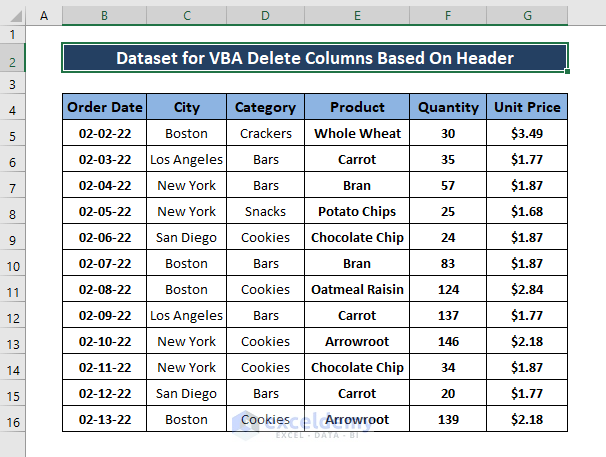
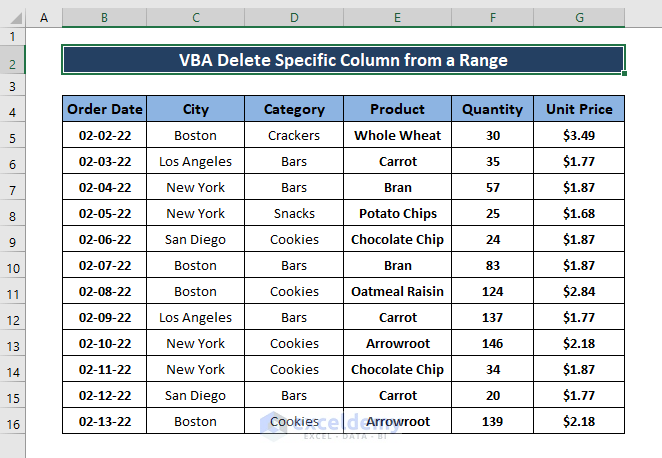
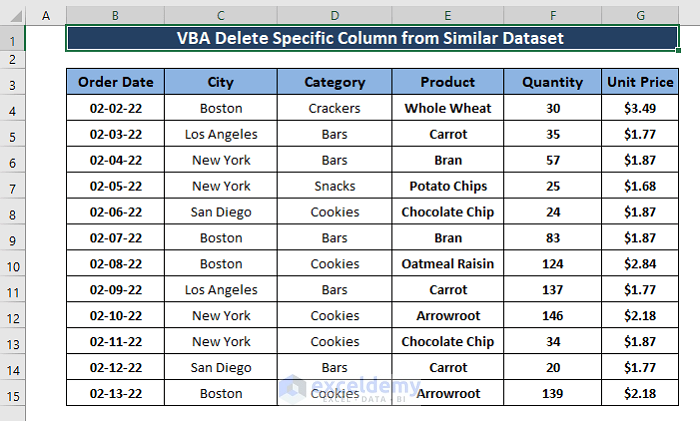
The sample dataset showcases sold Products, Order Date, City, Category, Quantity, and Unit Price. To delete columns:
Opening Microsoft Visual Basic and Entering a Code in the Module
There are 3 ways to open the Microsoft Visual Basic window.
Using Keyboard Shortcuts
- Press ALT+F11.
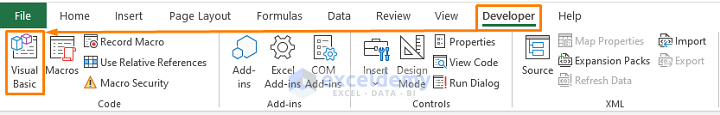
Using the Developer Tab
- Go to the Developer tab > Select Visual Basic.
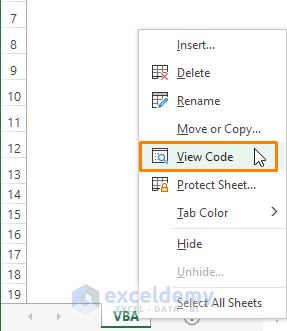
Using the Worksheet Tab
- Go to any worksheet, right-click it > Choose View Code.
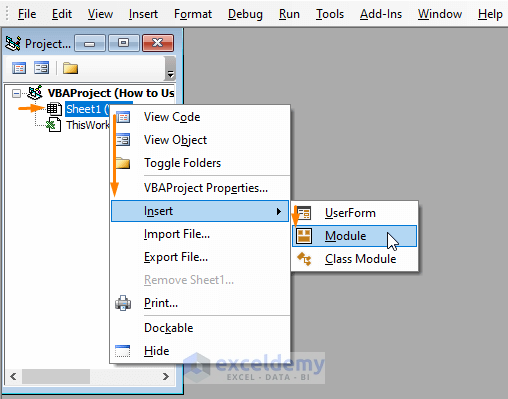
There are 2 ways to insert a Module in Microsoft Visual Basic window,
- After opening the Microsoft Visual Basic window, select a worksheet > Right-click it > Select Insert > Choose Module.
- You can also select Insert > Choose Module.
Method 1 – Excel VBA to Delete Specific Column from a Range Based on Header
The City column is no longer needed. To delete it:
- Open Microsoft Visual Basic and insert a Module.
- Enter the following code.
Sub Delete_Specifc_Column()
Set Data = Range("B4:G16")
For Each cell In Data
If cell.Value = "City" Then cell.EntireColumn.Delete
Next
End Sub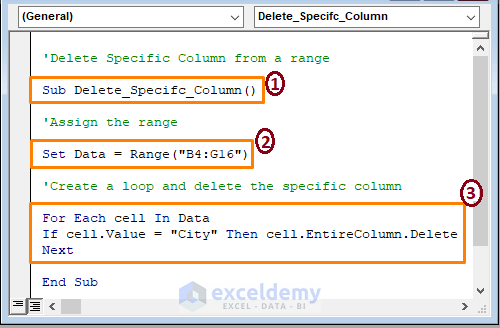
In the code,
1 – Start the macro procedure by declaring the Sub name.
2 – Assign the data to B4:G16.
3 – Create a loop and assign the cell value to a specific cell name (City). Check the cell values in B4:G16 and delete matched columns.
- Press F5 to run the macro.
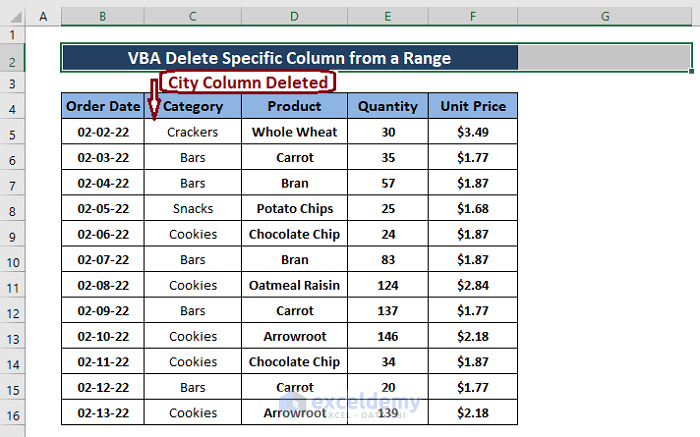
- Go back to the workbook.
The column is deleted.
Read More: VBA Macro to Delete Columns Based on Criteria in Excel
Method 2 – Deleting Similar Columns from All Worksheets Using VBA
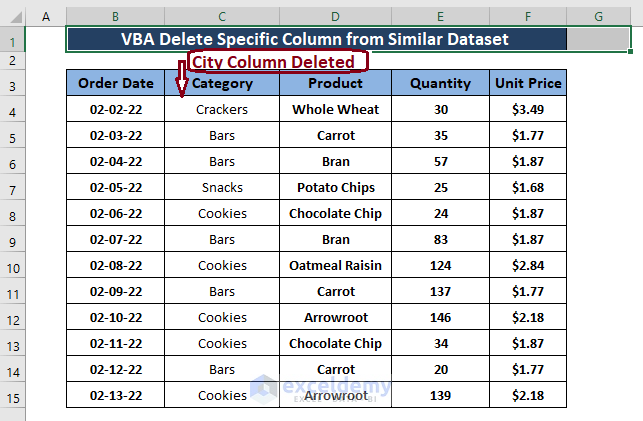
To delete the City column:
- Open Microsoft Visual Basic and insert a Module.
- Enter the following code.
Option Explicit
Sub Delete_SPColumn_fromAllWS()
Dim wrksht As Worksheet
Dim Rng As Range
For Each wrksht In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets
Do
Set Rng = wrksht.Rows(3).Find(What:="City", LookIn:=xlValues, lookat:=xlPart)
If Not Rng Is Nothing Then
Rng.EntireColumn.Delete
End If
Loop While Not Rng Is Nothing
Next
End Sub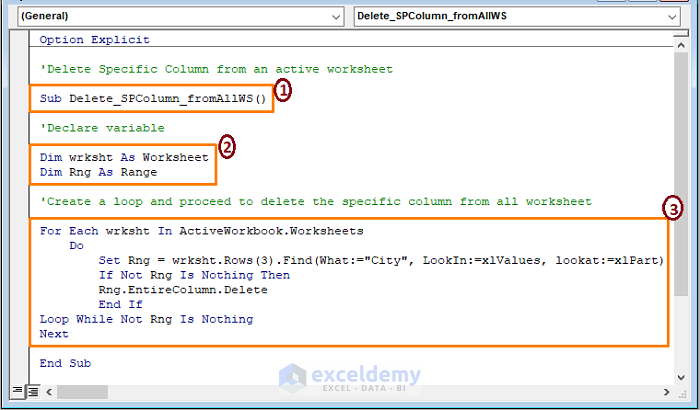
In the code:
1 – Start the macro code declaring the Sub name.
2 – Declare the variables as Worksheet and Range.
3 – Create a loop in which the macro finds the City column in row 3 and deletes it. The macro checks the other worksheets and matches the column name (City) in row 3. If a similar column is found at a similar position, it will be deleted.
- Press F5 to run the macro.
This is the output.
Method 3 – Using VBA to Delete a Specific Column from a Specific Worksheet
- Open Microsoft Visual Basic and insert a Module.
- Enter the following code.
Option Explicit
Sub Delete_SPColumn_fromSPWS()
Dim i As Long, cell As Long
cell = Cells(4, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
With Sheets("Sale").Cells(4, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
For i = cell To 1 Step -1
If InStr(Cells(4, i), "City") > 0 Then
Cells(4, i).EntireColumn.Delete
End If
Next i
End With
End Sub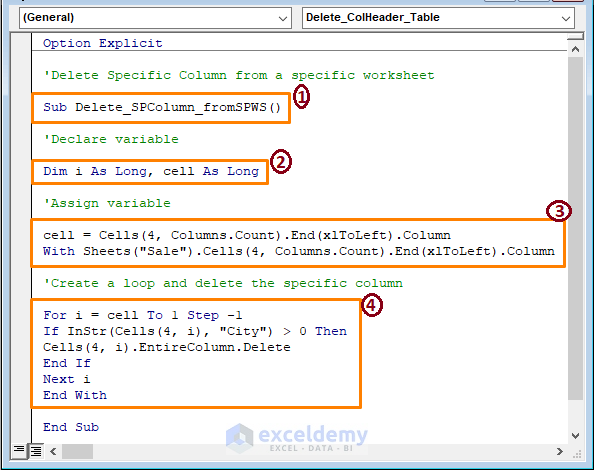
In the code:
1 – Start the macro procedure declaring the Sub name.
2 – Declare the variables as Long.
3 – Assign the cell variable from a particular position (row 4 and iterative column). Assign a specific worksheet (Sale).
4 – Create a loop with the VBA InStr function to search the City column in the assigned worksheet. VBA deletes the column using a delete command.
The VBA InStr function takes multiple strings. You can delete multiple column names. Here, only the City column was deleted.
- Press F5 to run the macro.
- Go back to the workbook.
This is the output.
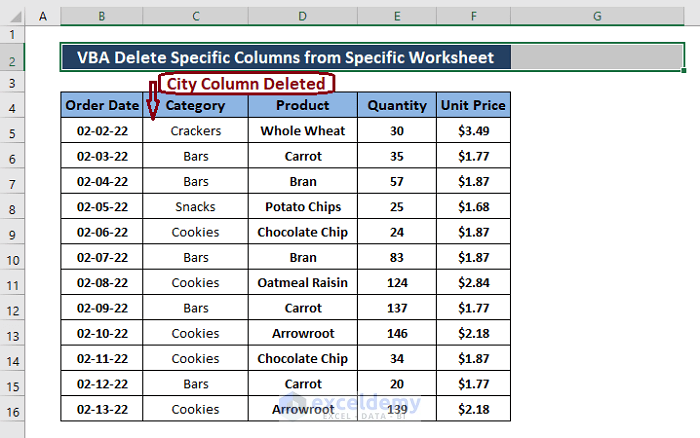
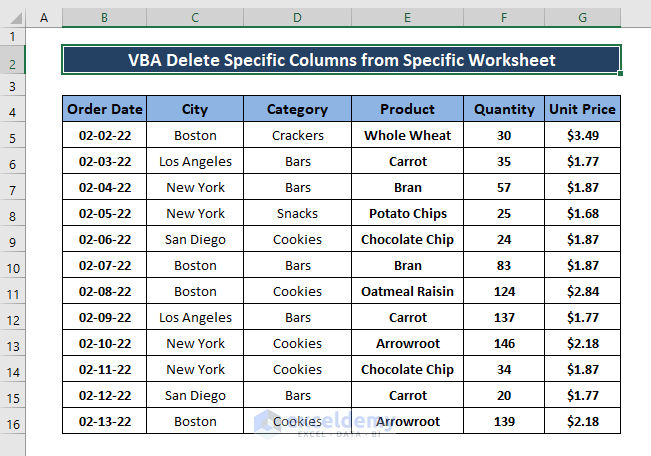
Method 4 – Deleting Assigned Columns from the Active Worksheet
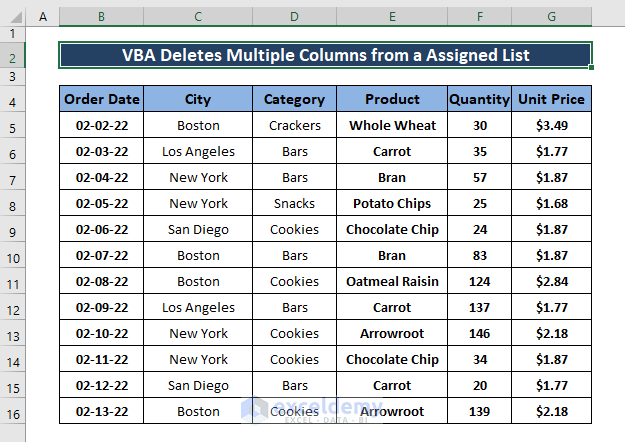
To delete the City and Category columns:
- Open Microsoft Visual Basic and insert a Module.
- Enter the following code.
Sub Delete_MultipleCol_List()
Dim i As Integer
For i = 1 To 6 Step 1
Select Case Cells(4, i).Value
Case "City", "Category"
Cells(4, i).EntireColumn.Delete
End Select
Next i
End Sub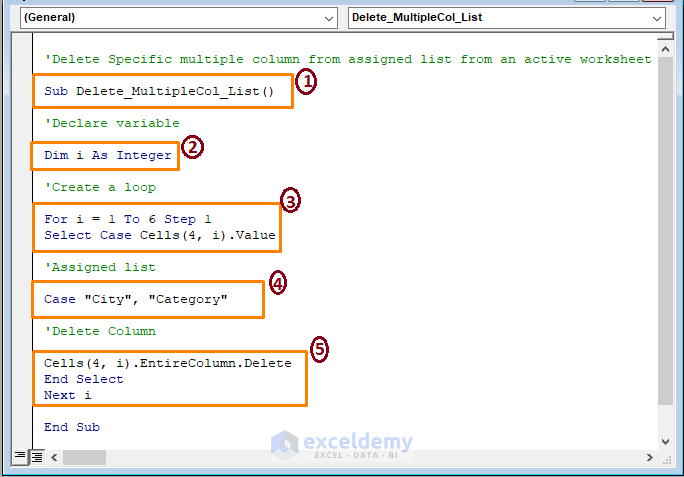
In the code:
1 – Start the macro setting the Sub name.
2 – Declare the variable as Integer.
3 – Create a loop of 6 iterations (6 columns in the dataset). It starts from row 4.
4 – The VBA Case assigns the column names (City and Category).
5 – Delete the assigned columns.
- Go back to the workbook.
- Pressing F5 for the 1st time deletes the 1st assigned column (City).
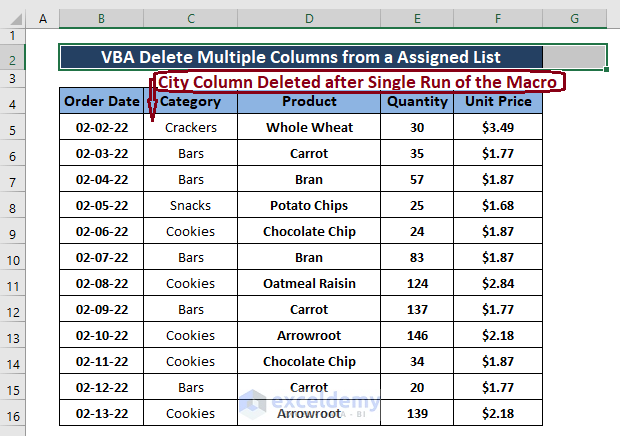
- To delete the 2nd assigned column, press F5 again. The macro deletes the 2nd assigned column.
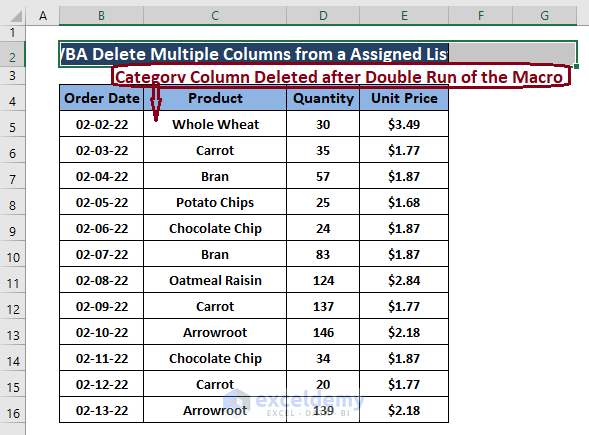
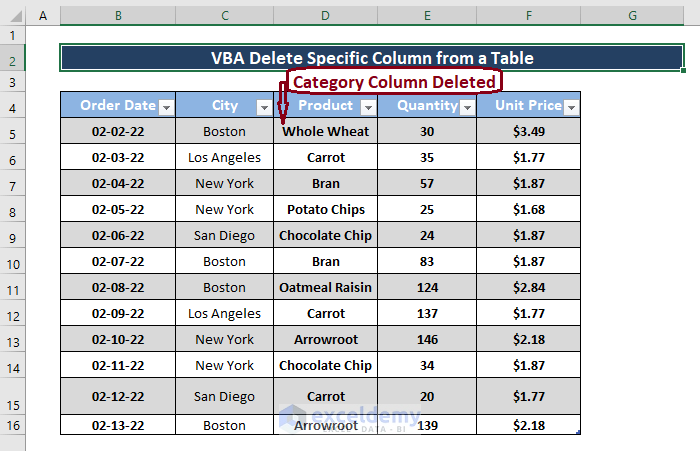
Method 5 – Deleting a Specific Column from a Table
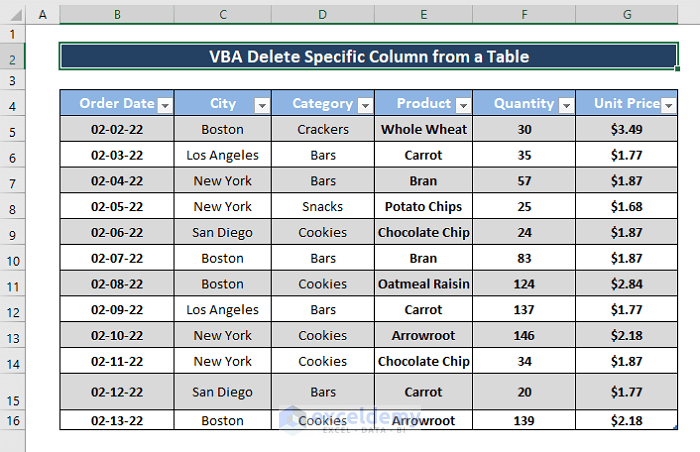
- Open Microsoft Visual Basic and insert a Module.
- Enter the following code.
Sub Delete_ColHeader_Table()
Dim wrkTable As ListObject
Dim wrkSheet As Worksheet
Dim i As Integer
Dim colNum As String
Set wrkTable = ActiveSheet.ListObjects("Table1")
Set wrkSheet = Sheet4
colNum = "Category" 'case sensitive name
For i = 1 To wrkTable.ListColumns.Count
With wrkSheet
If wrkTable.ListColumns(i).Name = colNum Then
wrkTable.ListColumns(i).Delete
Exit For
End If
End With
Next i
End Sub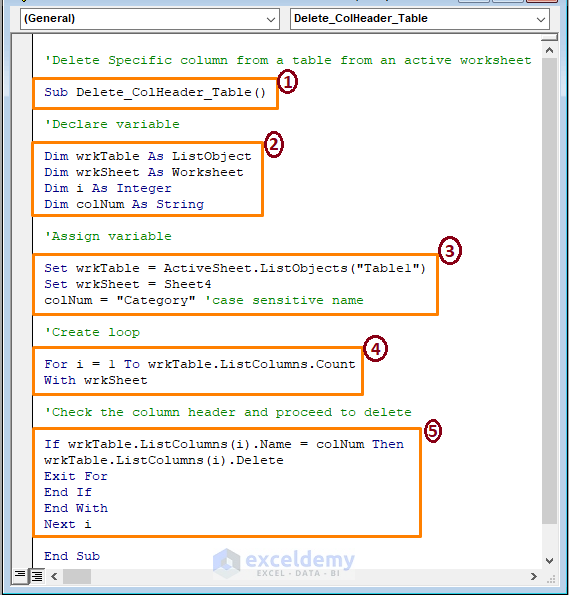
In the code:
1 – Start the macro by setting the Sub name.
2 – Declare the variables as ListObject, Worksheet, Integer, and String.
3 – Assign variables: wrkTable to Table1, wrkSheet to Sheet4 and colNum to Category.
4 – Create a loop to count the Table columns.
5 – Delete the column that matches the colNum.
- Press F5 to run the macro.
- Go back to the workbook.
This is the output.
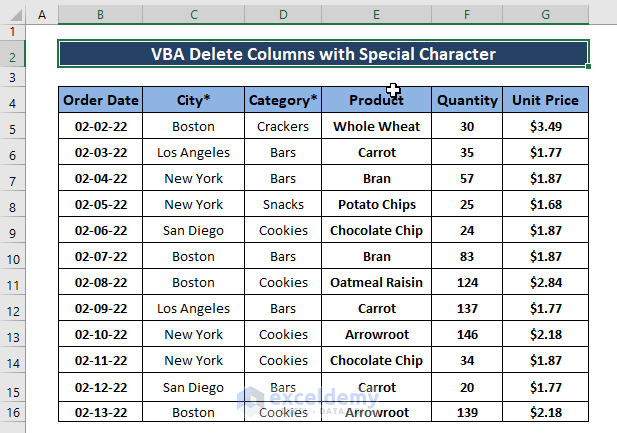
Method 6 – Using VBA to Delete Multiple Columns
Use an asterisk (*) to name one or two columns.
- Open Microsoft Visual Basic and insert a Module.
- Enter the following code.
Sub Delete_columns_withSPChrctr()
For i = ActiveSheet.Columns.Count To 1 Step -1
If InStr(1, Cells(4, i), "*") Then Columns(i).EntireColumn.Delete
Next i
End Sub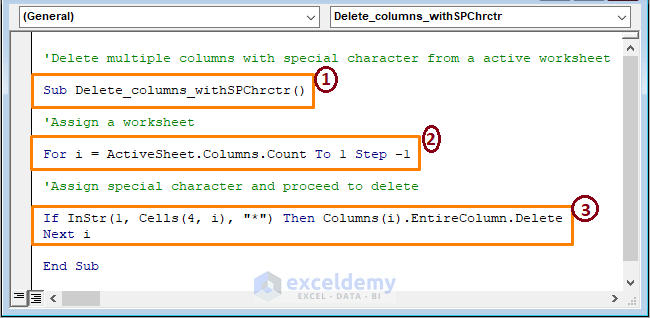
In the code:
1 – Start the macro by setting the Sub name.
2 – Assign the active worksheet to count columns.
3 – The VBA InStr function searches for the asterisk (*) in the column headers. After finding a match, VBA deletes the column.
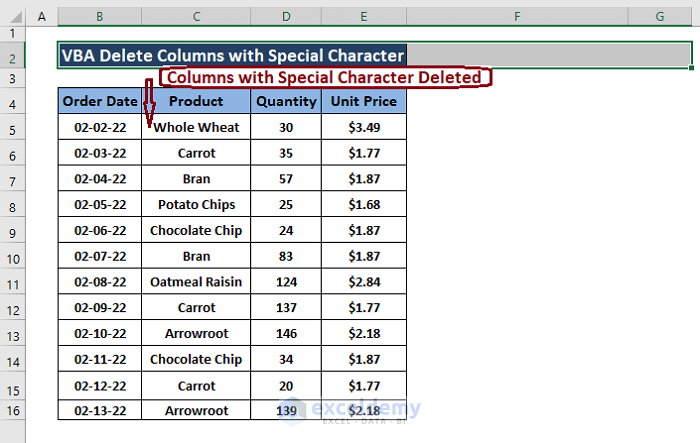
- Press F5 to run the macro.
- Go back to the worksheet.
This is the output.
Read More: How to Delete Multiple Columns by Number Using VBA in Excel
Download Excel Workbook


