Method 1 – Embed VBA to Copy One Worksheet to Another Excel Workbook and Rename It
Steps:
- Press Alt + F11 on your keyboard or go to the tab Developer -> Visual Basic to open Visual Basic Editor.
- In the pop-up code window, from the menu bar, click Insert -> Module.
- Following code and paste it into the code window.
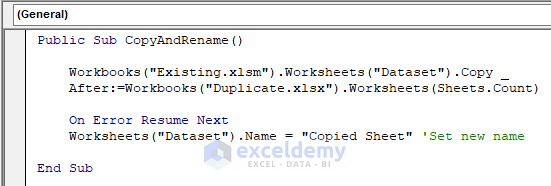
Public Sub CopyAndRename()
Workbooks("Existing.xlsm").Worksheets("Dataset").Copy After:=Workbooks("Duplicate.xlsx").Worksheets(Sheets.Count)
On Error Resume Next
Worksheets("Dataset").Name = "Copied Sheet" 'Set new name
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
Here,
- “Copied Sheet” is the new sheet name for the copied dataset sheet. You can rename it with any name that you want.
- Press F5 on your keyboard or select Run -> Run Sub/UserForm. You can also click on the small Play icon in the sub-menu bar to run the macro.
Look at the following image.
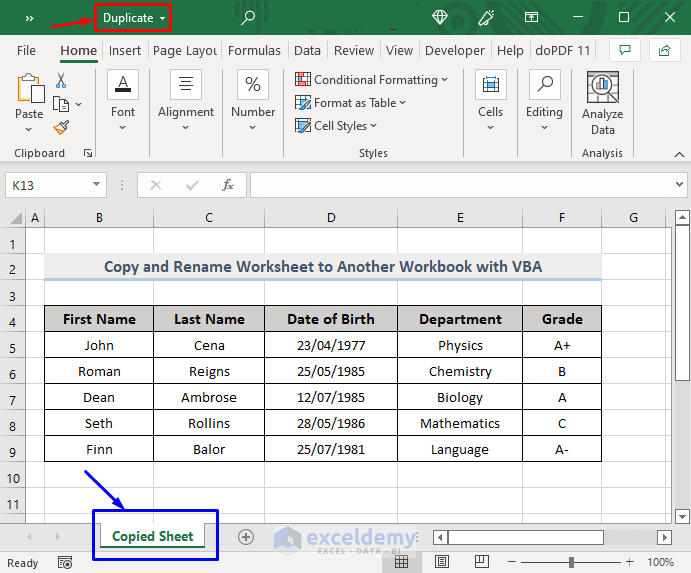
The Dataset sheet from the Existing workbook is now copied in the sheet named Copied Sheet sheet in the Duplicate workbook.
Method 2 – VBA Macro to Duplicate Worksheet to Another Workbook and Rename It by User
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- Copy the following code and paste it.
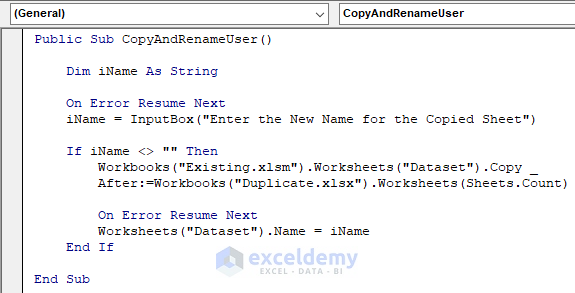
Public Sub CopyAndRenameUser()
Dim iName As String
On Error Resume Next
iName = InputBox("Enter the New Name for the Copied Sheet")
If iName <> "" Then Workbooks("Existing.xlsm").Worksheets("Dataset").Copy After:=Workbooks("Duplicate.xlsx").Worksheets(Sheets.Count)
On Error Resume Next
Worksheets("Dataset").Name = iName
End If
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
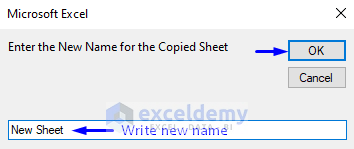
- Run the code as shown above. A pop-up input box will ask for a new name.
- Enter the name you want your copied sheet to have (we renamed our sheet as New Sheet).
- Press OK.
Notice in the image below.
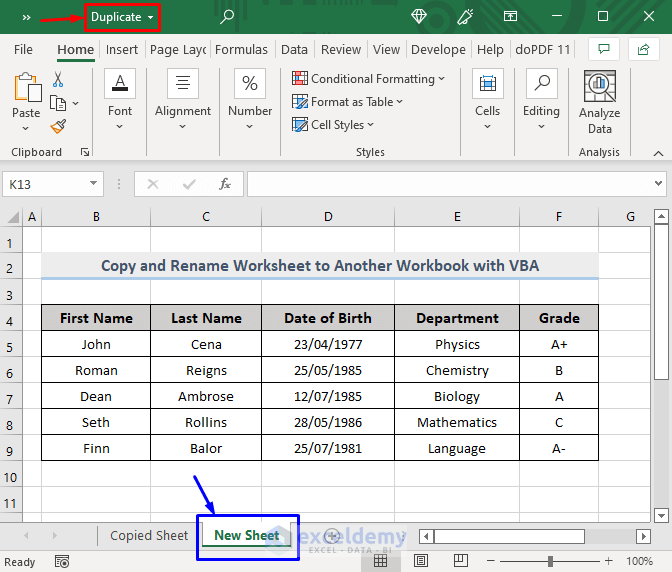
A newly inserted sheet named New Sheet is in the Duplicate workbook.
Method 3 – Macro to Copy Worksheet and Rename Based on Cell Value in Excel
Steps:
- Select the cell based on what you want to rename the sheet to make it the active cell. For instance, you want to rename the copied sheet with the name “Dean” which is in Cell B7. Make Cell B7 the active cell.
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- In the code window, copy the following code and paste it.
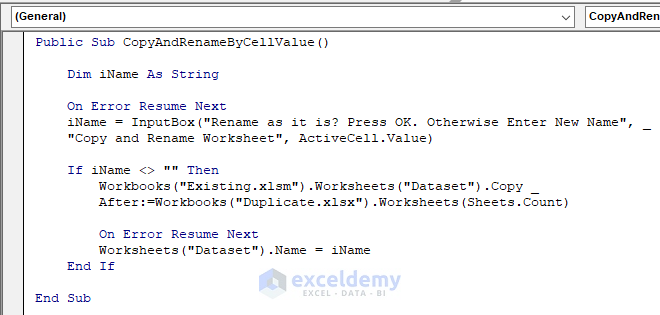
Public Sub CopyAndRenameByCellValue()
Dim iName As String
On Error Resume Next
iName = InputBox("Rename as it is? Press OK. Otherwise Enter New Name", "Copy and Rename Worksheet", ActiveCell.Value)
If iName <> "" Then
Workbooks("Existing.xlsm").Worksheets("Dataset").Copy After:=Workbooks("Duplicate.xlsx").Worksheets(Sheets.Count)
On Error Resume Next
Worksheets("Dataset").Name = iName
End If
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
- Run this piece of code and look at the following picture.
- Value from the cell (Cell B7) that we had as our active cell, Dean, is automatically predicted as the new name.
- Press OK.
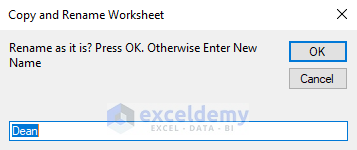
The result can be seen in the picture below.
There is a new sheet named Dean in the Duplicate workbook.
Method 4 – Insert VBA Code to Duplicate Spreadsheet and Rename It Specified by Cell Reference
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- Copy the code and paste it into the code window.
Public Sub CopyAndRenameByCellRef()
Dim iSheet As Worksheet
Set iSheet = ActiveSheet
Workbooks("Existing.xlsm").Worksheets("Dataset").Copy After:=Workbooks("Duplicate.xlsx").Worksheets(Sheets.Count)
If iSheet.Range("B4").Value <> "" Then
On Error Resume Next
Worksheets("Dataset").Name = iSheet.Range("B4").Value
End If
iSheet.Activate
End SubYour code is now ready to run.
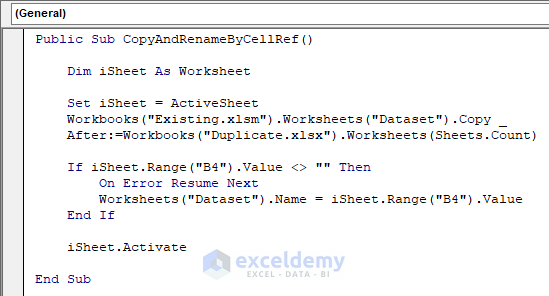
- Run this code. This piece of code holds the cell reference number B4 and Cell B4 has the value First Name.
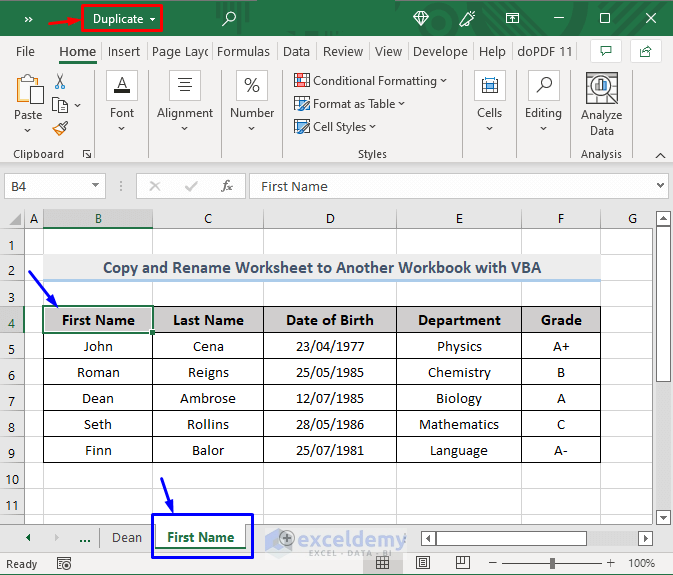
This image shows us that the Duplicate workbook now has the copied sheet with a new First Name.
Method 5 – Check Whether the Workbook is Close or Open; Copy the Sheet and Rename it in Excel
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- Copy the code and paste it into the code window.
Sub CopyAndRenameSheetToWorkbook()
Dim iFile
'To check whether the workbook is open or not
iFile = WorkbookOpenOrClose("H:\ExcelDemy\Excel Folder\Existing.xlsm")
If iFile = True Then
MsgBox "File is Open"
Else
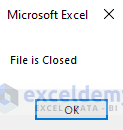
MsgBox "File is Closed"
End If
'To open the workbook if closed
If iFile = False Then
Workbooks.Open FileName:="H:\ExcelDemy\Excel Folder\Existing.xlsm"
End If
'To copy the worksheet Dataset to Duplicate workbook after the sheet First Name
Sheets("Dataset").Copy After:=Workbooks("Duplicate.xlsx").Sheets("First Name")
'To assign the new name via inputbox to rename the copied sheet
Sheets(Sheets.Count).Name = InputBox("Rename the Copied Sheet")
End Sub
'This function checks whether the workbook is open or not.
'If open, returns True. If close, returns False.
'Else, capture the error number of occured run-time error.
Function WorkbookOpenOrClose(FileName As String)
Dim iFreeFile As Integer
Dim iError As Integer
On Error Resume Next 'To turn off error checking
iFreeFile = FreeFile() 'To get a free file number by the inbuilt function
'To open FileName For Input Lock Read As #iFreeFile
'To open the file and lock it
Close iFreeFile 'To close the file
iError = Error 'To capture the error number
On Error GoTo 0 'To turn on error checking
'To Find which error happened
Select Case iError
'No error found
'File is closed
Case 0: WorkbookOpenOrClose = False
'Error message for "Permission Denied"
'File is already opened by another user
Case 70: WorkbookOpenOrClose = True
'Another error occurred
'To capture the error number for further action
Case Else: Error iError
End Select
End FunctionYour code is now ready to run.
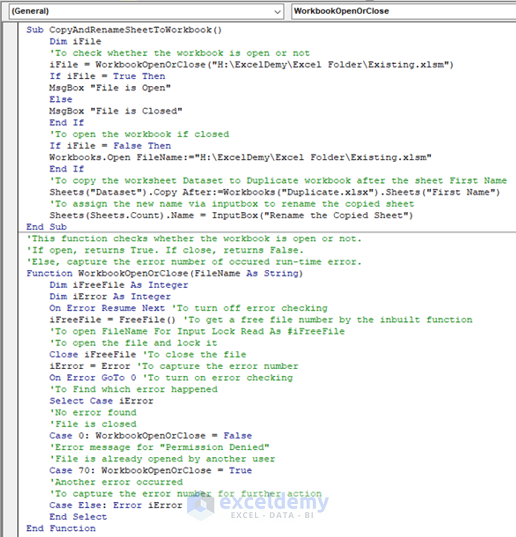
- Run this code.
- A pop-up message box will appear, showing you the result of whether your file is open or closed.
- Press OK.
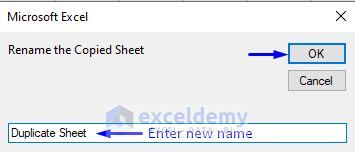
- Another pop-up input box will appear, asking you for a new name.
- Enter the name you want your copied sheet to have (we renamed our sheet as Duplicate Sheet).
- Press OK.
The result is shown in the picture below.
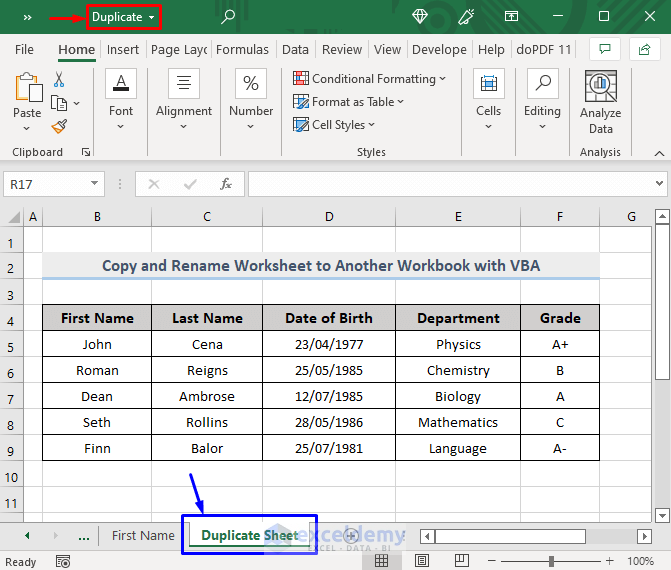
You got the copied Dataset sheet in the Duplicate workbook with the sheet name Duplicate Sheet.
Things to Remember
- Methods 1 to 4 require your workbooks to be opened. When executing the macro codes shown in those methods, don’t forget to keep both the source and destination workbooks open.
- While your workbooks are saved, write the file name and the file type inside the code. When the workbooks are not saved, then write only the file name without the type of the file. For example, if your workbook is saved, write “Duplicate.xlsx”; if the workbook is not saved, write “Duplicate” inside the code.
Download Workbook
You can download the free practice Excel workbook from here.
Related Articles
- Excel VBA: Copy Worksheet to Another Workbook Without Opening
- VBA to Copy Excel Worksheet to Another Workbook without Formulas


