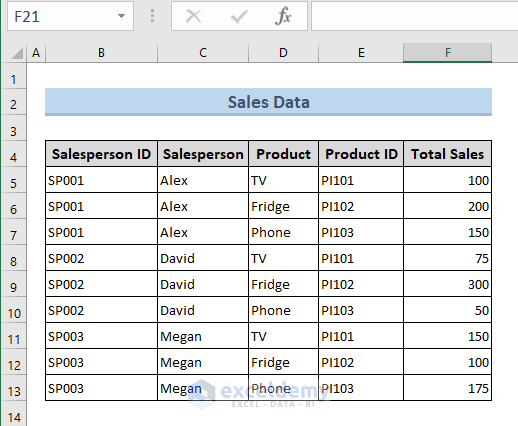
The sample dataset contains the sales data of a certain showroom.
Example 1 – Finding Only First Cell Address Based on Value
By default, find.Address returns the first cell address that contains the value we’re looking for. We will show you examples where we need to find the cell address that contains a certain Integer type value and String type value in the worksheet.
1.1 Finding Cell Address Based on Integer Value
See the following image to get an overview of what we’re doing to find out the cell address of an Integer value.
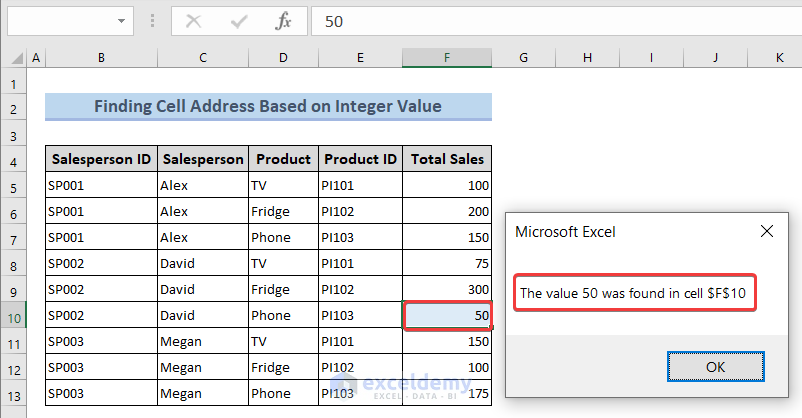
We will look for the cell address of a Total Sales value. Note that, the Total Sales values are Integer.
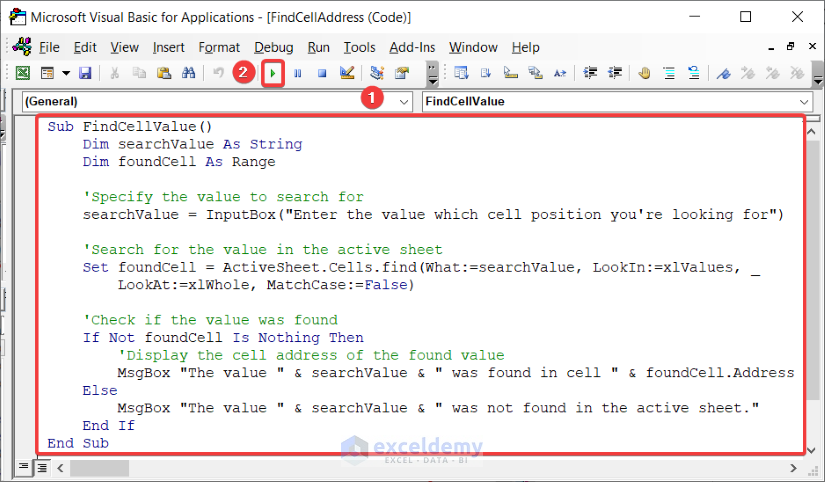
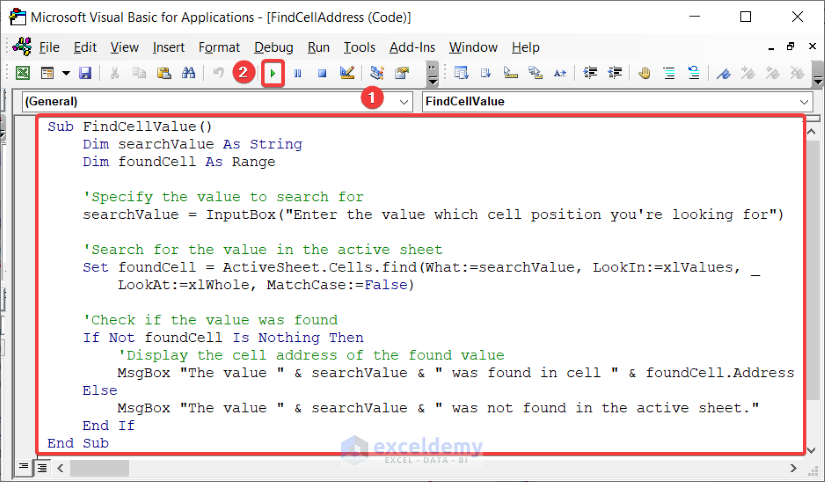
Sub FindCellValue()
Dim searchValue As String
Dim foundCell As Range
'Specify the value to search for
searchValue = InputBox("Enter the value which cell position you're looking for")
'Search for the value in the active sheet
Set foundCell = ActiveSheet.Cells.find(What:=searchValue, LookIn:=xlValues, _
LookAt:=xlWhole, MatchCase:=False)
'Check if the value was found
If Not foundCell Is Nothing Then
'Display the cell address of the found value
MsgBox "The value " & searchValue & " was found in cell " & foundCell.Address
Else
MsgBox "The value " & searchValue & " was not found in the active sheet."
End If
End SubCode Breakdown:
Sub FindCellValue()This statement defines the name of the subroutine.
Dim searchValue As String
Dim foundCell As RangeThese statements declare variables searchValue as a string to store the value to search for and variable foundCell as a range to store the cell address of the found value.
searchValue = InputBox("Enter the value which cell position you're looking for")This statement prompts the user to enter the value to search for using the InputBox function and stores the value in the searchValue.
Set foundCell = ActiveSheet.Cells.find(What:=searchValue, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, MatchCase:=False)This statement searches for the value in the active sheet using the find method of the cells object. The what parameter specifies the value to search for, LookIn specifies where to look(here, xlValues specifies to search in cell values), LookAt specifies how to look (here, xlWhole specifies to search for an exact match) and MatchCase specifies whether to match the case of the search value.
If Not foundCell Is Nothing Then
MsgBox "The value " & searchValue & " was found in cell " &
foundCell.Address
Else
MsgBox "The value " & searchValue & " was not found in the active sheet."
End IfThis block of statement checks if the value was found using the Not operator to nullify the Nothing value returned by the find method if no match is found. If the value was found, the address of the found cell is displayed using MsgBox function. If the value was not found, a message would be displayed that the value was not found.
End SubThe sub procedure ends.
When we run the macro by clicking the Run button, we’ll get output like this:
If the value that we are searching for does not exist in the worksheet, the output will be like this:
1.2 Getting First Cell Address Based on String Value
We will find out the cell address of a string type data. To demonstrate this, we’ll search for a name that exists under the Salesperson header. The code is:
Code Breakdown:
The code breakdown is exactly the same as the breakdown we have shown in section 1.1.
If we run the macro by clicking on the Run button, we’ll get output like this:
And if the value doesn’t exist in the worksheet, then we’ll get output like shown in the following video.
Example 2 – Extracting All Cell Addresses Based on Repeated Values
By default, the find.address method returns the address of the first cell where that information is foundIf the dataset contains repeating values, we won’t get all the cells’ addresses. We may use the Do…Loop statement to get all the cells’ addresses.
2.1. Finding All Cell Addresses of Duplicate Integer Value
See the following image to get an overview.
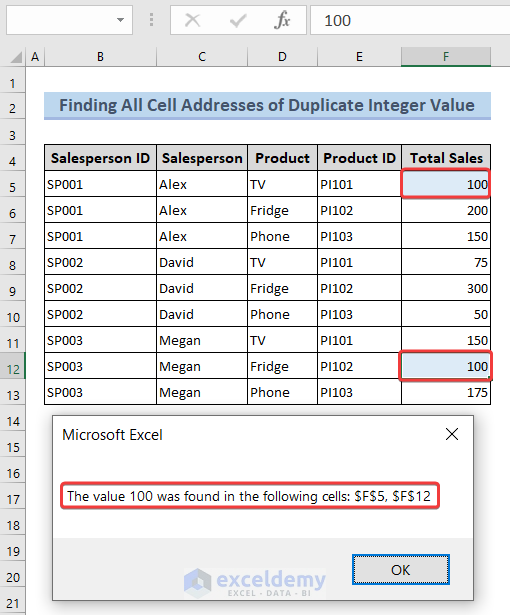
We are looking for integer values that may appear multiple times in the dataset. For example, we have 100 two times. To know the addresses of the integer value, we’ll use this code.
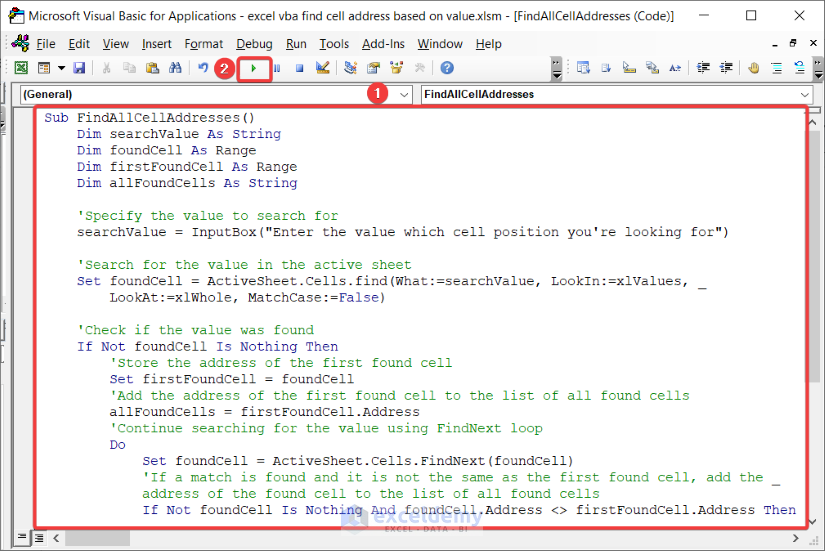
Sub FindAllCellAddresses()
Dim searchValue As String
Dim foundCell As Range
Dim firstFoundCell As Range
Dim allFoundCells As String
'Specify the value to search for
searchValue = InputBox("Enter the value which cell position you're looking for")
'Search for the value in the active sheet
Set foundCell = ActiveSheet.Cells.find(What:=searchValue, LookIn:=xlValues, _
LookAt:=xlWhole, MatchCase:=False)
'Check if the value was found
If Not foundCell Is Nothing Then
'Store the address of the first found cell
Set firstFoundCell = foundCell
'Add the address of the first found cell to the list of all found cells
allFoundCells = firstFoundCell.Address
'Continue searching for the value using FindNext loop
Do
Set foundCell = ActiveSheet.Cells.FindNext(foundCell)
'If a match is found and it is not the same as the first found cell, add the _
address of the found cell to the list of all found cells
If Not foundCell Is Nothing And foundCell.Address <> firstFoundCell.Address Then
allFoundCells = allFoundCells & ", " & foundCell.Address
End If
Loop Until foundCell Is Nothing Or foundCell.Address = firstFoundCell.Address
'Display the addresses of all found cells
MsgBox "The value " & searchValue & " was found in the following cells: " & allFoundCells
Else
MsgBox "The value " & searchValue & " was not found in the active sheet."
End If
End SubCode Breakdown:
Sub FindAllCellAddresses()This statement initiates a subroutine named FindAllCellAddresses.
Dim searchValue As String
Dim foundCell As Range
Dim firstFoundCell As Range
Dim allFoundCells As StringThis block of statements declares the variables we’ll use.
in this code. The names are pretty self-explanatory.
searchValue = InputBox("Enter the value which cell position you're looking for")This statement takes the search value from the user as input.
Set foundCell = ActiveSheet.Cells.find(What:=searchValue, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole, MatchCase:=False)This statement searches for the value in the active sheet using the find method of the cells object.
If Not foundCell Is Nothing Then
Set firstFoundCell = foundCell
allFoundCells = firstFoundCell.AddressThis block of statements checks if the search value is found in any cell. Then stores the address of the first found cell in the firstFoundCell variable and allFoundCells variable.
DoThis initiates a Do loop to search for all the cells containing the search value.
Set foundCell = ActiveSheet.Cells.FindNext(foundCell)This finds the next cell containing the search value and stores its address in the foundCell variable.
If Not foundCell Is Nothing And foundCell.Address <> firstFoundCell.Address ThenThis checks if the search value is found in any other cell and if it is not the same address as the first found cell.
allFoundCells = allFoundCells & ", " & foundCell.AddressThis adds the address of the found cell to the list of allFoundCells.
Loop Until foundCell Is Nothing Or foundCell.Address = firstFoundCell.AddressThis loop continues until no other cell containing the search value is found or it reaches the first found cell again.
MsgBox "The value " & searchValue & " was found in the following cells: " & allFoundCellsThis shows all the addresses of the cells that contain the values we are looking for.
MsgBox "The value " & searchValue & " was not found in the active sheet."Otherwise a message will display that the value is not found in the active sheet.
End IfEnds the if else condition.
End SubEnds the sub routine.
Run the code to get the output as shown below.
2.2. Getting All Cell Addresses of Repeated String Value
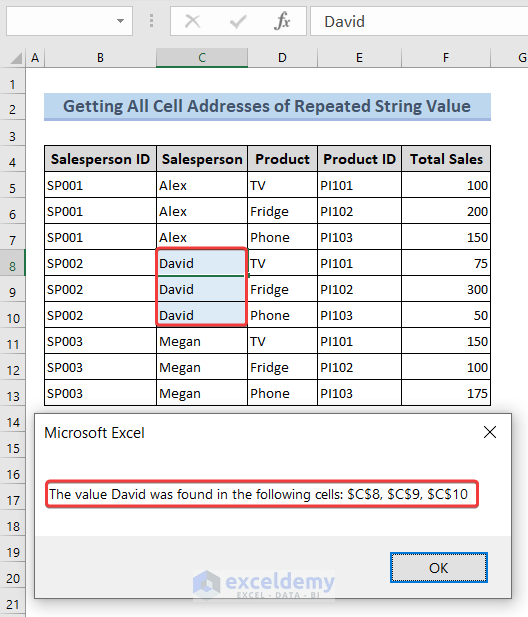
The value we are looking for now is of string data type. To get all the cells’ addresses we can use the same settings. We can use the following code to do so.
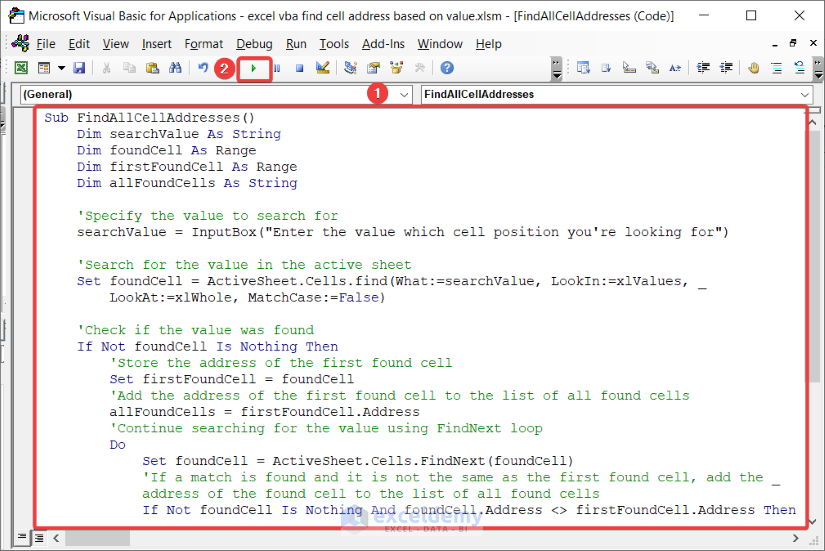
Sub FindAllCellAddresses()
Dim searchValue As String
Dim foundCell As Range
Dim firstFoundCell As Range
Dim allFoundCells As String
'Specify the value to search for
searchValue = InputBox("Enter the value which cell position you're looking for")
'Search for the value in the active sheet
Set foundCell = ActiveSheet.Cells.find(What:=searchValue, LookIn:=xlValues, _
LookAt:=xlWhole, MatchCase:=False)
'Check if the value was found
If Not foundCell Is Nothing Then
'Store the address of the first found cell
Set firstFoundCell = foundCell
'Add the address of the first found cell to the list of all found cells
allFoundCells = firstFoundCell.Address
'Continue searching for the value using FindNext loop
Do
Set foundCell = ActiveSheet.Cells.FindNext(foundCell)
'If a match is found and it is not the same as the first found cell, add the _
address of the found cell to the list of all found cells
If Not foundCell Is Nothing And foundCell.Address <> firstFoundCell.Address Then
allFoundCells = allFoundCells & ", " & foundCell.Address
End If
Loop Until foundCell Is Nothing Or foundCell.Address = firstFoundCell.Address
'Display the addresses of all found cells
MsgBox "The value " & searchValue & " was found in the following cells: " & allFoundCells
Else
MsgBox "The value " & searchValue & " was not found in the active sheet."
End If
End SubCode Breakdown:
The code breakdown is the same as the breakdown we have shown in section 2.1.
Run the code to get the output as shown below.
Read More: How to Get Cell Value by Address in Excel
How to Find Cell Address with Excel Formula
Method 1 – Using ADDRESS Function
You may use the ADDRESS function in Excel to get the address of a cell that contains the value you are looking for. If we use the ADDRESS function to get the cell address that contains the value David, we may use the following Excel formula to get that.
=ADDRESS(MATCH(I4, C:C, 0), COLUMN(C5))Steps:
- Insert the following formula in cell I5 and press ENTER.
=ADDRESS(MATCH(I4, C:C, 0), COLUMN(C5))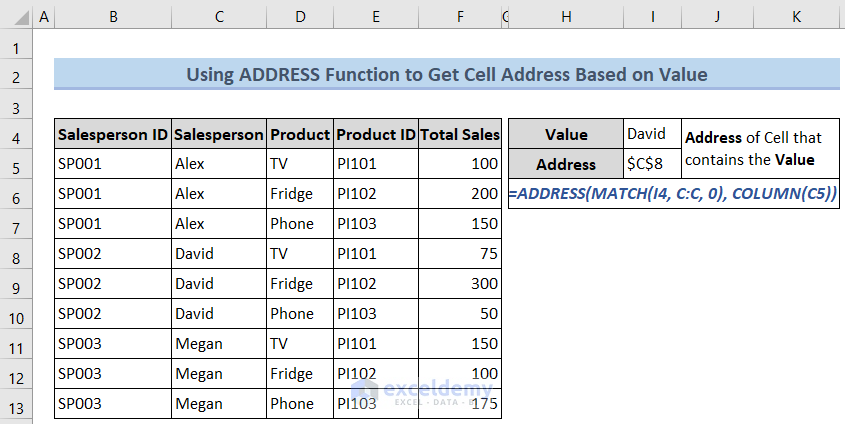
We will get the address of the cell that contains the value in cell I4 (David).
Method 2 – Utilizing CELL Function
We can use the CELL function to get the cell address that contains the value we are looking for. In this method, by default, we only get the first cell address of that value even if the value exists multiple times in the worksheet. If we’re looking for a cell address that contains the value Megan, use the following formula.
=CELL("address",INDEX($C$4:$F$13,MATCH($I$4,$C$4:$C$13,0),1)) 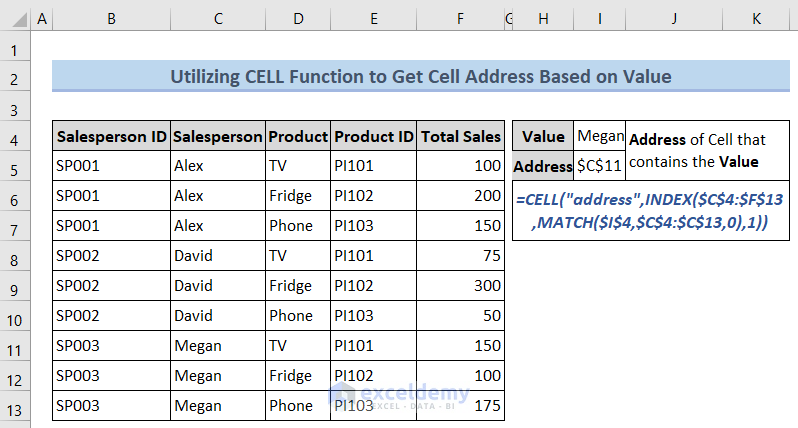
How to Get Row and Column Numbers from Cells in Excel VBA
Method 1 – Extracting Row and Column Numbers for Specific Cell
See the following image to get an overview.
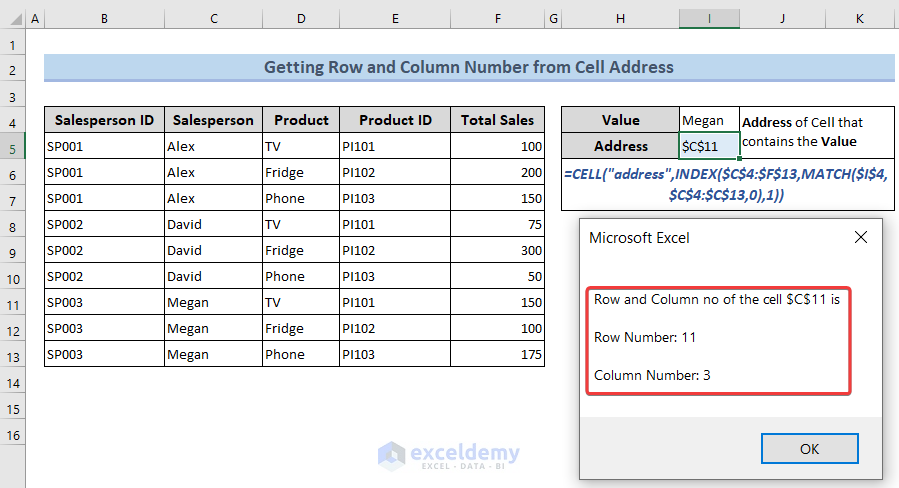
We want to get the Row and Column no. of a cell’s address. Cell I5 contains a cell’s address. We want to extract the Row and Column no of that value.
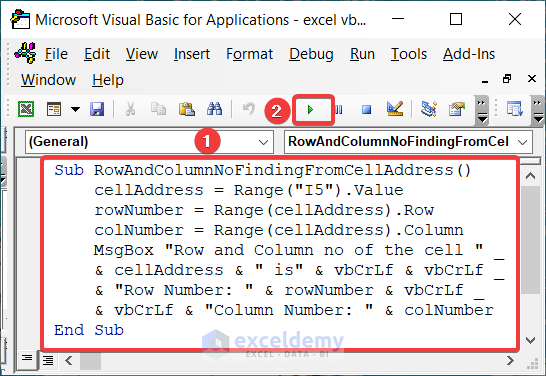
Sub RowAndColumnNoFindingFromCellAddress()
cellAddress = Range("I5").Value
rowNumber = Range(cellAddress).Row
colNumber = Range(cellAddress).Column
MsgBox "Row and Column no of the cell " _
& cellAddress & " is" & vbCrLf & vbCrLf _
& "Row Number: " & rowNumber & vbCrLf _
& vbCrLf & "Column Number: " & colNumber
End SubCode Breakdown:
Sub RowAndColumnNoFindingFromCellAddress()This statement defines a sub procedure named RowAndColumnNoFindingFromCellAddress.
cellAddress = Range("I5").ValueKeeps the value of cell I5 in a variable named cellAddress.
rowNumber = Range(cellAddress).RowGets the Row number of cellAddress and stores it in a variable named rowNumber.
colNumber = Range(cellAddress).ColumnGets the Column number of cellAddress and stores it in a variable named colNumber.
MsgBox "Row and Column no of the cell " & cellAddress & " is" & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & "Row Number: " & rowNumber & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & "Column Number: " & colNumberShows the Row and Column no of the cell.
End SubEnds the sub procedure.
Run the code to get the output as shown below.
Read More: How to Return Cell Address of Match in Excel
Method 2 – Finding Row and Column Numbers for Active Cell
Watch the video to get an overview.
We’re showing the Row and Column no. of the active cell in the active worksheet. We will use the Selection property. The following image contains the code.
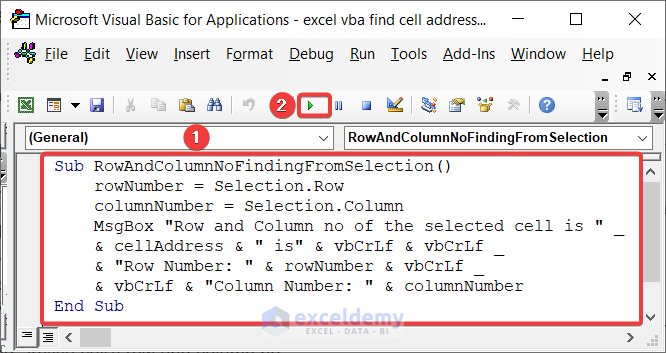
Sub RowAndColumnNoFindingFromSelection()
rowNumber = Selection.Row
columnNumber = Selection.Column
MsgBox "Row and Column no of the selected cell is " _
& cellAddress & " is" & vbCrLf & vbCrLf _
& "Row Number: " & rowNumber & vbCrLf _
& vbCrLf & "Column Number: " & columnNumber
End SubRun the code to get the output as shown below.
2.1. Using Basic Approach
See the following image to get an overview.
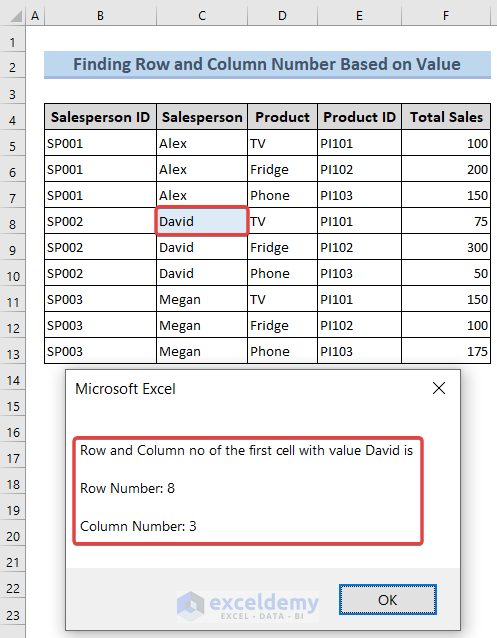
To get the Row and Column no. of that address, follow Method 1.1 and enter the following code:
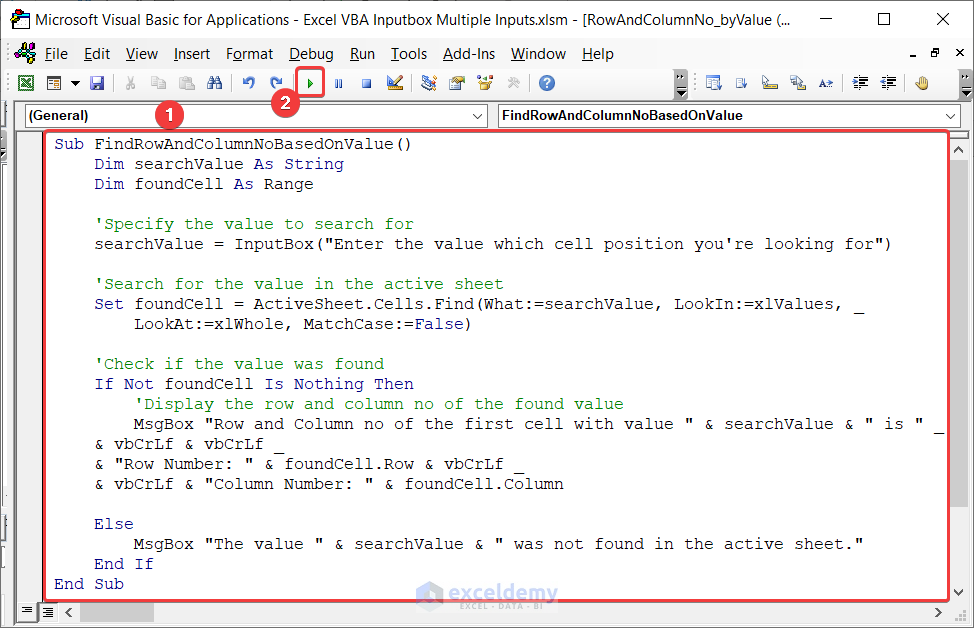
Sub FindCellValue()
Dim searchValue As String
Dim foundCell As Range
'Specify the value to search for
searchValue = InputBox("Enter the value which cell position you're looking for")
'Search for the value in the active sheet
Set foundCell = ActiveSheet.Cells.Find(What:=searchValue, LookIn:=xlValues, _
LookAt:=xlWhole, MatchCase:=False)
'Check if the value was found
If Not foundCell Is Nothing Then
'Display the row and column no of the found value
MsgBox "Row and Column no of the first cell with value " & searchValue & " is " _
& vbCrLf & vbCrLf _
& "Row Number: " & foundCell.Row & vbCrLf _
& vbCrLf & "Column Number: " & foundCell.Column
Else
MsgBox "The value " & searchValue & " was not found in the active sheet."
End If
End SubCode Breakdown:
MsgBox "Row and Column no of the first cell with value " & searchValue & " is " & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & "Row Number: " & foundCell.Row & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & "Column Number: " & foundCell.ColumnWe’ve used the Row and Column property to get the Row and Column no in foundCell.Row and foundCell.Column. And finally showed the values.
Run the code to get the output as shown below.
2.2. Utilizing VBA Split Function
See the following image to get an overview.
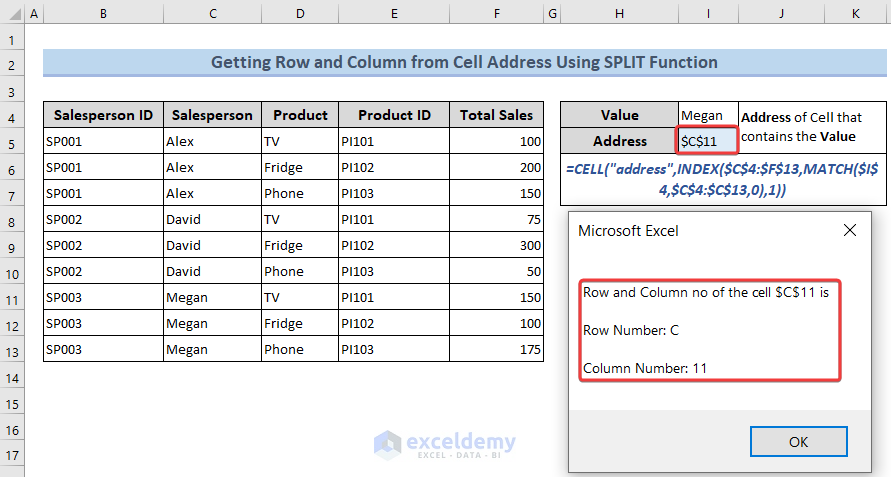
If you need only the relative cell reference, you may use the VBA SPLIT function to do that. Enter the following code:
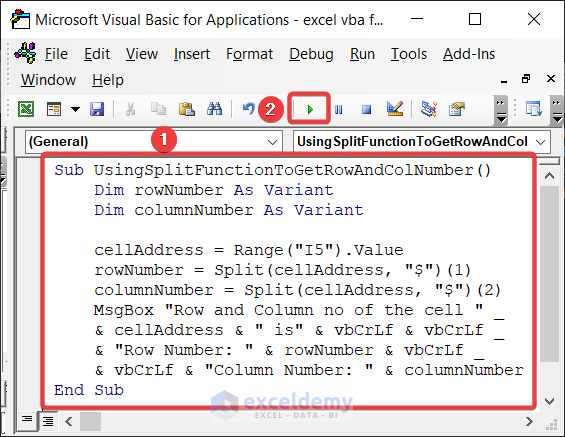
Sub UsingSplitFunctionToGetRowAndColNumber()
Dim rowNumber As Variant
Dim columnNumber As Variant
cellAddress = Range("I5").Value
rowNumber = Split(cellAddress, "$")(1)
columnNumber = Split(cellAddress, "$")(2)
MsgBox "Row and Column no of the cell " _
& cellAddress & " is" & vbCrLf & vbCrLf _
& "Row Number: " & rowNumber & vbCrLf _
& vbCrLf & "Column Number: " & columnNumber
End SubCode Breakdown:
rowNumber = Split(cellAddress, "$")(1)This splits the string in the cellAddress variable into an array of substrings using $ character as the delimiter. It selects the second(1+1) element of the array and stores it in the rowNumber variable.
columnNumber = Split(cellAddress, "$")(2)This splits the string in the cellAddress variable into an array of substrings using $ as the delimiter. After that, pass the third(2+1) element of the array in the columnNumber variable.
Run the code to het the output as shown below.
How to Set Variable to Cell Address in Excel VBA
Check the following video to get an overview.
Passing the cell address in a variable helps you refer to the cell whenever you need it. Keeping the cell address in a variable is quite similar to passing any values to a variable. The following code shows how we can do this.
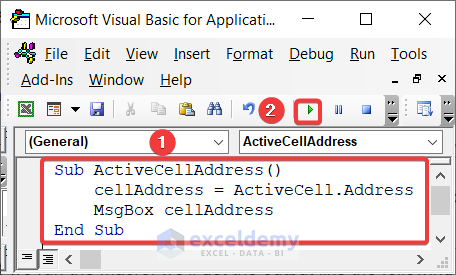
Sub ActiveCellAddress()
cellAddress = ActiveCell.Address
MsgBox cellAddress
End SubCode Breakdown:
We’re passing the cell address of the ActiveCell to the cellAddress variable and later showing this using a MsgBox.
If we run the macro, we’ll see a MsgBox containing the value of the variable cellAddress. The following video shows the output.
How to Insert Value to a Cell Based on Address in Excel VBA
See the following video to get an overview.
Although you can insert value to any cell directly by typing the value in the cell of the worksheet, you can also do it using VBA. In that case, you can use the Value property. I have shown how we can assign values in cells using ActiveCell as the reference. The following image contains the code.
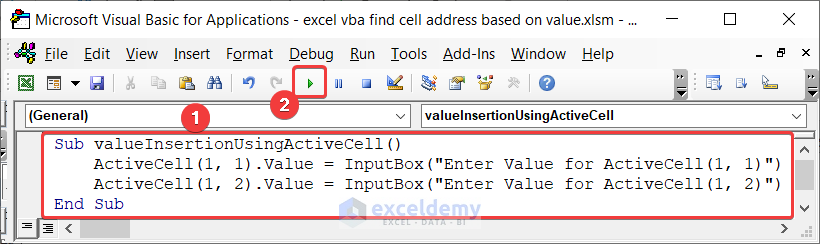
Sub valueInsertionUsingActiveCell()
ActiveCell(1, 1).Value = InputBox("Enter Value for ActiveCell(1, 1)")
ActiveCell(1, 2).Value = InputBox("Enter Value for one cell right from ActiveCell that is ActiveCell(1, 2)")
End SubCode Breakdown:
ActiveCell(1, 1).Value = InputBox("Enter Value for ActiveCell(1, 1)")This is assigning the value entered by the user in the ActiveCell of the current worksheet.
ActiveCell(1, 2).Value = InputBox("Enter Value for one cell right from ActiveCell that is ActiveCell(1, 2)")This statement does the same thing but this time one cell right to the ActiveCell.
Run the code to get the output a shown below.
Things to Remember
- Use the arguments of the find method properly or errors may happen.
- While using the loop, notice when to get out of the loop or you may fall in an infinite loop or may get repeated values.
- Note that the SPLIT function creates an array. And by default, the array index starts from 0 in Excel VBA.
Download Practice Workbook
Related Articles
<< Go Back to Excel ADDRESS Function | Excel Functions | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

