Formula 1 – Excel Subtraction Formula To Calculate Time Worked
The formula to calculate the time difference is to subtract the start time from the end time.
Time Worked = End Time – Start Time
The sample dataset below shows some time differences.
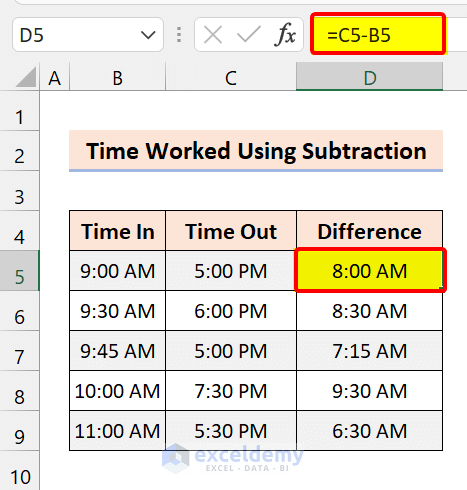
The formula we used:
=C5-B5
The problem is a difference in the time format. For the first day, we got 8:00 AM instead of 8 hours.
You need to change it to Custom format to get the result in hours, minutes, and seconds format.
- Select the range of cells.
- Press Ctrl+1 on your keyboard.
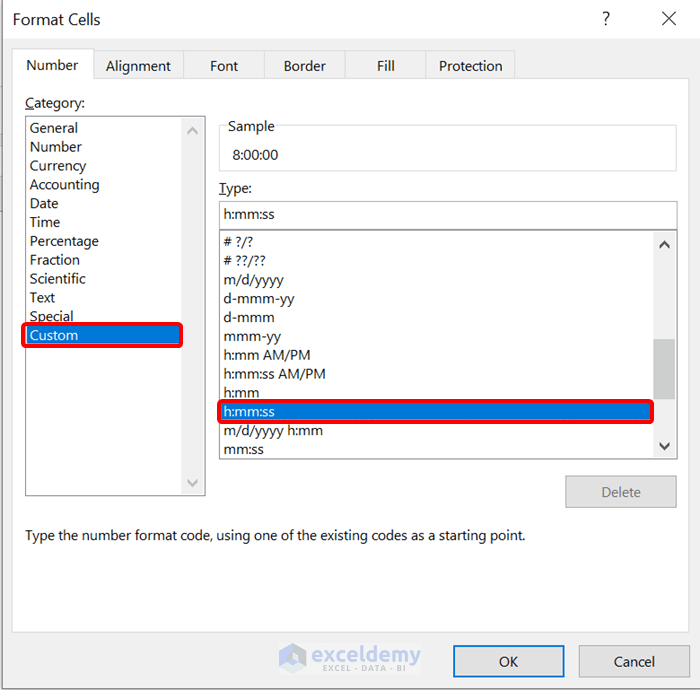
- From the Format Cells dialog box, click Number, select Custom from Category. From the Type, select h:mm: ss format. Click on OK.
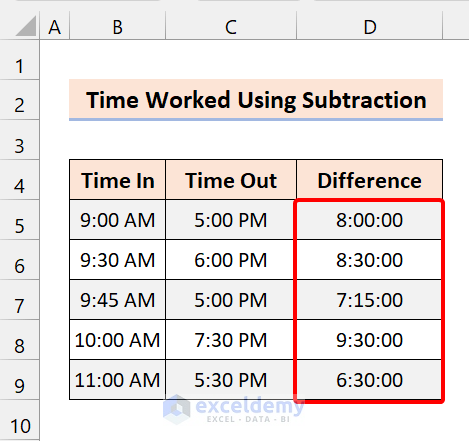
It will display the time worked in hours, minutes, and seconds format.
Read More: How to Calculate Hours Worked Minus Lunch with Excel Formula
Formula 2 – Excel Formula To Calculate Time Worked in Hours, Minutes, or Seconds
2.1 Time Worked in Hours
Add the following formula to calculate time difference in Excel:
=C5-B5
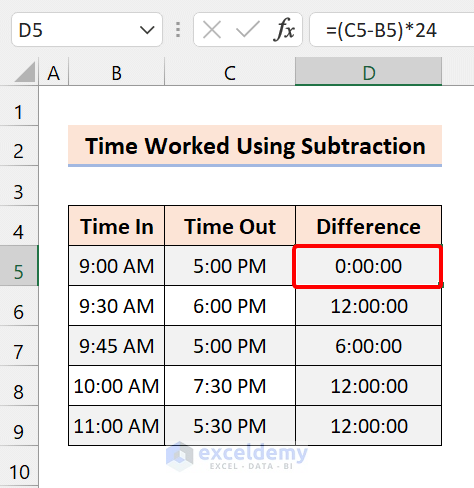
To calculate the time worked in only hours, modify the formula:
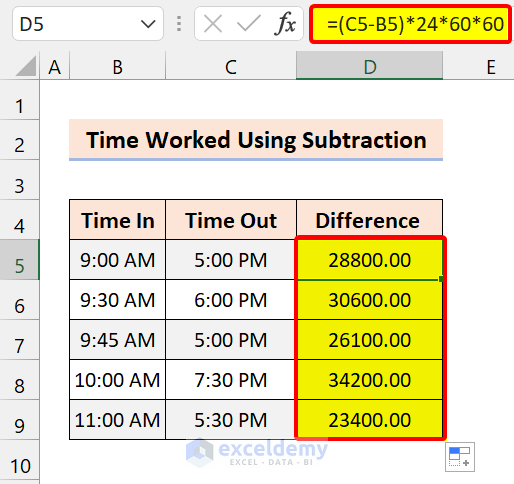
=(C5-B5)*24
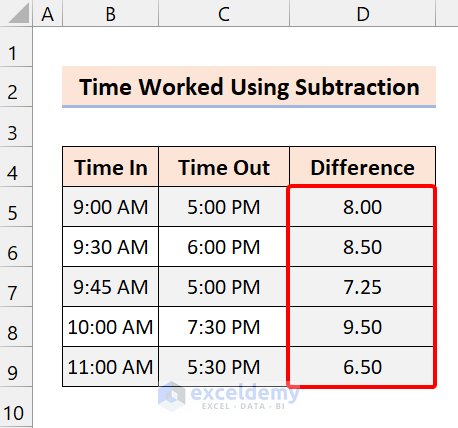
Excel will give you the result in time format. To change this, go to the Numbers format in the Home tab. Click on Number.
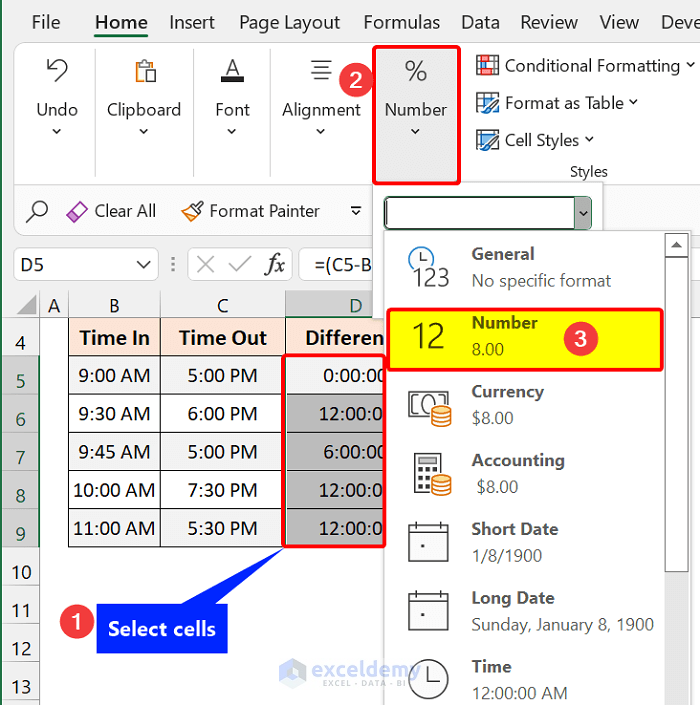
You will get the hours worked.
If you want the output in integer format instead of decimal format, use the INT function:
=INT((C5-B5)*24)
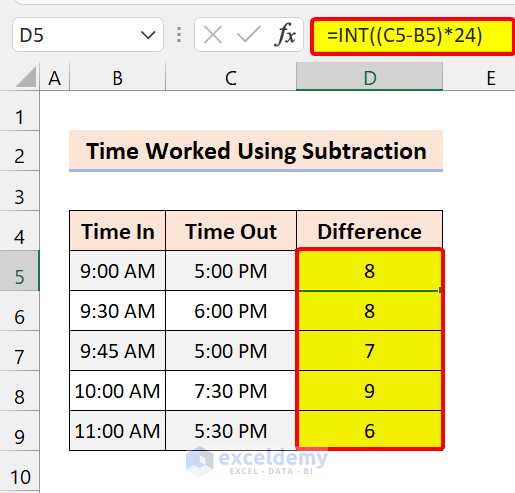
It will show hours worked in integer numbers.
2.2 Time Worked in Minutes
To estimate the time difference in minutes, multiply the times of that column by the total number of minutes in a day. That is, 1440 (24 hrs*60 min).
The formula:
=(C5-B5)*24*60
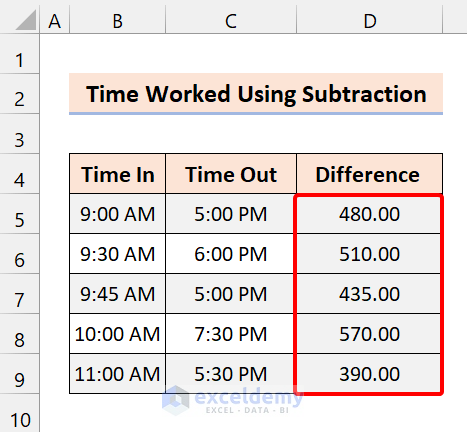
Excel will give the output in time format. Change the format as required from the Numbers group of the Home tab.
2.3 Time Worked in Seconds
To calculate the time difference in seconds, multiply the previous result by the total number of seconds in a day. That is, 86400 (24 hrs * 60 min * 60 sec).
Use the following formula:
=(C5-B5)*24*60*60
Note: This formula will only work if you are calculating the Excel time difference for the same day. If your time values are from different dates, this formula will return incorrect output.
Read More: How to Calculate Hours and Minutes for Payroll Excel
Formula 3 – Calculate Time Worked Using Excel TEXT Function
With the TEXT function, you don’t have to worry about changing the format.
The Generic Formula:
=TEXT(End Time – Start Time, Format)
The first argument is basic subtraction. And in the format, enter the time difference format that you want.
3.1 Display Only Hours
To display only hours worked, use the following formula:
=TEXT(C5-B5,"hh")
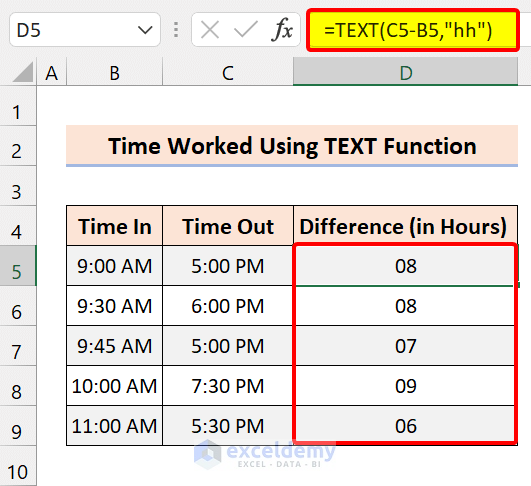
This formula will only deliver the outcome that displays the number of hours difference between the two-time values. If your outcome is 10 hours and 40 minutes, it will display 9 hours only.
3.2 Display Only Minutes
To display only minutes worked, use the following formula:
=TEXT(C5-B5,"[mm]")
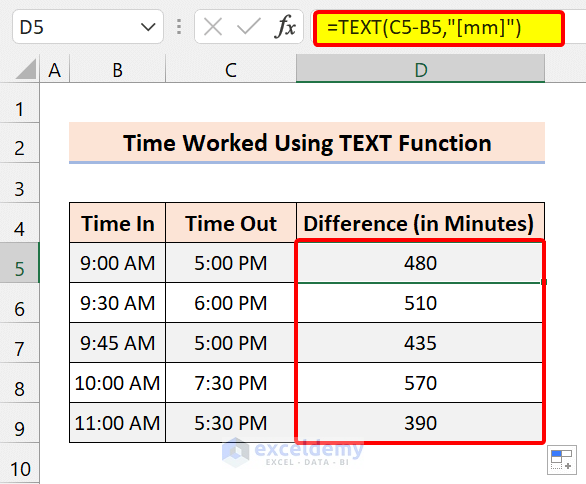
3.3 Display Only Seconds
To display only seconds worked, use the following formula:
=TEXT(C5-B5,"[ss]")
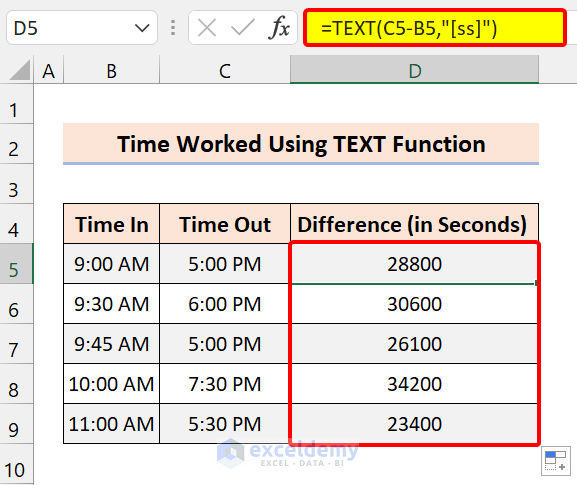
3.4 Display Hours and Minutes
To display hours and minutes worked, use the following formula:
=TEXT(C5-B5,"[hh]:mm")
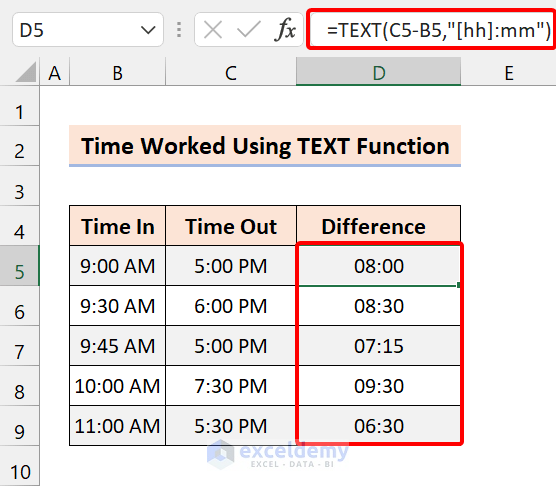
3.5 Display Hours, Minutes, and Seconds
To display hours, minutes, and seconds worked, use the following formula:
=TEXT(C5-B5,"hh:mm:ss")
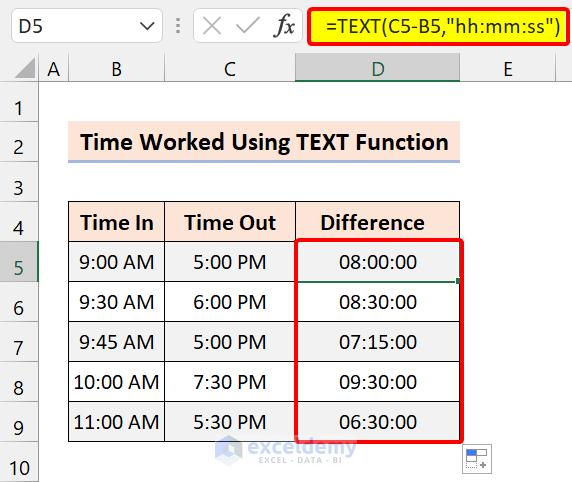
Read More: How to Calculate On Time Delivery Performance in Excel
Formula 4 – Calculate the Time Worked Till Now in Excel
To calculate the time worked between the start time and the current time, use the NOW function instead of the End Time in the Difference column.
The NOW function returns the present date and time from your device. It does not accept any input argument.
The Generic Formula:
Time Worked = NOW() – Start Time
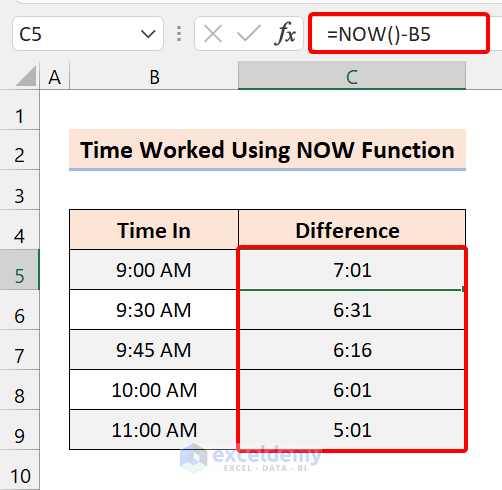
If the difference in time between the start time and the current time is greater than 24 hours, format the outcome to display the day with the time portion using the TEXT function.
The Formula:
=TEXT(NOW()-B5,"dd hh:ss:mm")
You can execute the same thing by modifying the custom formatting of the cell to display the day along with the time part.
Excel will automatically consider the day as 1st January 1990 if your start time only has the time portion.
For this reason, the NOW function will provide you with incorrect output while calculating the time worked. As mentioned, the resulting value would also have the total days that have passed since 1st Jan 1990.
To solve this, use the following formula:
=NOW()- INT(NOW())-B5
The INT function will clear the day part from the result produced by this function. It will use this to calculate the time difference.
The NOW function updates whenever you make a change in your Excel timesheet. But it does not rework in real time.
Read More: How to Calculate Production per Hour in Excel
Formula 5 – Formula to Calculate Hours Worked for A Day Shift
The sample dataset below has some start and end times of some employees. Our goal is to calculate the time worked in hours.
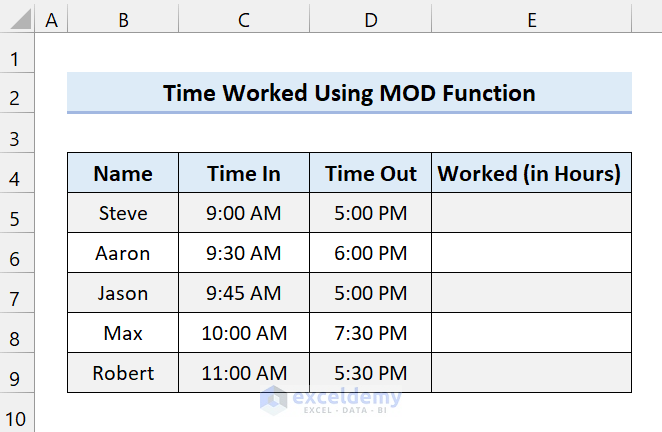
Select Cell E5 and add the following formula:
=MOD(D5-C5,1)*24
Our formula contains the MOD function to calculate the time worked in hours in an Excel timesheet.
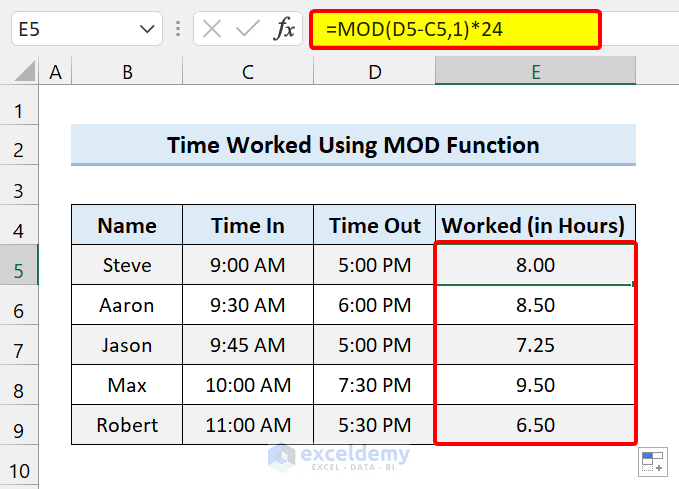
It calculates the total work hours.
Read More: How to Calculate Total Hours Worked in a Week in Excel
Formula 6 – Formula To Calculate Time Worked for a Night Shift
The next sample dataset is of a night shift where employees start work at night and finish the next day.
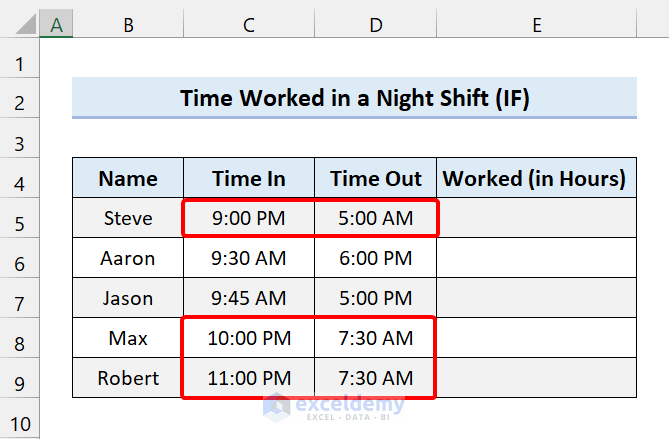
So, the date changes along with the time.
To solve this we are using an Excel formula with the IF function.
Select Cell E5 and add the following formula:
=IF((D5-C5)<0,1-(C5-D5),(D5-C5))
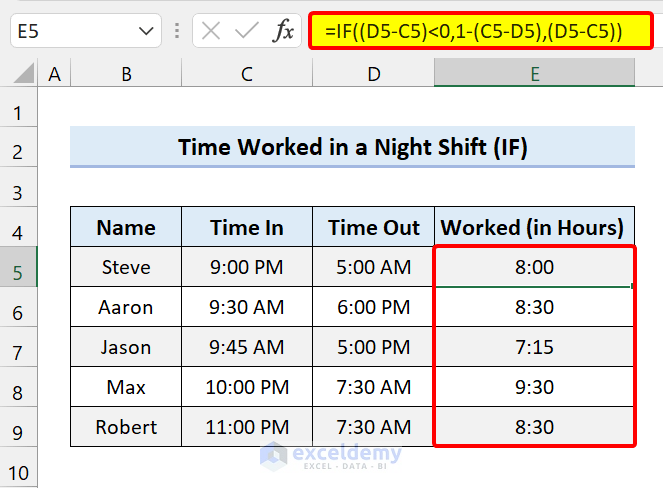
We calculated the time worked using the formula. Another way to solve this is by using the MOD function.
Select Cell E5 and add the following formula:
=MOD(D5-C5,1)*24
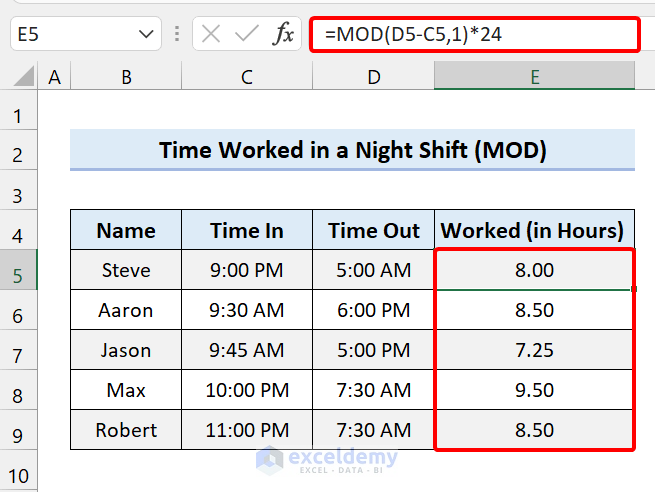
This formula handles the negative time by utilizing the MOD function to “reverse” negative values to the demanded positive value.
Note to Remember: This formula won’t work for a time greater than 24 hours.
Read More: How to Calculate Billable Hours in Excel
Formula 7 – Formula to Calculate Overtime in Excel
In this Excel timesheet, you can see the start time and end time, with the standard working hour being 8 hours. If anyone worked more than 8 hours, our formula will display that in the Overtime column. The Worked column, will only show the standard work time.
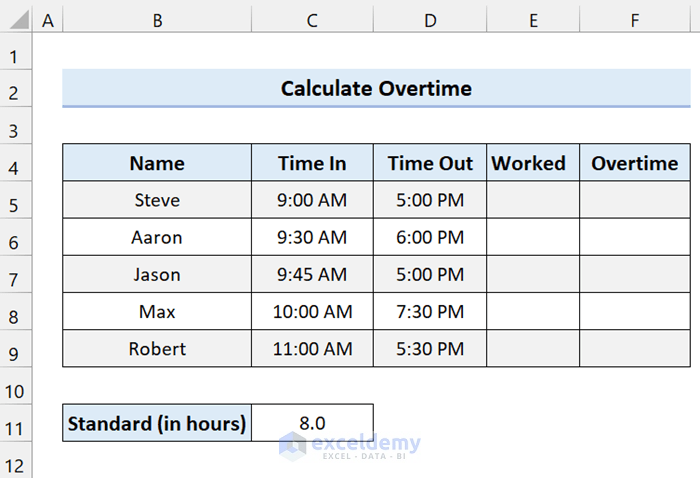
To calculate the usual time worked in a day, add the following formula in Cell E5 and drag the fill handle icon:
=IF((D5-C5)*24>$C$11,$C$11,(D5-C5)*24)
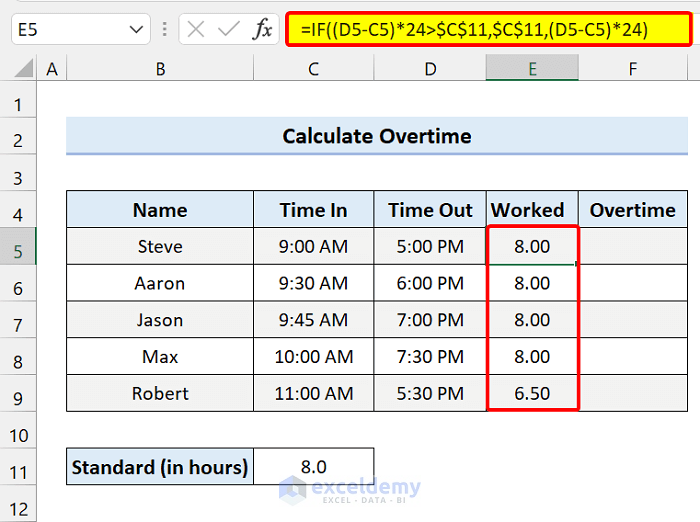
If the employee has operated for more than 8 hours, the formula will only produce a max of 8 hours.
To calculate the overtime in a day, add the following formula in Cell F5 and drag the fill handle icon:
=IF((D5-C5)*24>$C$11,((D5-C5)*24)-$C$11,0)
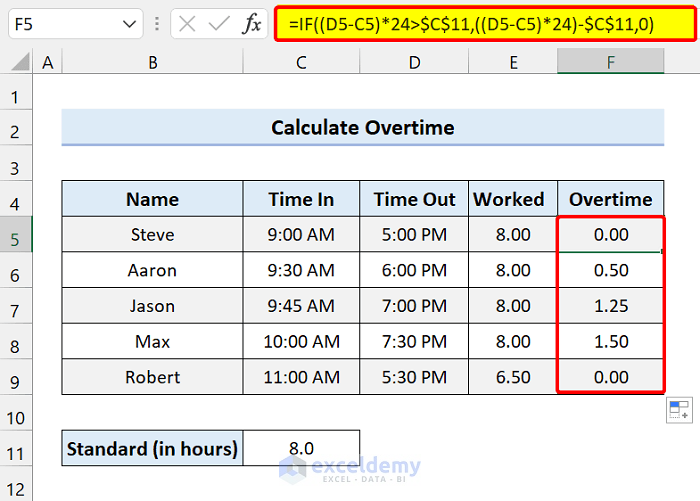
This formula basically extracts the extra hours after subtracting time in from time out.
Read More: Excel Formula for Overtime over 8 Hours
How to Calculate Hours Worked in Excel Using 24-Hour Clock
Use the MOD function for this.
=MOD(D5-C5,1)*24
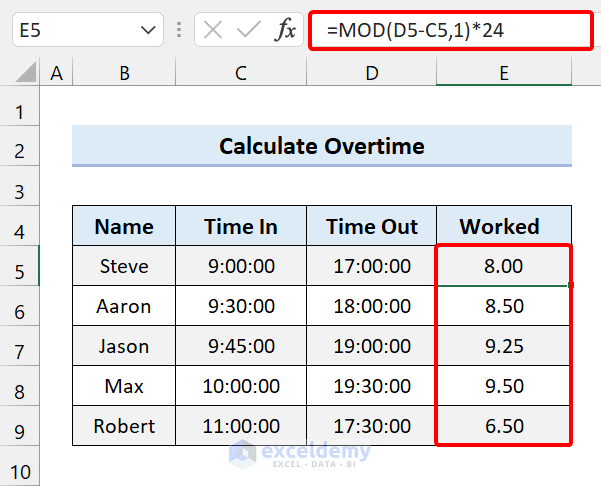
You can use any of the above formulas to calculate the time worked in an Excel timesheet for a 24-hour clock.
How to Calculate Total Hours in a Week in Excel?
To calculate total hours for a week, use the IF function, the MAX function, and the SUM function.
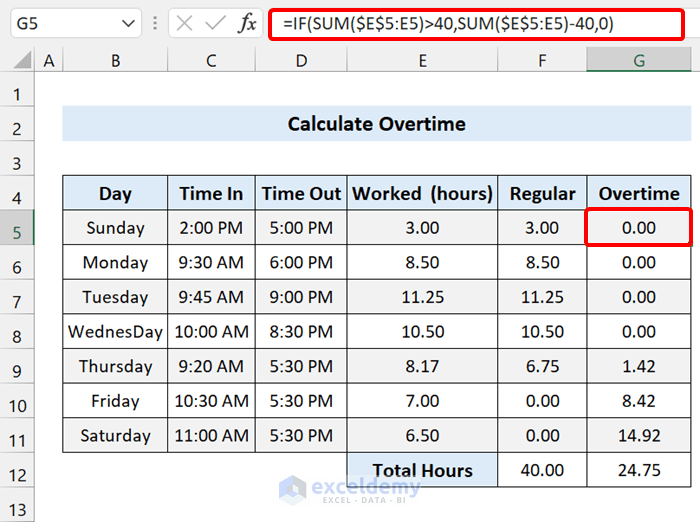
Apply the following formula:
=IF(SUM($E$5:E5)>40,SUM($E$5:E5)-40,0)
This function calculates overtime if a person works more than 40 hours a week.
The role of the first range of the SUM function is absolute, but the second part is not. When you copy this formula across the column, you will witness that the SUM function sums up all the Hours operated in Worked column. When the SUM range increases, the hours worked will also increase. Once the SUM reaches more than 40 hours, it will put the overtime hours.
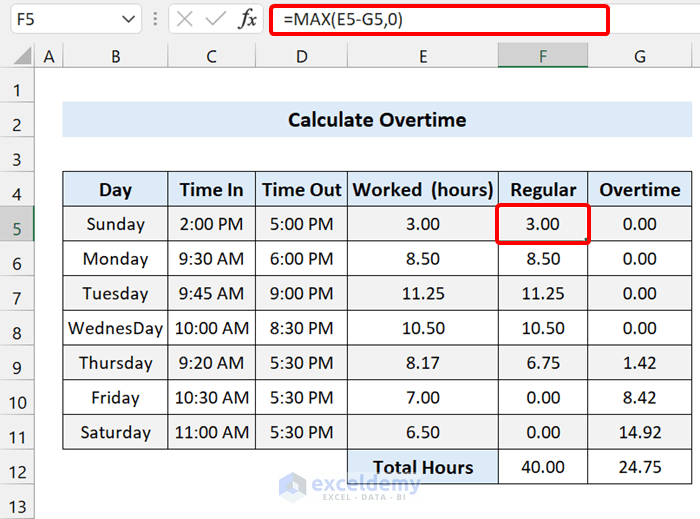
The regular hours are estimated based on the total hours, and the overtime operated:
=MAX(E5-G5,0)
We use the MAX function to not end up with Negative hours where the Employee has operated the overtime. If the formula returns a negative, the MAX function will return a zero in the Excel timesheet.
Read More: How to Calculate Hours Worked and Overtime Using Excel Formula
How to Calculate Total Hours in a Month in Excel?
You can calculate the total time (hours) worked in a month using the NETWORKDAYS function in Excel.
The Generic Formula:
=NETWORKDAYS(start date,end date)*working hour per day
The Formula we used:
=NETWORKDAYS(B5,C5)*8
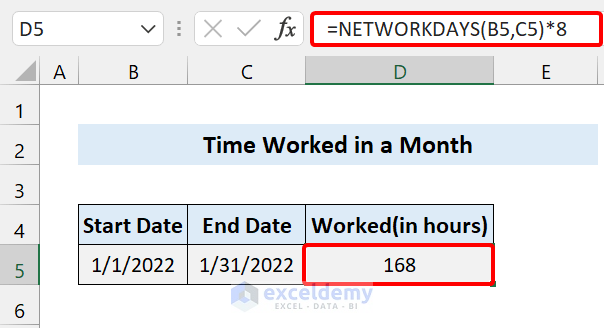
You can see the total hours worked in an entire month. We didn’t include holidays.
To get the total hours worked without holidays, the formula will be:
=NETWORKDAYS(start date,end date,holiday_list)*working hour per day
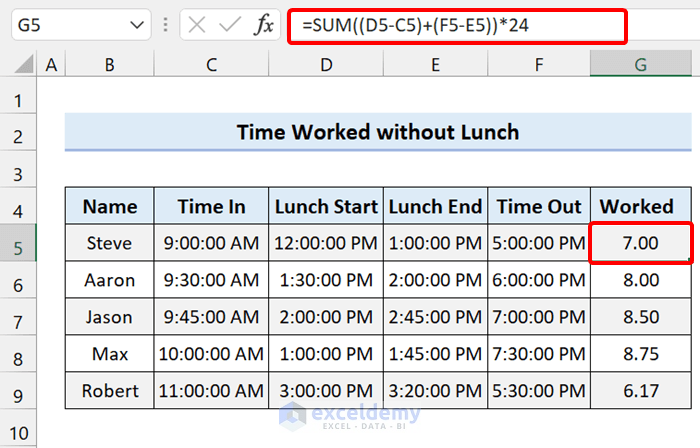
Excel Formula to Calculate Hours Worked Minus Lunch
We can calculate hours worked minus the lunch time by using the SUM function.
The Generic Formula:
=SUM((Lunch_start-start_time)+(end_time-lunch_end))*24
Formula used for sample dataset:
=SUM((D5-C5)+(F5-E5))*24
Things to Remember
✎ Make sure to change the time format to number or general if it is not showing in decimal format.
✎ If the formula returns ####, it means your value is negative or the column width is too small.
Download Practice Workbook
Related Articles
- Excel Formula to Calculate Overtime and Double Time
- Man Hours Calculation in Excel
- How to Create an Injection Molding Cycle Time Calculator in Excel
<< Go Back to Calculate Total Time | Calculate Time | Date-Time in Excel | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

