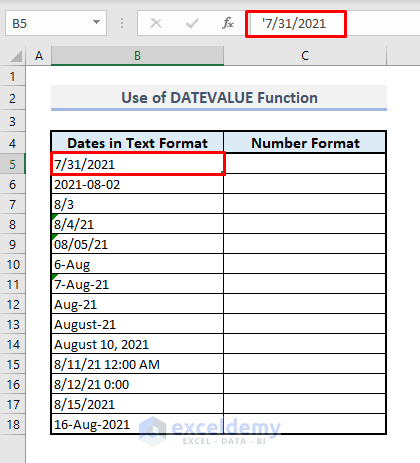
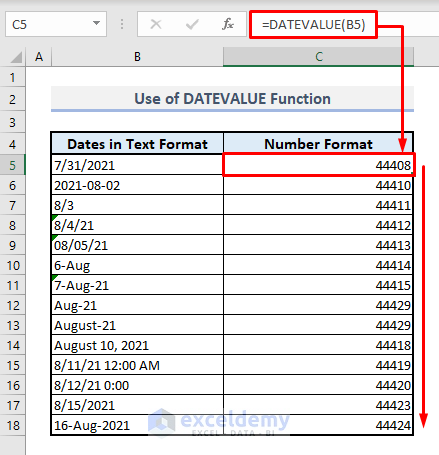
- Select the output Cell C5.
- Enter the formula:
=DATEVALUE(B5)- Press Enter.
- Autofill the entire column using the Fill Handle.
- Column C will now display numbers representing the date-time codes.
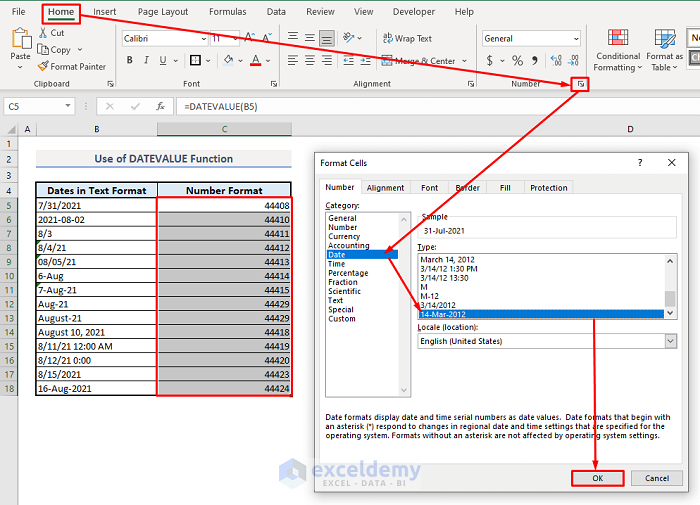
- To customize the number format:
- Select all the numbers in Column C.
- Under the Home ribbon, click the Format Cell dialogue box icon.
- From the Date category, choose your preferred date format.
- Press OK to apply the format.
You’ll see all the dates in the correct and selected format in Column C.
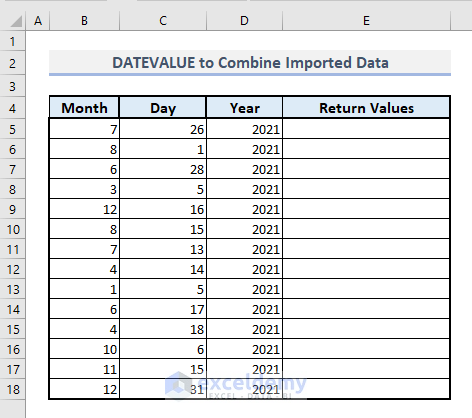
Method 2 – Combining Day, Month, and Year Numbers
When importing date data from another source, you may encounter split texts for days, months, and years.
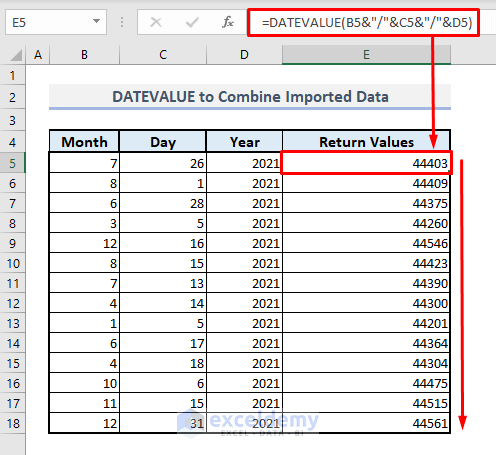
- In Cell E5, enter the following formula:
=DATEVALUE(B5&"/"&C5&"/"&D5)This uses the Ampersand (&) to concatenate data from Columns B, C, and D, with slashes (/) as separators.
- Press Enter and autofill the entire column with the Fill Handle.
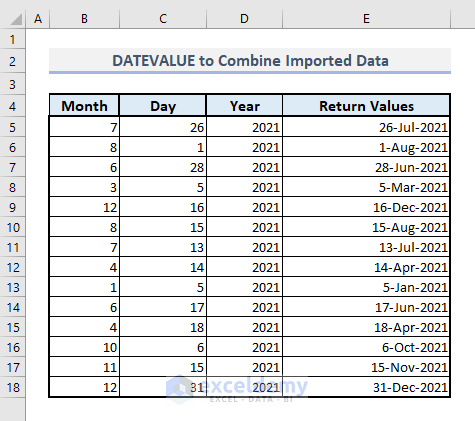
- Format the date-time code numbers in Column E as described in the Method 1.
Method 3 – Show Both Dates and Times
Suppose Column B contains dates with times (in text format).
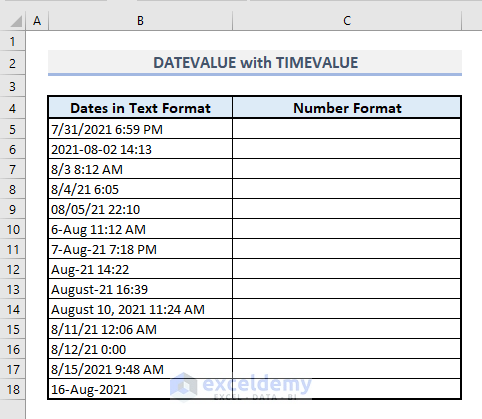
- In Cell C5, enter the formula:
=DATEVALUE(B5)+TIMEVALUE(B5)This combines the DATEVALUE function with the TIMEVALUE function to extract both date and time.
- Press Enter and fill down the rest of the cells with the Fill Handle option.
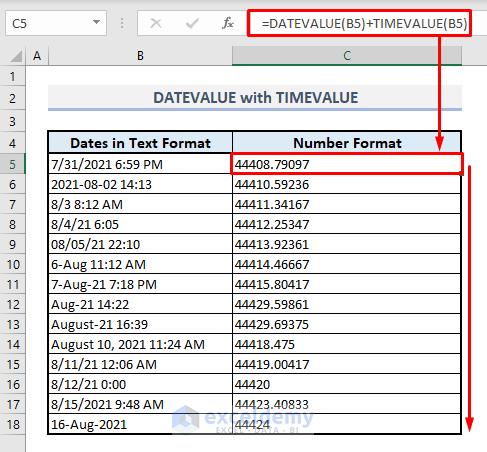
- Open the Format Cells dialog box again from the Number group of commands.
- Select a suitable format from the Date category that displays both date and time.
- Press OK to apply the format.
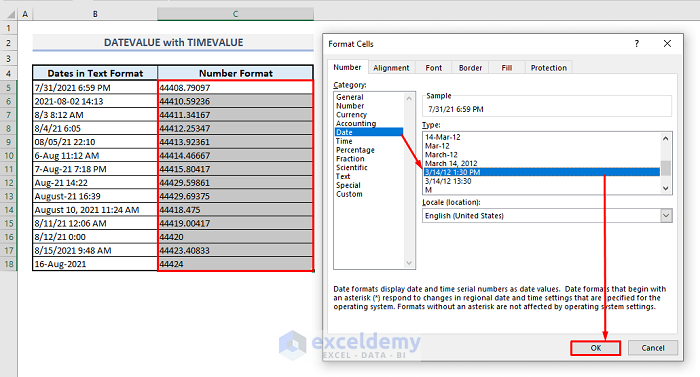
As shown in the screenshot below, Column C will now display dates and times in the proper format.
Method 4 – Extracting a Date from the Beginning of a Text String with DATEVALUE and LEFT Functions
When a date appears at the beginning of a cell, alongside other data, the DATEVALUE function alone cannot extract the date-time code. Instead, it results in a #VALUE! error message.
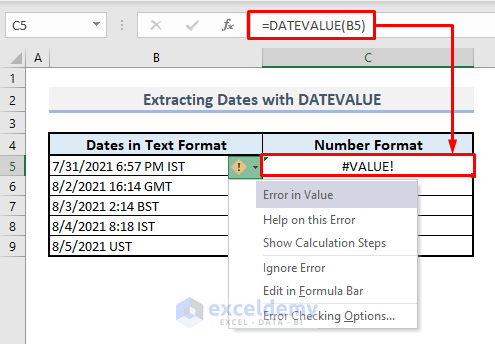
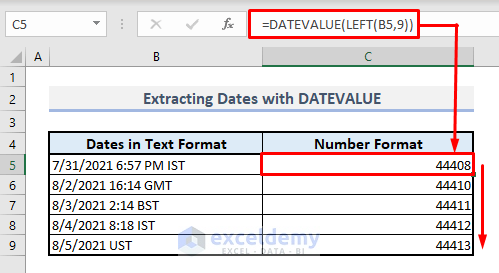
- In Cell C5, enter the following formula:
=DATEVALUE(LEFT(B5,9))The LEFT function extracts the first 9 characters from the text string (which corresponds to the date format).
- Press Enter and autofill the entire column with the Fill Handle. Column C will display the date-time codes as return values.
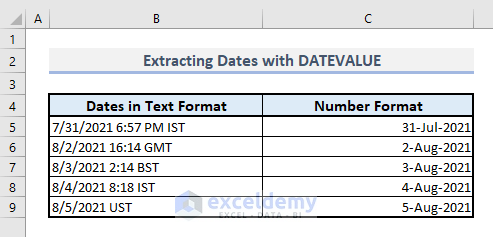
- Convert the number format to the desired date format for Column C to obtain the proper date values.
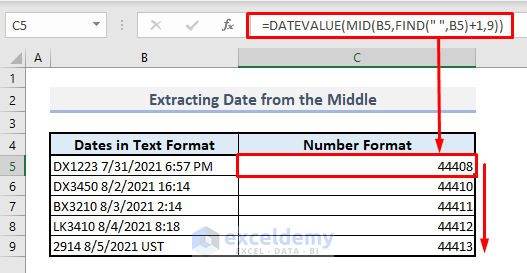
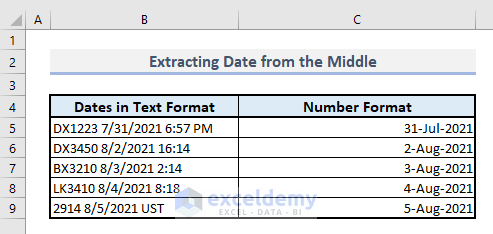
Method 5 – Pulling Out a Date from the Middle of a Text String with DATEVALUE, MID, and FIND Functions
- In Cell C5, enter the following formula:
=DATEVALUE(MID(B5,FIND(" ",B5)+1,9))-
- The FIND function locates the position of the first space character in the text string.
- The MID function extracts 9 characters starting from the position found by the FIND function.
- After pressing Enter, autofill the entire column with the Fill Handle. Column C will now contain the date-time codes.
- Modify the number format for Column C to display the expected results in the exact date format.
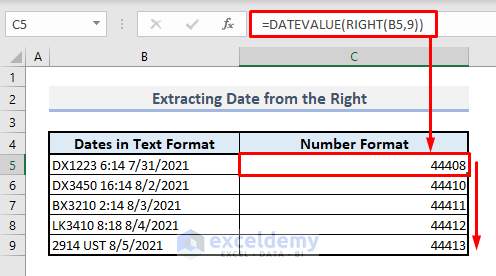
Method 6 – Extracting the Date from the Right of a Text String with DATEVALUE and RIGHT Functions
- In Cell C5, enter the following formula:
=DATEVALUE(RIGHT(B5,9))The RIGHT function extracts the last 9 characters from the text string (representing the date format).
- Press Enter and autofill the remaining cells in Column C with the Fill Handle.
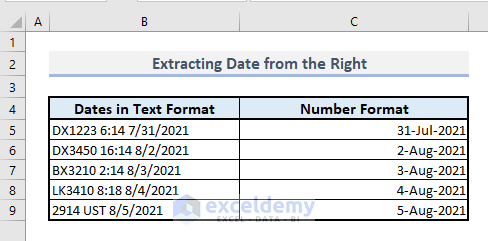
- Convert the date-time codes into the desired date format to obtain the desired results.
Things to Keep in Mind
- The DATEVALUE function returns only the date portion. If a time is present alongside the date in text format, the function will ignore the time value.
- The date code starts with 1 for January 1, 1900, and increases sequentially for subsequent dates. The DATEVALUE function assigns this date code when extracting dates from text format.
- If the DATEVALUE function cannot recognize a date from a text format, it will display a #VALUE! error.
Download the Practice Workbook
You can download the practice workbook from here:
<< Go Back to Excel Functions | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

