The image below illustrates the functionality of the Excel NETWORKDAYS function.
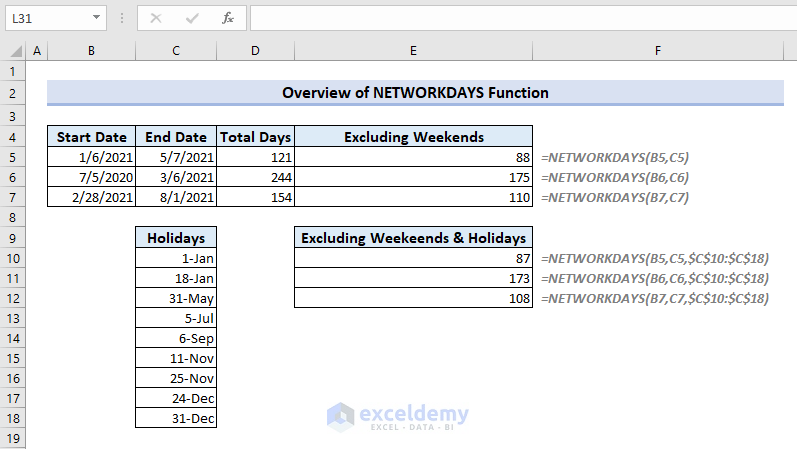
Introduction to the NETWORKDAYS Function
- Function Objective:
Returns the number of whole workdays between two dates.
- Syntax:
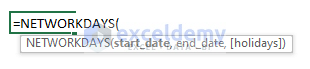
- Arguments Explanation:
| Arguments | Compulsory/Optional | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| start_date | Compulsory | Starting date between two specified dates. |
| end_date | Compulsory | End date between two specified dates. |
| [holidays] | Optional | Range of cells containing holidays as date format. |
- Output:
The number of days in numerical value.
- Version:
The NETWORKDAYS function is available in Microsoft Excel 2007 and all later versions, including Excel 2010 onward and Microsoft Excel 365.
How to Use the NETWORKDAYS Function in Excel: 6 Suitable Examples
Example 1 – Count Days Between Two Dates Excluding Weekends with the NETWORKDAYS Function
In the picture below, column B and column C contain a few start dates and end dates. Column D represents the total number of days between two dates from the previous two columns (calculated with the DAYS function). In Column E, we want to find out the number of working days excluding the default weekends (Saturday and Sunday).
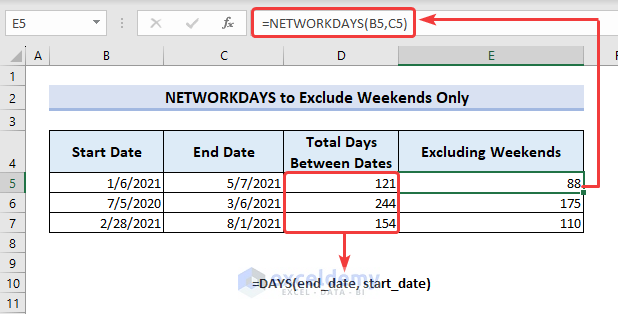
- Apply the following formula in cell E5.
=NETWORKDAYS(B5,C5)- B5= start_date
- C5= end_date
You will see that the normal difference between dates was 121 for the first pair of dates but excluding the weekends, the network days turn out to be 88.
- Drag the Fill Handle to copy the formula for other cells in column E.
Example 2 – Use the NETWORKDAYS Function to Count Days Between Two Dates Excluding Weekends and Given Holidays
We have listed holidays in a range of cells D10:D18, but are using the same dataset as in the previous example.
- Apply the formula below:
=NETWORKDAYS(B5,C5,$D$10:$D$18)Here,
- B5= start_date
- C5= end_date
- D10:D18= holidays
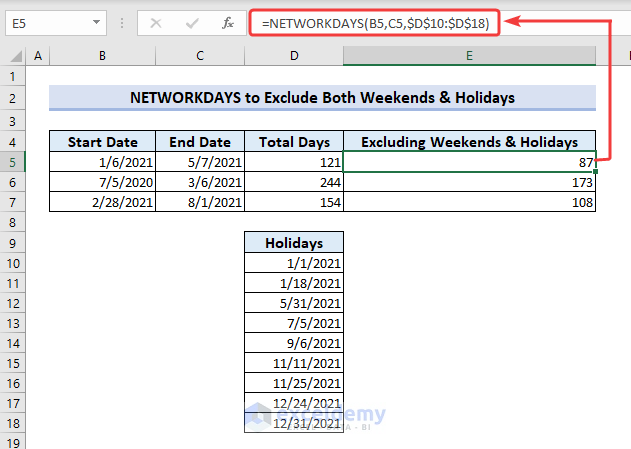
We have used absolute cell references for the range of cells containing holidays. If you don’t use absolute cell references here, then the cell references will change while autofilling the cells in Column E, leading to wrong results.
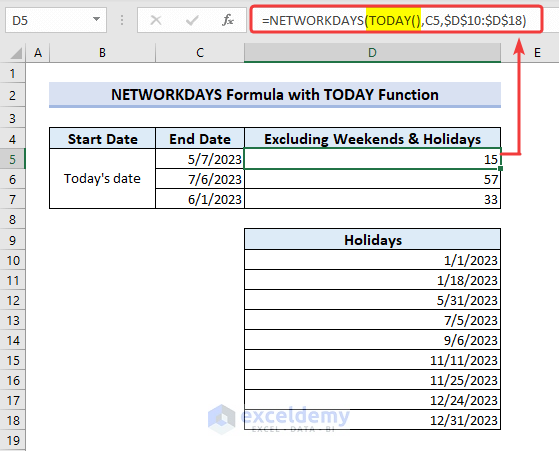
Example 3 – Apply the NETWORKDAYS Formula with the TODAY Function to Find the Number of Working Days from Today
- We have entered the first argument start_date of the NETWORKDAYS function as the TODAY function.
=NETWORKDAYS(TODAY(),C5,$D$10:$D$18)The TODAY function will return today’s date, and later the NETWORKDAYS will count the difference excluding the holidays.
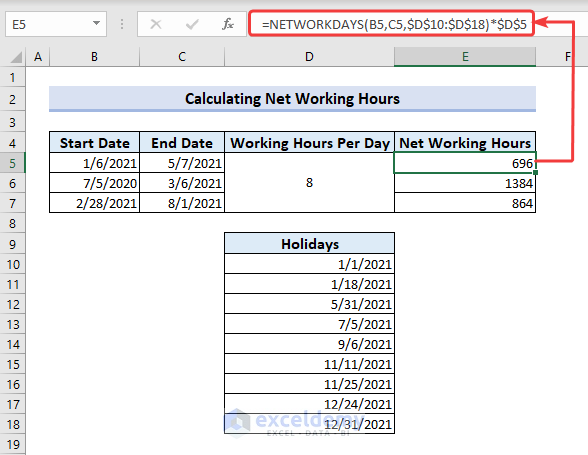
Example 4 – Calculate Working Hours Using the NETWORKDAYS Function
- Multiply the working hours per day (listed in D5) by the working days and use this formula in E5.
=NETWORKDAYS(B5,C5,$D$10:$D$18)*$D$5💡 Formula Breakdown
The NETWORKDAYS function first returns the number of working days.
NETWORKDAYS(B6,C6,$D$10:$D$18) results in 173.
Then we multiplied the function by the cell reference of working hours per day which will return total working hours as output.
NETWORKDAYS(B6,C6,$D$10:$D$18)*$D$5 = 173*8 = 696.
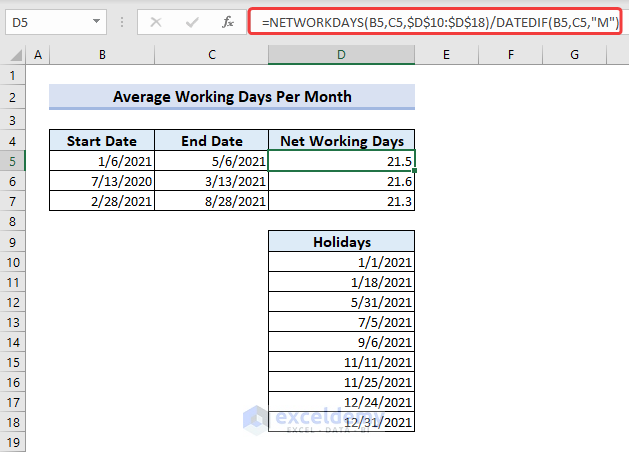
Example 5 – Combine DATEDIF with NETWORKDAYS to Find the Average Number of Working Days Per Month Between Same Dates
- Divide the NETWORKDAYS function by the month returned by the DATEDIF function considering two similar dates.
=NETWORKDAYS(B5,C5,$D$10:$D$18)/DATEDIF(B5,C5,"M")💡 Formula Breakdown
NETWORKDAYS(B5,C5,$D$10:$D$18) returns => 86.
As we have used the 3rd argument of DATEDIF as “M”, it will return the month.
DATEDIF(B5,C5,”M”) returns => 4.
Then we divide the working days returned by NETWORKDAYS (excluding holidays) by DATEDIF. So, the working days per month are found subsequently.
NETWORKDAYS(B5,C5,$D$10:$D$18)/DATEDIF(B5,C5,”M”) = 86/4 =21.5
Example 6 – Use the NETWORKDAYS Function in a VBA Macro
- Press Alt + F11 to open the Visual Basic Editor window.
- Click Insert and select Module.
- Insert the following code in the Module window.
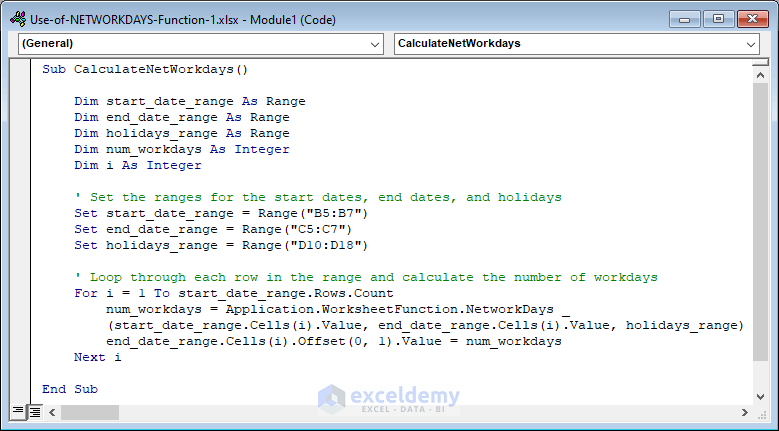
Code:
Sub CalculateNetWorkdays()
Dim start_date_range As Range
Dim end_date_range As Range
Dim holidays_range As Range
Dim num_workdays As Integer
Dim i As Integer
' Set the ranges for the start dates, end dates, and holidays
Set start_date_range = Range("B5:B7")
Set end_date_range = Range("C5:C7")
Set holidays_range = Range("D10:D18")
' Loop through each row in the range and calculate the number of workdays
For i = 1 To start_date_range.Rows.Count
num_workdays = Application.WorksheetFunction.NetworkDays _
(start_date_range.Cells(i).Value, end_date_range.Cells(i).Value, holidays_range)
end_date_range.Cells(i).Offset(0, 1).Value = num_workdays
Next i
End Sub- Click Run from the toolbar option of the VBA window.
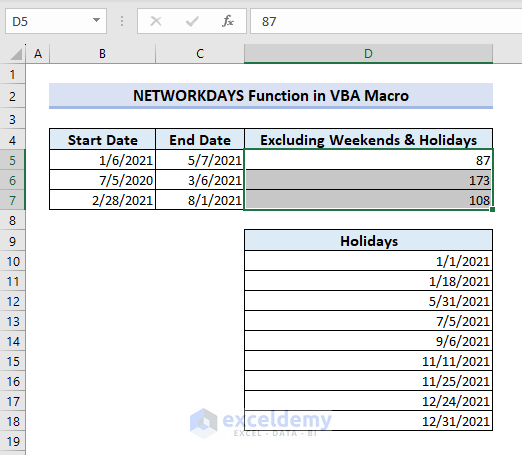
- VBA will calculate the network days by implementing the function.
The NETWORKDAYS.INTL Function in Excel (Alternative to NETWORKDAYS)
The extra feature of NETWORKDAYS.INTL is that it allows the user to specify custom weekend days.
=NETWORKDAYS.INTL(start_date, end_date, [weekend], [holidays])It excludes Saturday and Sunday by default just like NETWORKDAYS.
The NETWORKDAYS.INTL function has different index numbers for different custom weekends. If you want Friday and Saturday as weekends for the previous example, our formula will be:
=NETWORKDAYS.INTL(B5,C5,7,$E$10:$E$18)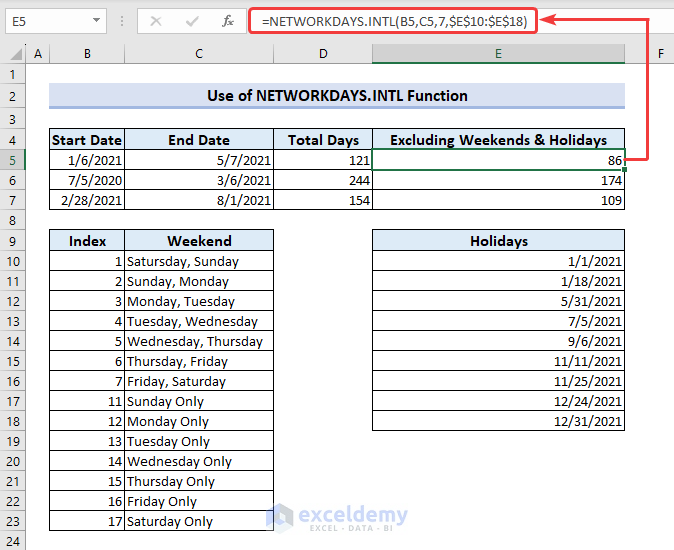
Excel NETWORKDAYS Formula Is Not Working
Sometimes you may find the Excel NETWORKDAYS function not working and returning a #VALUE error. This may happen from inserting an invalid date format.
For example, if your system format is “mm/dd/yyyy” but you enter the date formatted as “dd/mm/yyyy”, Excel will return you a #VALUE error.
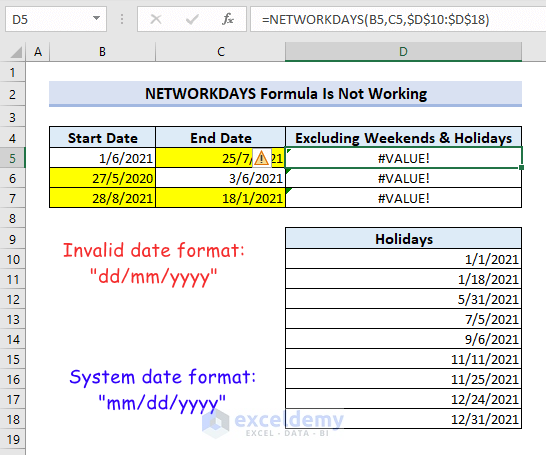
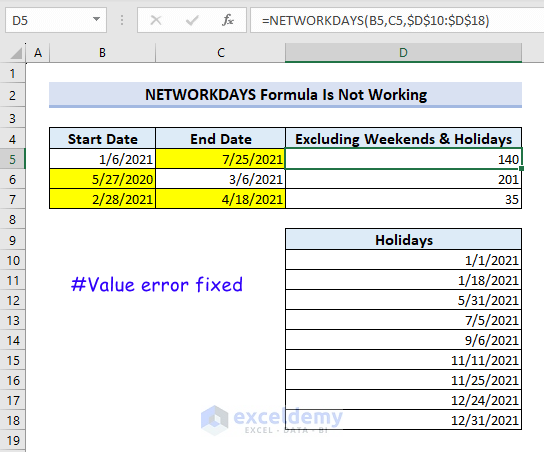
Following the system format will fix this issue.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between NETWORKDAYS and WORKDAY functions in Excel?
NETWORKDAYS calculates the number of working days between two dates, while WORKDAY calculates the date that is a specified number of working days away from a given start date.
Can I use the NETWORKDAYS function to calculate the number of working days for multiple date ranges at once?
Yes, you can use the NETWORKDAYS function in Excel to calculate the number of working days for multiple date ranges at once by entering the function as an array formula. To do this, select the cells where you want to display the results, enter the formula as an array formula, and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter .
Takeaways from this Article
- The NETWORKDAYS function in Excel can be used to calculate the number of working days between two dates, excluding weekends and holidays.
- By default, the NETWORKDAYS function considers Saturday and Sunday as non-working days, but you can customize the weekend days using the NETWORKDAYS.INTL function.
- The NETWORKDAYS function can be particularly useful in business and finance applications, where it’s important to calculate the number of working days between two dates for various purposes.
Things to Remember
- By default, the NETWORKDAYS function recognizes only Saturday and Sunday as weekends and you cannot customize these weekends. In this case, you have to use NETWORKDAYS.INTL function to customize weekends.
- You have to be careful about inserting the start_date and the end_date argument sequences. Otherwise, the function will return a negative value.
- Make sure to use absolute cell references for the holiday argument.
- If your data has a date in text format, convert it to the date format with the DATEVALUE function.
Download the Practice Workbook
<< Go Back to Excel Functions | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

