A ComboBox allows users to select from a list of predefined items. However if the list is too big, It may become difficult to find a required item. We can solve this issue by filtering the items in the ComboBox according to different criteria by using VBA.
How to Open the VBA Macro Editor in Excel
Steps:
- Click on the Developer tab and select Visual Basic. Alternatively, press Alt+F11.
The Visual Basic Editor window will appear.
- To write new code, go to Insert >> Module.
- In the module, write the code.
- Click on the Run button or press the F5 key to run the code.
4 Methods to Create ComboBox and Filter Data in Excel VBA
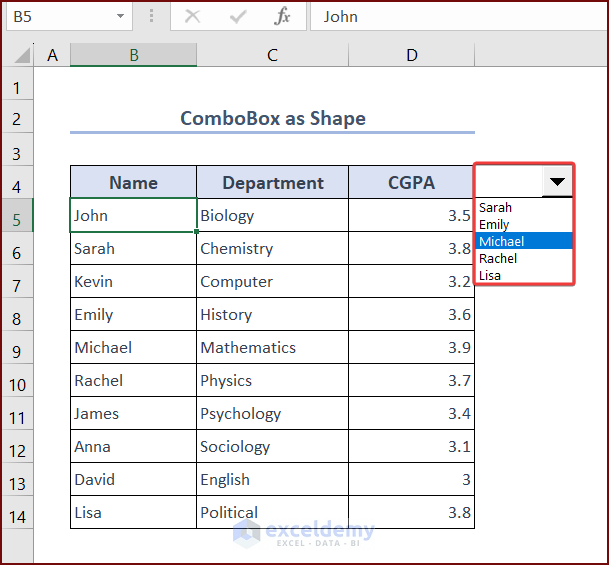
To demonstrate our methods to create a ComboBox and filter data in Excel VBA, we’ll use a sample dataset containing the academic records of ten students. The dataset includes their Names, Departments, and CGPAs. We will create a ComboBox that will show the names of the students. Then, we will filter the ComboBox such that it will show only those students who have a CGPA greater than 3.5.
Method 1 – Using ActiveX Controls and Filter Data
ActiveX Controls are pre-built user interface elements that can be easily added to an Excel worksheet.
Step 1 – Create ActiveX Controls ComboBox
- Go to the Developer tab >> Insert >> Combo Box (ActiveX Controls).
- Create a ComboBox from the plus icon.
- Right-click on the ComboBox and select Properties.
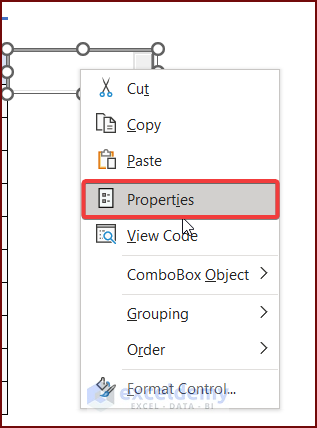
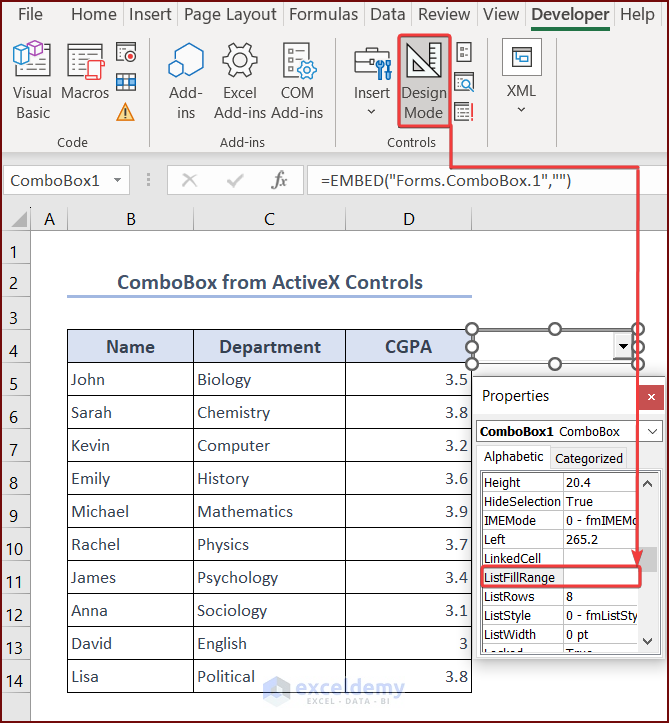
- Set the ListFillRange property to the range of cells that you want to show in the ComboBox dropdown list. Here, ActiveX_Controls_ComboBox!B5:B14.
Note: You can use a named range or a Table name here instead of the cell references.
- Turn off Design Mode from the Developer tab.
The dropdown list showing all the names from B5:B14 appears in the ComboBox.
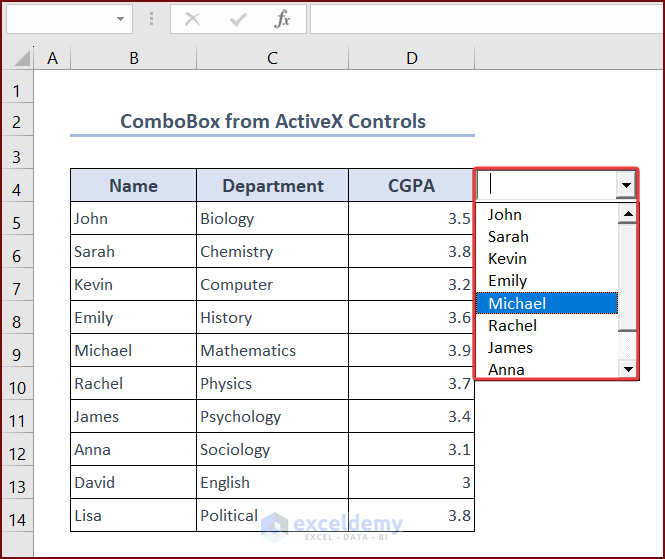
Step 2 – Filter Data from the ActiveX Controls ComboBox
Use the following VBA code to filter data in the ActiveX Controls ComboBox:
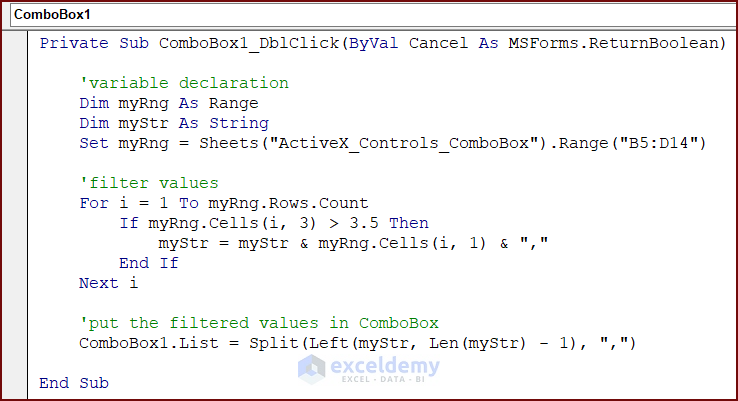
- Turn on Design Mode.
- Clear the ListFillRange Property of the ComboBox.
- Double-click on the ComboBox.
- In the window that opens, enter the following code:
Private Sub ComboBox1_DblClick(ByVal Cancel As MSForms.ReturnBoolean)
'variable declaration
Dim myRng As Range
Dim myStr As String
Set myRng = Sheets("ActiveX_Controls_ComboBox").Range("B5:D14")
'filter values
For i = 1 To myRng.Rows.Count
If myRng.Cells(i, 3) > 3.5 Then
myStr = myStr & myRng.Cells(i, 1) & ","
End If
Next i
'put the filtered values in ComboBox
ComboBox1.List = Split(Left(myStr, Len(myStr) - 1), ",")
End Sub- Return to the main sheet and turn off Design Mode.
- Double-click on the ComboBox to activate the code.
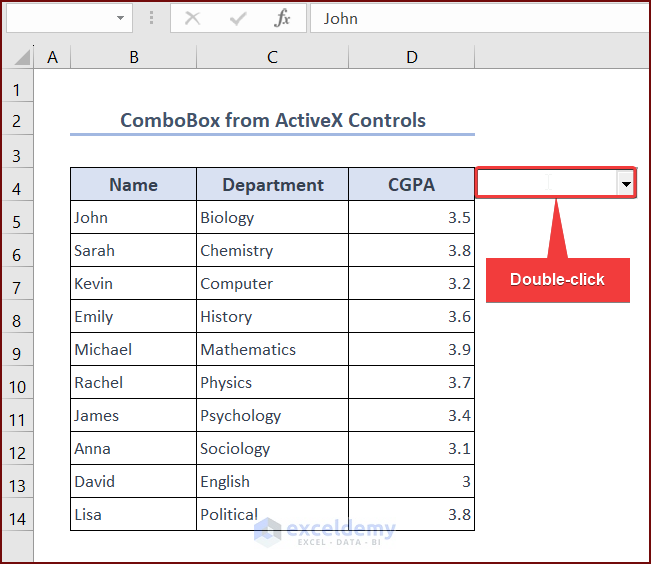
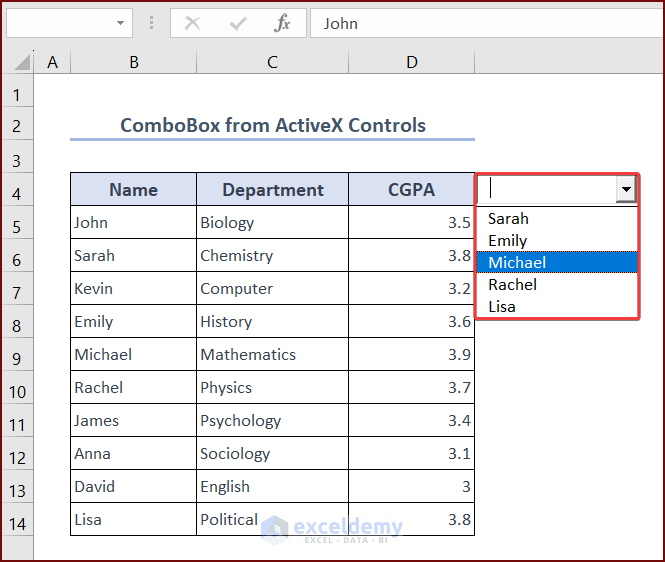
- The dropdown list in the ComboBox now contains only the filtered data (the students with a CGPA of more than 3.5).
VBA Breakdown
Private Sub ComboBox1_DblClick(ByVal Cancel As MSForms.ReturnBoolean)Starts a procedure that runs when the ComboBox1 is double-clicked. The Cancel parameter is a boolean value that determines if the event should be canceled or not.
Dim myRng As Range
Dim myStr As String
Set myRng = Sheets("ActiveX_Controls_ComboBox").Range("B5:D14")These lines declare two variables, myRng and myStr, and then set the value of myRng to a range object that represents cells B5:D14 on the named sheet.
ActiveX_Controls_ComboBox.
For i = 1 To myRng.Rows.Count
If myRng.Cells(i, 3) > 3.5 Then
myStr = myStr & myRng.Cells(i, 1) & ","
End If
Next iThis For loop block loops through each row of the range object myRng, and checks the value of the cell in the third column of the current row. If the value is greater than 3.5, then the value in the first column of that row is added to the string variable myStr followed by a comma.
ComboBox1.List = Split(Left(myStr, Len(myStr) - 1), ",")
End SubSplits the string myStr into an array using the comma character as a delimiter, then assigns the resulting array to the List property of ComboBox1. The Left function is used to get all characters in the string except for the last comma, which is removed by subtracting 1 from the length of the string.
Method 2 – Using a Shape
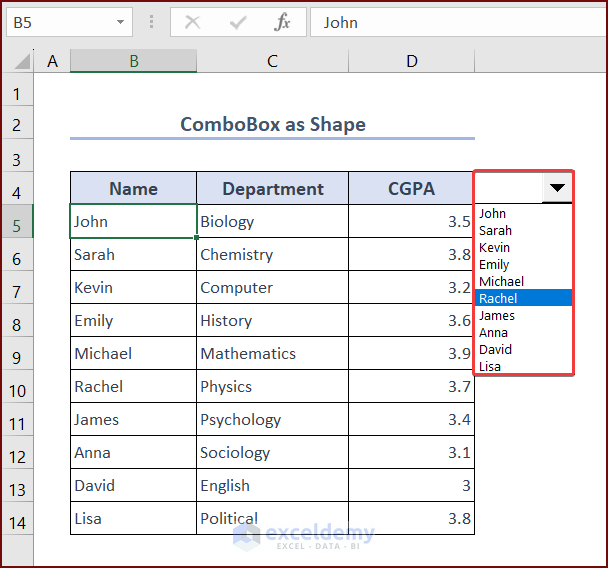
In this method, we will create a ComboBox shape in VBA and add the student names to the dropdown list of the ComboBox. Then we will modify the VBA code to filter the dropdown list so that we can see only those students who have CGPAs of more than 3.5 in the ComboBox.
Step1 – Create the Shape ComboBox
Use the following code to create a ComboBox with Excel VBA:
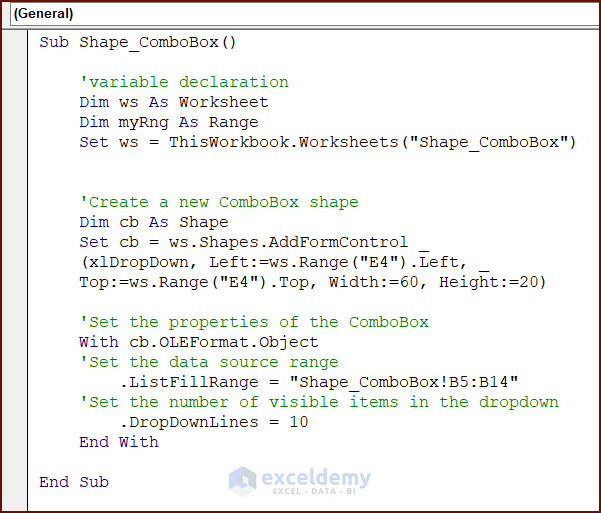
Enter the following code in your VBA Editor and press the Run button or F5 key to run it:
Sub Shape_ComboBox()
'variable declaration
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim myRng As Range
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Shape_ComboBox")
'Create a new ComboBox shape
Dim cb As Shape
Set cb = ws.Shapes.AddFormControl _
(xlDropDown, Left:=ws.Range("E4").Left, Top:=ws.Range("E4").Top, Width:=60, Height:=20)
'Set the properties of the ComboBox
With cb.OLEFormat.Object
'Set the data source range
.ListFillRange = "Shape_ComboBox!B5:B14"
'Set the number of visible items in the dropdown
.DropDownLines = 10
End With
End SubVBA Breakdown
Sub Shape_ComboBox()Declares the start of a new subroutine named Shape_Combobox.
Shape_ComboBox. Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim myRng As Range
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Shape_ComboBox")These lines declare two variables, ws and myRng, and then set the value of ws to the worksheet named Shape_ComboBox within the current workbook.
Dim cb As Shape
Set cb = ws.Shapes.AddFormControl _
(xlDropDown, Left:=ws.Range("E4").Left, Top:=ws.Range("E4").Top, Width:=60, Height:=20)These lines create a new ComboBox shape and set the value of cb to the new shape object. The AddFormControl method of the Shapes object is used to add a new form control to the worksheet, with the type of control being xlDropDown (which represents a ComboBox). The Left, Top, Width, and Height parameters specify the position and size of the new ComboBox, which is positioned at cell E4 in this case.
With cb.OLEFormat.Object
.ListFillRange = "Shape_ComboBox!B5:B14"
.DropDownLines = 10
End With
End SubThis block of code sets the properties of the new ComboBox. The With statement is used to refer to the Object property of the OLEFormat property of the cb shape object. The ListFillRange property is set to the range B5:B14 on the Shape_ComboBox worksheet, which will be used as the data source for the ComboBox. The DropDownLines property is set to 10, which determines the number of visible items in the ComboBox when it is dropped down.
In summary, this VBA code creates a new ComboBox shape on the Shape_ComboBox worksheet and sets its properties, including the data source range and the number of visible items in the dropdown.
Step2 – Filter Data in the Shape ComboBox
Use the following VBA code (modified from the code in the previous method) to filter data in the ComboBox:
Enter the following code in your VBA Editor and press the Run button or F5 key to run the code:
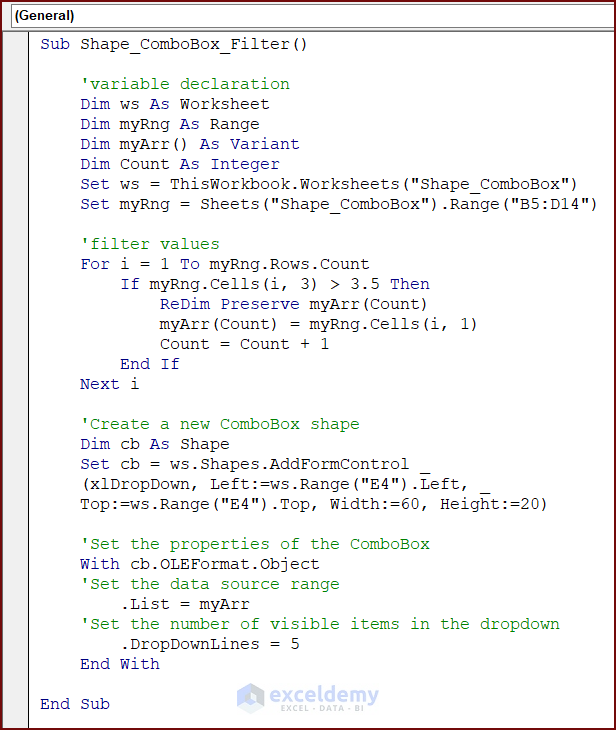
Sub Shape_ComboBox_Filter()
'variable declaration
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim myRng As Range
Dim myArr() As Variant
Dim Count As Integer
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Shape_ComboBox")
Set myRng = Sheets("Shape_ComboBox").Range("B5:D14")
'filter values
For i = 1 To myRng.Rows.Count
If myRng.Cells(i, 3) > 3.5 Then
ReDim Preserve myArr(Count)
myArr(Count) = myRng.Cells(i, 1)
Count = Count + 1
End If
Next i
'Create a new ComboBox shape
Dim cb As Shape
Set cb = ws.Shapes.AddFormControl _
(xlDropDown, Left:=ws.Range("E4").Left, Top:=ws.Range("E4").Top, Width:=60, Height:=20)
'Set the properties of the ComboBox
With cb.OLEFormat.Object
'Set the data source range
.List = myArr
'Set the number of visible items in the dropdown
.DropDownLines = 5
End With
End SubVBA Breakdown
Sub Shape_ComboBox_Filter()Declares the start of a new subroutine named Shape_ComboBox_Filter.
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim myRng As Range
Dim myArr() As Variant
Dim Count As Integer
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Shape_ComboBox")
Set myRng = Sheets("Shape_ComboBox").Range("B5:D14")These lines declare several variables including ws, myRng, myArr, and Count. The ws variable is set to the worksheet named Shape_ComboBox within the current workbook. The myRng variable is set to the range B5:D14 on the same worksheet. The myArr variable is declared as a dynamic array of Variants, which will be used to store the filtered values. The Count variable is used to keep track of the number of filtered values.
For i = 1 To myRng.Rows.Count
If myRng.Cells(i, 3) > 3.5 Then
ReDim Preserve myArr(Count)
myArr(Count) = myRng.Cells(i, 1)
Count = Count + 1
End If
Next iThis block of code loops through each row in the myRng range, and if the value in the third column (column D) is greater than 3.5, it adds the value in the first column (column B) to the myArr array. The ReDim Preserve statement is used to resize the myArr array to accommodate the new value. The Count variable is incremented by 1 to keep track of the number of filtered values.
Dim cb As Shape
Set cb = ws.Shapes.AddFormControl _
(xlDropDown, Left:=ws.Range("E4").Left, Top:=ws.Range("E4").Top, Width:=60, Height:=20)
With cb.OLEFormat.Object
.List = myArr
.DropDownLines = 5
End With
End SubThese lines create a ComboBox as described in the previous step. The filtered values stored in myArr are shown in the ComboBox.
In summary, this VBA code filters a range of cells based on a condition, stores the filtered values in an array, and then creates a new ComboBox shape on the Shape_ComboBox worksheet and sets its properties, including the data source range and the number of visible items in the dropdown.
Method 3 – Using a UserForm
We can easily create a ComboBox in a UserForm, since the ComboBox is available as a control element in the Toolbox of a UserForm. We will add a ComboBox with the list of student names, then filter the list and add it back to the UserForm with a VBA code.
Step1 – Create a ComboBox in a UserForm
- Go to Insert >> UserForm.
- Create a UserForm.
- Select a ComboBox from the Toolbox.
- Press F4 to open the Properties Window.
- Change the properties of the ComboBox. For example, we set the RowSource property to UserForm_ComboBox!B5:B14. So, the ComboBox will show values from cells B5:B14 from the worksheet UserForm_ComboBox.
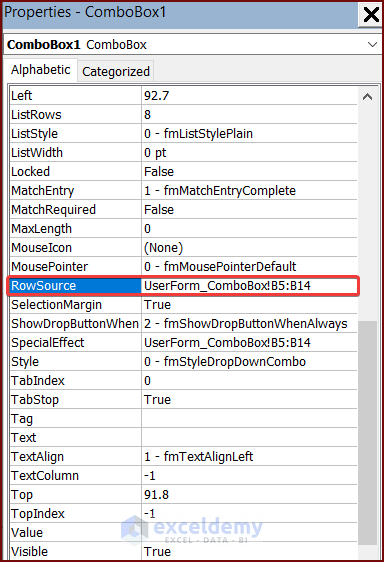
- Run the UserForm to see the results.
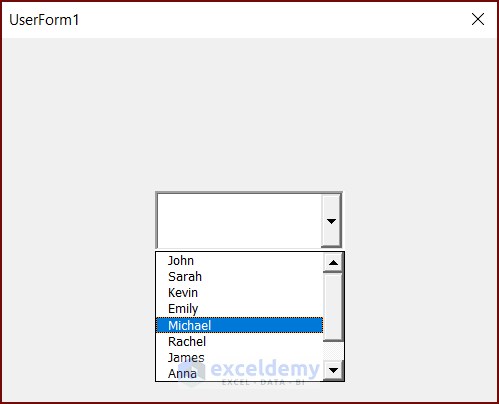
Step2 – Filter the Data
Use this code to filter data in the ComboBox in UserForm:
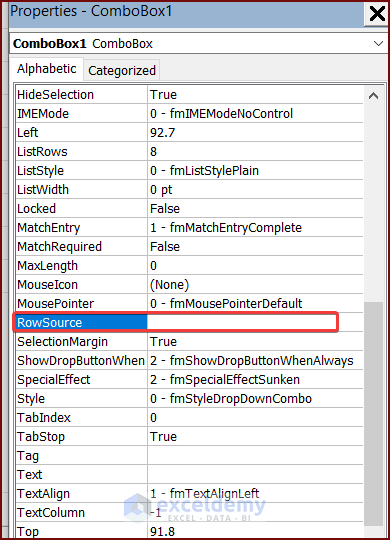
- Clear the RowSource property if a range of cells is specified there.
- Double-click on the UserForm.
- In the new window that opens, enter the following code:
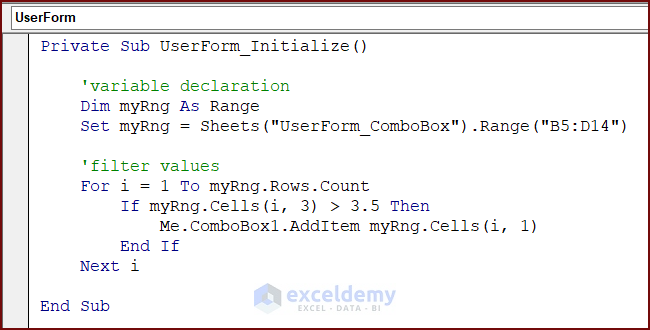
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
'variable declaration
Dim myRng As Range
Set myRng = Sheets("UserForm_ComboBox").Range("B5:D14")
'filter values
For i = 1 To myRng.Rows.Count
If myRng.Cells(i, 3) > 3.5 Then
Me.ComboBox1.AddItem myRng.Cells(i, 1)
End If
Next i
End Sub- Run the code to see the filtered data in the ComboBox.
VBA Breakdown
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()Declares a Sub procedure that is triggered when the UserForm is initialized, i.e., when it is opened.
Dim myRng As Range
Set myRng = Sheets("UserForm_ComboBox").Range("B5:D14")Creates a Range object named myRng that represents a range of cells (B5:D14) in the worksheet UserForm_ComboBox.
For i = 1 To myRng.Rows.Count
If myRng.Cells(i, 3) > 3.5 Then
Me.ComboBox1.AddItem myRng.Cells(i, 1)
End If
Next i
End SubThe For loop iterates through each row in the range myRng and checks if the value in the third column of that row is greater than 3.5. If the value is greater than 3.5, the code adds the corresponding value in the first column of that row to the ComboBox using the AddItem method. The Me keyword refers to the UserForm that contains the ComboBox control. Once the loop has finished, the ComboBox will contain only those items from the first column of the myRng range where the corresponding value in the third column is greater than 3.5.
Method 4 – Using a Dependent ComboBox from a UserForm
We can create a ComboBox which depends on the items of another ComboBox. This is called a dependent ComboBox. Here, we will create two ComboBoxes in the UserForm, then filter data from the independent ComboBox and display the filtered data in the dependent ComboBox.
Step1 – Create the Dependent ComboBox in a UserForm
- Create two ComboBoxes by following Method 3. We will consider the second one as a dependent ComboBox.

Step2 – Filter the Data in the Dependent ComboBox
Use this VBA code to filter data and put it into the dependent ComboBox:
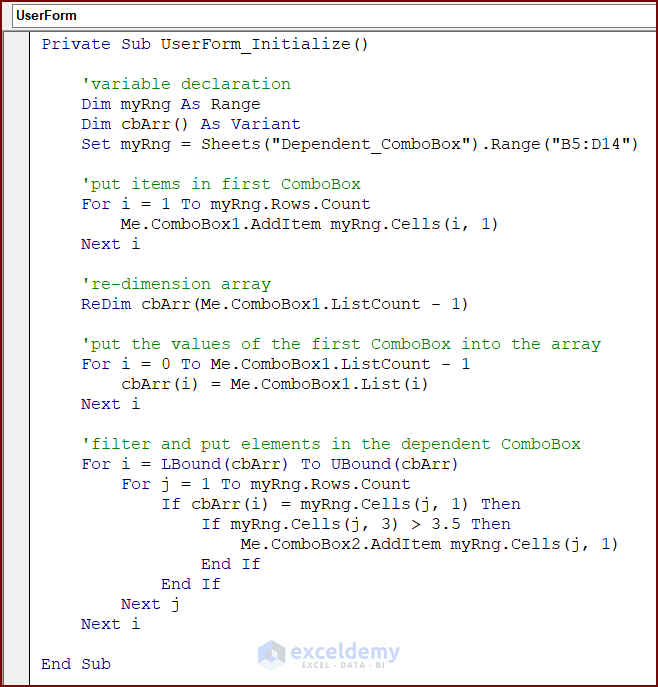
- Double-click on the UserForm.
- In the new window that opens, enter the following code:
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
'variable declaration
Dim myRng As Range
Dim cbArr() As Variant
Set myRng = Sheets("Dependent_ComboBox").Range("B5:D14")
'put items in first ComboBox
For i = 1 To myRng.Rows.Count
Me.ComboBox1.AddItem myRng.Cells(i, 1)
Next i
're-dimension array
ReDim cbArr(Me.ComboBox1.ListCount - 1)
'put the values of the first ComboBox into the array
For i = 0 To Me.ComboBox1.ListCount - 1
cbArr(i) = Me.ComboBox1.List(i)
Next i
'filter and put elements in the dependent ComboBox
For i = LBound(cbArr) To UBound(cbArr)
For j = 1 To myRng.Rows.Count
If cbArr(i) = myRng.Cells(j, 1) Then
If myRng.Cells(j, 3) > 3.5 Then
Me.ComboBox2.AddItem myRng.Cells(j, 1)
End If
End If
Next j
Next i
End Sub- Run the code to see the filtered data in the dependent ComboBox.
VBA Breakdown
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize() Declares an event procedure that is triggered when the user form is initialized.
Dim myRng As Range
Dim cbArr() As VariantThese lines declare two variables: myRng as a Range data type and cbArr as an empty array that can store a variable number of elements of the Variant data type.
Set myRng = Sheets("Dependent_ComboBox").Range("B5:D14")This line sets the value of myRng to a Range object that represents the range of cells from B5:D14 in the Dependent_ComboBox worksheet.
For i = 1 To myRng.Rows.Count
Me.ComboBox1.AddItem myRng.Cells(i, 1)
Next iThis loop adds items to the first ComboBox (ComboBox1) on the UserForm. The items are taken from the first column of the myRng range.
ReDim cbArr(Me.ComboBox1.ListCount - 1)This line resizes the cbArr array to have the same number of elements as there are items in the first ComboBox.
For i = 0 To Me.ComboBox1.ListCount - 1
cbArr(i) = Me.ComboBox1.List(i)
Next iThis loop copies the items from the first ComboBox into the cbArr array.
For i = LBound(cbArr) To UBound(cbArr)
For j = 1 To myRng.Rows.Count
If cbArr(i) = myRng.Cells(j, 1) Then
If myRng.Cells(j, 3) > 3.5 Then
Me.ComboBox2.AddItem myRng.Cells(j, 1)
End If
End If
Next j
Next i
End SubThis loop populates the dependent ComboBox (ComboBox2) with items from the myRng range, filtered by the selected item in the first ComboBox. Specifically, it checks each element of cbArr to see if it matches the value in the first column of the myRng range. If it does, and the value in the third column of the same row is greater than 3.5, then the value from the first column is added to the second ComboBox.
Things to Remember
- Enter property values manually in the ActiveX Controls ComboBox.
- Activate the code in the ActiveX Controls ComboBox by following the appropriate method.
- Choose the correct ComboBox from the proper sheet with the exact name.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can I filter data in a Worksheet based on the selected value in a ComboBox?
Yes, by using the Autofilter command or a pivot table.
2. How do I clear Contents in a ComboBox?
Use the code ComboBox.Clear for clearing the items in a ComboBox. The word ComboBox must be replaced with the name of the ComboBox.
3. How do I handle errors while using ComboBoxes in VBA?
Use error handling codes at the beginning of the code such as On Error Resume Next
Download Practice Workbook
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!


