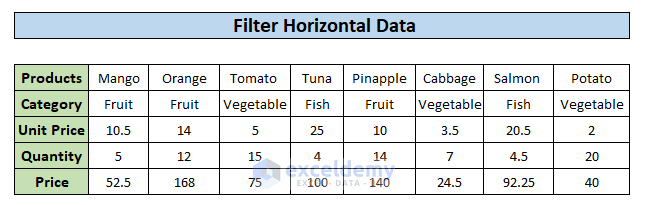
The sample dataset contains sales data for 8 products that fall into 3 different categories. We will discuss 3 suitable methods to filter this dataset based on categories.
Method 1 – Use of the FILTER Function to Filter Horizontal Data in Excel
The FILTER function can filter data horizontally based on predefined criteria.
Syntax:
=FILTER(array, include, [if_empty])
Arguments:
| Argument | Required/Optional | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| array | Required | Range of data to be filtered. |
| include | Required | A Boolean array has an identical height or width to the array. |
| if_empty | Optional | If the criteria don’t match outputs a predefined string. |
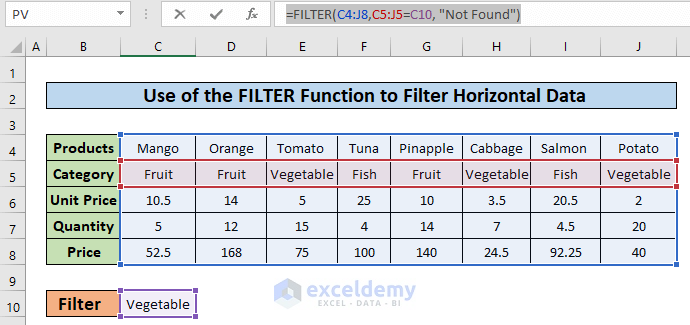
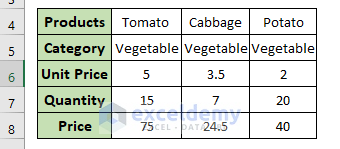
In this example, we will filter the dataset based on three different categories i.e., Fruit, Vegetable, and Fish.
Steps:
- In cell C10, enter the category name “Vegetable” to use as the criteria to filter the dataset. An output table is also added to store the filtered data.
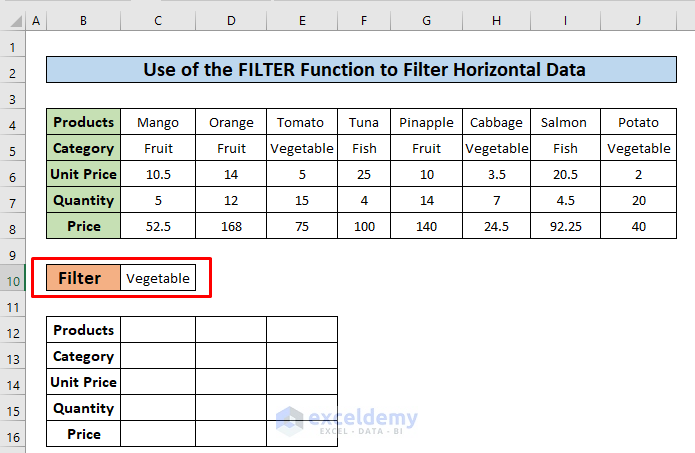
- In the cell, C12 enter the following formula.
=FILTER(C4:J8,C5:J5=C10, "Not Found")The FILTER function takes two arguments – data and logic.
- In this formula, cells C4:J8(Blue colored box ) represent data to be filtered. Cells C5:J5 are the categories in the red-colored box from where we set the criteria.
- The formula checks the value of cell C10 against each of the cell values of C5:J5. This returns an array, {FALSE, FALSE, TRUE, FALSE, FALSE, TRUE, FALSE, TRUE}. We see that TRUE values represent cells containing the category vegetable.
The formula returns a dynamic solution. It means that whenever we change cell data the output is going to adjust its value.
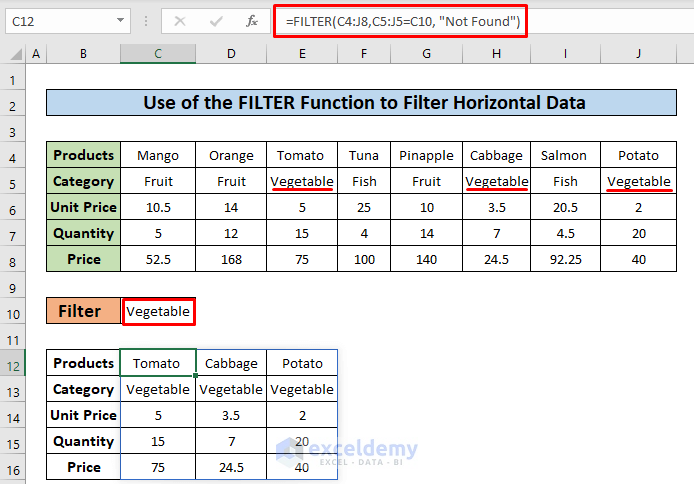
- Currently the result shows only the columns with the category Vegetable.
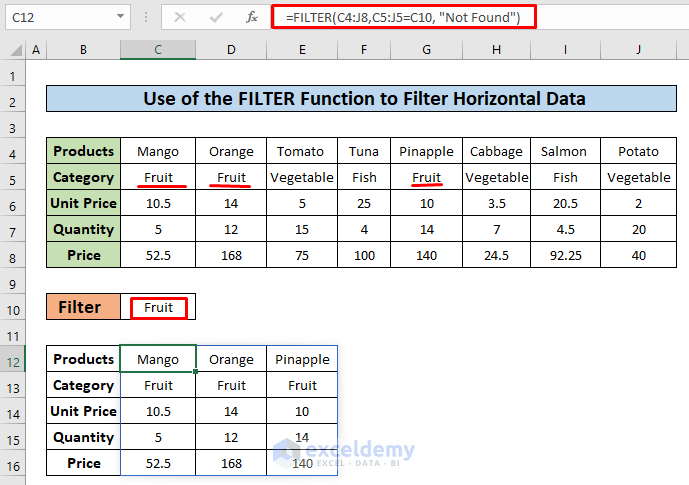
- We changed the value of cell C10 to Fruit, and the data filtered horizontally for that category.
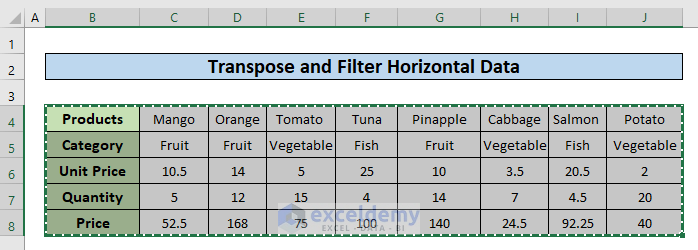
Method 2 – Transpose and Filter Horizontal Data in Excel
Steps:
- Select the whole dataset, press Ctrl + C on the keyboard, or right–click the mouse to choose copy from the context menu.
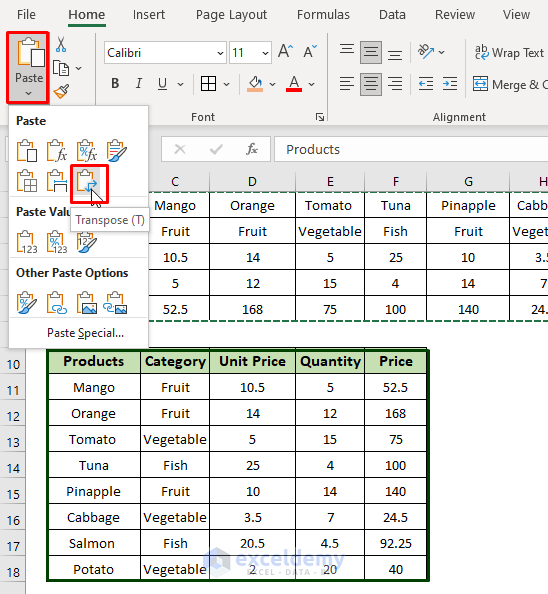
- Paste the copied dataset with the Transpose option.
- Select the cell where you want to paste the data.
- In this example, we selected cell B10.
- On the Home Tab click on Paste arrow to select the Transpose option.
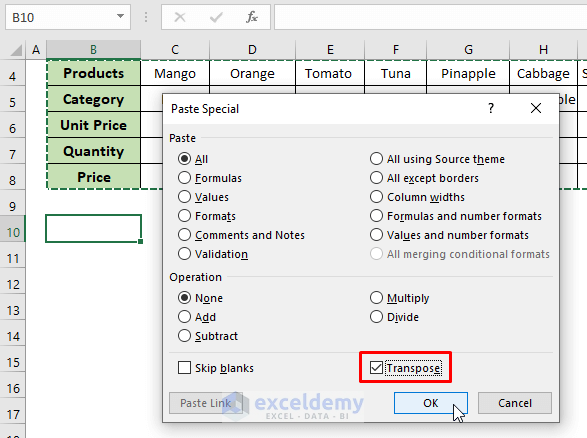
Alternatively, open the Paste Special window either from the context menu or from the Home tab.
From the Operation options, click the Transpose checkbox and hit OK.
- Select the transposed dataset and from the Data Tab click on the Filter option.
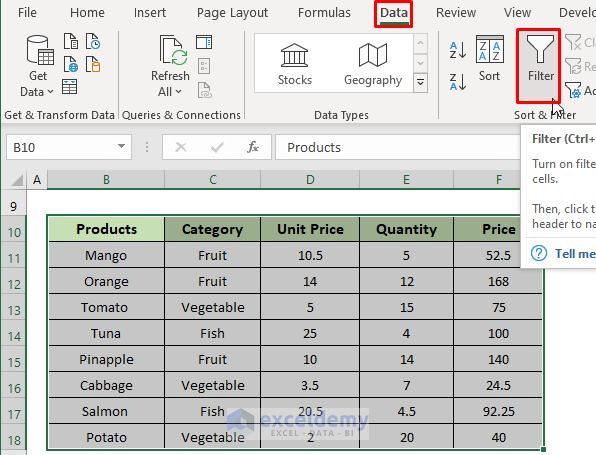
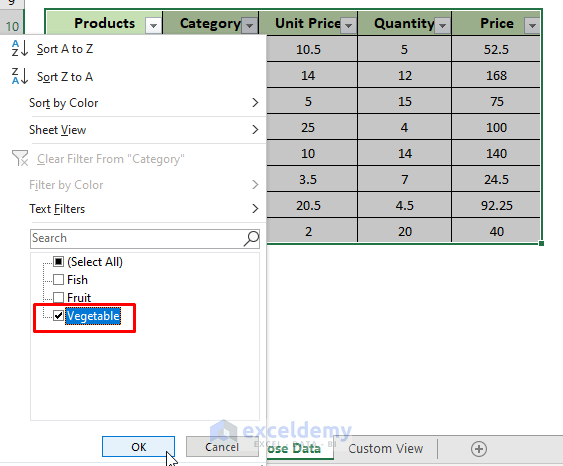
- Once filtering options have been enabled on each of the columns, click on the Category Filter option and check the Vegetable.
Method 3 – Create Custom Views to Filter Data Horizontally in Excel
Steps:
- To create a custom view with the full dataset, go to the View Tab in the Excel Ribbon and then select the Custom Views option.
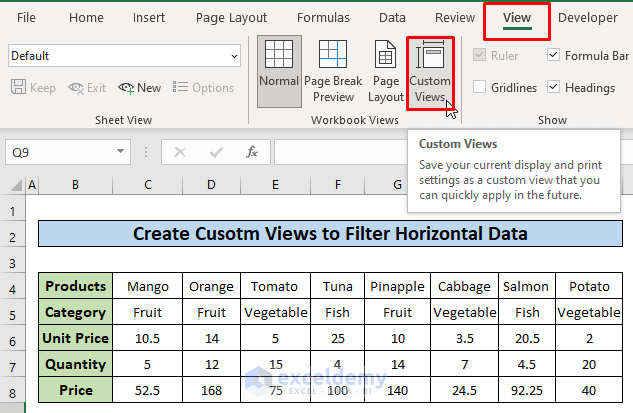
- Click the Add button.
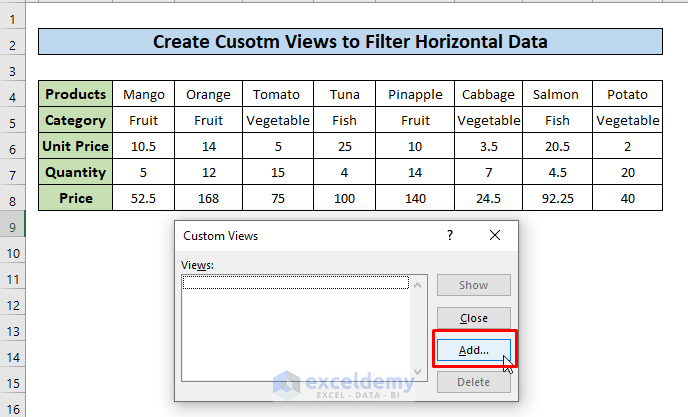
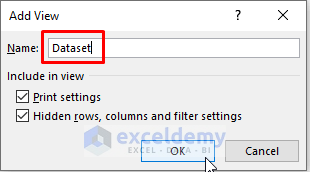
- Put Dataset in the input box as the name and press OK.
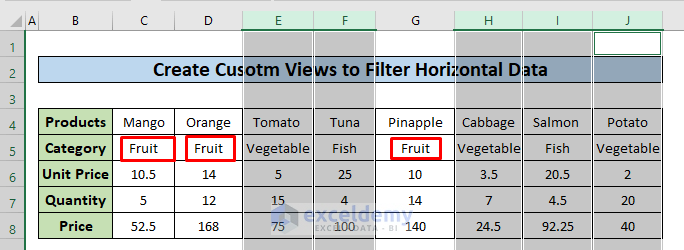
- To create a custom view for the Fruit category, hide all the columns other than the Fruit category.
- Select the columns E, F, H, I, and J that have data for Vegetable and Fish
- Right–click on the top of the column bar and choose Hide from the context menu.
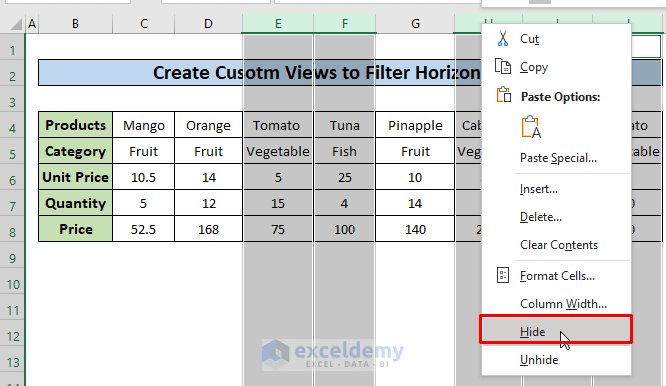
- All the columns other than the Fruit category are hidden.
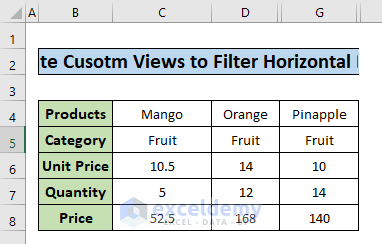
- Add a custom view named Fruit for the Fruit category.
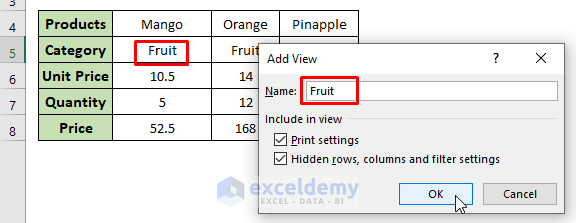
- Add another two custom views for the Vegetable and Fish categories named Vegetable and Fish. Finally, we have created 4 custom views.
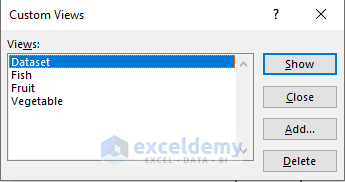
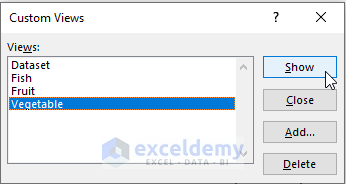
- We can now select any of the custom views from the list, and click the Show button to view that corresponding product category.
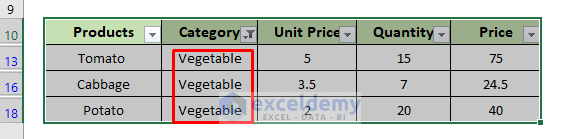
- Here is the filtered dataset for the Vegetable category.
Notes
- The FILTER function is a new function that can only be used in Excel 365. It is not available in older versions.
Download Practice Workbook
Download this practice workbook to exercise while you are reading this article.
<< Go Back to Filter in Excel | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

