The image below showcases how three results can be obtained, using the ByRef argument in the Excel VBA function.
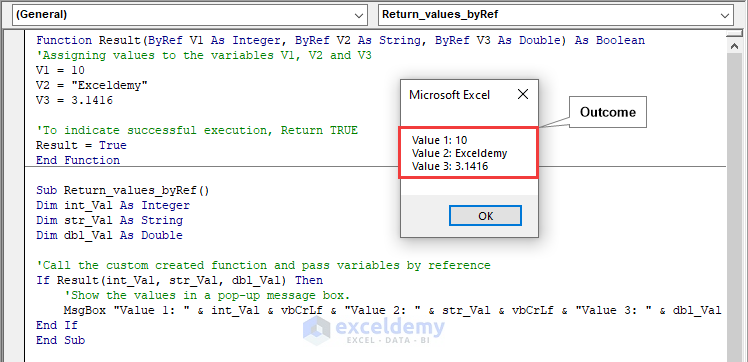
Method 1 – Returning Multiple Values through Reference using the by Passing Argument
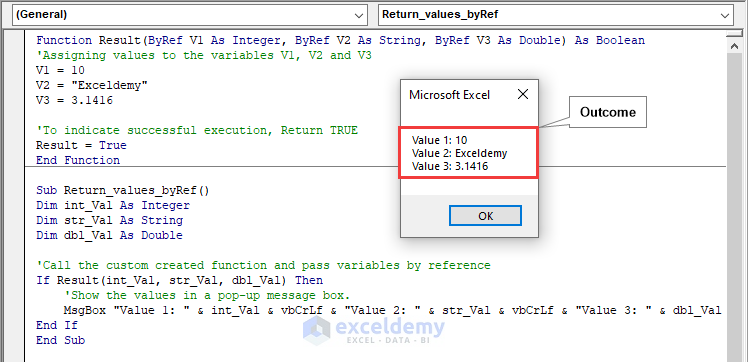
Code:
Function Result(ByRef V1 As Integer, ByRef V2 As String, ByRef V3 As Double) As Boolean
'Assigning values to the variables V1, V2 and V3
V1 = 1
V2 = "Exceldemy"
V3 = 3.1416
'To indicate successful execution, Return TRUE
Result = True
End Function
Sub Return_values_byRef()
Dim int_Val As Integer
Dim str_Val As String
Dim dbl_Val As Double
'Call the custom created function and pass variables by reference
If Result(int_Val, str_Val, dbl_Val) Then
'Show the values in a pop-up message box.
MsgBox "Value 1: " & int_Val & vbCrLf & "Value 2: " & str_Val & vbCrLf & "Value 3: " & dbl_Val
End If
End SubCode Breakdown
- Function Result(ByRef V1 As Integer, ByRef V2 As String, ByRef V3 As Double) determines a function where the passing argument By Ref is a read-only variable that can’t change its value inside the Excel VBA function in the 1st sub-procedure.
- The assigned value in the V1, V2, and V3 and the Boolean value TRUE indicate the execution.
- Dim int_Val As Integer, Dim str_Val As String Dim dbl_Val As Double represent the data value type of a custom function argument in the 2nd sub-procedure.
- If Result(int_Val, str_Val, dbl_Val) declares that the function is TRUE and shows the concatenated the values in the message box.
`
Read More: How to Execute VBA Function Procedure in Excel
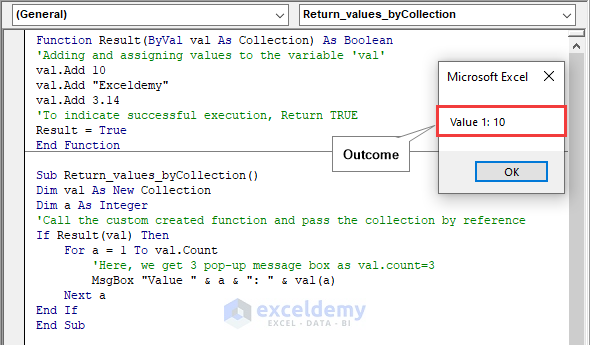
Method 2 – Returning Two or More Values Using a Collection Object
Code:
Function Result(ByVal val As Collection) As Boolean
'Adding and assigning values to the variable 'val'
val.Add 10
val.Add "Exceldemy"
val.Add 3.14
'To indicate successful execution, Return TRUE
Result = True
End Function
Sub Return_values_byCollection()
Dim val As New Collection
Dim a As Integer
'Call the custom created function and pass the collection by reference
If Result(val) Then
For a = 1 To val.Count
'Here, we get 3 pop-up message box as val.count=3
MsgBox "Value " & a & ": " & val(a)
Next a
End If
End SubCode Breakdown
- Function Result(ByVal val As Collection) As Boolean; the val variable is declared as a Collection object, and Boolean determines the logical operation based on TRUE or FALSE.
- val.Add adds different items to the variable.
- In the 2nd Sub-Procedure, val is declared as the new collection.
- If Result(val) calls all values assigned in the val variable if the condition is TRUE.
- For a = 1 To val.Count is the loop that returns the number of outcomes.
- MsgBox “Value ” & a & “: ” & val(a) shows the value for each item.
Method 3 – Returning Values by Using the Dictionary Object
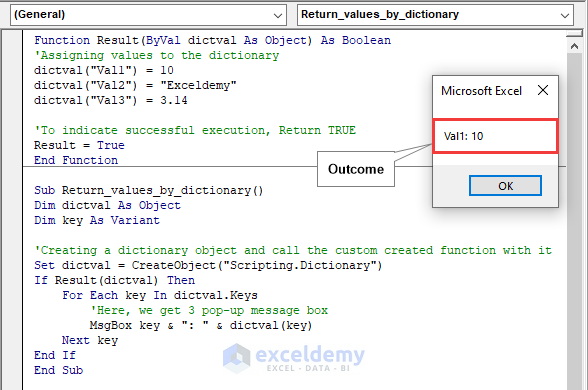
Code:
Function Result(ByVal dictval As Object) As Boolean
'Assigning values to the dictionary
dictval("Val1") = 10
dictval("Val2") = "Exceldemy"
dictval("Val3") = 3.14
'To indicate successful execution, Return TRUE
Result = True
End Function
Sub Return_values_by_dictionary()
Dim dictval As Object
Dim key As Variant
'Creating a dictionary object and call the custom created function with it
Set dictval = CreateObject("Scripting.Dictionary")
If Result(dictval) Then
For Each key In dictval.Keys
'Here, we get 3 pop-up message box
MsgBox key & ": " & dictval(key)
Next key
End If
End SubCode Breakdown
- Function Result(ByVal dictval As Object) As Boolean; the dictval variable is declared as dictionary object and Boolean determines the logical operation based on TRUE or FALSE.
- dictval(“Val1”) assigns values.
- In the 2nd sub-procedure, Dim dictval As Object declares dictval as a dictionary object. The key variable is also declared as a variant.
- Set dictval = CreateObject(“Scripting.Dictionary”) holds the values from the code.
- If Result(dictval) calls all the values if the logic is TRUE.
- For Each key In dictval.Keys; the For loop selects all values.
- Finally, MsgBox shows values in a pop-up message box.
Method 4 – Return Several Values Using an Array
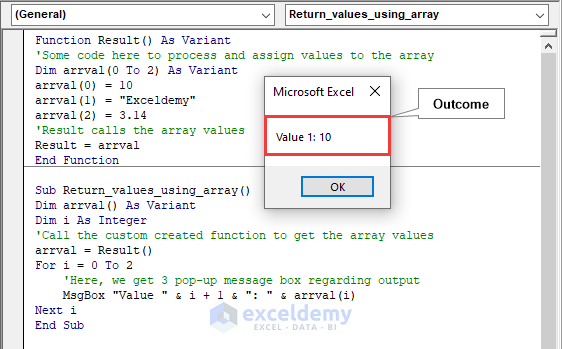
Code:
Function Result() As Variant
'code to process and assign values to the array
Dim arrval(0 To 2) As Variant
arrval(0) = 10
arrval(1) = "Exceldemy"
arrval(2) = 3.14
'Result calls the array values
Result = arrval
End Function
Sub Return_values_using_array()
Dim arrval() As Variant
Dim i As Integer
'Call the custom created function to get the array values
arrval = Result()
For i = 0 To 2
'Here, we get 3 pop-up message box regarding output
MsgBox "Value " & i + 1 & ": " & arrval(i)
Next i
End SubCode Breakdown
- Function Result() As Variant creates a function with an array.
- Dim arrval(0 To 2) As Variant determines the variable with an index of 0 to 2.
- arrval(0)=10 defines the value for the 1st array.
- In the 2nd sub-procedure, the variable is declared as an array: Dim arrval() As Variant
- arrval = Result() selects the values.
- For i = 0 To 2; Selects all the values in the array.
- MsgBox “Value ” & i + 1 & “: ” & arrval(i) display 3 outputs in a message box.
Method 5 – Returning Values From an CSV String
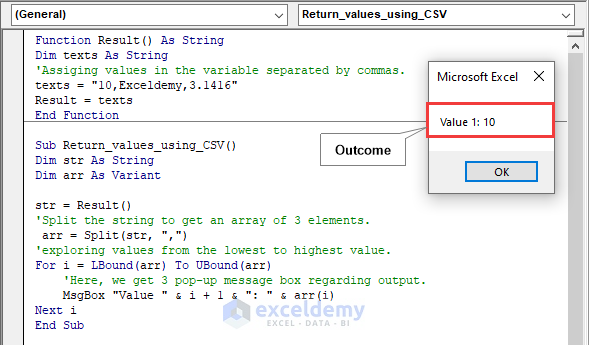
Code:
Function Result() As String
Dim texts As String
'Assigning values in the variable separated by commas.
texts = "10,Exceldemy,3.1416"
Result = texts
End Function
Sub Return_values_using_CSV()
Dim str As String
Dim arr As Variant
str = Result()
'Split the string to get an array of 3 elements.
arr = Split(str, ",")
'exploring values from the lowest to highest value.
For i = LBound(arr) To UBound(arr)
'Here, we get 3 pop-up message box regarding output.
MsgBox "Value " & i + 1 & ": " & arr(i)
Next i
End SubCode Breakdown
- In the 1st sub-procedure, texts = “10,Exceldemy,3.1416” assigns values in the texts variable and declares a variable as string: Dim texts as String.
- In the 2nd sub-procedure, str and arr are declared as a string and a variant.
- str = Result() selects values.
- arr = Split(str, “,”) separates the string values based on commas.
- For i = LBound(arr) To UBound(arr); the For loop selects the values and shows them in the MsgBox function.
Method 6 – Returning Different Values with a User-Defined Type
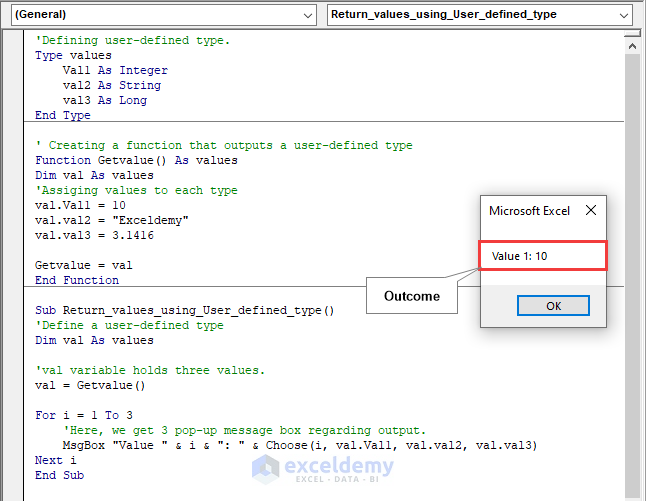
Code:
'Defining user-defined type.
Type values
Val1 As Integer
val2 As String
val3 As Long
End Type
' Creating a function that outputs a user-defined type
Function Getvalue() As values
Dim val As values
'Assiging values to each type
val.Val1 = 10
val.val2 = "Exceldemy"
val.val3 = 3.1416
Getvalue = val
End Function
Sub Return_values_using_User_defined_type()
'Define a user-defined type
Dim val As values
'val variable holds three values.
val = Getvalue()
For i = 1 To 3
'Here, we get 3 pop-up message box regarding output.
MsgBox "Value " & i & ": " & Choose(i, val.Val1, val.val2, val.val3)
Next i
End SubCode Breakdown
- In the 1st sub-procedure, all data types are declared. Type values represent the User Defined Type.
- Function Getvalue() As values creates a function: Getvalue and declares the value type values. The val variable is declared as values in the 2nd sub-procedure.
- val.Val1=10 assigns a value for the variable val.
- Getvalue = val all the values of val are assigned to the Getvalue function.
- val = Getvalue() assigns the values in val from the Getvalue function in the 3rd sub-procedure.
- For i = 1 To 3; For loop selects 3 values and shows them in message boxes.
Read More: How to Use VBA User Defined Function
Download Practice Workbook
Download the Excel Workbook.
Related Articles
- How to Return a Value in VBA Function
- How to Make VBA Function with Arguments in Excel
- How to Use VBA Input Function in Excel
- VBA Sub Vs Function in Excel
- How to Create and Use ColorFunction in Excel
- Difference Between Subroutine and Function in Excel VBA
- How to Create Custom Function in Excel VBA