This article is part of the series: Excel VBA & Macros – A Step by Step Complete Guide.
Download Practice Workbook
What Are VBA Objects?
The VBA (Visual Basic Application) is an object-oriented programming language. The object is one of the elements of VBA.
An object has its property and method. The method is the operation performed by that object and the property explains the characteristics of that object.
Attributes of VBA Objects
To apply a VBA object, there must be a method or property in the Object. We will discuss those attributes here.
Properties
Excel has many objects. Most of the objects in Excel VBA we work with have properties.
Example:
- Range object has properties. Some of them are Column, Formula, Row, Width, and Value.
- A Chart object has properties, such as Legend, ChartArea, ChartStyle, and so on.
- ChartTitle is also an object, with properties such as Font, Format, and Border.
Use of VBA Object Properties:
We can write VBA code to do the following:
- You can examine an object’s current property settings and do something based on these settings.
- You can change the object’s property settings by setting new values.
Look at this VBA statement:
Range("E10").Value
In this statement, Range is an object, Value is one of the properties. In the VBA statement, objects and properties are placed side by side separating them by a period (.). Objects are placed first, then their properties.
For example, the following VBA statement sets the Value property of Range E10:100.
Range("E10").Value = 100 That statement will cause the number 100 to display in Cell E10.
Methods:
Objects also have methods. For example, Range objects have a Clear method. The following VBA statement clears a Range. This statement is equivalent to selecting the Range and then choosing Home ➪ Editing ➪ Clear ➪ Clear All:
Range("A10:C20").ClearIn VBA code, methods look like properties. Methods are connected to the objects with a separating operator (.). However, methods and properties are different concepts in VBA.
10 Mostly Used VBA Objects in Excel
There is a hierarchy followed by Excel in the case of objects which is:
Application → Workbook → Worksheet → Range
We will discuss a list of the most commonly used objects of Excel VBA in detail.
Object 1 – Application Object
The Application object is used to represent the total Excel application.
| Methods | Properties |
|---|---|
| Calculate | ActiveCell |
| CalculateFull | ActiveSheet |
| InputBox | ActiveWindow |
| Quit | ActiveWorkbook |
| Run | DisplayScrollBars |
| Undo | DisplayFormulaBar |
| Wait | Path |
| StatusBar |
We need to add the required property or method while applying this object in Excel.
Example 1:
The Calculate method is used for the calculation of all open workbooks.
Sub Calculate_All_Opened_Workbooks()
Application.Calculate
End Sub 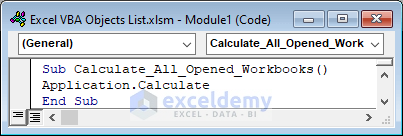
Example 2:
The DisplayScrollBars property with the Application object is used to hide the scroll bar.
Sub Hide_Status_Bar()
Application.DisplayScrollBars = False
End Sub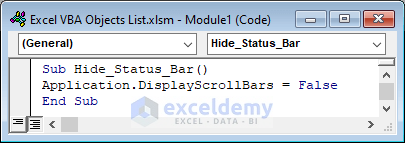
The status is set to False, which means it will not display the scroll bars of the Excel sheet.
Read More: How to Open Workbook from Path Using Excel VBA (4 Examples)
Object 2 – Workbooks Object
Workbooks object denotes the list of presently opened workbooks on an Excel application.
| Methods | Properties |
|---|---|
| Add | Application |
| CheckOut | Count |
| Close | Creator |
| Open | Item |
| Parent |
Example 1:
This VBA code is based on the Workbooks object that will close the Excel workbook.
Sub Close_All_Opened_Workbooks()
Workbooks.Close
End Sub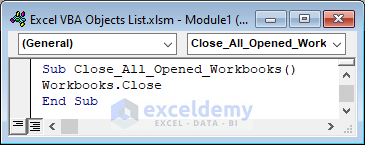
Example 2:
This code will add a new variable page_1 on the Disney.xlsx workbook.
Sub Add_Variable_to_Specific_Workbook()
Set page_1 = Workbooks.Item("Disney.xlsx")
End Sub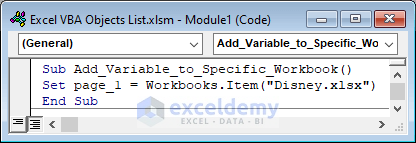
Object 3 – Workbook Object
The Workbook object represents a single workbook. It is a member of Workbooks that are currently active or open. A workbook is a collection of worksheets.
| Methods | Properties |
|---|---|
| Active | ActiveChart |
| AddToFavourite | ActiveSheet |
| Close | AutoSaveOn |
| DeleteNumberFormat | FullName |
| Save | UserStatus |
| SaveAs |
Example 1:
Close the current workbook.
Sub Close_Single_Workbook()
ActiveWorkbook.Close
End Sub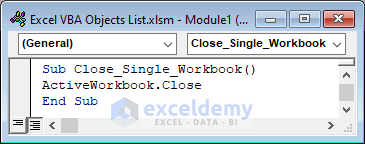
We applied a similar code to the close workbook. The Workbooks object is applied to all the opened workbooks. But the Workbook object is applicable only to the active workbook.
Example 2:
Name a cell using the Workbook object.
Sub Name_A_Cell()
ActiveWorkbook.Names.Add Name:="myName", RefersToR1C1:="=Sheet1!R5C5"
End Sub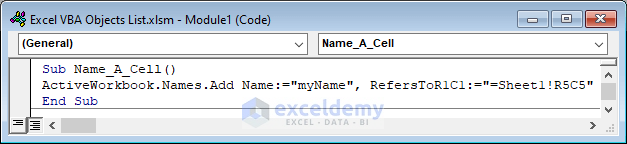
Object 4 – Sheets Object
The Sheets object is related to all kinds of sheets of the specified or active Excel workbook. Sheets may be worksheets, chart sheets micro sheets.
| Methods | Properties |
|---|---|
| Add | Application |
| Add2 | Count |
| Copy | Item |
| Delete | Parent |
| Move | Visible |
| PrintOut | |
| PrintPreview | |
| SelectCalculate |
Example 1:
This VBA code will activate the 2nd sheet of the workbook.
Sub Activate_Workbook()
Worksheets(2).Activate
End Sub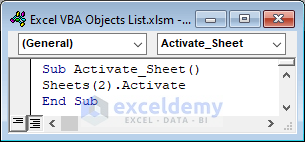
Example 2:
This will add a new sheet after the 1st sheet.
Sub Add_New_Sheet()
Sheets.Add after:=Sheets(1)
End Sub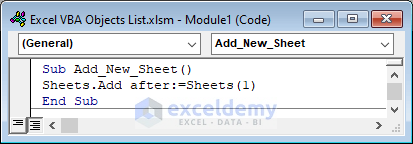
Object 5 – Worksheets Object
This Worksheets object is a part of the Sheets object. It is the collection of only the worksheets. But the Sheets object also includes chart sheets and micro sheets.
| Methods | Properties |
|---|---|
| Copy | Application |
| Delete | Count |
| Move | Creator |
| PrintOut | Item |
| PrintPreview | Parent |
| Select | Visible |
| Add | |
| Add2 |
Example 1:
Activate the 2nd worksheet of the following workbook.
Sub Activate_Worksheet()
Worksheets(2).Activate
End Sub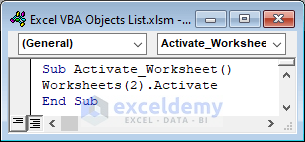
We may also use the Sheets object. But if we use the Sheets object, that may activate a chart or micro sheet also depends on the location of the specified workbook.
Example 2:
Copy a sheet on our desired location on the workbook.
Sub Copy_A_Worksheet()
Worksheets("Disney").Copy Before:=Worksheets("Sheet1")
End Sub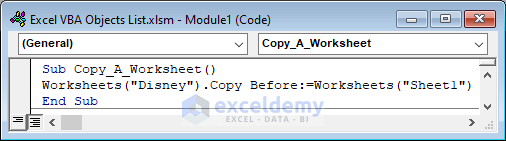
Similar Readings
- 22 Macro Examples in Excel VBA
- 20 Practical Coding Tips to Master Excel VBA
- How to Write VBA Code in Excel (With Easy Steps)
- Types of VBA Macros in Excel (A Quick Guide)
- Introduction to VBA Features and Applications
Object 6 – Worksheet Object
The Worksheet object is a part of the Worksheets. It represents a single worksheet. This section will show a sample VBA code based on the Worksheet object that renames a worksheet.
| Methods | Properties |
|---|---|
| Activate | Application |
| Calculate | Cells |
| CheckSpelling | Columns |
| Copy | Comments |
| Delete | Name |
| Evaluate | Next |
| Move | Outline |
| Paste | PageSetup |
| PasteSpecial | Parent |
| PrintOut | Range |
| PrintPreview | Rows |
| SaveAs | Shapes |
| Select | Sort |
| Tab | |
| Type | |
| Visible |
Example 1:
Change the name of the active worksheet.
Sub Rename_A_Worksheet()
ActiveSheet.Name = "Data Set -2"
End Sub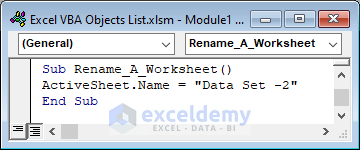
Example 2:
Show the name of the current worksheet.
Sub Show_Worksheet_Name()
MsgBox ActiveSheet.Name
End Sub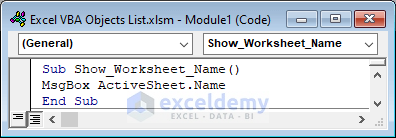
Object 7 – Range Object
The Range object is related to cells of the Excel file. It is used to select a single cell, row, column, or a certain number of cells, rows, or columns from an Excel Worksheet. We have to put the cell reference in the argument.
| Methods | Properties |
|---|---|
| Activate | Address |
| AutoFill | Application |
| Calculate | Areas |
| Clear | Cells |
| Copy | Column |
| Delete | Count |
| Find | End |
| Insert | Font |
| PasteSpecial | Height |
| Replace | Item |
| Run | Left |
| Select | ListObject |
| Show | Name |
| Sort | Next |
| Table | Parent |
| Range | |
| Row | |
| Rows | |
| Top | |
| Validation | |
| Value | |
| Width |
Example 1:
Select cell range B5:D5.
Sub Select_A_Range()
Range("B5:D5").Select
End Sub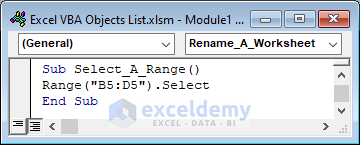
Example 2:
Copy a certain range from the active sheet.
Sub Copy_A_Range1()
Range("A1:E1").Copy
End Sub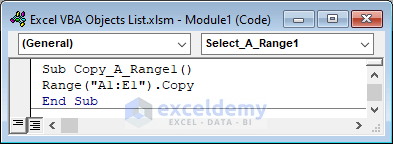
Object 8 – Shapes Object
The Shapes object is related to all shapes that exist in a worksheet. We can select and delete or perform other tasks using this object.
| Methods | Properties |
|---|---|
| AddCallout | Application |
| AddConnector | Count |
| AddLine | Creator |
| AddPicture | Parent |
| AddShape | Range |
| Item | |
| SelectAll |
Example 1:
Select all kinds of shapes from a worksheet.
Sub All_Shapes_of_A_Worksheet()
ActiveSheet.Shapes.SelectAll
End Sub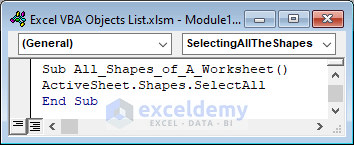
Example 2:
Apply the desired action to the existing shapes of the active worksheet.
Sub Apply_A_Procedure_on_Shapes()
ActiveSheet.Shapes(1).OnAction = "ShapeClick"
End Sub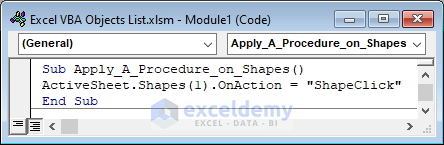
Object 9 – Shape Object
The Shape object is a part of the Shapes. It indicates a single shape in an active worksheet. It is used with the Shapes object.
| Methods | Properties |
|---|---|
| Apply | Application |
| Copy | AutoShapeType |
| Cut | BackgroundStyle |
| Delete | Chart |
| Duplicate | Connector |
| Select | Fill |
| Height | |
| Left | |
| Name | |
| OnAction | |
| Parent | |
| Reflection | |
| Title | |
| Top | |
| Type | |
| Visible | |
| Width |
Example:
Create a star with 5 edges.
Sub Create_A_Shape()
ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape msoShape5pointStar, 300, 100, 60, 60
End Sub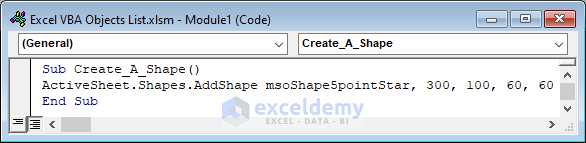
We can draw any kind of shape by changing the msoShape5pointStar command.
Object 10 – ListObject Object
ListObject is a part of ListObjects Object. A ListObject indicates a single table of the worksheet.
| Methods | Properties |
|---|---|
| Delete | Active |
| Publish | Application |
| Refresh | AutoFilter |
| Resize | Comment |
| Creator | |
| Name | |
| Parent | |
| Range | |
| Sort | |
| Summary |
Example:
Extract data from a table and store it in the array.
Sub Store_Data_From_Table_To_Array()
Dim D_Table As ListObject
Dim D_Array As Variant
Dim N As Long
Set D_Table = ActiveSheet.ListObjects("My_Data")
D_Array = D_Table.DataBodyRange
For N = LBound(D_Array) To UBound(D_Array)
Debug.Print D_Array(N, 2)
Next N
End Sub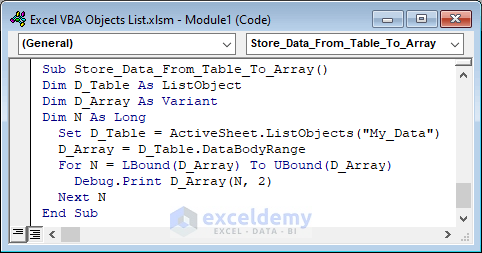
Read More: Excel VBA to Populate Array with Cell Values (4 Suitable Examples)
Related Articles
- What You Can Do with VBA (6 Practical Uses)
- [Fixed!] Border Not Showing in Excel (6 Solutions)
- How to Use Select Case Statement in Excel VBA (2 Examples)
- 6 Best Excel VBA Programming Books (For Beginners & Advanced Users)
- How Different Is VBA from Other Programming Languages
- Learn Excel VBA Programming & Macros (Free Tutorial – Step by Step)


