Method 1 – Using Match Function to Find One Matching Value in Column
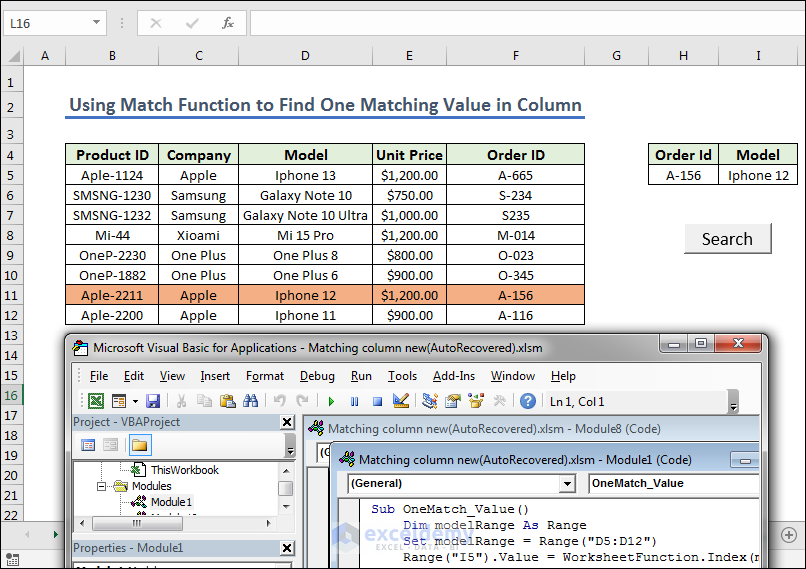
Find the Match value of the Model according to order ID.
- Prepare some cells for Order ID and Model in range H4:I5.
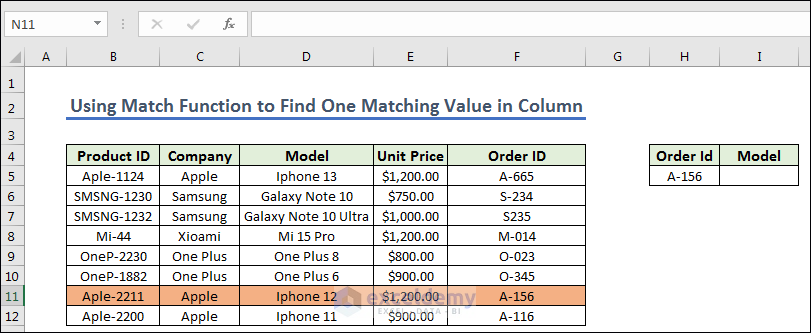
- Give the code in Module.
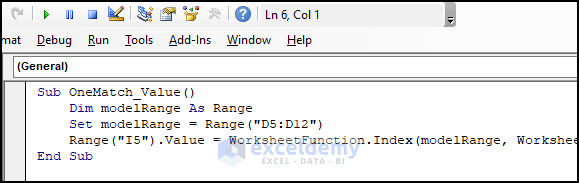
- Copy the code.
Sub OneMatch_Value()
Dim modelRange As Range
Set modelRange = Range("D5:D12")
Range("I5").Value = WorksheetFunction.Index(modelRange, WorksheetFunction.Match(Range("H5").Value, Range("F5:F12"), 0))
End Sub- If you insert the order ID beforehand, running it will yield the result. We are going to assign it to a Command Button.
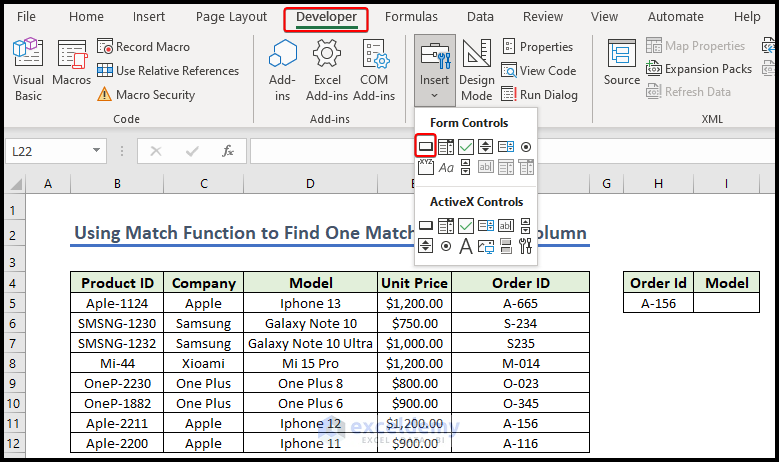
- Create a button; name it “Search” and assign the Macro. Right-click on the button, select Assign Macro from the context menu and select the proper code through the sub name.
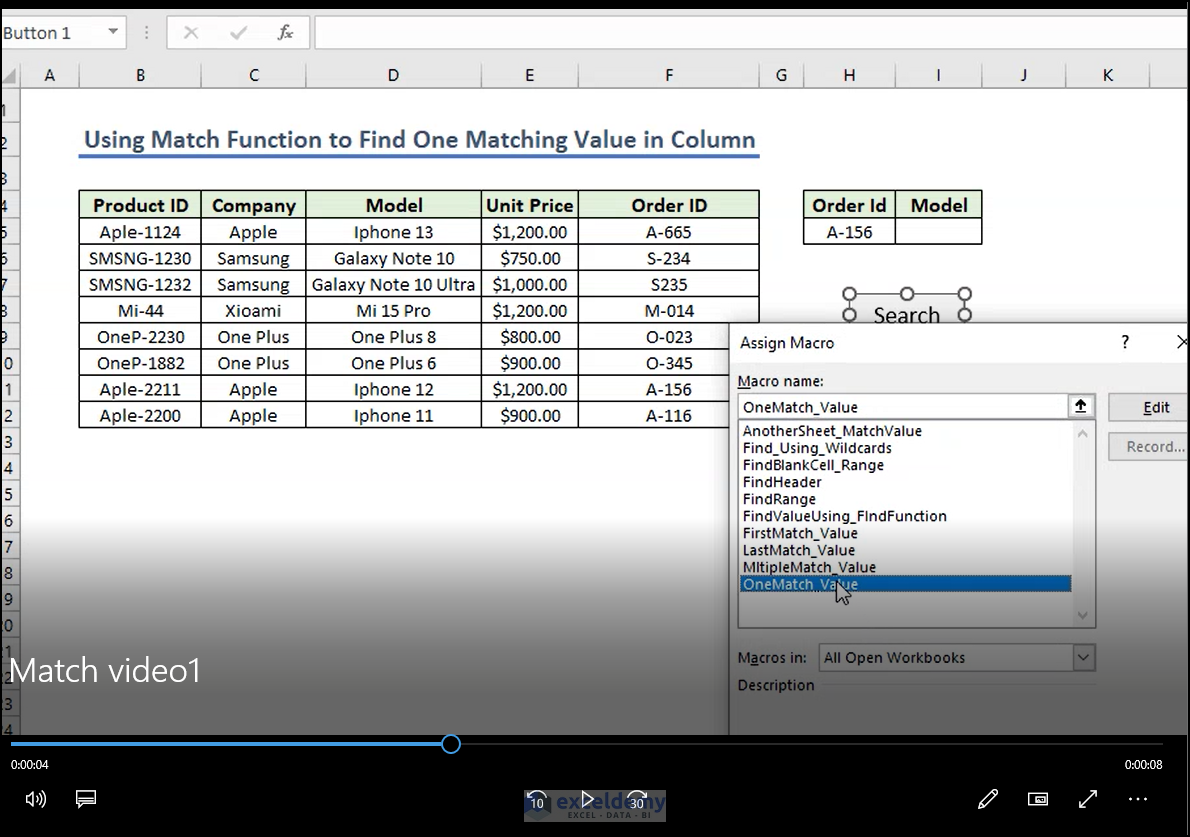
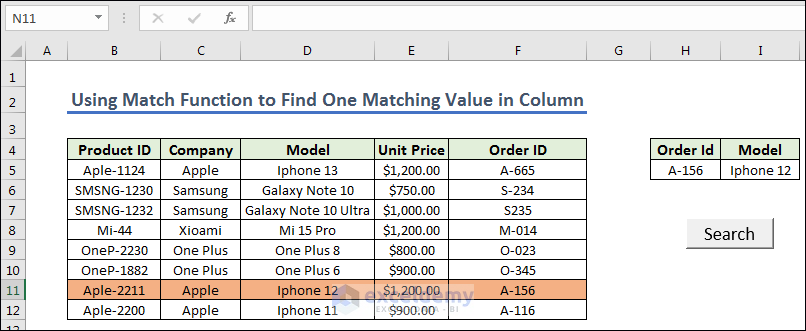
- Click the “Search” button and get the final output.
Code Explanation
Sub OneMatch_Value()
Dim modelRange As Range
Set modelRange = Range("D5:D12")The first line creates a Range object called modelRange that refers to the range of cells D5:D12.
Range("I5").Value = WorksheetFunction.Index(modelRange, WorksheetFunction.Match(Range("H5").Value, Range("F5:F12"), 0))The second line sets the value of cell I5 to the result of a formula that uses the INDEX and MATCH functions. The INDEX function takes a range of cells as its first argument (modelRange), and the MATCH function takes a value to search for as its first argument (Range(“H5”).Value), and a range of cells to search in as its second argument (Range(“F5:F12”)). The third argument of the MATCH function is 0, which means that it should find an exact match. The result of the MATCH function is used as the second argument of the INDEX function, which returns the value from the corresponding cell in the range modelRange.
Method 2 – Utilizing Match Function to Find Multiple Matching Values in Column
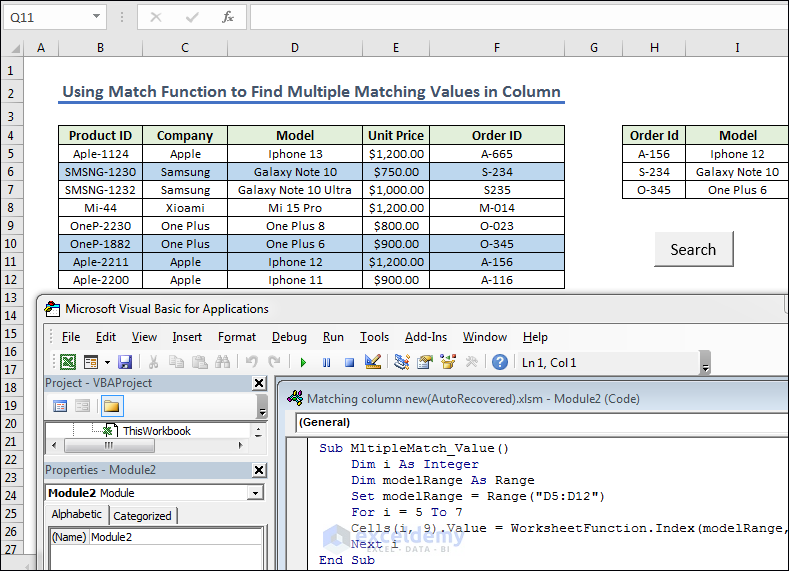
- Give the Order Id in the H column and select the I column for Model.
- Create a module and write the following code.
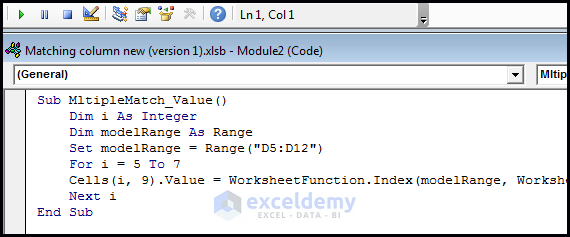
- Copy the code.
Sub MutipleMatch_Value()
Dim i As Integer
Dim modelRange As Range
Set modelRange = Range("D5:D12")
For i = 5 To 7
Cells(i, 9).Value = WorksheetFunction.Index(modelRange, WorksheetFunction.Match(Cells(i, 8).Value, Range("F5:F12"), 0))
Next i
End Sub- Create a Command button and assign the macro named MultipleMatch_Value.
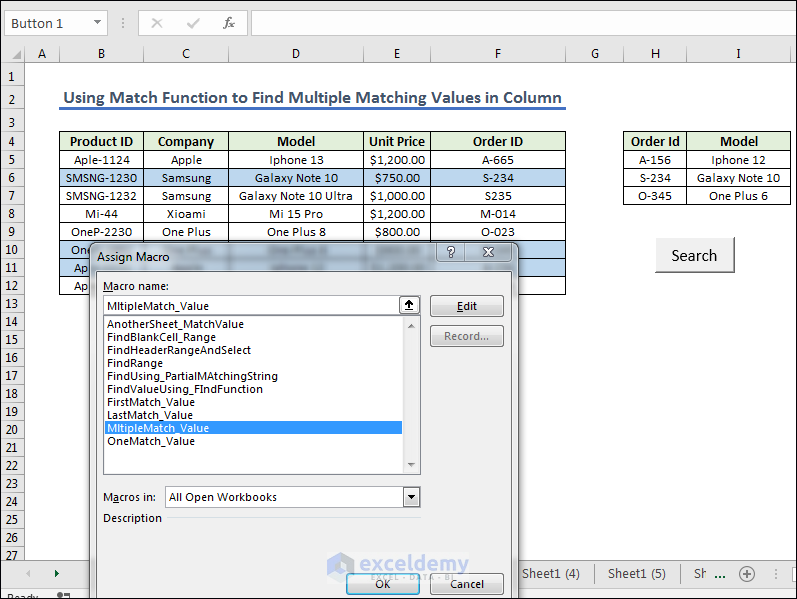
- Press the Search button, you will get the Model according to Order ID.
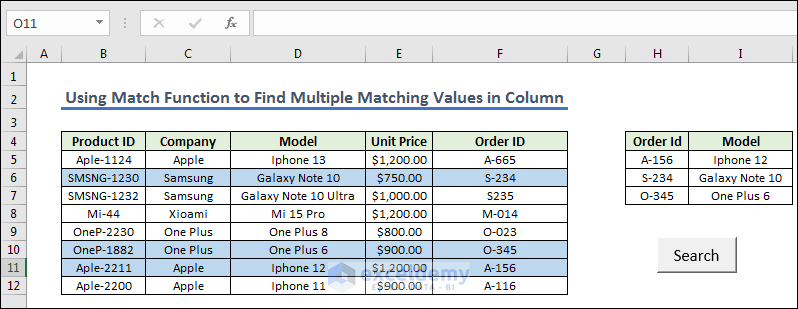
Code Explanation
Sub MutipleMatch_Value()
Dim i As Integer
Dim modelRange As Range
Set modelRange = Range("D5:D12")The first two lines create a Range object called modelRange that refers to the range of cells.
D5:D12.
For i = 5 To 7
Cells(i, 9).Value = WorksheetFunction.Index(modelRange, WorksheetFunction.Match(Cells(i, 8).Value, Range("F5:F12"), 0))
Next i
End Sub- The For loop iterates over a range of cells from row 5 to row 7 in column 8 (i.e., range H5:H7).
- Inside the For loop, the MATCH function is used to find the position of the value in cell (i, 8 i.e., the current cell in column 8) within the range F5:F12. This is done using the Match method.
- The INDEX function is then used to return the value from the corresponding cell in the modelRange. The position of the cell is determined by the result of the MATCH.
- The value returned by the INDEX function is written to the corresponding cell in column 9 (i.e., Cells(i, 9)).
Method 3 – Finding Matching Value in Column in Another Worksheet
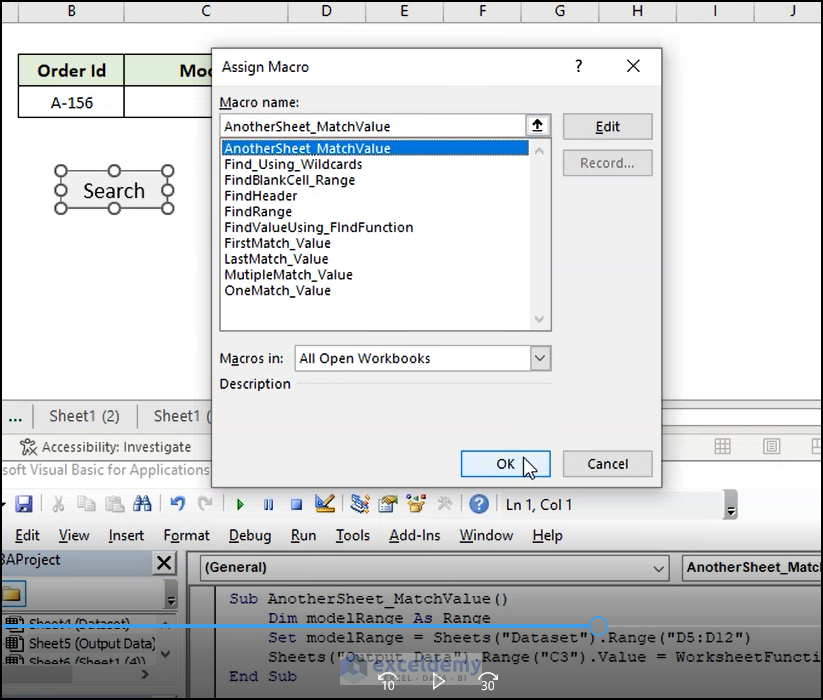
- Create a worksheet and name it “Dataset” (you can give anything you like and change the code accordingly) and “Output Data”, another worksheet with the intended Order ID.
- Open a module and write the code below.
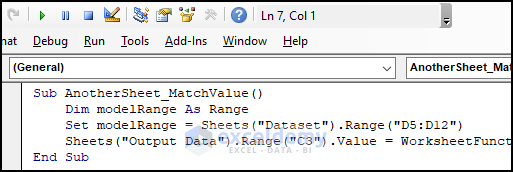
- Copy the code.
Sub AnotherSheet_MatchValue()
Dim modelRange As Range
Set modelRange = Sheets("Dataset").Range("D5:D12")
Sheets("Output Data").Range("C3").Value = WorksheetFunction.Index(modelRange, WorksheetFunction.Match(Sheets("Output Data").Range("B3").Value, Sheets("Dataset").Range("F5:F12"), 0))
End Sub- Add a search button and assign the macro with it by right-clicking on it, selecting Assign Macro from the context menu, and then selecting the proper macro.
- Get the output in the Output Data worksheet by clicking the search button.
Code Explanation
Sub AnotherSheet_MatchValue()
Dim modelRange As Range
Set modelRange = Sheets("Dataset").Range("D5:D12")This line creates a Range object called modelRange that refers to the range of cells D5:D12 on the worksheet named “Dataset”. The worksheet is specified using the Sheets method.
Sheets("Output Data").Range("C3").Value = WorksheetFunction.Index(modelRange, WorksheetFunction.Match(Sheets("Output Data").Range("B3").Value, Sheets("Dataset").Range("F5:F12"), 0))This line sets the value of cell C3 on the worksheet named “Output Data“. The worksheet is specified using the Sheets method. The value is written to cell C3 is the result of a formula that uses the INDEX and MATCH functions. The MATCH function takes a value to search for as its first argument (Sheets(“Output Data”).Range(“B3”).Value), and a range of cells to search in as its second argument (Sheets(“Dataset”).Range(“F5:F12”)). The third argument of the MATCH function is 0, which means that it should find an exact match. The result of the MATCH function is used as the second argument of the INDEX function, which returns the value from the corresponding cell in the range modelRange. The value returned by the INDEX function is written to cell C3 on the worksheet named “Output Data”
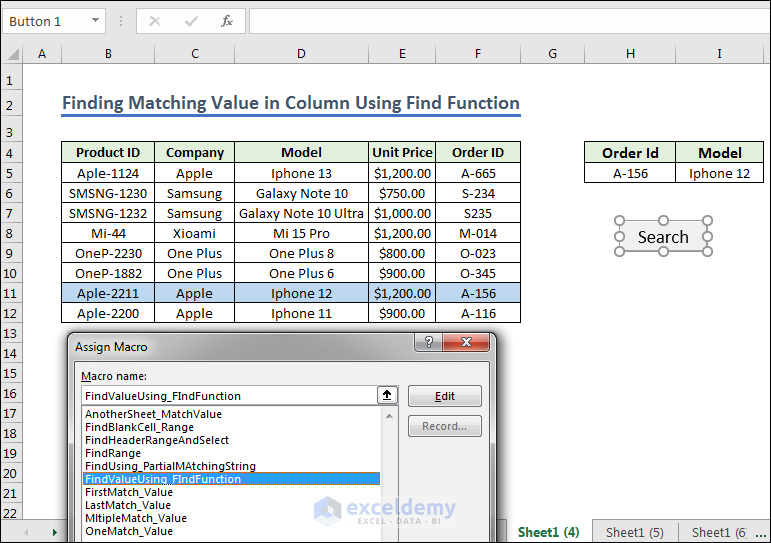
Method 4 – Finding Matching Value in Column Using Find Function
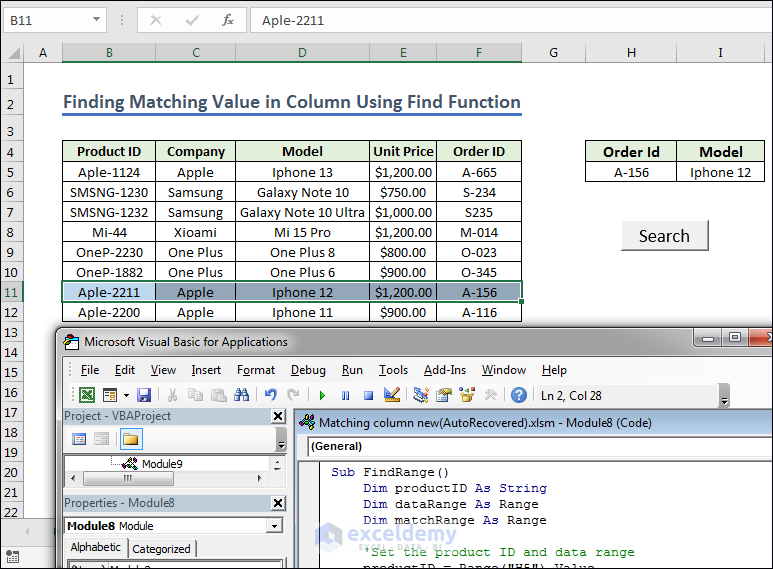
- In example 1 we prepared the range H4:I5 for the searching and created a button, named it Search. Give any Order Id from the left dataset.
- Create a module and write the following code below.
- Copy the code.
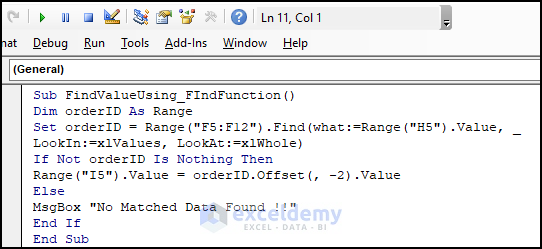
Sub FindValueUsing_FIndFunction()
Dim orderID As Range
Set orderID = Range("F5:F12").Find(what:=Range("H5").Value, _
LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole)
If Not orderID Is Nothing Then
Range("I5").Value = orderID.Offset(, -2).Value
Else
MsgBox "No Matched Data Found !!"
End If
End Sub- Assign the Macro in the Search button like the assign Macro shown in example 1.
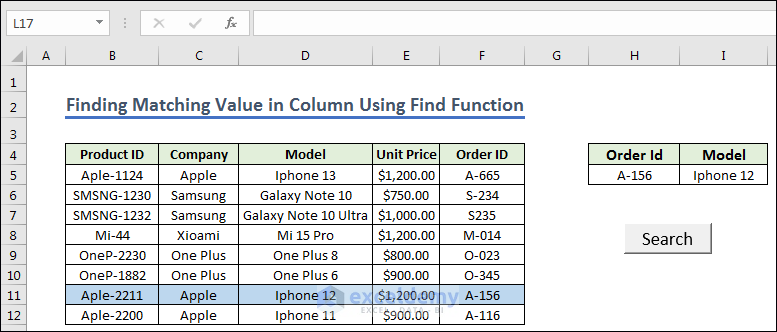
- Press the Search button we will finally get the result.
Code Explanation
Sub FindValueUsing_FIndFunction()This line starts the definition of a new subroutine called FindValueUsing_FindFunction.
Dim orderID As RangeIt declares a new variable called orderID of type Range.
Set orderID = Range("F5:F12").Find(what:=Range("H5").Value, _
LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole)This part uses the Find() method to search for a specific value (Range(“H5”).Value) in the range F5:F12. The Find() method returns a Range object representing the first cell that matches the search criteria, or Nothing if no match is found. The Set keyword assigns this Range object to the orderID variable.
If Not orderID Is Nothing ThenThis line starts an If statement that checks if orderID is not Nothing (i.e., a match was found).
Range("I5").Value = orderID.Offset(, -2).ValueIf a match is found, this line sets the value of cell I5 to the value of the cell two columns to the left of the matched cell (orderID). Achieve it using the Offset() method, which returns a cell that is a specified number of rows and columns away from a reference cell. The orderID.Offset(, -2) returns a cell with two columns to the left of orderID.
Else
MsgBox "No Matched Data Found !!"
End IfIf no match was found, this line displays a message box with the text “No Matched Data Found !!”.
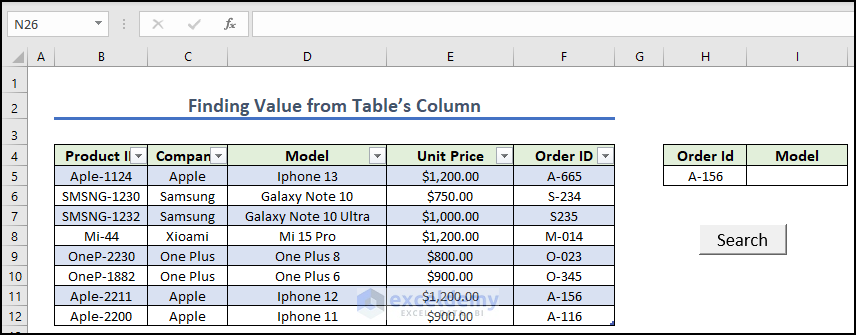
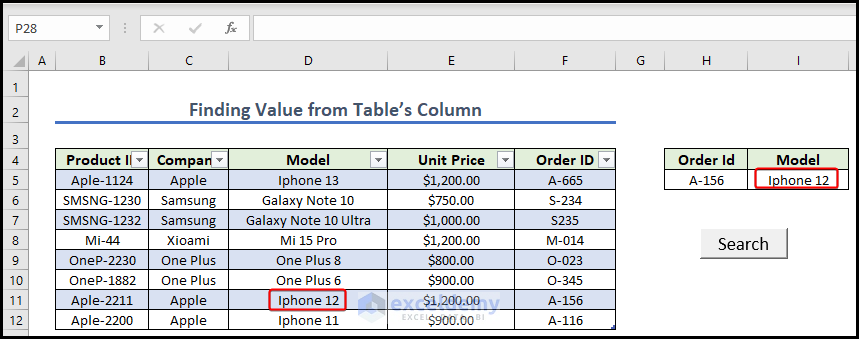
Method 5 – Finding Matching Value from Table’s Column
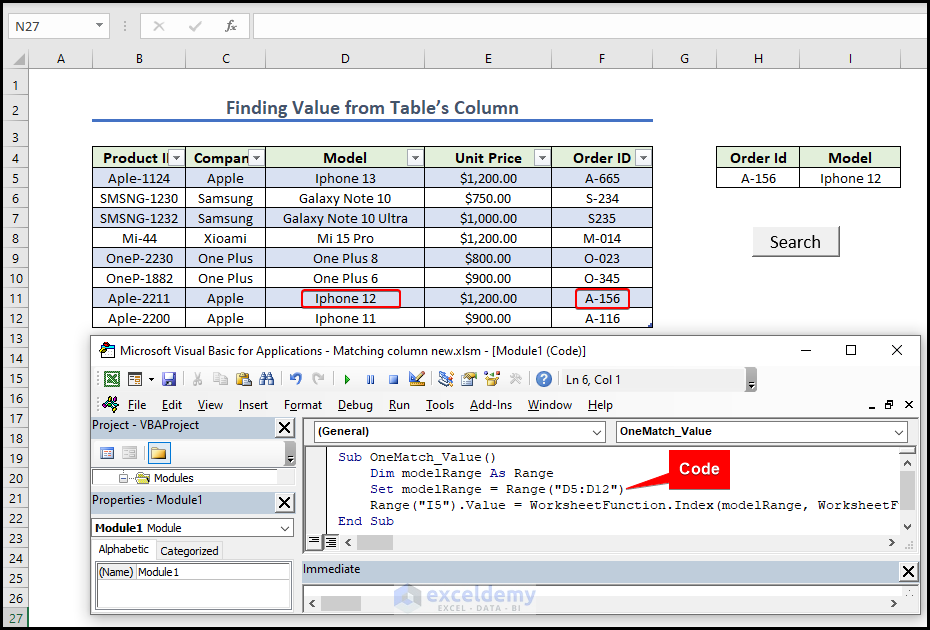
- Give the Dataset and press Ctrl+T to turn your dataset into a table and create a button naming it Search. Give any Order Id from the left dataset.
- Open a module and write the following code.
Sub OneMatch_Value()
Dim modelRange As Range
Set modelRange = Range("D5:D12")
Range("I5").Value = WorksheetFunction.Index(modelRange, WorksheetFunction.Match(Range("H5").Value, Range("F5:F12"), 0))
End Sub- Assign the macro in the Search Button like in the previous examples.
- Press the Search button to get the final result.
Code Explanation
Sub OneMatch_Value()
Dim modelRange As Range
Set modelRange = Range("D5:D12")The first line creates a Range object called modelRange that refers to the range of cells D5:D12.
Range("I5").Value = WorksheetFunction.Index(modelRange, WorksheetFunction.Match(Range("H5").Value, Range("F5:F12"), 0))The second line sets the value of cell I5 to the result of a formula that uses the INDEX and MATCH functions. The INDEX function takes a range of cells as its first argument (modelRange), and the MATCH function takes a value to search for as its first argument (Range(“H5”).Value), and a range of cells to search in as its second argument (Range(“F5:F12”)). The third argument of the MATCH function is 0, which means that it should find an exact match. The result of the MATCH function is used as the second argument of the INDEX function, which returns the value from the corresponding cell in the range modelRange.
Method 6 – Find String With Partial Match in VBA
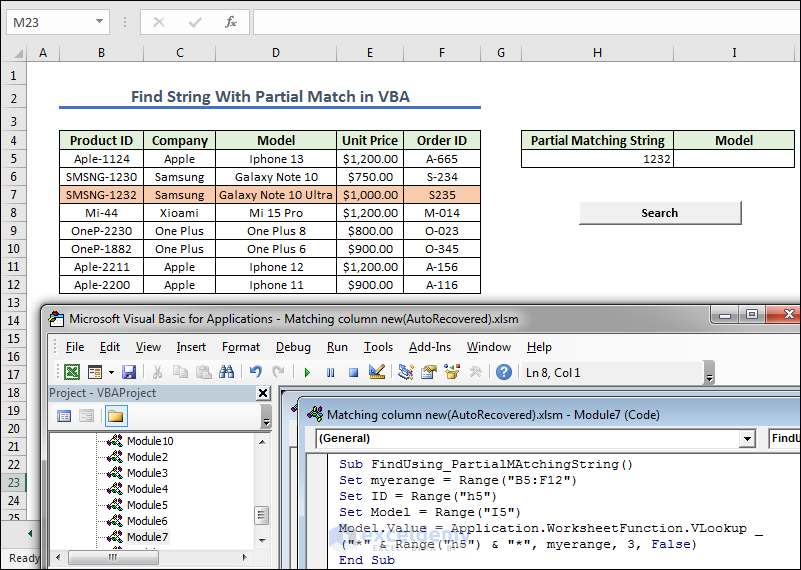
- Create a button naming it as Search. Now we give any Partial MatchingString of Product ID from the left dataset.
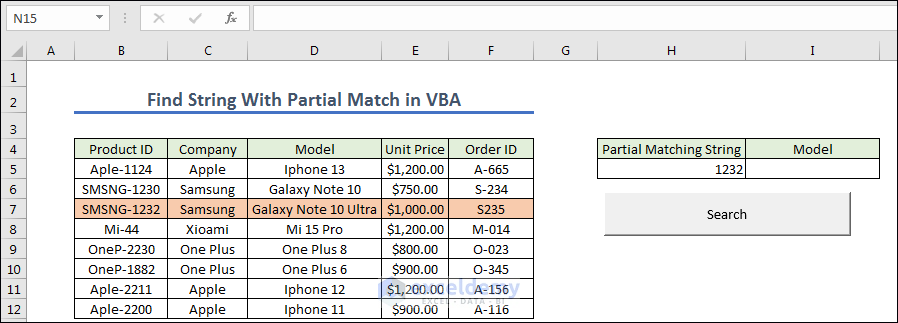
- Create a module and write the code below.
- Copy the code.
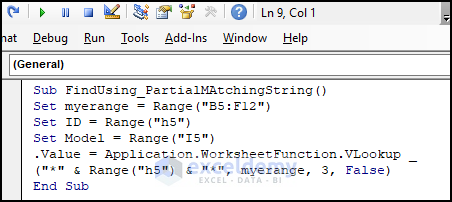
Sub FindUsing_PartialMAtchingString()
Set myerange = Range("B5:F12")
Set ID = Range("h5")
Set Model = Range("I5")
Model.Value = Application.WorksheetFunction.VLookup _
("*" & Range("h5") & "*", myerange, 3, False)
End Sub- Assign the macro Search button.
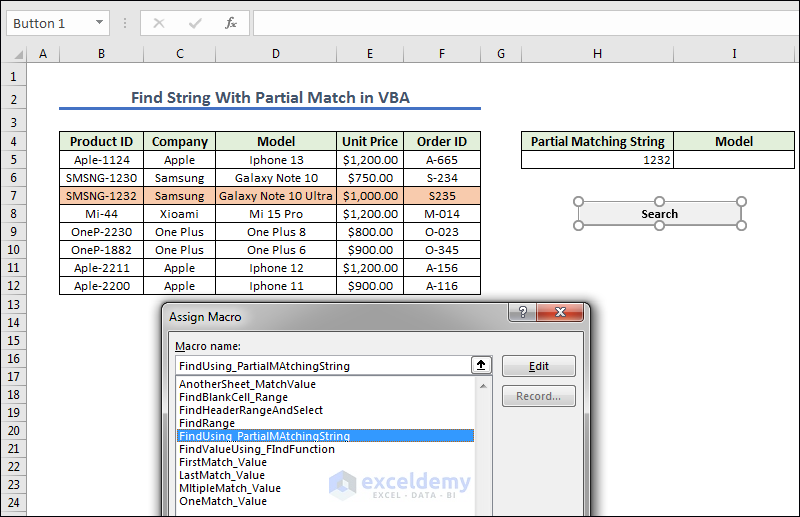
- Assign the macro in the Search button by pressing it to get the result.
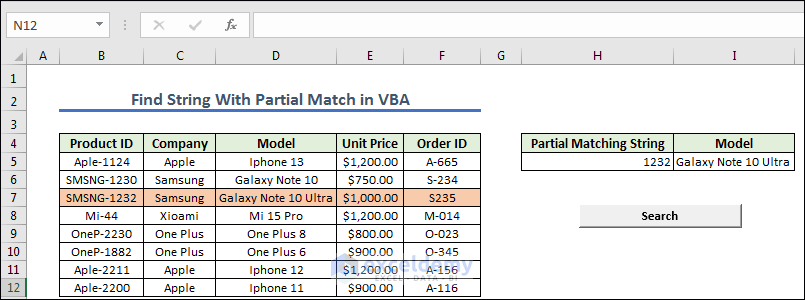
Code Explanation
Set myerange = Range("B5:F12")This line sets the myerange variable to the range B5:F12.
Set ID = Range("h5")It sets the ID variable to cell H5.
Set Model = Range("I5")This line sets the Model variable to cell I5.
Model.Value = Application.WorksheetFunction.VLookup _
("*" & Range("h5") & "*", myerange, 3, False)It uses the VLookup() function to search for a partial match of the value in cell H5 within the range B5:F12.
What each argument of the VLookup() function means:
- “*” & Range(“h5”) & “*”: This concatenates an asterisk (*) character before and after the value in cell H5. This is necessary to perform a partial match search using the VLookup().
- myerange: This is the range of cells to search within.
- ‘3’: This is the column number within myerange from which to return a value. In this case, it returns the value from the third column (C) of the range B5:F12.
- False: This specifies that the search should only return exact matches or partial matches, and not approximate matches.
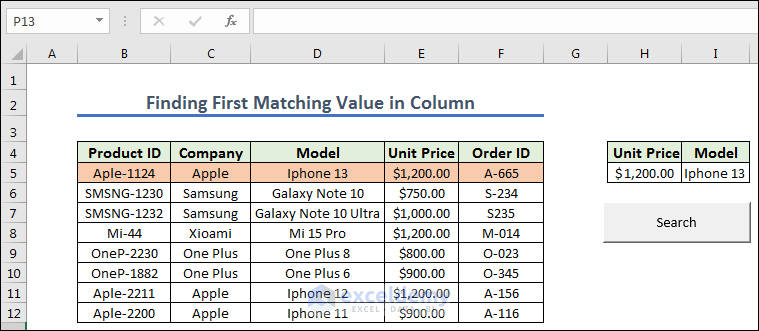
Method 7 – Finding First Matching Value in Column
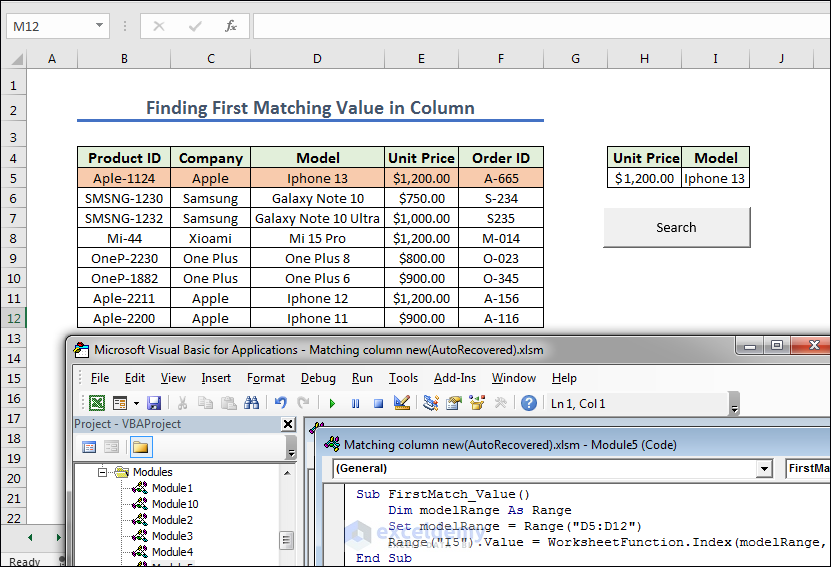
- We prepared the cells and created a button naming it Search. Now we give any Unit Price from the left dataset.
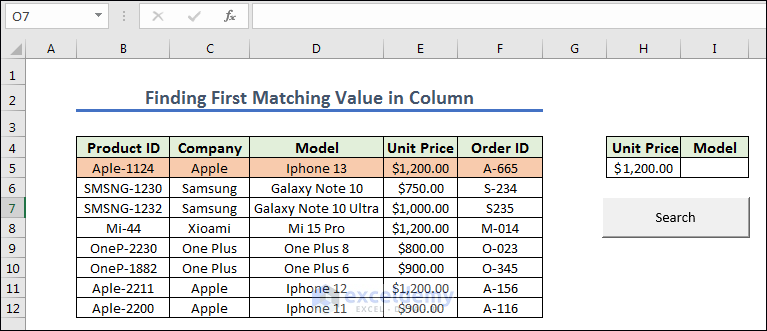
- Create a module, write the code below and assign the macro in the Search.
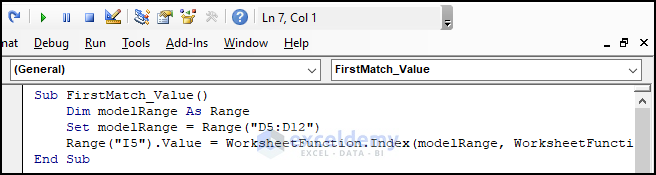
- Copy the code.
Sub FirstMatch_Value()
Dim modelRange As Range
Set modelRange = Range("D5:D12")
Range("I5").Value = WorksheetFunction.Index(modelRange, WorksheetFunction.Match(Range("H5").Value, Range("E5:E12").Value, 0))
End Sub- Assign the macro FirstMatch_Value using the search button.
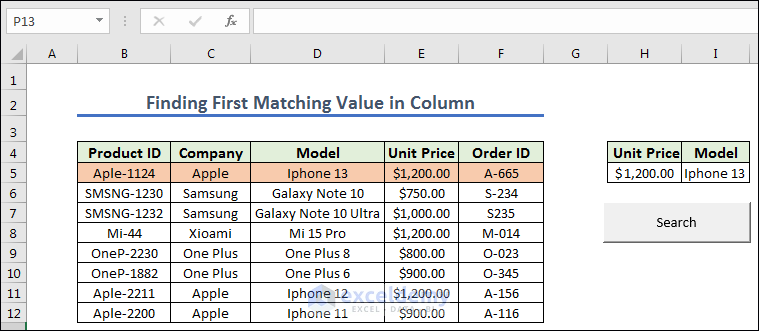
- Get the result after pressing the Search.
Code Explanation
Dim modelRange As Range
Set modelRange = Range("D5:D12")These lines declare a Range object variable called “modelRange” that refers to the range of cells from D5 to D12.
Range("I5").Value = WorksheetFunction.Index(modelRange, WorksheetFunction.Match(Range("H5").Value, Range("E5:E12").Value, 0))This line sets the value of cell I5 to the first match of the value in cell H5 within the range E5:E12 using the INDEX and MATCH worksheet functions. The INDEX function returns the value from the modelRange that corresponds to the row number returned by the MATCH function. The MATCH function searches for the value in cell H5 within the range E5:E12 and returns the relative position of the first match (i.e., its row number) using a match type of 0, which specifies an exact match.
End Sub
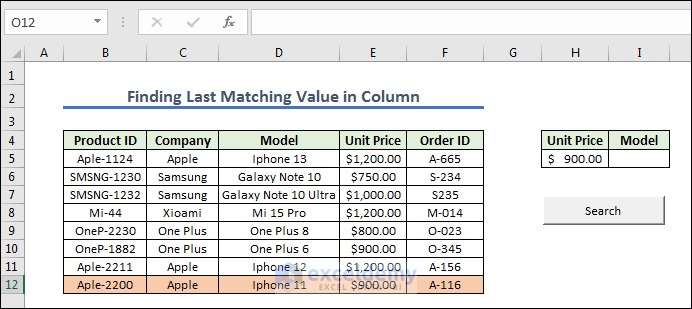
Method 8 – Finding Last Matching Value in Column
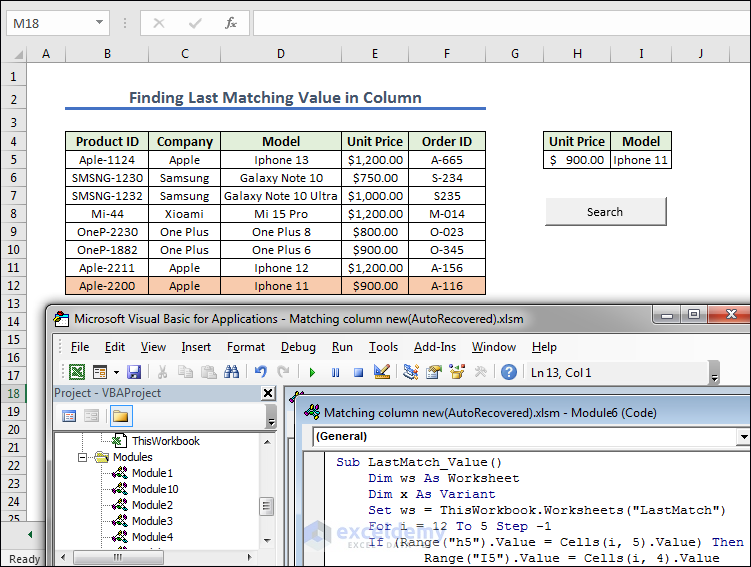
- We prepared the cells and created a button naming it as Search. Now we give any Unit Price from the left dataset.
- Create a module, write the code below and assign the macro in the Search.
- Copy the code.
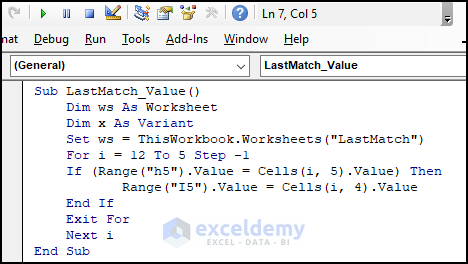
Sub LastMatch_Value()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim x As Variant
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("LastMatch")
For i = 12 To 5 Step -1
If (Range("h5").Value = Cells(i, 5).Value) Then
Range("I5").Value = Cells(i, 4).Value
End If
Exit For
Next i
End Sub- Assign the macro LastMatch_Value in Search.
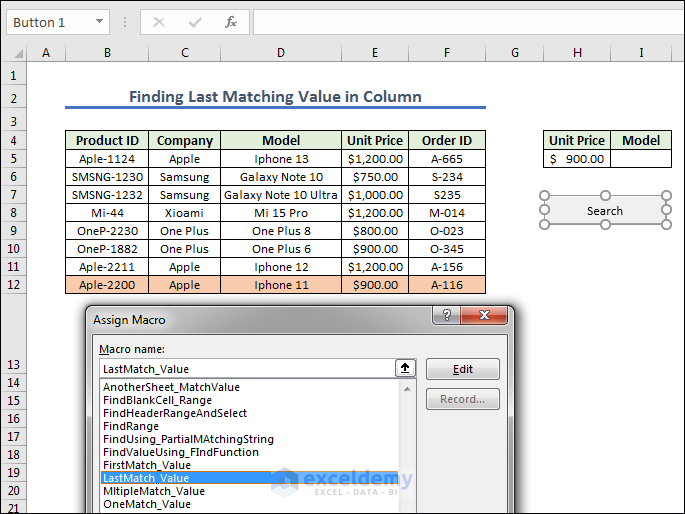
- Get the result after pressing the Search button.

Code Explanation
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim x As Variant
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("LastMatch")This line declares a Worksheet object variable called “ws” and assigns it to the worksheet named “LastMatch” in the current workbook.
For i = 12 To 5 Step -1The line defines a For loop that iterates through a range of rows from 12 to 5, with a step value of –1. This means that the loop starts at row 12 and ends at row 5, iterating through each row in descending order.
If (Range("h5").Value = Cells(i, 5).Value) ThenThis line checks if the value in cell H5 is equal to the value in column E of the current row (I).
Range("I5").Value = Cells(i, 4).ValueIf there is a match, the value in column D of the current row (i) is assigned to cell I5.
End If
Exit ForThis line immediately exits the loop after the first match, iterating from bottom to top.
How to Find Range of Matching Value in Excel VBA
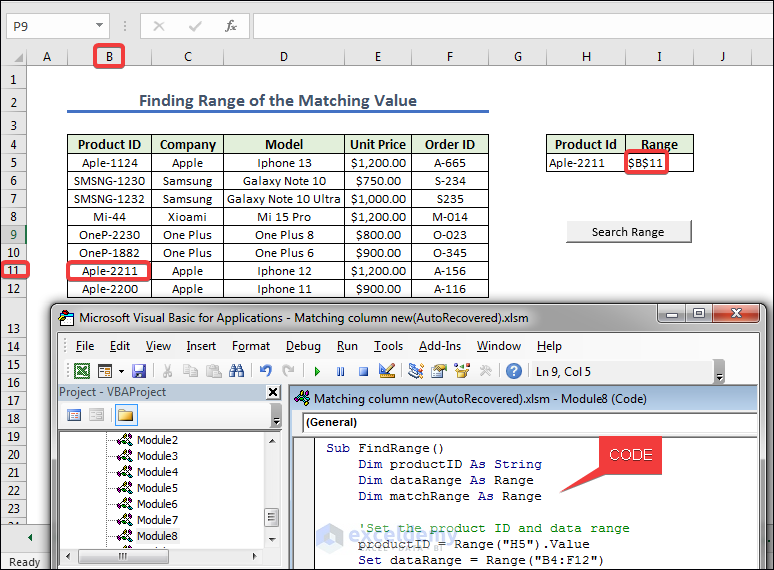
- We created a button naming it Search. Give any Unit Price from the left dataset.
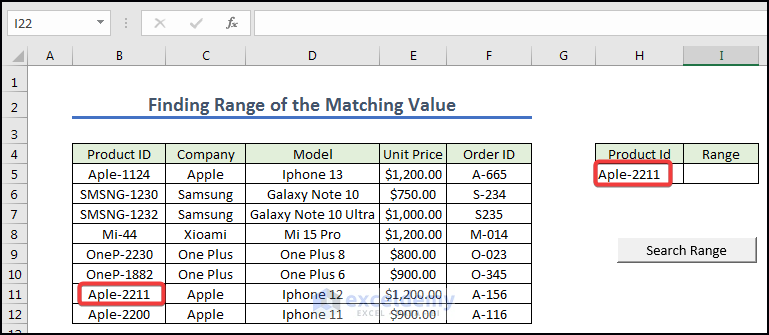
- Open a module you can write down the code below and assign the macro in the search range.
- Copy the code.
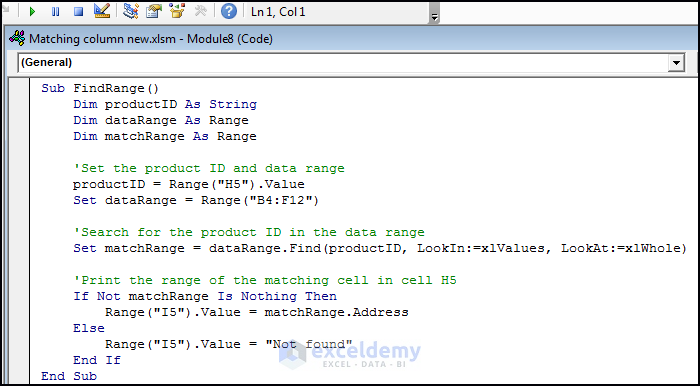
Sub FindRange()
Dim productID As String
Dim dataRange As Range
Dim matchRange As Range
'Set the product ID and data range
productID = Range("H5").Value
Set dataRange = Range("B4:F12")
'Search for the product ID in the data range
Set matchRange = dataRange.Find(productID, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole)
'Print the range of the matching cell in cell H5
If Not matchRange Is Nothing Then
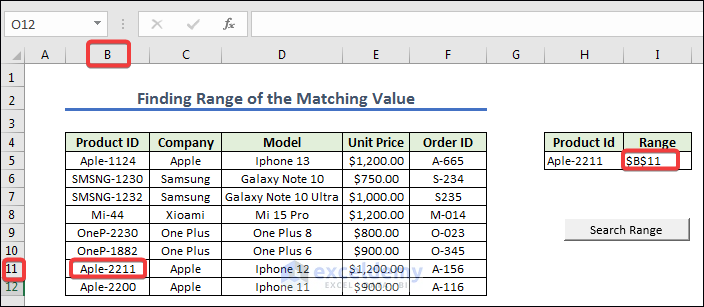
Range("I5").Value = matchRange.Address
Else
Range("I5").Value = "Not found"
End If
End Sub- Assign the Macro FindRange in Search Range button.
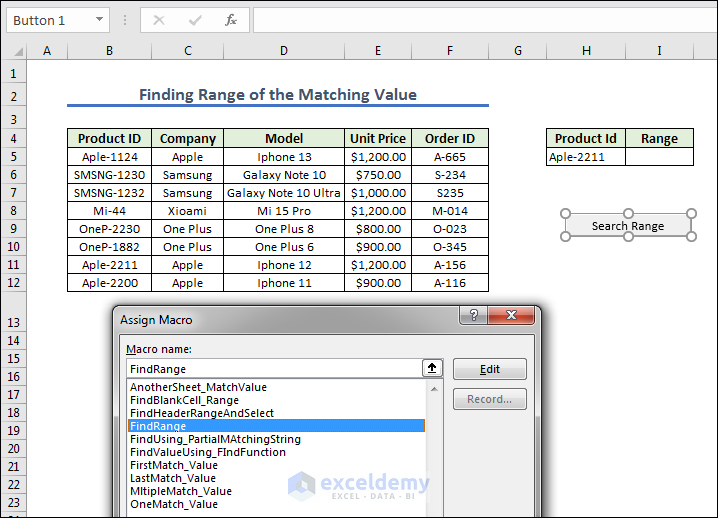
- Press search range to get the range of the Product Id.
Code Explanation
Sub FindRange()
Dim productID As String
Dim dataRange As Range
Dim matchRange As Range
'Set the product ID and data range
productID = Range("H5").Value
Set dataRange = Range("B4:F12")
'Search for the product ID in the data rangeThe variables “productID”, “dataRange”, and “matchRange” are declared as String, Range, and Range, respectively.The value of cell H5 is assigned to the variable “productID“.The range B4:F12 is assigned to the variable “dataRange“.
Set matchRange = dataRange.Find(productID, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole)The “Find” method is used to search for the product ID in the data range. The “LookIn” parameter specifies that the search should be done in the values of the cells, and the “LookAt” parameter specifies that the search should be for an exact match.
'Print the range of the matching cell in cell H5
If Not matchRange Is Nothing Then
Range("I5").Value = matchRange.Address
Else
Range("I5").Value = "Not found"
End IfIf a matching cell is found, the address of the cell is printed in cell I5. If no matching cell is found, the message “Not found” is printed in cell I5.
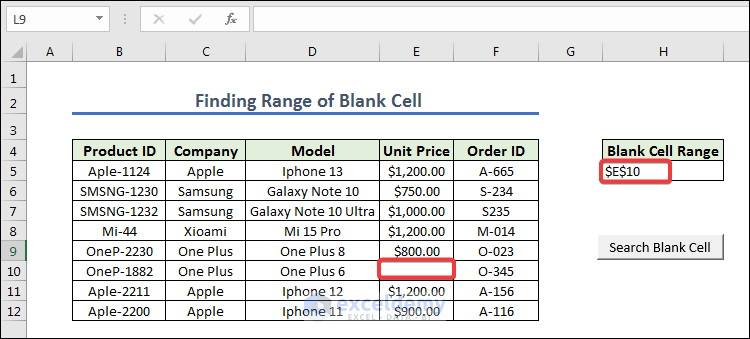
How to Find The Range of Blank Cell in a Column with Excel VBA
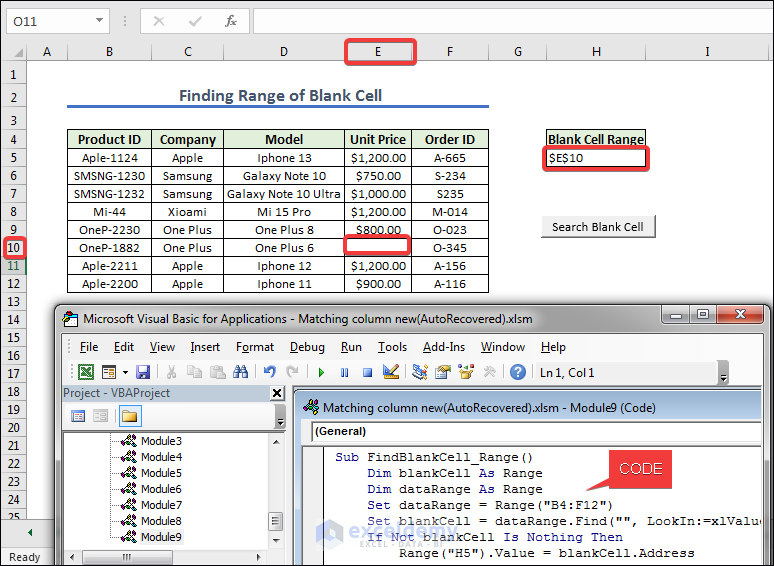
- We gave names BlanK Cell in H4 cells and created a button naming it as Search Blank Cell.
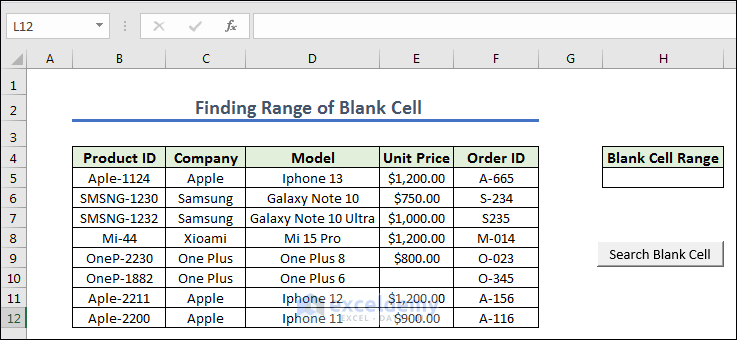
- Open a module you can write down the code below and assign the macro in the Search Blank Cell.
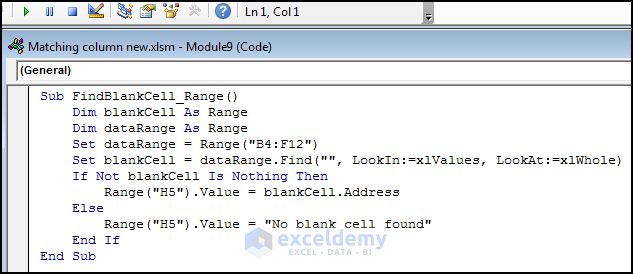
- Copy the code.
Sub FindBlankCell_Range()
Dim blankCell As Range
Dim dataRange As Range
Set dataRange = Range("B4:F12")
Set blankCell = dataRange.Find("", LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole)
If Not blankCell Is Nothing Then
Range("H5").Value = blankCell.Address
Else
Range("H5").Value = "No blank cell found"
End If
End Sub- Assign the FindBlankCell_Range in Search Blank Cell.
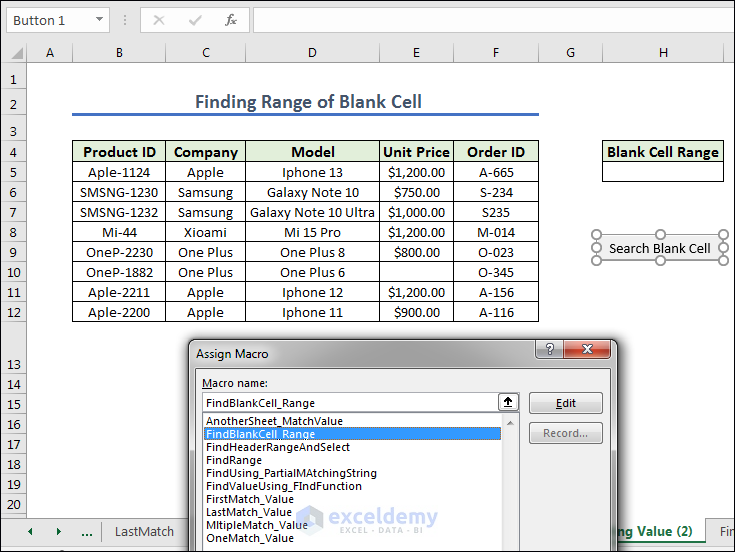
- Assign the macro FindBlankCell_Range in the Search Blank Cell button, press Finally to get the range of blank cells.
Code Explanation
Dim blankCell As Range
Dim dataRange As Range
Set dataRange = Range("B4:F12")
Set blankCell = dataRange.Find("", LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole)The variables “blankCell” and “dataRange” are declared as Range. The range B4:F12 is assigned to the variable “dataRange”. The “Find” method is used to search for a blank cell in the data range. The empty string “” is used as the search value, which means the method will search for a cell with no value. The “LookIn” parameter specifies that the search should be done in the values of the cells, and the “LookAt” parameter specifies that the search should be for an exact match.
If Not blankCell Is Nothing Then
Range("H5").Value = blankCell.Address
Else
Range("H5").Value = "No blank cell found"
End IfIf a blank cell is found, the address of the cell is printed in cell H5. If no blank cell is found, the message “No blank cell found” is printed in cell H5.
How to Find Column Range of a Specific Header in Excel VBA
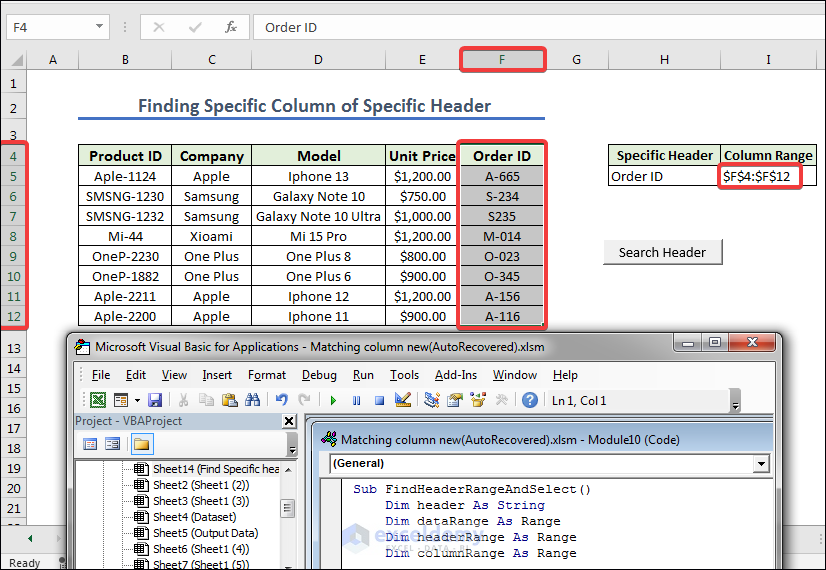
- Like in example 1 first we have to give names Specific Header and Column Range in H4 and I4 cells respectively, and create a button naming it as Search Header. Now we give any Column Header from the left dataset.
- Write the code below and assign the macro in the Search Header.
- Copy the code.
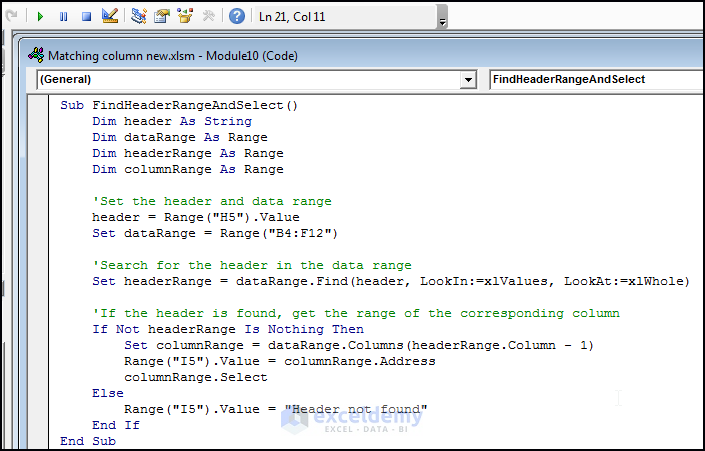
Sub FindHeaderRangeAndSelect()
Dim header As String
Dim dataRange As Range
Dim headerRange As Range
Dim columnRange As Range
'Set the header and data range
header = Range("H5").Value
Set dataRange = Range("B4:F12")
'Search for the header in the data range
Set headerRange = dataRange.Find(header, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole)
'If the header is found, get the range of the corresponding column
If Not headerRange Is Nothing Then
Set columnRange = dataRange.Columns(headerRange.Column - 1)
Range("I5").Value = columnRange.Address
columnRange.Select
Else
Range("I5").Value = "Header not found"
End If
End Sub- Assign the Macro FindHeaderRangeAndSelect in the Search Header button.
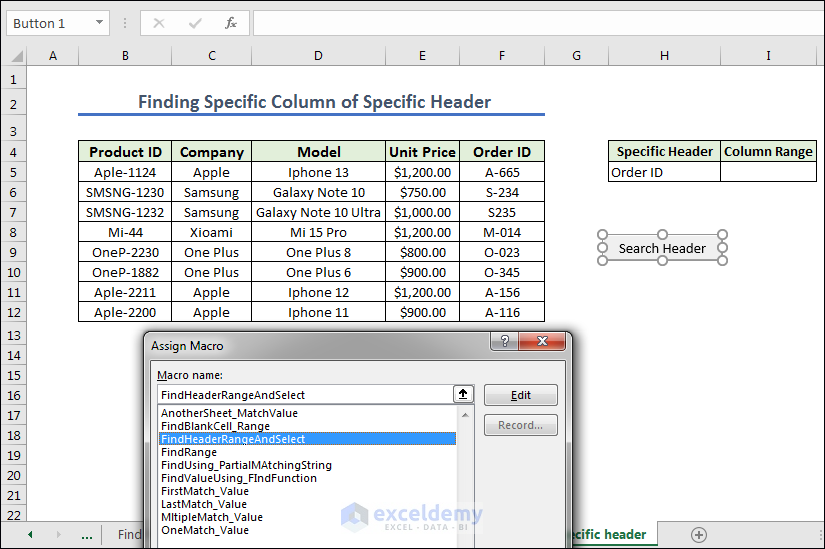
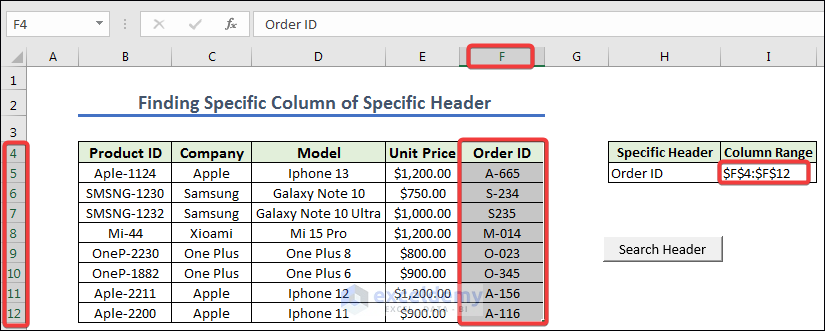
- Assign the macro FindHeaderRangeAndSelect in the Search Header button, we are going to press Search Header. Get the final column of the specific header.
Code Explanation
Sub FindHeaderRangeAndSelect()
Dim header As String
Dim dataRange As Range
Dim headerRange As Range
Dim columnRange As RangeThis code starts by declaring four variables: “header” to store the value of the header we want to search for, “dataRange” to store the range of data we want to search in, “headerRange” to store the range of the cell containing the header, and “columnRange” to store the range of the column to the left of the header.
'Set the header and data range
header = Range("H5").Value
Set dataRange = Range("B4:F12")This part sets the values of “header” and “dataRange” based on the values in cells H5 and B4:F12, respectively.
'Search for the header in the data range
Set headerRange = dataRange.Find(header, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole)Use the “Find” method to search for the value of “header” within the “dataRange”. It stores the range of the cell containing the header in the “headerRange” variable.
'If the header is found, get the range of the corresponding column
If Not headerRange Is Nothing Then
Set columnRange = dataRange.Columns(headerRange.Column - 1)
Range("I5").Value = columnRange.Address
columnRange.Select
Else
Range("I5").Value = "Header not found"
End IfThis code checks if the “headerRange” variable is not empty. If the header is found, it sets the “columnRange” variable to the range of the column to the left of the header. It then prints the address of the “columnRange” variable to cell I5 and selects that column. If the header is not found, it prints a message to cell I5 indicating that the header was not found.
Things to Remember
- Use the “Find” method: VBA provides a built-in “Find” method that can be used to search for a specific value in a range or column.
- Define the search range: Before using the “Find” method, you need to define the range to search within. This can be done using the “Range” method.
- Use variables to store values: It’s a good practice to use variables to store the values you’re searching for, as well as the results of the search.
- Check for errors: When using the “Find” method, it’s important to check for errors, such as when the value is not found in the range.
- Use loops for multiple searches: If you need to search for multiple values in a column, you can use a loop to iterate through each value and perform the search.
- Consider performance: If you’re searching through a large range of cells, it’s important to consider performance and optimize your code to avoid slowing down the application.
- Use the “Offset” property to return adjacent values: Once you’ve found a matching value in a column, you can use the “Offset” property to return the value in an adjacent column or row.
- Use the “Cells” property to return the cell address: If you need to return the address of the cell containing the matching value, you can use the “Cells” property.
- Test your code: Always test your code thoroughly to ensure it’s working as expected before using it in a production environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is VBA?
A: VBA stands for Visual Basic for Applications, and it is a programming language that is used to automate tasks in Microsoft Office applications, including Excel.
Q: How can I find a matching value in a column using VBA?
A: You can use the “Find” method in VBA to search for a specific value in a range or column. First, define the range to search within using the “Range” method, and then use the “Find” method to search for the value. You can also use a loop to search for multiple values in a column.
Q: What should I do if the value I’m searching for is not found in the column?
A: When using the “Find” method, it’s important to check for errors, such as when the value is not found in the range. You can use an “If” statement to check if the value was found, and then take appropriate action if it was not found.
Q: How can I return the value in an adjacent column or row when a matching value is found?
A: Once you’ve found a matching value in a column using the “Find” method, you can use the “Offset” property to return the value in an adjacent column or row. The “Offset” property allows you to specify the number of rows and columns to move from the current cell.
Q: How can I return the address of the cell containing the matching value?
A: If you need to return the address of the cell containing the matching value, you can use the “Cells” property. This property allows you to specify the row and column index of the cell you want to return.
Q: How can I optimize my VBA code for performance when searching through a large range of cells?
A: If you’re searching through a large range of cells, it’s important to optimize your code for performance. This can include using variables to store values and results, avoiding unnecessary loops, and using the “Application.ScreenUpdating” property to disable screen updating while the code is running.
Download Practice Workbook
You can download the Excel workbook that we have used to prepare this article.
Related Articles
- How to Find Blank Cells Using VBA in Excel
- How to Find Last Row Using Excel VBA
- Find the Last Row with Data in a Range Using Excel VBA Macros
- Excel VBA: Find the Next Empty Cell in the Range
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!


