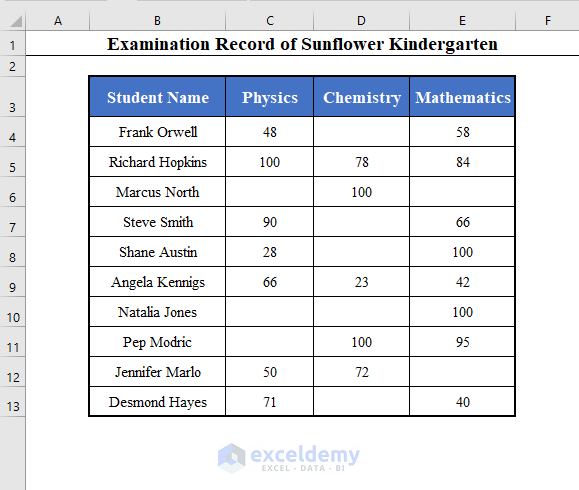
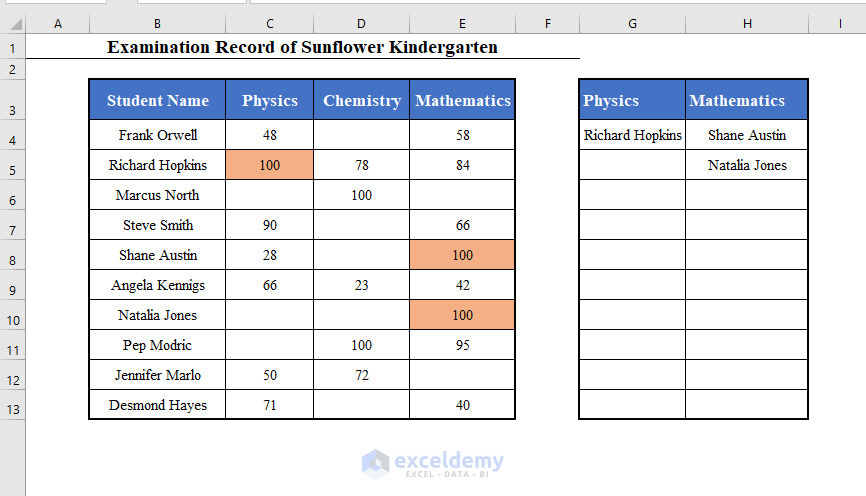
In the sample dataset of examination record for Sunflower Kindergarten school, the blank cells mean that the student was absent for that particular exam.
⧪ Step 1 – Declaring the Cell
Let’s analyze whether Jennifer Marlo appeared in the Physics exam.
We need to check whether cell C12 contains a value or not.
Declare cell C12.
Use the following code:
Set Cell = Range("C12").Cells(1, 1)⧪ Step 2 – Checking If the Cell Contains a Value (Including a Particular Value)
Use the following code:
If Cell.Value <> "" ThenThis code will be executed if the cell contains any value. To check for a value (For example, whether it contains 100 or not), use that specific value with an Equal to symbol.
If Cell.Value <> "" Then⧪ Step 3 – Allotting the Task
You have to set up a task that’ll be executed if the cell contains a value (or a specific value).
We want to display the message “Jennifer Marlo appeared in Physics exam”. So the line of code will be:
MsgBox "Jennifer Marlo appeared in Physics exam."⧪ Step 4 – Ending the If Block
You have to declare an end to the If block.
End IfSo the complete VBA code will be:
⧭ VBA Code:
Sub If_Cell_Contains_Value()
Set Cell = Range("C12").Cells(1, 1)
If Cell.Value <> "" Then
MsgBox "Jennifer Marlo appeared in Physics exam."
End If
End Sub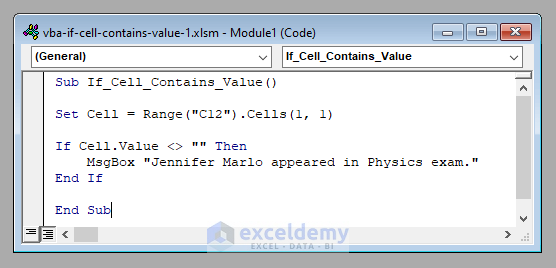
⧭ Output:
Run this code by clicking the Run Sub/UserForm button on the toolbar.
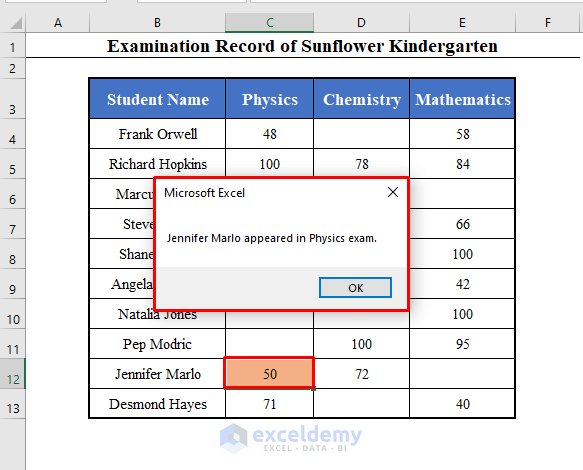
It will display the message “Jennifer Marlo appeared in Physics exam.” as the cell C12 contains a value of 50.
Examples Involving If Cell Contains a Value Then a Specified Output with Excel VBA
We’ve learned to analyze if a cell contains a value or not in VBA. Now, let’s explore some examples to make the understanding clear.
Example 1 – Developing a Macro to Filter Out a Value If the Corresponding Cell Contains any Value then in Excel VBA
Let’s develop a Macro to filter out the students who appeared in each of the exams.
We have to check the cells containing the marks of each of the subjects and see whether they contain a value or not.
If they do, sort out the name of the corresponding student.
The complete VBA code to accomplish this will be:
⧭ VBA Code:
Sub Sorting_Out_Cells_that_Contain_Values()
Starting_Cell = InputBox("Enter the Reference of the First Cell of the Filtered Data: ")
For i = 2 To Selection.Columns.Count
Range(Starting_Cell).Cells(1, i - 1) = Selection.Cells(1, i)
Next i
Count = 2
For i = 2 To Selection.Columns.Count
For j = 2 To Selection.Rows.Count
Set Cell = Selection.Cells(j, i)
If Cell.Value <> "" Then
Range(Starting_Cell).Cells(Count, i - 1) = Selection.Cells(j, 1).Value
Count = Count + 1
End If
Next j
Count = 2
Next i
End Sub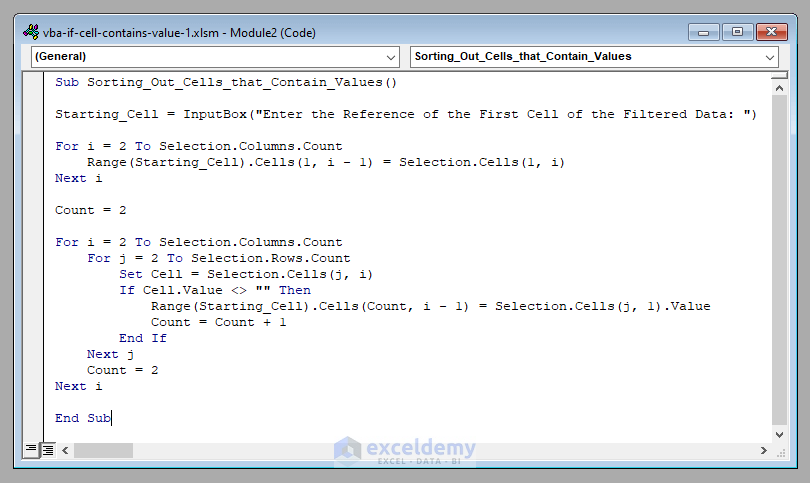
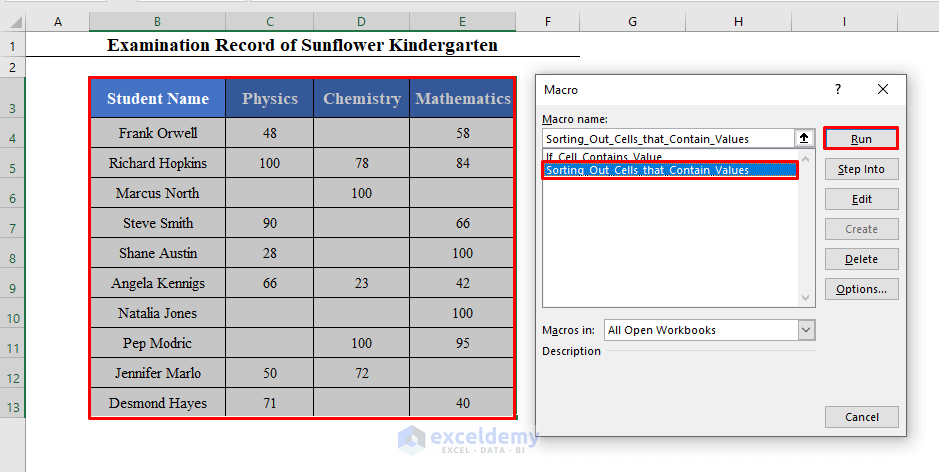
⧭ Output:
Select the data set (Including the Headers) and run this Macro.
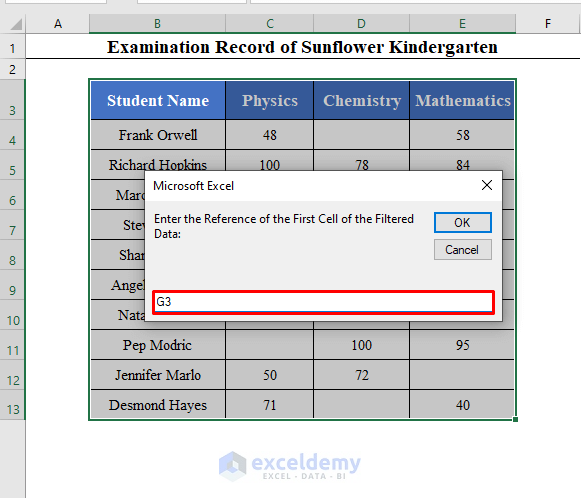
You will be asked to enter the reference of the first cell where you want the filtered data. I’ve entered G3.
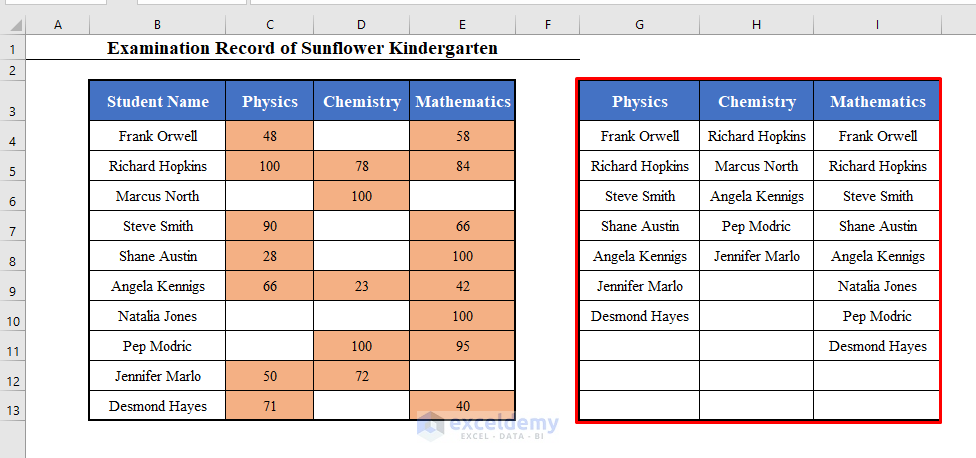
Click OK. You’ll get the names of the students who appeared in each of the exams (Including the Headers) in a new data set starting from cell G3.
Read More: Excel VBA: If Statement Based on Cell Value
Example 2 – Creating a User-Defined Function to Sort Out a Value If the Corresponding Cell Contains a Specific Value then in Excel VBA
We will create a user-defined function that will return the names of the students who got a specific mark in each of the subjects.
We have to check the cells containing the marks of each of the subjects and see whether they are equal to a specific value or not.
If they are, we will return the name of the corresponding student.
The VBA code will be:
⧭ VBA Code:
Function Cells_with_Values(Rng As Range, Data As Variant)
Dim Output() As Variant
ReDim Output(Rng.Rows.Count, Rng.Columns.Count - 1)
For i = 0 To Rng.Columns.Count - 2
Output(0, i) = Rng.Cells(1, i + 2)
Next i
Count = 1
For i = 2 To Rng.Columns.Count
For j = 2 To Rng.Rows.Count
Set Cell = Rng.Cells(j, i)
If Cell.Value = Data Then
Output(Count, i - 2) = Rng.Cells(j, 1).Value
Count = Count + 1
End If
Next j
Count = 1
Next i
For i = LBound(Output, 1) To UBound(Output, 1)
For j = LBound(Output, 2) To UBound(Output, 2)
If Output(i, j) = 0 Then
Output(i, j) = ""
End If
Next j
Next i
Cells_with_Values = Output
End Function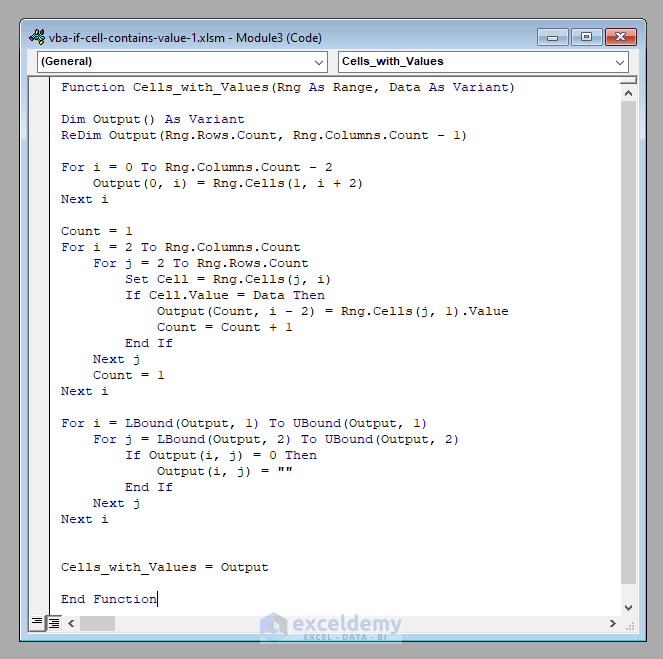
⧭ Output:
The code creates a function called Cells_with_Values that takes two arguments, a Range and a Value.
Let’s find out the students who got 100 in each of the subjects using this function.
Select a range of cells in your worksheet and enter this function in the first cell of the range:
=Cells_with_Values(B3:E13,100)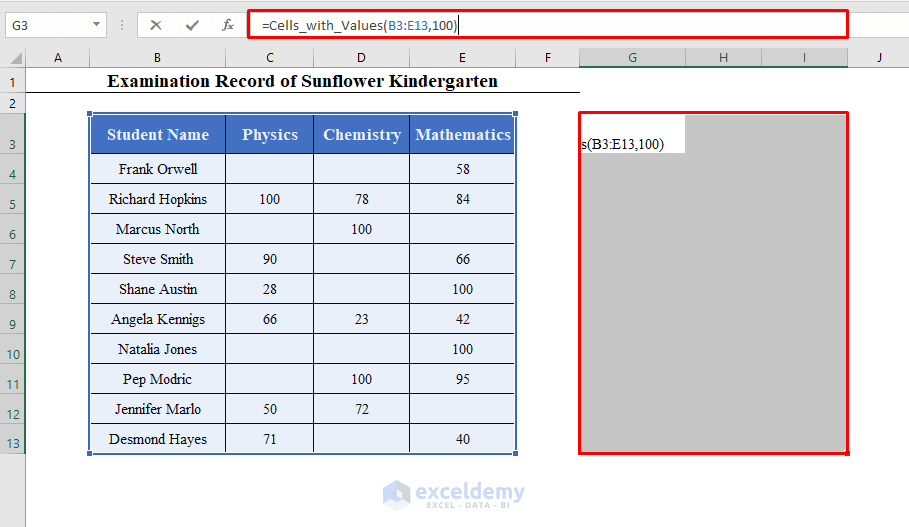
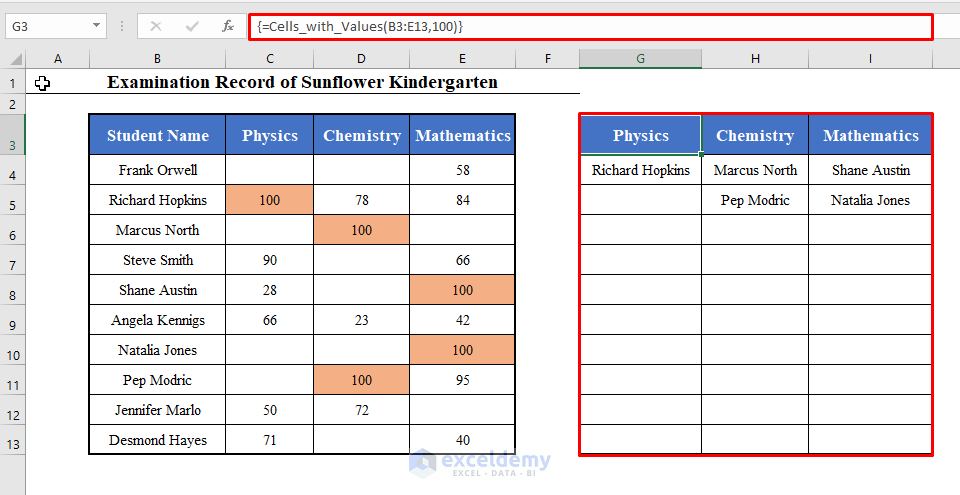
Press CTRL + SHIFT + ENTER (Array Formula). It will return an array consisting of the names of the students who got 100 in each subject, including the Headers.
Read More: VBA IF Statement with Multiple Conditions in Excel
Example 3 – Developing a UserForm to Extract Out a Value if the Corresponding Cell Contains any Value (Or a Specific Value) in Excel VBA
We will develop a UserForm to extract the names of students who appeared (or got specific marks) in some specific exams.
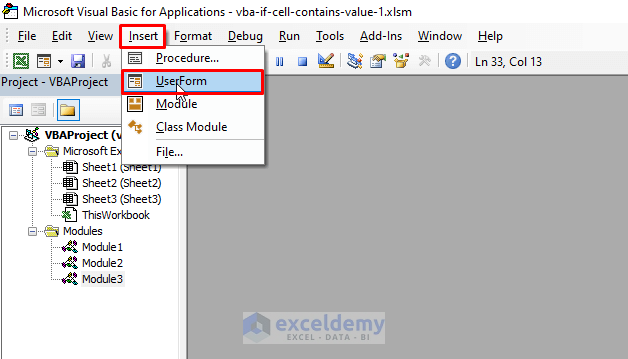
⧪ Step 1 – Opening the UserForm
In the VBA editor, Go to Insert > UserForm. A new UserForm called UserForm1 will be opened.
⧪ Step 2 – Dragging Tools to the UserForm
In addition to the UserForm, you will get the Toolbox. Move your cursor over the Toolbox and drag 4 Labels (Label1, Label2, Label3, Label4) and 3 ListBoxes (ListBox1, ListBox2, ListBox3) and a TextBox (TextBox1) in a rectangular shape over the UserForm.
Drag another Label (Label5) and a TextBox (TextBox2) to the bottom left corner of the UserForm.
Drag a CommandButton (CommandButton1) to the bottom right corner.
Change the displays of the Labels to Lookup Column, Return Column, Any Value or a Specific Value, Value, and Starting Cell.
Change the display of the CommandButton1 to OK.
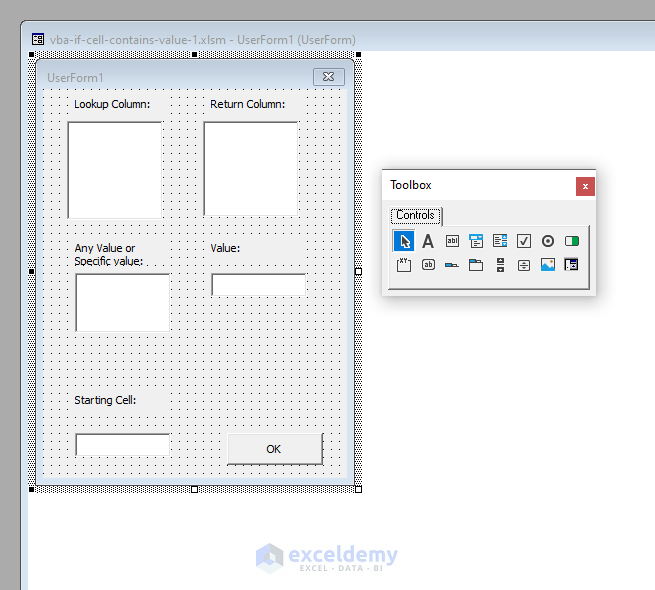
⧪ Step 3 – Writing Code for ListBox3
Double click on ListBox3. A Private Subprocedure called ListBox3_Click will open. Enter the following code there.
Private Sub ListBox3_Click()
If UserForm1.ListBox3.Selected(0) = True Then
UserForm1.Label4.Visible = False
UserForm1.TextBox1.Visible = False
ElseIf UserForm1.ListBox3.Selected(1) = True Then
UserForm1.Label4.Visible = True
UserForm1.TextBox1.Visible = True
End If
End Sub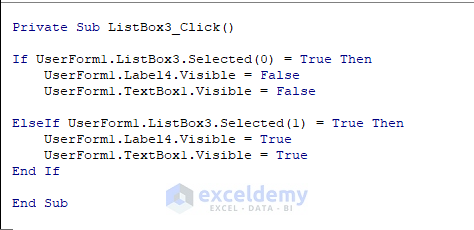
⧪ Step 4 – Writing Code for CommandButton1
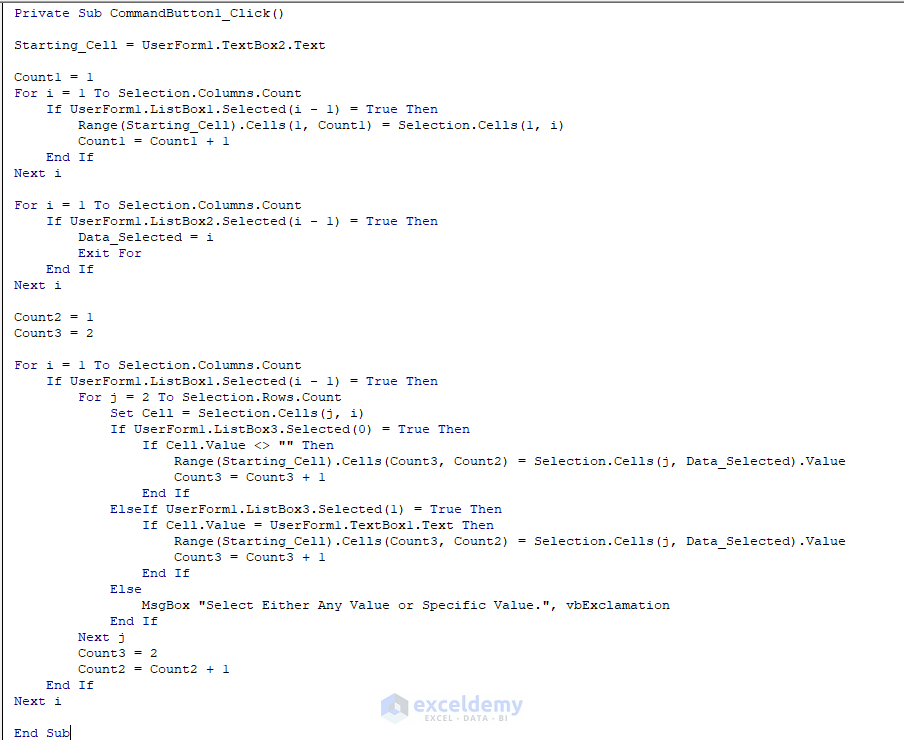
Double-click on CommandButton1. Another Private Subprocedure called CommandButton1_Click will open. Enter the following code there.
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
On Error GoTo Message
Starting_Cell = UserForm1.TextBox2.Text
Count1 = 1
For i = 1 To Selection.Columns.Count
If UserForm1.ListBox1.Selected(i - 1) = True Then
Range(Starting_Cell).Cells(1, Count1) = Selection.Cells(1, i)
Count1 = Count1 + 1
End If
Next i
If Count1 = 1 Then
MsgBox "Select at Least One Lookup Column.", vbExclamation
Exit Sub
End If
Data_Selected = 0
For i = 1 To Selection.Columns.Count
If UserForm1.ListBox2.Selected(i - 1) = True Then
Data_Selected = i
Exit For
End If
Next i
If Data_Selected = 0 Then
MsgBox "Select One Return Column.", vbExclamation
Exit Sub
End If
Count2 = 1
Count3 = 2
For i = 1 To Selection.Columns.Count
If UserForm1.ListBox1.Selected(i - 1) = True Then
For j = 2 To Selection.Rows.Count
Set Cell = Selection.Cells(j, i)
If UserForm1.ListBox3.Selected(0) = True Then
If Cell.Value <> "" Then
Range(Starting_Cell).Cells(Count3, Count2) = Selection.Cells(j, Data_Selected).Value
Count3 = Count3 + 1
End If
ElseIf UserForm1.ListBox3.Selected(1) = True Then
If Cell.Value = UserForm1.TextBox1.Text Then
Range(Starting_Cell).Cells(Count3, Count2) = Selection.Cells(j, Data_Selected).Value
Count3 = Count3 + 1
End If
Else
MsgBox "Select Either Any Value or Specific Value.", vbExclamation
Exit For
End If
Next j
Count3 = 2
Count2 = Count2 + 1
End If
Next i
Exit Sub
Message:
MsgBox "Enter a Valid Cell Reference as the Starting Cell.", vbExclamation
End Sub
⧪ Step 5 – Writing Code for Running the UserForm
Insert a new Module from the VBA toolbar and insert the following code there.
Sub Run_UserForm()
UserForm1.Caption = "Filtering Cells that Contain Values"
UserForm1.ListBox1.BorderStyle = fmBorderStyleSingle
UserForm1.ListBox1.ListStyle = fmListStyleOption
UserForm1.ListBox2.BorderStyle = fmBorderStyleSingle
UserForm1.ListBox2.ListStyle = fmListStyleOption
UserForm1.ListBox3.BorderStyle = fmBorderStyleSingle
UserForm1.ListBox3.ListStyle = fmListStyleOption
For i = 1 To Selection.Columns.Count
UserForm1.ListBox1.AddItem Selection.Cells(1, i)
UserForm1.ListBox2.AddItem Selection.Cells(1, i)
Next i
UserForm1.ListBox1.MultiSelect = fmMultiSelectMulti
UserForm1.ListBox3.AddItem "Any Value"
UserForm1.ListBox3.AddItem "Specific value"
UserForm1.Label4.Visible = False
UserForm1.TextBox1.Visible = False
Load UserForm1
UserForm1.Show
End Sub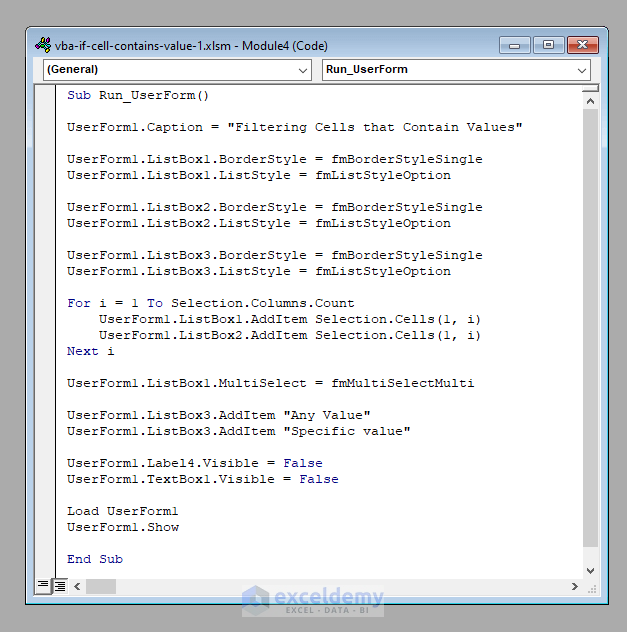
⧪ Step 6 – Running the UserForm (The Final Output)
Your UserForm is now ready to use. Select the data set from the worksheet (B3:E13 here) (Including the Headers) and run the Macro called Run_UserForm.
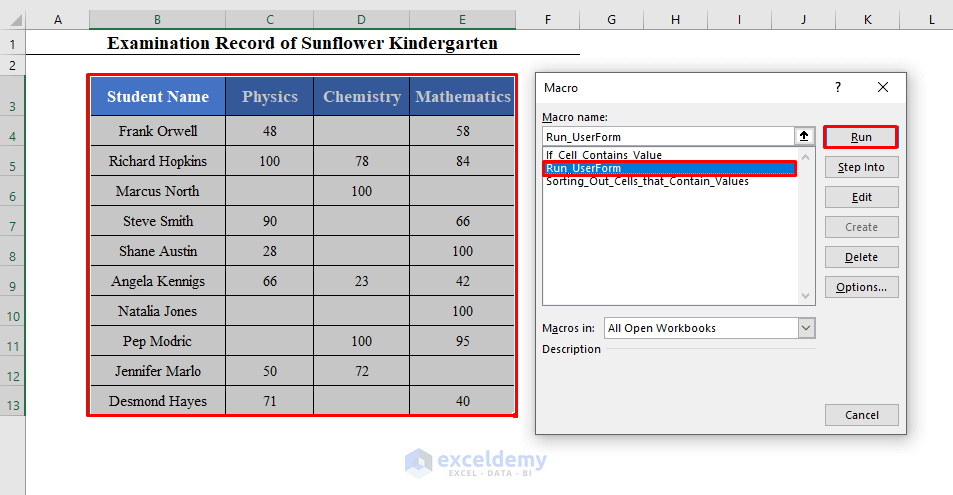
The UserForm will be loaded in the worksheet. From the Lookup Column table, I have selected Physics and Mathematics, because I want to get the names of the students who appeared in Physics and Mathematics exams.
From the Return Column table, I have selected Student Name.
From the Any Value or Specific Value table,select Any Value.
In the Starting Cell box, I have put G3.
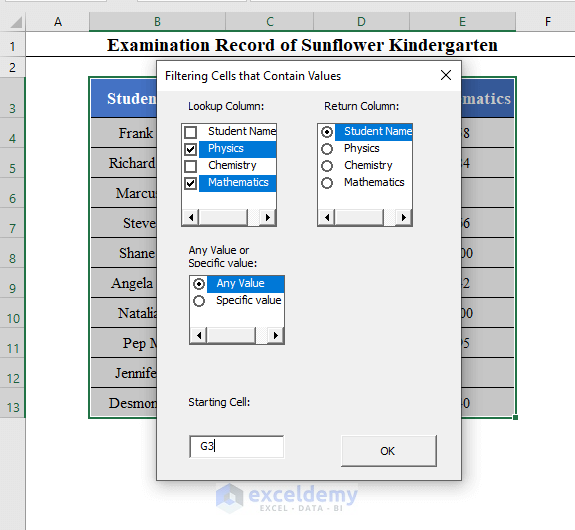
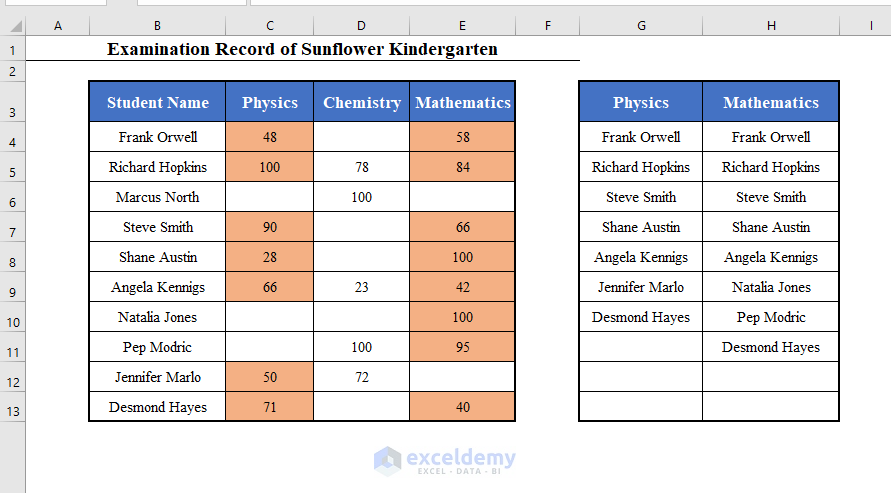
Click OK to get the names of the students who appeared in Physics and Mathematics exams starting from cell G3.
If you had selected Specific Value from the Any Value or Specific Value table, you would have got another TextBox to enter the specific value.
I have entered 100.
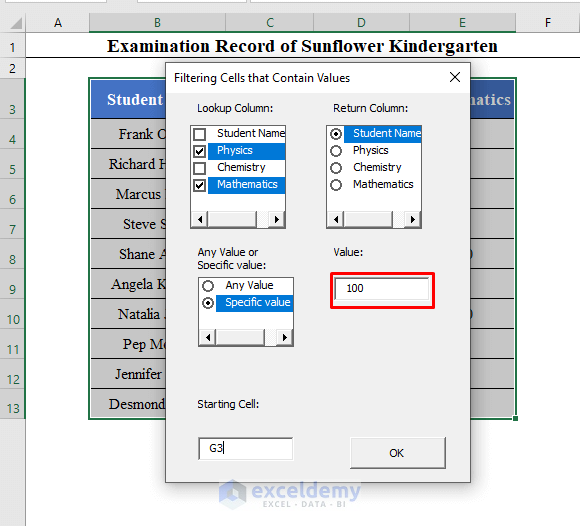
Click OK to get the students who got 100 in Physics and Chemistry.
Read More: Excel VBA to Check If String Contains Letters
Download Practice Workbook
Related Articles
- Excel VBA: Combining If with And for Multiple Conditions
- Excel VBA Nested If Then Else in a For Next Loop
- Else Without If Error VBA in Excel
- Excel VBA: Check If a Sheet Exists


