Here’s an overview of various types of inputs in an InputBox.
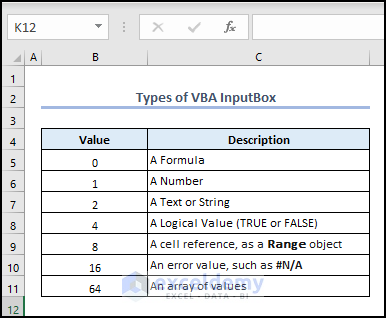
Overview of an Excel VBA InputBox
Using the VBA InputBox() function, we can easily display an InputBox to the viewers and request responses from them. This is especially useful for obtaining a single input from the user.
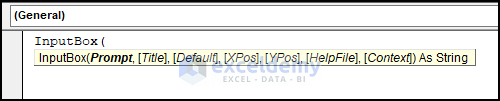
Syntax
The syntax of this function is as follows:
InputBox(Prompt, [Title], [Default], [Xpos], [Ypos], [Helpfile], [Context] )Parameters or Arguments

Return value
An InputBox returns a value as a variant.
Differences Between InputBox and Application.InputBox in Excel VBA
| InputBox or VBA InputBox | Application.InputBox |
|---|---|
| It is a standardized VBA function for gathering data from a user. | This is an updated version of the generic InputBox. |
| This InputBox does not allow you to specify the variable type. | This enables you to mention the type of the variable, such as number, string, array, etc. |
| It will not return an error whatever you provide as input. | If the variable type does not match the input, then the InputBox will not take the input and will return an error. |
How to Create an InputBox with Excel VBA
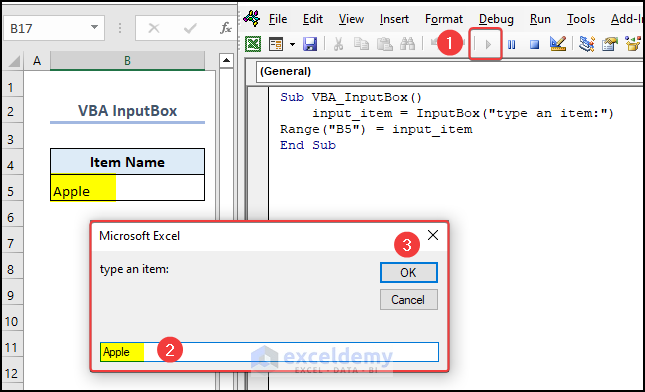
In the following video, we have created a VBA InputBox. This InputBox takes any item and shows the value in cell B5.
- To create a simple InputBox, you can copy the following VBA code.
Sub VBA_InputBox()
input_item = InputBox("type an item:")
Range("B5") = input_item
End Sub- After running the code, insert a value in the InputBox. We typed “Apple”.
- Click OK in the InputBox.
- You can see the item in cell B5.
Creating an Application.InputBox
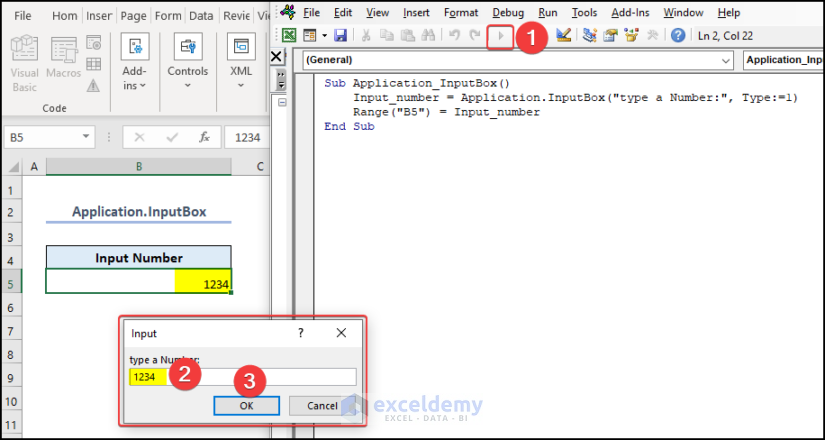
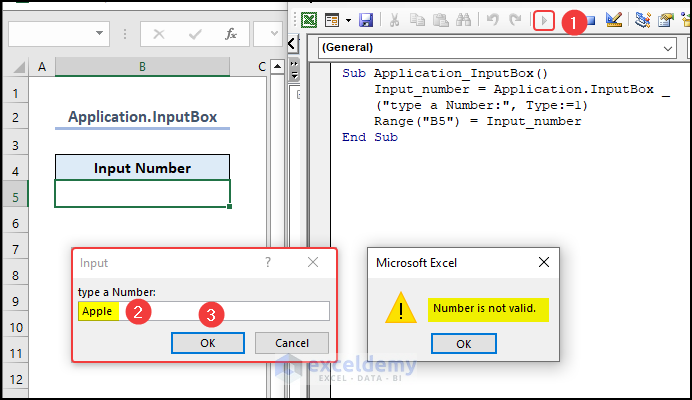
In the following video, we have created an Application.InputBox. We defined Type 1 for this InputBox so it accepts a number. The number is then shown in cell B5.
- To create an Application.InputBox, you can copy the following VBA code.
Sub Application_InputBox()
Input_number = Application.InputBox("type a Number:", Type:=1)
Range("B5") = Input_number
End Sub- After running the code, type a Number in the InputBox.
- Click OK in the InputBox.
You can see the Number in cell B5.
- If you provide a string instead of a number in the InputBox, it will return an error.
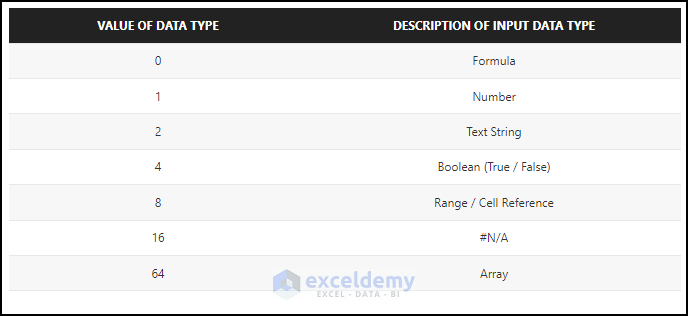
Excel VBA: InputBox Type (Based on Value of Data Type)
Application.InputBox has 7 variable types.
Type 0 – InputBox with Formula
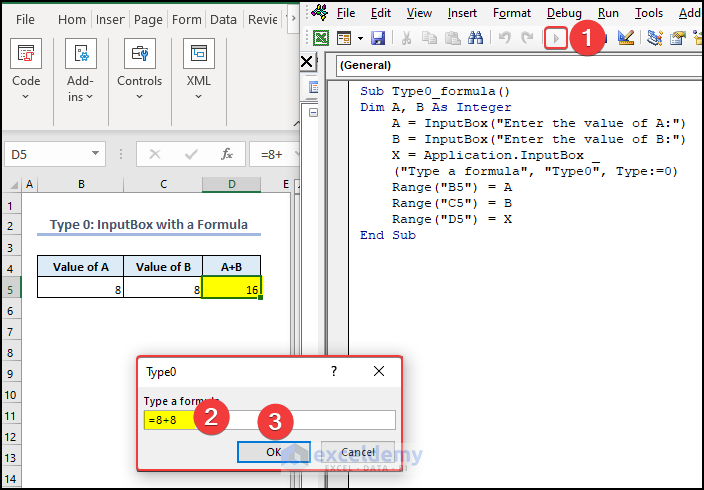
Type 0 is used for a formula in the Application.InputBox. This is the first type of InputBox in Excel VBA. When a user defines Type 0, then the user must input a formula in the InputBox. In the following video, you can see how Type 0: InputBox with formula works. Using the formula of the InputBox, we have calculated the sum of two cells. Also, we put the calculated result in cell D5. Next, we will describe how you can do the task.
- Here’s the associated code.
Sub Type0_formula()
Dim A, B As Integer
A = InputBox("Enter the value of A:")
B = InputBox("Enter the value of B:")
X = Application.InputBox("Type a formula", "Type0", Type:=0)
Range("B5") = A
Range("C5") = B
Range("D5") = X
End SubCode Breakdown:
Sub Type0_formula()
Dim A, B As IntegerWe take Type0_formula as the Sub procedure and declare A,B as Integer.
A = InputBox("Enter the value of A:")
B = InputBox("Enter the value of B:")Two InputBox functions are used to input the value of A and B. And these InputBoxes are assigned to variables A and B.
X = Application.InputBox("Type a formula", "Type0", Type:=0)Application.InputBox is assigned to variable X. Type 0 indicates that the InputBox will only take the formula as input. This, this InputBox prompts the user to input a formula.
Range("B5") = A
Range("C5") = B
Range("D5") = XThe value of A will be stored in cell B5.
The value of B will be stored in cell C5.
The value of X will be stored in cell D5.
End SubFinally, we end the Sub procedure.
- Run the code.
- Enter A and B in the InputBox.
- Type a formula in the Type0 InputBox.
You can see the result of the formula in cell D5.
Read More: Excel VBA: Custom Input Box
Type 1 – InputBox with Number
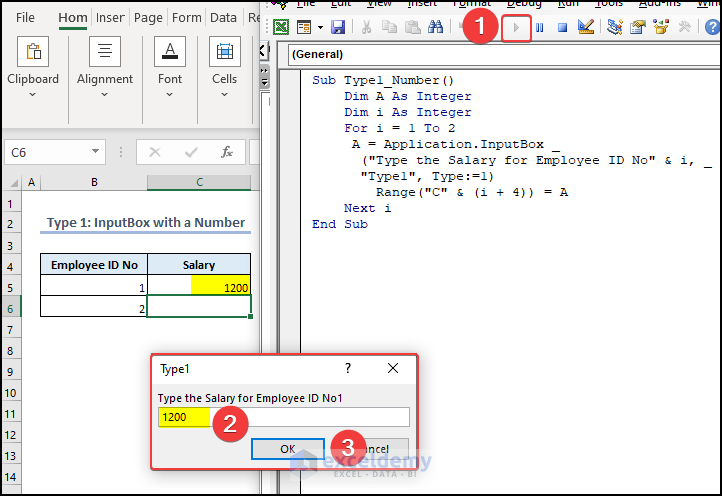
In the following video, you can see how Type 1: InputBox with number works. Using the number of the InputBox, we will get the Salary of two employees. The result will be shown in cell C5 and C6, respectively.
- Here’s the VBA code:
Sub Type1_Number()
Dim A As Integer
Dim i As Integer
For i = 1 To 2
A = Application.InputBox _
("Type the Salary for Employee ID No" & i, "Type1", Type:=1)
Range("C" & (i + 4)) = A
Next i
End SubCode Breakdown:
Sub Type1_Number()
Dim A As Integer
Dim i As IntegerWe take Type1_Number as the Sub procedure and declare A, and i as Integer.
For i = 1 To 2We used the For..Next loop which will execute twice, once for each employee.
A = Application.InputBox _
("Type the Salary for Employee ID No" & i, "Type1", Type:=1)Application.InputBox is assigned to variable A. Type 1 indicates that the InputBox will only take Number as input. Thus, this InputBox prompts the user to input a number.
Range("C" & (i + 4)) = A
The salary value will be stored in the corresponding cell in column C. The row number is determined by the loop iteration count plus 4 (since the first cell to be written to is C5).
Next iThis ends the For loop.
End SubFinally, we end the Sub procedure.
- Run the code.
- You will see an InputBox.
- Put 1200 as the Salary for Employee ID No 1 and click OK.
- Insert the next salary for the cell C6 and click OK.
Read More: Excel VBA InputBox with Number Only Criteria
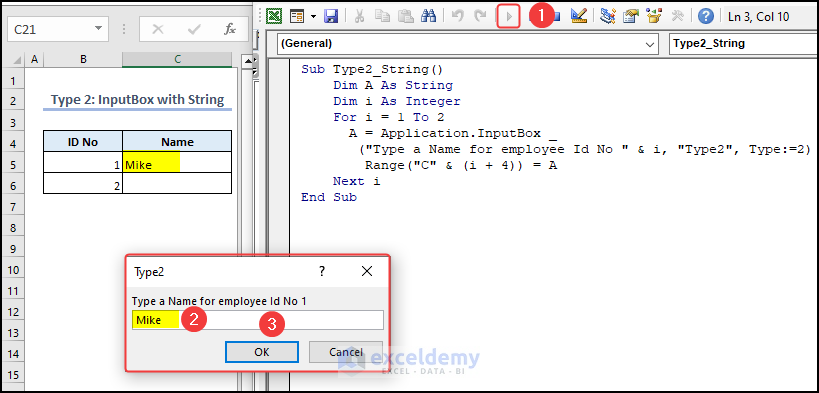
Type 2 – InputBox with Text
When a user defines Type 2, they must input a text or string in the InputBox. In the following video, you can see how an InputBox with text works. Using the text of the InputBox, we will get the Name of two employees.
- We used the following code:
Sub Type2_String()
Dim A As String
Dim i As Integer
For i = 1 To 2
A = Application.InputBox _
("Type a Name for employee Id No " & i, "Type2", Type:=2)
Range("C" & (i + 4)) = A
Next i
End SubCode Breakdown:
Sub Type2_String()Takes Type2_String as the Sub procedure.
Dim A As String
Dim i As IntegerDeclares A and i as Integer.
For i = 1 To 2Uses the For loop which will execute twice, once for each employee.
A = Application.InputBox _
("Type a Name for employee Id No " & i, "Type2", Type:=2)Application.InputBox is assigned to variable A. Type 2 indicates that the InputBox will only take String as input. Thus, this InputBox prompts the user to input a Text or String.
Range("C" & (i + 4)) = AThe employee name will be stored in the corresponding cell in column C. The row number is determined by the loop iteration count plus 4 (since the first cell to be written to is C5).
Next iThis ends the For loop.
End SubFinally, we end the Sub procedure.
- Run the code.
- You will see an InputBox will prompt up.
- Put Mike as the Name for employee ID No 1 and click OK.
- Enter the second name and click OK.
You can see the name Mike in cell C5.
Read More: Excel VBA: InputBox Date Format
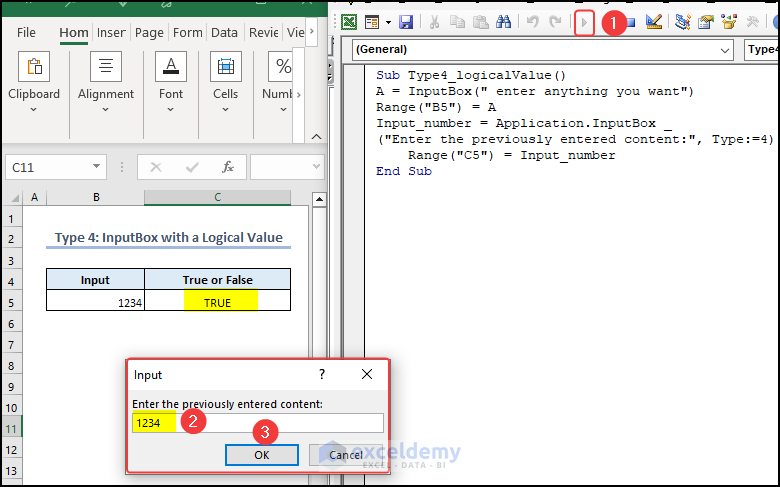
Type 4 – InputBox with a Logical Value
If the logical value is true, the InputBox will return TRUE, otherwise, it will return FALSE. In the following video, you can see that when we enter a number in the InputBox, it returns TRUE. If, however, you input a comparison or condition that isn’t true, it will return FALSE.
- We used the following code:
Sub Type4_logicalValue()
A = InputBox(" enter anything you want")
Range("B5") = A
Input_number = Application.InputBox _
("Enter the previously entered content:", Type:=4)
Range("C5") = Input_number
End SubCode Breakdown:
Sub Type4_logicalValue()Takes Type4_logicalValue as the Sub procedure.
A = InputBox(" enter anything you want")This line takes an InputBox to input any value, and we assign that InputBox to A.
Range("B5") = ASets B5 to store the input assigned to variable A.
Input_number = Application.InputBox _
("Enter the previously entered content:", Type:=4)Application.InputBox is assigned to the variable Input_Number. Type 4 indicates that the InputBox will show TRUE when the input is logical, otherwise, it will show FALSE.
Range("C5") = Input_number
We stire the result of the InputBox in cell C5.
End SubWe end the Sub procedure.
- Run the code.
- You will see an InputBox.
- We typed 1234 and clicked OK.
You can see TRUE in cell C5.
Read More: Excel VBA: InputBox with Default Value
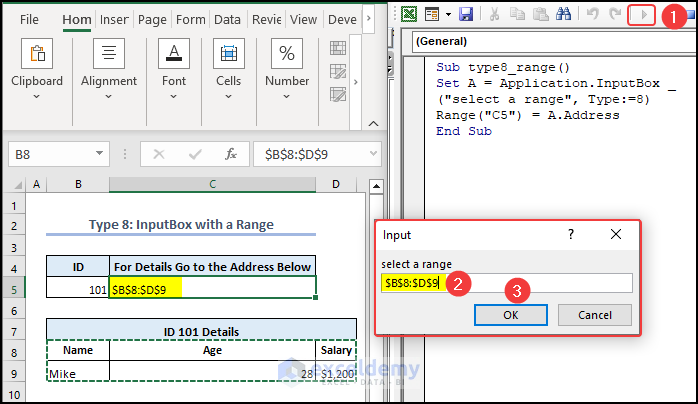
Type 8 – InputBox with a Cell Reference/Range
In the following video, you can see how Type 8: InputBox with Cell Reference works. The details for the employee ID 101 are presented in cells B8:D9. Using a Type 8 Application.InputBox, we will get the ID Details and put the address in cell C5.
- We used the following code:
Sub type8_range()
Set A = Application.InputBox("select a range", Type:=8)
Range("C5") = A.Address
End SubCode Breakdown:
Sub type8_range()We take type8_range as the Sub procedure.
Set A = Application.InputBox("select a range", Type:=8)Application.InputBox is set for variable A. Type 8 indicates that the InputBox will take cell reference.
Range("C5") = A.Address. Address method is used to find the address of A, and then the address is stored in cell C5.
End SubWe end the Sub procedure.
- Run the code.
- You will see an InputBox.
- Select the range B8:D9 in the InputBox and click OK.
You can see the range B8:D9 in cell C5.
Read More: VBA InputBox for Integer Value Only in Excel
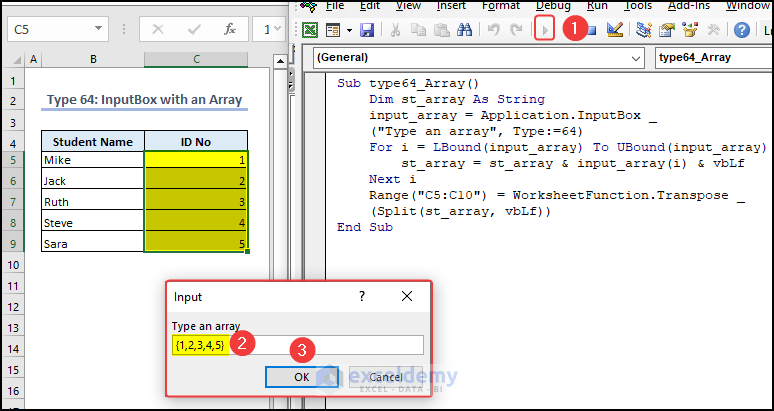
Type 64 – InputBox with an Array
In the following video, we have 5 student names in cells B5:B9. We’ll use an InputBox to enter an array of ID values.
- We used the following code:
Sub type64_Array()
Dim st_array As String
input_array = Application.InputBox _
("Type an array", Type:=64)
For i = LBound(input_array) To UBound(input_array)
st_array = st_array & input_array(i) & vbLf
Next i
Range("C5:C10") = WorksheetFunction.Transpose _
(Split(st_array, vbLf))
End SubCode Breakdown:
Sub type64_Array()We take type64_Array as the Sub procedure.
Dim st_array As String We declare st_array as a String.input_array = Application.InputBox _ ("Type an array", Type:=64)
We assign Application.InputBox in the input_array variable. Also, we declare Type 64 for an array.
For i = LBound(input_array) To UBound(input_array)For loop is used for each element of the input array to determine the lower and upper bounds of the array using the LBound and UBound functions.
st_array = st_array & input_array(i) & vbLf
The current array element is concatenated by st_array variable, then we used a line feed character (vbLf) to separate the elements.
Next iThis ends the For loop.
Range("C5:C10") = WorksheetFunction.Transpose _
(Split(st_array, vbLf))This line uses the SPLIT function and the line feed character (vbLf) as the delimiter to split the concatenated string in st array into an array. The array that results is then transposed and written to the range C5:C10.
End SubFinally, we end the subprocedure.
- Run the code.
- You will see an InputBox.
- Type the array {1,2,3,4,5} in the InputBox and click OK.
You can see the ID No. in cells C5:C9.
Other Types of a VBA InputBox in Excel
1. VBA InputBox with Options
VBA InputBox can have multiple options. The user can select one of the options and input the selected option in the InputBox. We have a Student Name in cell B5 and want a Group in cell C5. We set two groups, A and B, as two messages in the InputBox. We will input one group name in the InputBox. Since the InputBox has two messages as two options, this will make it as the InputBox with Options.
- We used the following code:
Sub inputbox_with_options()
Dim student_name As String, msg_1 As String, _
msg_2 As String, msg_3 As String, _
b_title As String, b_default As String
Dim Grade As String
msg_1 = "Enter the Group Name Here"
msg_2 = "Group A" & vbTab & _
"student who got over 80% in all subjects"
msg_3 = "Group B" & vbTab & _
"student who got below 80% in all subjects"
b_title = "XYZ School"
b_default = "Be Cautious"
student_name = InputBox _
("Enter Name of the Student", b_title, b_default)
Grade = InputBox(msg_1 & _
vbCrLf & vbCrLf & msg_2 & vbCrLf & msg_3, b_title, b_default)
Range("B5").Value = student_name
Range("C5").Value = Grade
End SubCode Breakdown:
Sub inputbox_with_options()Here, we take inputbox_with-options as the Sub procedure.
Dim student_name As String, msg_1 As String, _
msg_2 As String, msg_3 As String, _
b_title As String, b_default As String
Dim Grade As StringWe declare student_name, msg_1, msg_2, msg_3, b_title,b_default, and Grade as String.
msg_1 = "Enter the Group Name Here"
msg_2 = "Group A" & vbTab & _
"student who got over 80% in all subjects"
msg_3 = "Group B" & vbTab & _
"student who got below 80% in all subjects"
b_title = "XYZ School"
b_default = "Be Cautious"We assign value to the above-declared variables.
student_name = InputBox _
("Enter Name of the Student", b_title, b_default)An InputBox is assigned to student_name variable. The user will type a student name when the InputBox will pop up. The InputBox will have a title and a default value.
Grade = InputBox(msg_1 & _
vbCrLf & vbCrLf & msg_2 & vbCrLf & msg_3, b_title, b_default)This InputBox is assigned to Grade variable. This InputBox has 3 messages. We seperated the messages by & operator and vbCrLf constant. The vbCrLf adds a line break between the messages.
Range("B5").Value = student_name
Range("C5").Value = GradeThese lines assign the values of “student_name” and “Grade” to cells B5 and C5, respectively.
End SubFinally, we end the Sub procedure.

2. Excel VBA Multiple InputBox for Multiple Inputs
We can insert multiple InputBoxes in one VBA code. These multiple InputBoxes will take multiple inputs. These inputs can be of the same or different types. You can also add an InputBox and an Application.Inputbox in the same VBA code.
We want Student Name in cell B5 and the State in cell C5. We will use two InbutBoxes. In one InputBox, we will input the Student Name, and in the next one, we will input the State name.
- Here’s the code:
Sub InputBox_with_Mutiple_Inputs()
Dim student_name As String
Dim state As String
student_name = InputBox _
("Enter the Student Name:", "Enter Here")
state = InputBox("Enter the state Name:")
Range("B5") = student_name
Range("C5") = state
End SubCode Breakdown:
Sub InputBox_with_Mutiple_Inputs()Takes InputBox_with_Multiple_Inputs as the Sub procedure.
Dim student_name As String
Dim state As StringDeclare studnet_name and state as String.
student_name = InputBox _
("Enter the Student Name:", "Enter Here")
state = InputBox("Enter the state Name:")Takes the first InputBox for student_name and the second InputBox for the state.
Range("B5") = student_name
Range("C5") = stateThese lines take Range B5 to show student_name and Range C5 to show state.
End SubFinally, we end the Sub procedure.
- Run the code.
- You will see two InputBoxes.
- Input the values one after another.
Read More: Vbscript InputBox with Multiple Fields in Excel
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do I use an InputBox in Excel VBA?
You can use InputBox by typing in the InputBox or Application.InputBox function.
Student_name= InputBox("Enter the name here:")How to get an input from a TextBox in VBA?
We normally use TextBoxes to collect input from users. They are a part of UserForms. A text box can be displayed on the UserForm so the user can enter data. It also allows users to enter data on the worksheet using simple codes.
For a better understanding, you can read the following article: Excel VBA: Get Value From Userform Textbox
What is Type:=8 InputBox in VBA?
In Application. InputBox, Type 8 is used for Cell Reference. When a user defines Type 8, then the user must input a cell or a range of cells in InputBox
How Do I Input a Box Value in a Cell in Excel VBA?
To input a box value in a cell in Excel VBA, you can use the Range(“Cell”) method:
Student_name= InputBox("Enter the name here:")
Range("D5") = Student_nameThis assigns an InputBox to the Student_name variable. Then, it specifies cell D5 using the Range method, so that the Student_name variable’s value is stored there.
Download the Practice Workbook
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!


Hello Afia. Thank you for your tutoring however even having followed it my InputBox is not performing as expected. Essentially, I am asking the User to input the number of rows they wish to fill (with numbers) before moving onto the next column and starting the process of populating the cells again with numbers. I have set a default value, 20 as it happens but it could be any number, but the User can delete this value and leave the input box empty (null value) and click on OK or they can click the Cancel button (which comes with the InputBox whether you want it or not) and likewise the ‘X’ to close the InputBox. However, whenever those choices are made my project treats the input as an error condition and crashes the program. I have tried defining the InputBox as an Application type with both Type: = 1 and Type: = 2 being tried, changing the variable (the InputBox name) to numeric and string respectively but that makes no difference. When the User blanks the default value and does not replace it with another number the value of the variable comes up a “” but that and vbNull or Empty does not trap the fault condition. Have you any suggestion as to where I might be going wrong and how I might correct it. Hoping you can make sense of my ramblings and thank you in advance if you do give my problem your time. Kind regards Keith
Dear KEITH BASKETT,
Thanks for sharing your problem with us. I understand that you are using InputBox to take the number of rows you wish to fill in a column and then repeat the process for the next columns. However, you are facing errors when you enter a text or invalid input or press the OK, Cancel, or X button without entering any value.
To fix these errors, you have to include a few error-handling situations in your code. Here, I have provided a sample code that contains error handling for your described situations:
Here’s how this code operates:
You can preview the output in the following GIF:
I hope this example will be helpful for you to understand how to handle errors while working with an InputBox in Excel VBA. Let us know your feedback.
Regards,
Seemanto Saha
Team ExcelDemy