Sometimes due to technical issues AutoFilter gets hidden, or even though there is no filter applied, Excel shows that there is. In both cases, it can be difficult to determine whether AutoFilter is enabled or not. In this article we will use VBA in 4 different ways to check.
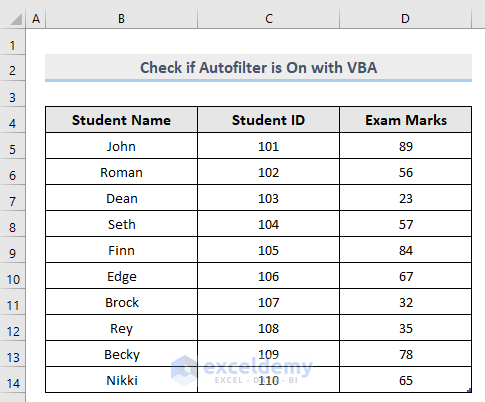
Above is the example dataset that this article will use to illustrate the methods.
Method 1 – Check Whether AutoFilter is Turned On or Off in a Worksheet
Steps:
- Press Alt + F11 on your keyboard or go to the tab Developer -> Visual Basic to open Visual Basic Editor.
- In the pop-up code window, from the menu bar, click Insert -> Module.
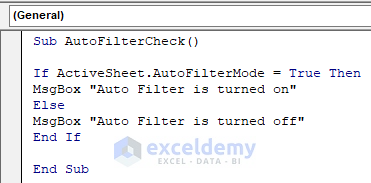
- Copy the following code and paste it into the code window:
Sub AutoFilterCheck()
If ActiveSheet.AutoFilterMode = True Then
MsgBox "Auto Filter is turned on"
Else
MsgBox "Auto Filter is turned off"
End If
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
- Press F5 on your keyboard, or from the menu bar select Run -> Run Sub/UserForm, or just click on the Run icon in the sub-menu bar to run the macro.
After successful code execution, a message box is returned.
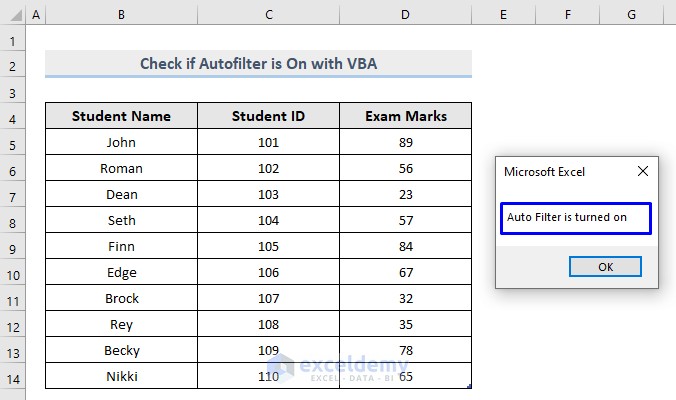
Even though there is no filter arrow visible in the dataset, Excel MsgBox is telling us that the AutoFilter is turned on in this sheet.
VBA Code Explanation
If ActiveSheet.AutoFilterMode = True Then
MsgBox "Auto Filter is turned on"
Else
MsgBox "Auto Filter is turned off"
End IfIf the auto filter mode is true for the active sheet, then the code returns the “Auto Filter is turned on” message in the Excel MsgBox; Otherwise, it throws the “Auto Filter is turned off” message.
Method 2 – Debug VBA Code to Get the Count of AutoFilters in Active Sheet
Another approach to figuring out if AutoFilter is enabled using VBA, is to count how many AutoFilters are active in an Excel sheet by debugging the code. After executing the code, the result will appear in VBA‘s Immediate window.
Steps:
- Same way as before, open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- Copy the following code and paste it into the code window:
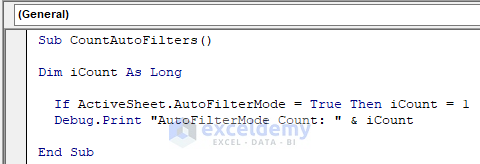
Sub CountAutoFilters()
Dim iCount As Long
If ActiveSheet.AutoFilterMode = True Then iCount = 1
Debug.Print "AutoFilterMode Count: " & iCount
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
- Run the macro in the same way as above.
The result is shown in the image below.
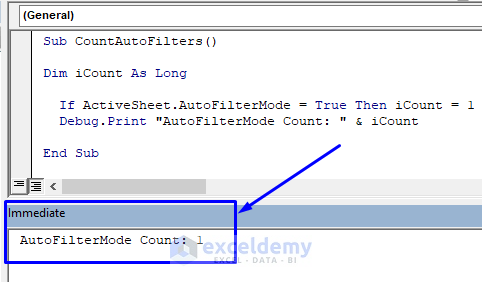
In the Immediate window we have the total count of enabled AutoFilters in the worksheet.
VBA Code Explanation
Dim iCount As LongDeclares the variable.
If ActiveSheet.AutoFilterMode = True Then iCount = 1
Debug.Print "AutoFilterMode Count: " & iCountIf the Autofilter mode is true for the active sheet, then start counting and print the total count.
Method 3 – Check If a Specific Column is Filtered or Not
In addition to checking a worksheet, we can check whether a specific column is filtered or not with VBA.
Steps:
- As shown before, open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- Copy the following code and paste it into the code window:
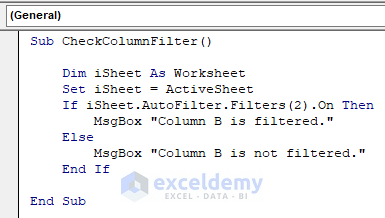
Sub CheckColumnFilter()
Dim iSheet As Worksheet
Set iSheet = ActiveSheet
If iSheet.AutoFilter.Filters(2).On Then
MsgBox "Column B is filtered."
Else
MsgBox "Column B is not filtered."
End If
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
- Run the macro to return the output.
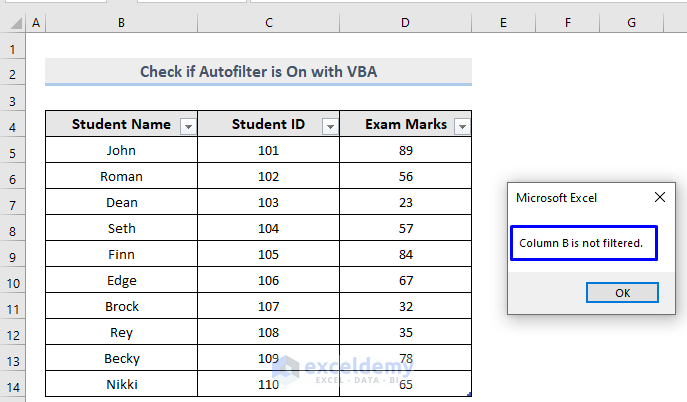
Consider the image above. Even though there is a filter arrow in column B, the macro is telling us that there is not. So, after successful code execution, we can say that column B is not Autofiltered.
VBA Code Explanation
Dim iSheet As WorksheetDeclares the variable for the worksheet.
Set iSheet = ActiveSheetStores the active sheet in the declared variable.
If iSheet.AutoFilter.Filters(2).On Then
MsgBox "Column B is filtered."
Else
MsgBox "Column B is not filtered."
End IfIf the auto filter for Column 2 or Column B is true for the active sheet, then it returns the “Column B is filtered.” message in the Excel MsgBox; Otherwise, it throws the “Column B is not filtered.” message.
Method 4 – Check for Enabled AutoFilter in Excel Workbook
We can also check if Autofilter is enabled throughout an entire Excel workbook.
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- Copy the following code and paste it into the code window:
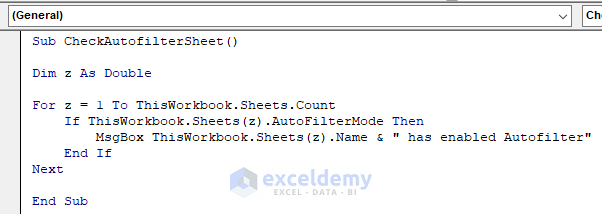
Sub CheckAutofilterSheet()
Dim z As Double
For z = 1 To ThisWorkbook.Sheets.Count
If ThisWorkbook.Sheets(z).AutoFilterMode Then
MsgBox ThisWorkbook.Sheets(z).Name & " has enabled Autofilter"
End If
Next
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
- Run the macro to return the result.
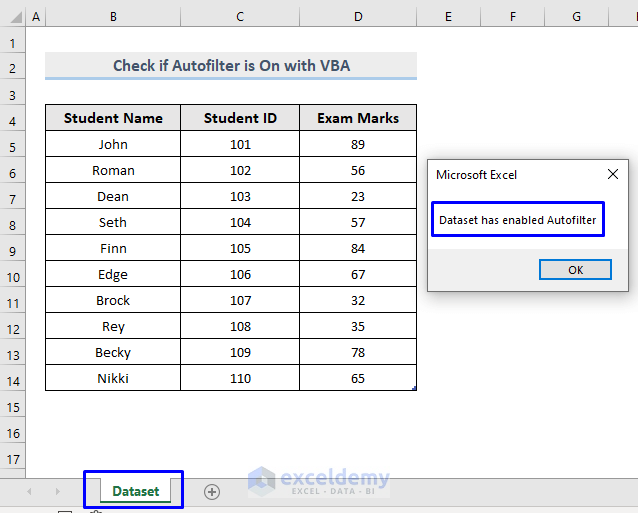
Our workbook has a worksheet named “Dataset”, which the MsgBox is telling us has an AutoFilter enabled. If other spreadsheets within your workbook also have an Autofilter enabled, they will display here too.
VBA Code Explanation
Dim z As DoubleDeclares the variable.
For z = 1 To ThisWorkbook.Sheets.CountStarts looping from the 1st sheet to the total sheet count of the existing workbook.
If ThisWorkbook.Sheets(z).AutoFilterMode Then
MsgBox ThisWorkbook.Sheets(z).Name & " has enabled Autofilter"
End If
NextIf the first sheet has auto filter mode on, then throw the message in the MsgBox and iterate to the next sheet to perform the check. This continues until it reaches the count (or total number of) worksheets in the current workbook.
Read More: Excel VBA: Remove AutoFilter If It Exists
Download Practice Workbook
Related Articles
- VBA to AutoFilter with Multiple Criteria on Same Field in Excel
- VBA Autofilter: Sort Smallest to Largest
- How to Autofilter Values Not Equal to a Certain Value with VBA in Excel


