In this article, we will use the following dataset to demonstrate four methods to add a sheet with a name derived from a cell using Excel VBA. In the first three methods, we will add a single sheet with the sheet name extracted from the “ID” column in each case. For the last method, we will add six sheets by taking the values from the column “Name”.
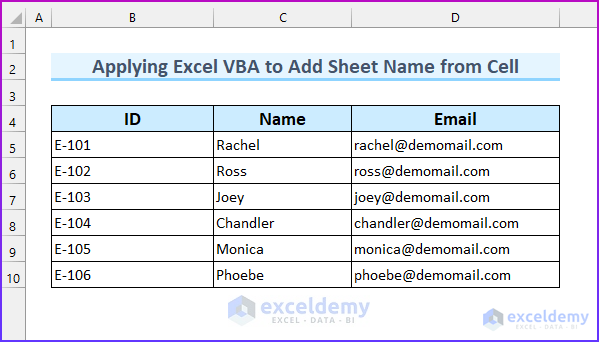
Method 1 – Adding a Single Sheet with Name from a Cell
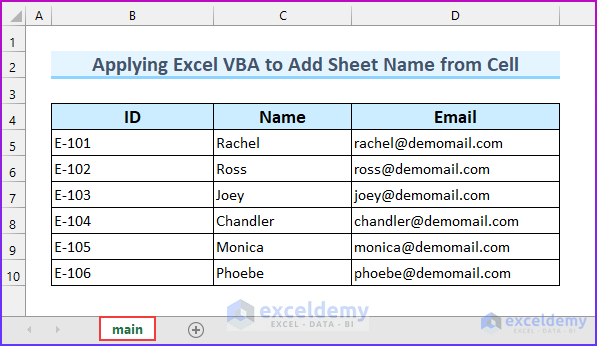
By default in Excel, a new sheet will be added on the left side of our reference sheet. We have named this original sheet “main”.
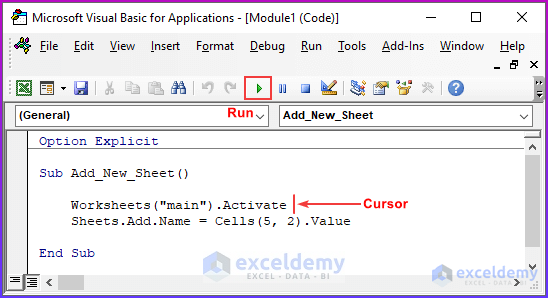
First, we bring up the VBA Module window, where we type our codes.
- From the Developer tab → select Visual Basic. Alternatively, press ALT+F11.
The VBA window will pop up.
- From the Insert tab, select Module.
- In the module window that opens, enter the following code in the VBA Module window:
Option Explicit
Sub Add_New_Sheet()
Worksheets("main").Activate
Sheets.Add.Name = Cells(5, 2).Value
End Sub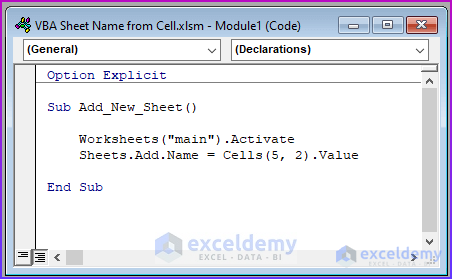
VBA Code Breakdown
- We name the Sub procedure as Add_New_Sheet.
- We activate the “main” sheet to ensure that the code will run if we are on another sheet.
- We use the Add.Name method to name the newly created sheet.
- We use the Cells property to refer to a cell value. Cells(5,2) signifies the cell at row 5 and column 2, namely cell B5.
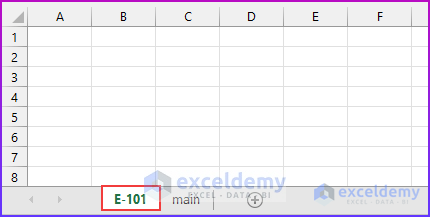
Our code will execute and add a sheet named “E-101”, the value in cell B5.
Read More: Excel Macro: Create New Sheet and Rename
Method 2 – Adding a Sheet After a Specific Sheet
We can also add a sheet after a specific sheet using Excel VBA.
2.1 – After a Specific Sheet
Steps:
- As shown in the first method, bring up the Module window.
- Enter the following code in it:
Option Explicit
Sub Add_New_Sheet_After_Specific_Sheet()
Worksheets("main").Activate
Sheets.Add(After:=Sheets("E-101")).Name = Range("B7").Value
End Sub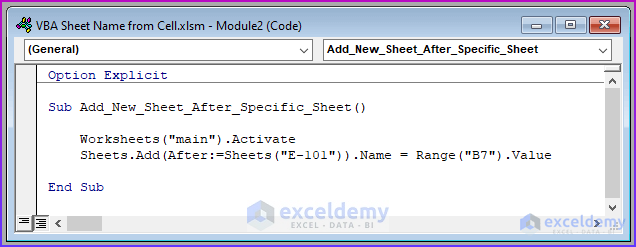
VBA Code Breakdown
- We name the Sub procedure Add_New_Sheet_After_Specific_Sheet.
- We activate the “main” sheet to ensure the code will run if we are on another sheet.
- We use the Add.Name method to name the newly created sheet. This sheet will be created after the “E-101” sheet that we created in the last method.
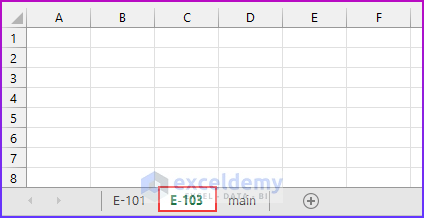
- We use the Range property to refer to the value in cell B7, which is “E-103”.
- As shown in method 1, Save and Run this Module.
The code will add a sheet named “E-103” after sheet “E-101”.
Read More: How to Add Sheet After Current One with Excel VBA
2.2 – After the Last Sheet
Now let’s add a sheet after the last sheet of the workbook.
Steps:
- As shown in the first method, bring up the Module window.
- Enter the following code in it:
Option Explicit
Sub Sheet_Start_Workbook()
Worksheets("main").Activate
Sheets.Add(After:=Sheets(Sheets.Count)).Name = Range("B10").Value
End Sub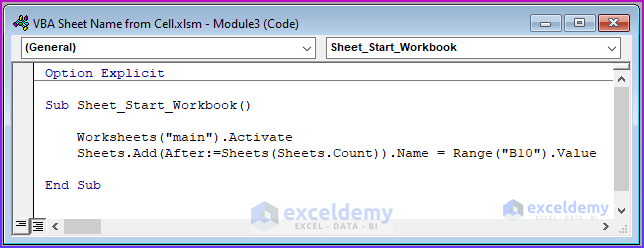
VBA Code Breakdown
- We name the Sub procedure Add_New_Sheet_After_Specific_Sheet.
- We activate the “main” sheet to ensure the code will run if we are on another sheet.
- We use the Add.Name method to name the newly created sheet. This sheet will be created after the last sheet in the workbook. This last sheet number is obtained from the “Sheets.Count” property.
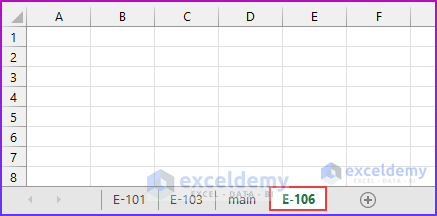
- We use the Range property to refer to the value in cell B10, which is “E-106”.
- As shown in method 1,Save and Run this Module.
The code adds a sheet after the last sheet.
Method 3 – Adding a Sheet Before a Specific Sheet
3.1 – Before a Specific Sheet
Steps:
- As shown in the first method, bring up the Module window.
- Enter the following code in it:
Option Explicit
Sub Add_New_Sheet_Before_Specific_Sheet()
Worksheets("main").Activate
Sheets.Add(Before:=Sheets("E-103")).Name = Range("B6").Value
End Sub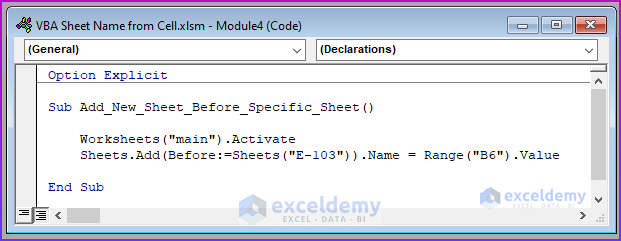
VBA Code Breakdown
- We name the Sub procedure Add_New_Sheet_Before_Specific_Sheet.
- We activate the “main” sheet to ensure the code will run if we are on another sheet.
- We use the Add.Name method to name the newly created sheet. This sheet will be created before the sheet called “E-103”.
- We use the Range property to refer to the value in cell B6, which is “E-102”.
- As shown in method 1, Save and Run this Module.
The code will add a sheet “E-102” before sheet “E-103”.
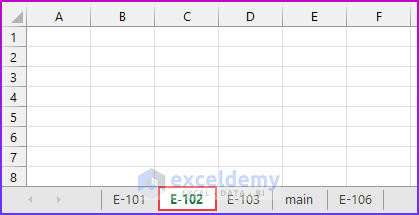
3.2 – At the Start of a Workbook
We can insert a sheet right at the beginning, before the first sheet.
Steps:
- As shown in the first method, bring up a Module window.
- Enter the following code in it:
Option Explicit
Sub Sheet_Start_Workbook()
Worksheets("main").Activate
Sheets.Add(Before:=Sheets(1)).Name = Cells(8, 2).Value
End Sub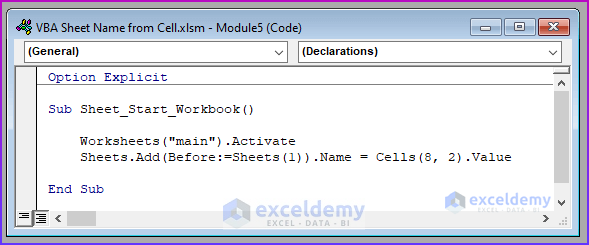
VBA Code Breakdown
- We name the Sub procedure as Sheet_Start_Workbook.
- We activate the “main” sheet to ensure the code will run if we are on another sheet.
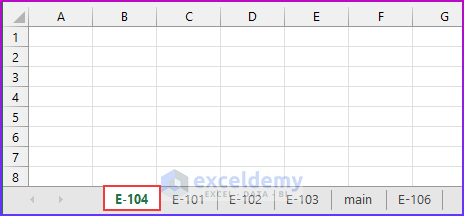
- We use the Add.Name method to name the newly created sheet. This sheet will be created before the first sheet from the workbook. This action will be executed before the first sheet, as denoted by the “Sheets(1)” property.
- We use the Cells property to refer to a cell value. Cells(8,2) signify row 8 and column 2, which means cell B8.
- As shown in method 1, Save and Run this Module.
Method 4 – Inserting Multiple Sheets with Name from Cell
For the last method, we will add multiple sheets to the workbook with names from a range of cells using Excel VBA. We will ask the user to input the range from which to take the names. We’ll then use a For Each Next loop to go through all the cells.
Steps:
- As shown in the first method, bring up a Module window.
- Enter the following code in it:
Option Explicit
Sub Add_Sheets_from_Cell_Value()
Dim xRange As Range
Dim qq As Range
Set xRange = Application.InputBox("Select Cell Range" _
& "to Create Sheets", "ExcelDemy", Type:=8)
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
For Each qq In xRange
On Error Resume Next ' This will ignore any error
Sheets.Add(After:=Sheets(Sheets.Count)).Name = qq.Value
Next qq
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End Sub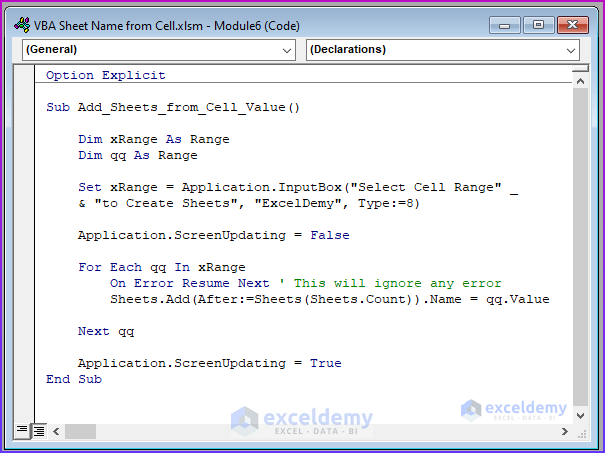
VBA Code Breakdown
- We name the Sub procedure as Add_Sheets_from_Cell_Value.
- We define the variable types.
- We use an InputBox to get the range data from the user.
- We use a For Next loop to go through the selected cell range cell-by-cell.
- We use the Add.Name method to name the newly created sheet. This sheet will be created after the last sheet in the workbook. This last sheet is determined by the “Sheets.Count” property.
- We add the “On Error Resume Next” statement before the loop. This will ignore any errors and continue the looping process.
- As shown in method 1, Save and Run this Module.
A Message Box opens asking to input the range.
- Select the cell range C5:C10 and press OK.
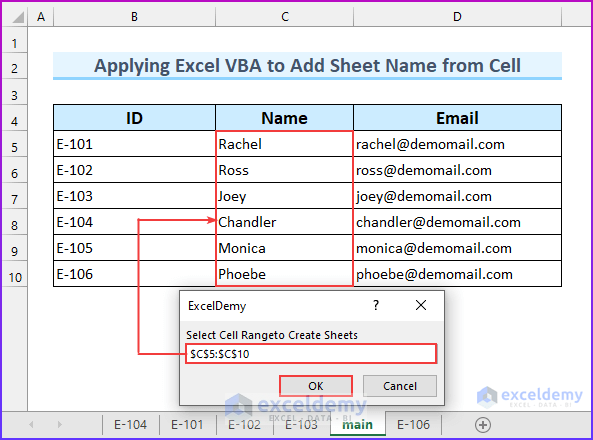
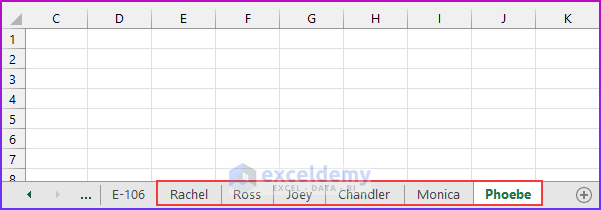
As a result, six new sheets are created in the workbook. Additionally, we set the code to ignore any errors, so if your cell range has duplicate values, the code will not terminate; rather, for that duplicate value, it will give a generic name (for example “sheet16”) to the newly created sheet.
Read More: Excel VBA to Add Sheet with Variable Name
Things to Remember
- A worksheet name cannot be blank.
- Sheet names can contain a maximum of 31 characters.
- There should not be any slashes, question marks, asterisks, third brackets, or colons.
- The sheet name should not begin or end with an apostrophe.
- Don’t name the sheet with reserved words such as “History”.
Download Practice Workbook
Related Articles
- Excel Macro to Create New Sheet and Copy Data
- Excel VBA to Add Sheet If It Does Not Exist
- How to Create New Sheet from Template Using Macro in Excel


