The If, IsError, and VLookup Functions in VBA
The syntax of the If function is:
If (condition) Then
' code to execute if condition is true
Else
' code to execute if condition is false
End If- It checks if a a condition is met.
The syntax of the IsError function is:
Dim result As Variant
result = 10 / 0
If IsError(result) Then
MsgBox "Error: " & result
Else
MsgBox "Result: " & result
End If- It works as a gatekeeper for all errors inside a code. It returns logical TRUE or FALSE based on the occurrence of errors.
The syntax of the VLookup function is:
Dim result As Variant
Dim lookup_value As Variant
Dim table_array As Range
Dim column_index As Integer
lookup_value = "John"
Set table_array = Range("A1:B10")
column_index = 2
result = Application.VLookup(lookup_value, table_array, column_index, False)
MsgBox "Result: " & result- It finds specific values in a range and returns values from a specific column with exact matches.
Note:
The VLookup function is part of the Application object in VBA, so it needs to be called with the Application prefix. The range_lookup argument is optional, and False is used for an exact match.
How to Launch the VBA Editor in Excel
- Go to the Developer tab and click Visual Basic.
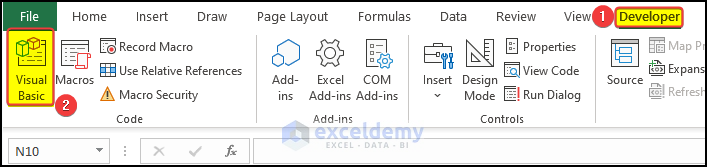
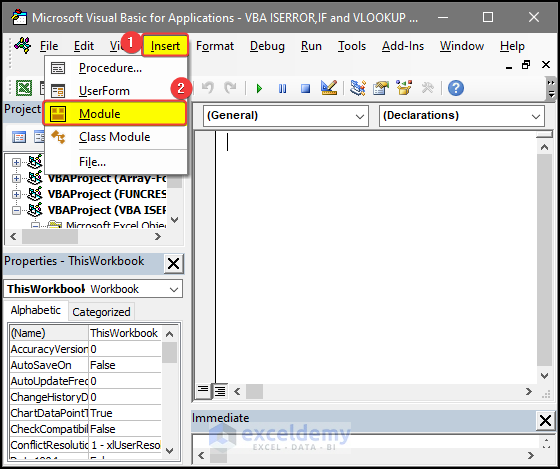
- Go to Insert > Module.
- Enter the code in the Module window.
Note:
If you can’t find the Developer tab on the ribbon, you must enable it.
Is It Possible to Use the IsError Function with the VLookup in One Statement in Excel VBA?
Yes. Mind the example below:
Dim lookupValue As Variant
Dim result As Variant
lookupValue = "John"
result = Application.VLookup(lookupValue, Range("A1:B10"), 2, False)
If IsError(result) Then
MsgBox "Error: " & result
Else
MsgBox "Result: " & result
End IfThis code is used in the following dataset.
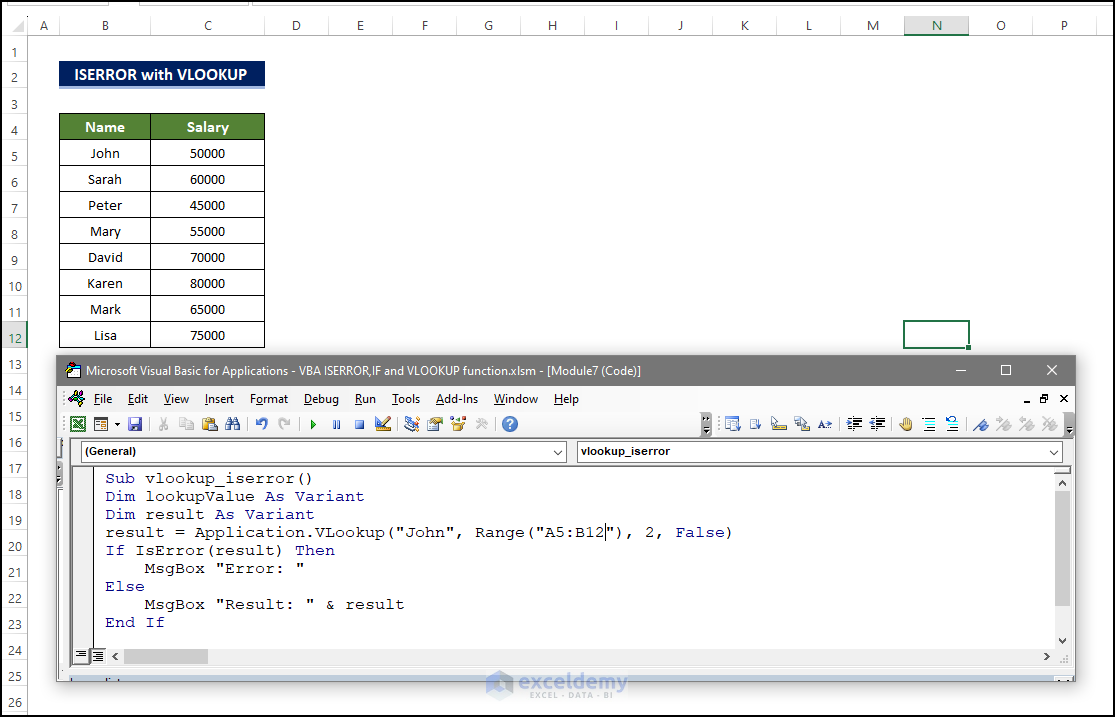
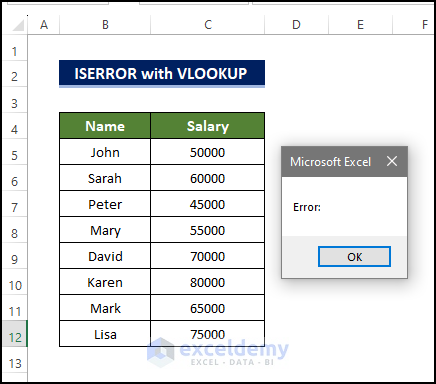
The VLookup function searches for the lookup value in A1:B10. If an error occurs, the VLookup function will return TRUE, and an error message box will be displayed. Otherwise, the result will be shown.
Using the If, IsError, and VLookup Functions in Excel VBA – 3 Examples
Example 1 – Extracting the Marks from Students Who Failed
Marks over 60 are presented as Passed.
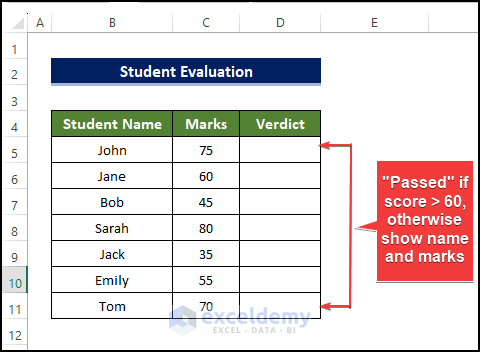
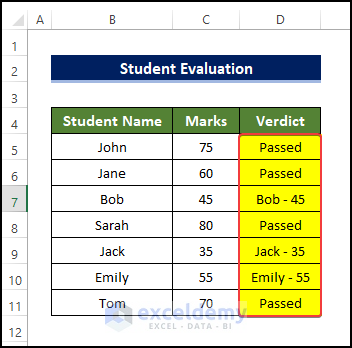
This will be the output.
Steps:
- Open the VBA editor window by pressing Alt+F11.
- Enter the following code in the code window.
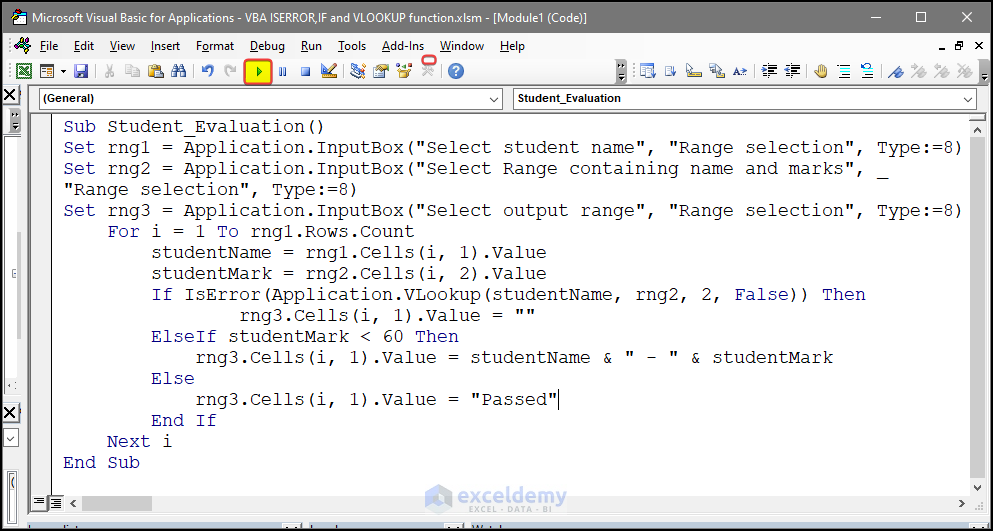
Sub Student_Evaluation()
Set rng1 = Application.InputBox("Select student name", "Range selection", Type:=8)
Set rng2 = Application.InputBox("Select Range containing name and marks", _
"Range selection", Type:=8)
Set rng3 = Application.InputBox("Select output range", "Range selection", Type:=8)
For i = 1 To rng1.Rows.Count
studentName = rng1.Cells(i, 1).Value
studentMark = rng2.Cells(i, 2).Value
If IsError(Application.VLookup(studentName, rng2, 2, False)) Then
rng3.Cells(i, 1).Value = ""
ElseIf studentMark < 60 Then
rng3.Cells(i, 1).Value = studentName & " - " & studentMark
Else
rng3.Cells(i, 1).Value = "Passed"
End If
Next i
End SubVBA Code Breakdown
Sub Student_Evaluation()starts the Subroutine: Student_Evaluation.
Sub Student_Evaluation()prompts the user to select a range containing students’ names. The InputBox function displays a dialog box that allows the user to select a range. It is assigned to the rng1 variable.
Set rng2 = Application.InputBox("Select Range containing name and marks", "Range selection", Type:=8)prompts the user to select a range containing students’ names and their marks. The InputBox function displays a dialog box that allows the user to select a range. It is assigned to the rng2 variable.
Set rng2 = Application.InputBox("Select Range containing name and marks", "Range selection", Type:=8)prompts the user to select an output range to display the results. The InputBox function displays a dialog box that allows the user to select a range. It is assigned to the rng3 variable.
For i = 1 To rng1.Rows.Countiterates over each row in rng1, which contains the students’ names.
studentName = rng1.Cells(i, 1).ValuestudentMark = rng2.Cells(i, 2).Valueassigns the value of the current student name and mark to the studentName and studentMark variables.
If IsError(Application.VLookup(studentName, rng2, 2, False)) Thenchecks if the student’s name exists in rng2 (which contains the students’ names and their marks). If the student’s name is not found, the output cell is set to blank.
ElseIf studentMark < 60 Then
rng3.Cells(i, 1).Value = studentName & " - " & studentMarkIf the student name is found in rng2 and the student mark is less than 60, the output cell is set to concatenate the student’s name and mark with a hyphen.
Else
rng3.Cells(i, 1).Value = "Passed"If the student’s name is found in rng2 , and the student’s mark is greater than or equal to 60, the output cell is set to “Passed”.
Next iends the loop.
End Subends the subroutine.
- Press F5 or click Run.
- The first input range asks for the students’ names: here, B5:B11.
- Press Enter.
- Another range selection asks for name and marks: here, B5:C11.
- Press Enter.
- Enter the output range: here, D5:D11.
- Press Enter.
This is the output.

Read More: Excel VBA Vlookup with Multiple Criteria
Example 2 – Determine the Salary of an Employee
The dataset below showcases Employees’ Names and their position.
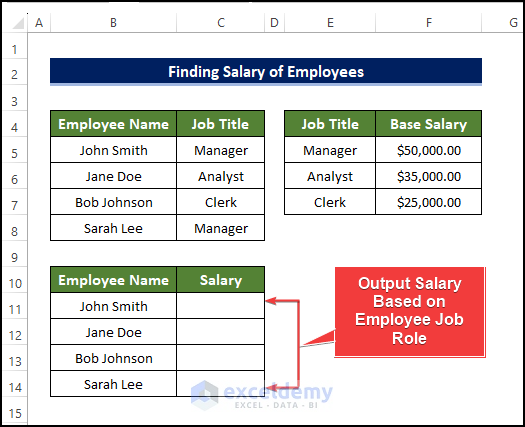
This will be the output.
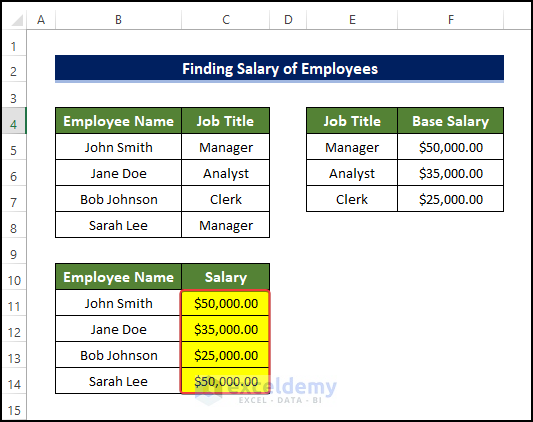
Steps:
- Open the VBA editor window by pressing Alt+F11.
- Enter the following code in the code window.
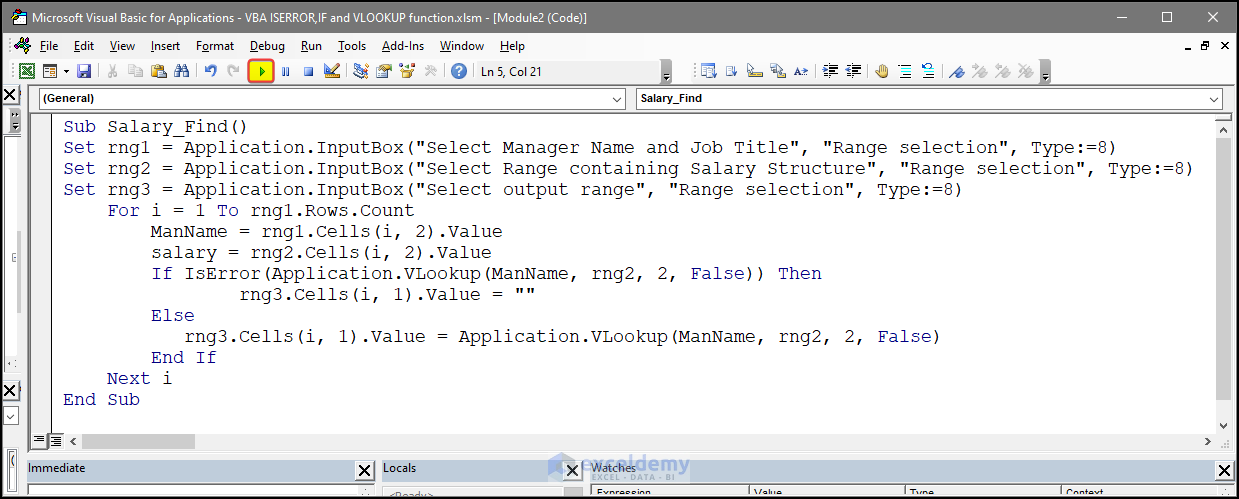
Sub Salary_Find()
Set rng1 = Application.InputBox("Select Manager Name and Job Title", "Range selection", Type:=8)
Set rng2 = Application.InputBox("Select Range containing Salary Structure", "Range selection", Type:=8)
Set rng3 = Application.InputBox("Select output range", "Range selection", Type:=8)
For i = 1 To rng1.Rows.Count
ManName = rng1.Cells(i, 2).Value
salary = rng2.Cells(i, 2).Value
If IsError(Application.VLookup(ManName, rng2, 2, False)) Then
rng3.Cells(i, 1).Value = ""
Else
rng3.Cells(i, 1).Value = Application.VLookup(ManName, rng2, 2, False)
End If
Next i
End SubCode Breakdown
Sub Salary_Find()starts the Subroutine: Salary_Find.
Set rng1 = Application.InputBox("Select Manager Name and Job Title", "Range selection", Type:=8)prompts the user to select a range containing Manager Names and their Job Titles. The InputBox function displays a dialog box that allows the user to select a range. It is assigned to the rng1 variable.
Set rng2 = Application.InputBox("Select Range containing Salary Structure", "Range selection", Type:=8)prompts the user to select a range containing the Salary. The InputBox function displays a dialog box that allows the user to select a range. It is assigned to the rng2 variable.
Set rng3 = Application.InputBox("Select output range", "Range selection", Type:=8)prompts the user to select an output range to display the results. The InputBox function displays a dialog box that allows the user to select a range. It is assigned to the rng3 variable.
For i = 1 To rng1.Rows.Countiterates over each row in rng1, which contains the Manager Names and Job Titles.
ManName = rng1.Cells(i, 2).Valueexcel vba if iserror vlookupassigns the value of the current Manager Name and Salary to the ManName and salary variables.
If IsError(Application.VLookup(ManName, rng2, 2, False)) Then
rng3.Cells(i, 1).Value = ""checks if the Manager’s Name exists in rng2 (which contains the salary). If the Manager’s Name is not found, the output cell is set to blank.
Elserng3.Cells(i, 1).Value = Application.VLookup(ManName, rng2, 2, False)If the Manager Name is found in rng2, the output cell is set to display the Salary based on the VLookup function.
Next iends the loop.
End Subends the subroutine.
- Press F5 or click Run.
- You will be asked to enter the Managers’ Names and Job Titles. Here, B5:C8.
- Press Enter.
- You will be asked to enter the range containing the Salary. Here, E5:F7.
- Press Enter.
- You will be asked to enter the output range. Here, C11:C14.
- Click OK.
This is the output.

Read More: Excel VBA to Vlookup Values for Multiple Matches
Example 3 – Determine a Budget Based on Difficulty
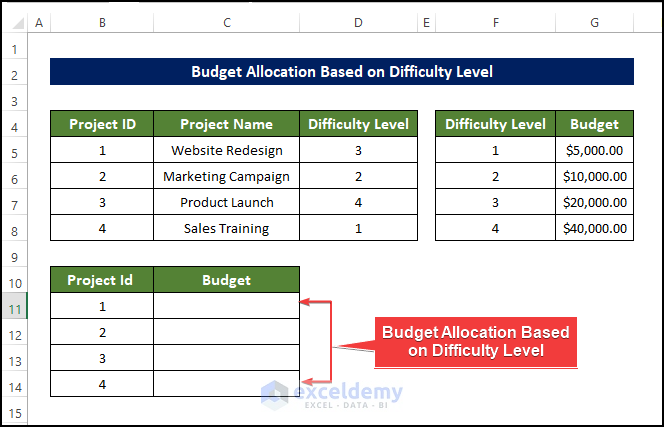
This will be the output.
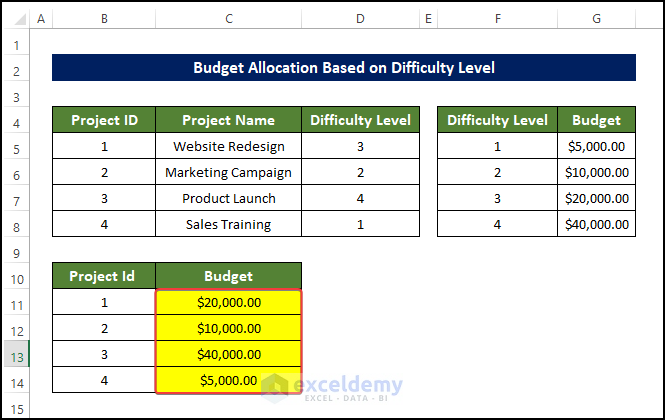
Steps:
- Open the VBA editor window by pressing Alt+F11.
- Enter the following code in the code window.
Sub budget_alloation()
Set rng1 = Application.InputBox("Select Project Name and Difficulty level", _
"Range selection", Type:=8)
Set rng2 = Application.InputBox("Select range containing Budget Structure", _
"Range selection", Type:=8)
Set rng3 = Application.InputBox("Select Output range", "Range selection", Type:=8)
For i = 1 To rng1.Rows.Count
ManName = rng1.Cells(i, 2).Value
salary = rng2.Cells(i, 2).Value
If IsError(Application.VLookup(ManName, rng2, 2, False)) Then
rng3.Cells(i, 1).Value = ""
Else
rng3.Cells(i, 1).Value = Application.VLookup(ManName, rng2, 2, False)
End If
Next i
End SubCode Breakdown
Sub budget_alloation()starts the subroutine: budget_allocation().
Set rng1 = Application.InputBox("Select Project Name and Difficulty level", _
"Range selection", Type:=8)prompts the user to select a range containing Project Names and their Difficulty Level. The InputBox function displays a dialog box that allows the user to select a range. It is assigned to the rng1 variable.
Set rng2 = Application.InputBox("Select range containing Budget Structure", _
"Range selection", Type:=8)prompts the user to select a range containing the budget structure. The InputBox function displays a dialog box that allows the user to select a range. It is assigned to the rng2 variable.
Set rng3 = Application.InputBox("Select Output range", "Range selection", Type:=8)prompts the user to select an output range to display the results. The InputBox function displays a dialog box that allows the user to select a range. It is assigned to the rng3 variable.
For i = 1 To rng1.Rows.Countiterates through each row in rng1.
ManName = rng1.Cells(i, 2).Value
salary = rng2.Cells(i, 2).ValueWithin the loop, the ManName and salary variables are set to the values of the cells in the current row of rng1 and rng2.
If IsError(Application.VLookup(ManName, rng2, 2, False)) Then
rng3.Cells(i, 1).Value = ""
Else
rng3.Cells(i, 1).Value = Application.VLookup(ManName, rng2, 2, False)
End Ifchecks if the value of ManName is found in the first column of rng2 using the VLookup function. If the value is not found, the output cell is set to an empty string.
If the value is found, the output cell is set to display the value in the second column of the row containing the matching value of ManName in rng2.
Next iends the For loop.
End SubThe code appears to be incomplete or erroneous since it uses ManName and salary variables inconsistently, and the budget allocation calculation is missing. More information about budget allocation process is needed.
- Press F5 or click Run.
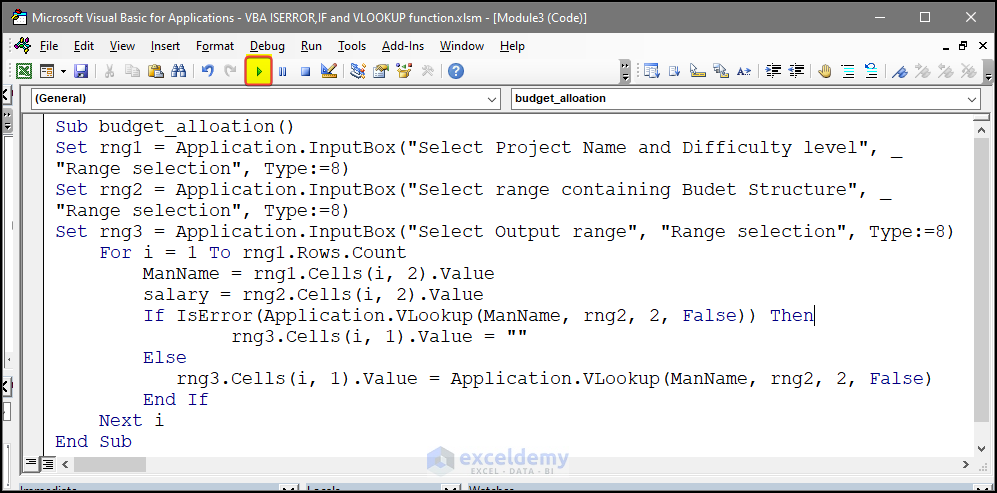
- You will be asked to enter the range containing the project name and difficulty level. Here, C5:D8.
- Press Enter.
- Another input box asks for the Budget. Here, F5:G8.
- Press Enter.
- Enter the output value C11:C14 in the next box.
- Click OK.
This is the output.

Read More: How to Use Excel VBA VLookup with Named Range
Issues Regarding Using If, IsError, and VLookup Together in Excel VBA
1. Avoid using the Worksheet Function in Excel
- Use the Application instead of the WorksheetFunction.
Sub use_of_worksheet_function()
Output = Application.WorksheetFunction.VLookup(Range("A1"), Range("B1:C4"), 2, False)
Debug.Print Output
End Sub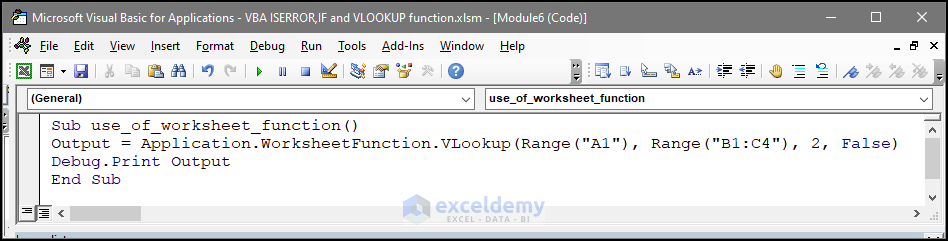
With the worksheet function, if the value in A1 is not found in B1:C4, there will be a runtime error.
Using the application solves the problem.
Sub use_of_worksheet_function()
Output = Application.VLookup(Range("A1"), Range("B1:C4"), 2, False)
Debug.Print Output
End Sub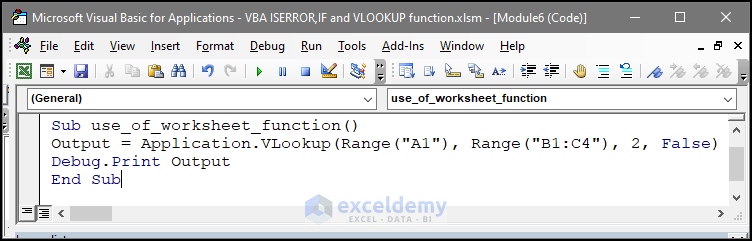
If there is any issue in the dataset, there will be no run time error, but a warning in the immediate window. Combine the IsError with the If function to avoid errors.
2. No Error Handling Used in Excel
- Use error-handling operators like On Error…Go To.
If an error occurs, the code will move to another location, avoiding the error.
Sub use_of_worksheet_function()
On Error Resume Next
Output = Application.WorksheetFunction.VLookup(Range("A1"), Range("B1:C4"), 2, False)
Debug.Print Output
End Sub
‘In the previous code, the code will resume as usual if there is any error.
Sub use_of_worksheet_function()
On Error GoTo ErrorHandler
Output = Application.WorksheetFunction.VLookup(Range("A1"), Range("B1:C4"), 2, False)
ErrorHandler:
MsgBox "Error: " & Err.Description
Err.Clear
Debug.Print Output
End Sub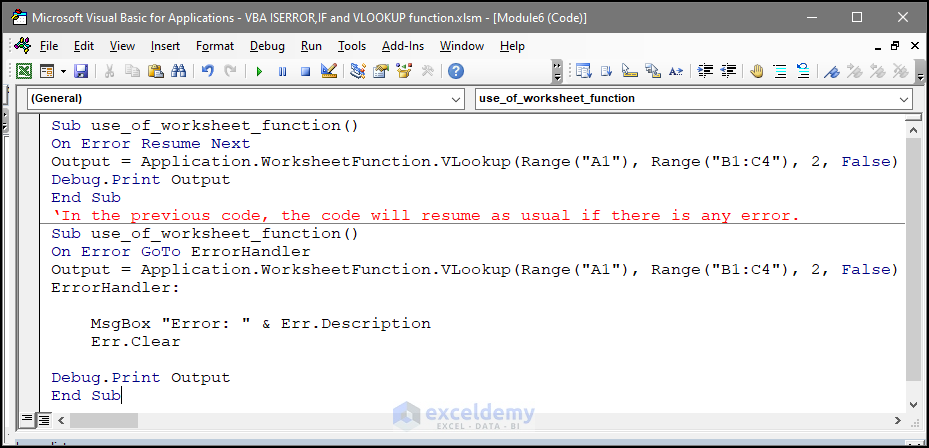
In the code above, if an error occurs in the output part, the code will go to the error handling portion and show an error message.
3. Issues with the Dataset or the Formula
If data is not found in the target range, the code will return an error.
F5:G7 was selected instead of the E5:G7, which led to an empty output range.
How to Use the If with the VLOOKUP Formula in VBA
1. Using a Generic Formula
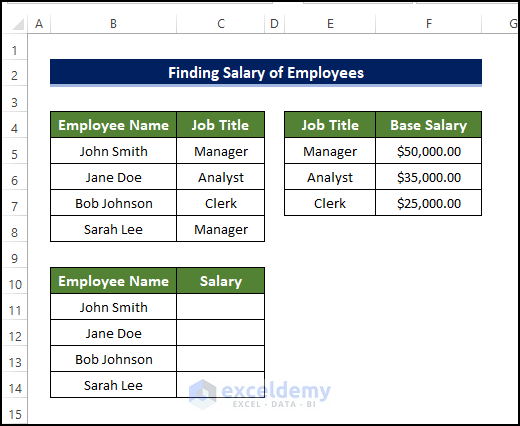
To determine whether the value of a product is greater than or less than 2 dollars:
- Use the following formula in F6:
=IF(VLOOKUP(F5,$B$5:$D$9,3,FALSE)>=2,"Price >= $2.00","Price < $2.00")
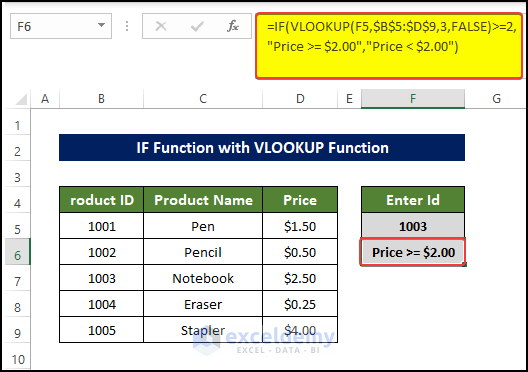
2. Using a VBA Macro
To check whether prices are greater than 2 dollars:
- In the code editor, enter the following code and run it by pressing F5 or clicking Run.
Sub IF_with_VLOOKUP()
If Application.VLookup(Range("F5"), Range("B5:D9"), 3, False) >= 2 Then
ActiveSheet.Cells(6, 6).Value = "The Product Price>=2$"
Else
ActiveSheet.Cells(6, 6).Value = "The Product Price <2$"
End If
End SubFrequently Asked Questions
1. How do I use the VLOOKUP Function with the ISERROR Function
In the following dataset the VLOOKUP function is used:
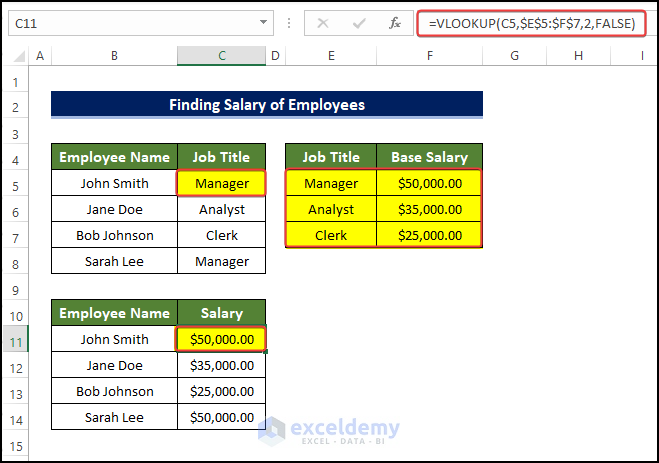
In image below, the VLOOKUP function is combined with the ISERROR function to avoid errors.
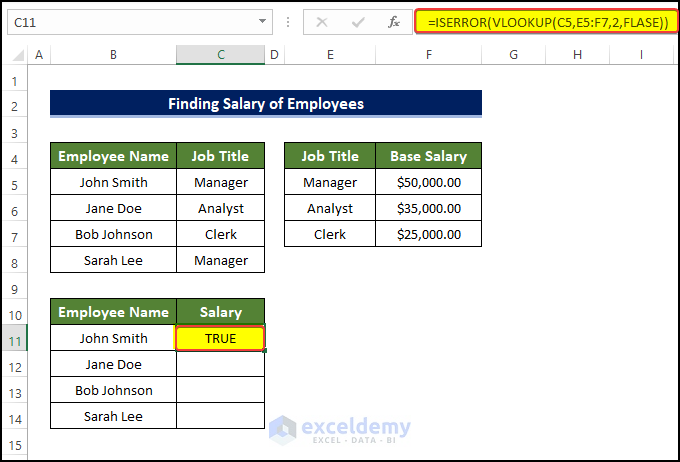
2. Can I use the VLOOKUP function with the IF function?
In the example below, a combination of the IF function and the VLOOKUP function is used to check whether a product value is greater than or less than 2 dollars:
- Enter the formula in F6.
=IF(VLOOKUP(F5,$B$5:$D$9,3,FALSE)>=2,"Price >= $2.00","Price < $2.00")

3. How do you Handle a VLOOKUP Error in VBA?
Use the On Error Resume Next:
On Error Resume Next
result = Application.WorksheetFunction.VLookup(lookup_value, Range("A1:B5"), 2, False)Adding the On Error Resume Next before the VLookup function makes the code move forward if there an error occurs.
You can also use the Err. Number statement:
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
MsgBox "Value not found"
Err.Clear
Else
MsgBox "Result: " & result
End IfIt finds the errors that occurred and counts them. If there is an error, a message box is displayed.
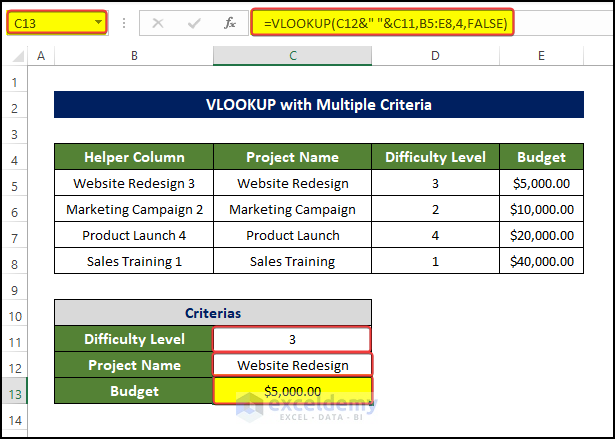
4. Can I Use VLOOKUP with Two Conditions?
To use two criteria: Project Name and Difficulty Level, insert a helper column.
Download Practice Workbook
Download the workbook to practice.
Related Articles
- Use Excel VBA VLOOKUP to Find Values in Another Worksheet
- How to Use Excel VBA VLookup Within Loop
- Excel VBA to Vlookup in Another Workbook Without Opening


