Introduction to Excel VBA Range Function
Function Objective: The Excel VBA Range function references a range in a worksheet.
Syntax:
Range(Cell1,[Cell2])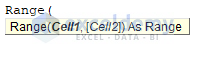
Referencing Cells Using Excel VBA Range Function
We can use the Range function to reference a single cell or a range of cells.
1 – Referencing Single Cell
To refer to a single cell, use the following syntax:
Range(“D5”)2 – Referencing Range of Cells
We can reference a range of cells in a couple of ways.
2.1 – Using Cells Property
To reference a range of cells, use either of the following syntaxes:
Range("B5:D10")Range("B5", "D10")The above syntax refers to the range B5 to D10.
2.2 – Using Offset Property
We can also use the Offset property to refer to a range.
The following syntax references cell D10 from cell B5:
Range("B5").Offset(4,3)Read More: VBA to Set Range in Excel
3 – Referencing Entire Row
The following syntax references the entire row 4.
Range("4:4")4 – Referencing Entire Column
To reference column C we can use the following syntax:
Range("C:C")5 – Referencing Named Range
To refer to a range named Sales_Data, we can use the following syntax:
Range("Sales_Data")Examples of Using Excel VBA Range Function
Example 1 – Selecting Cells
1.1 – Single Cell
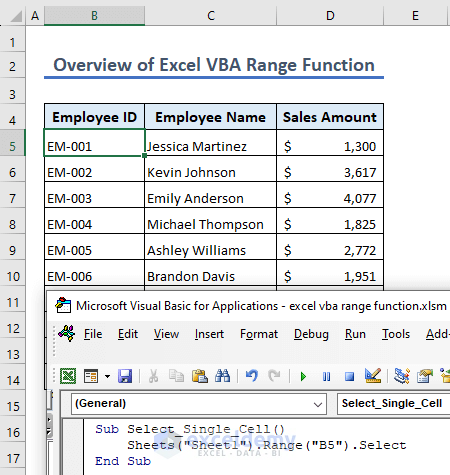
STEPS:
- Go to Developer > Visual Basic.
- Insert a new module by going to Insert > Module.
- Insert the following code in the module:
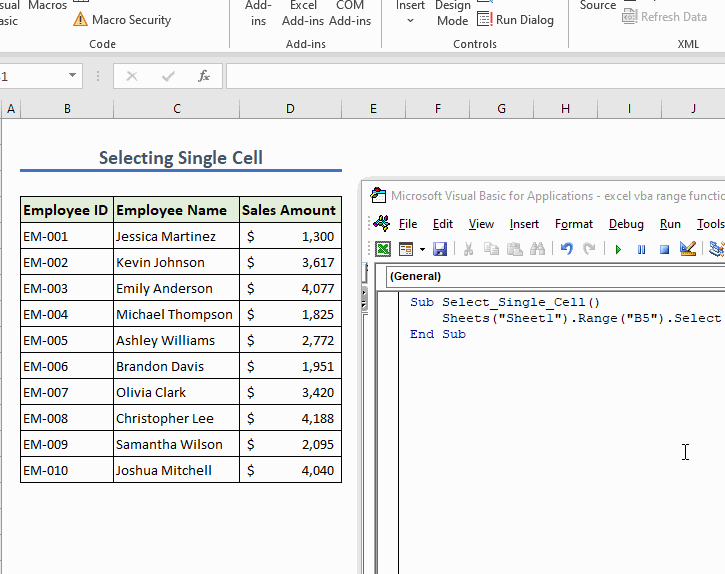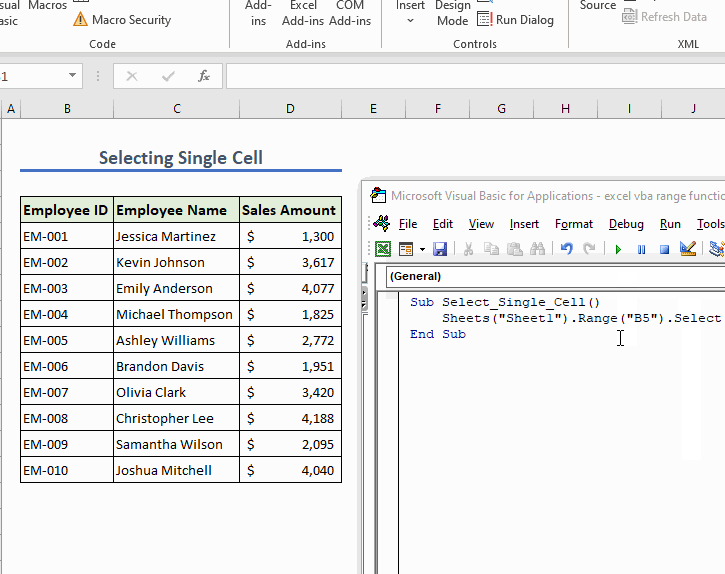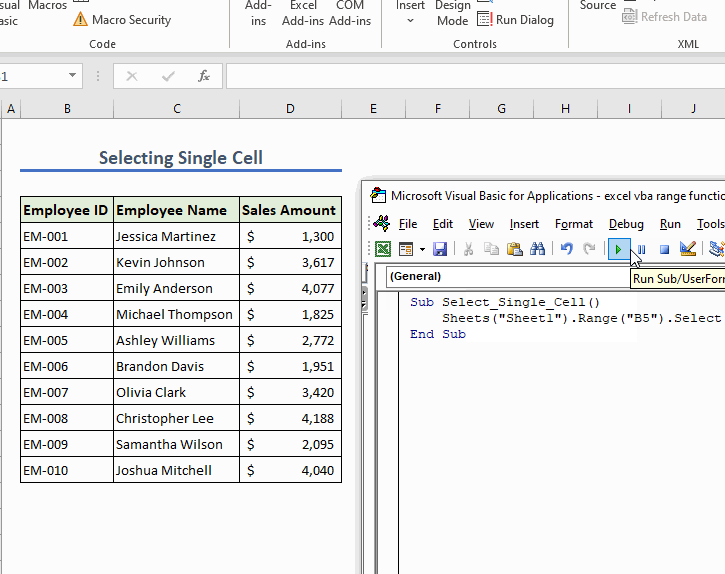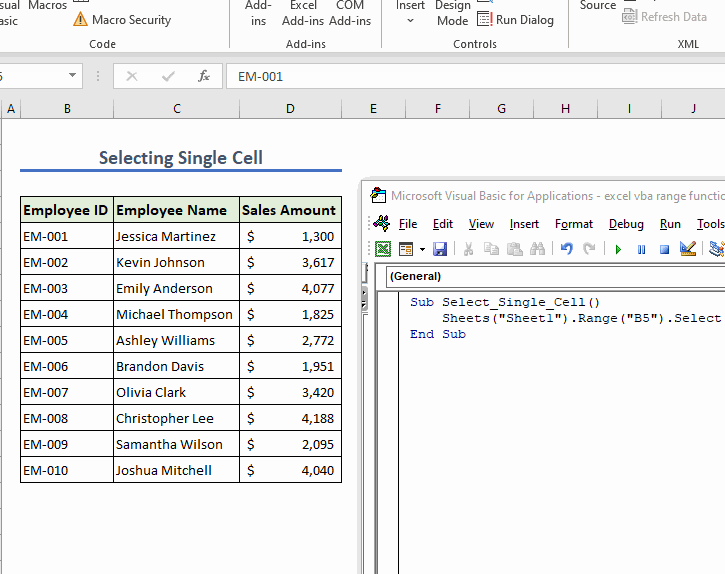
Sub Select_Single_Cell()
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("B5").Select
End Sub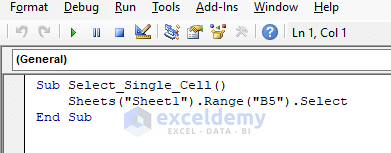
- Run the code by pressing F5 on your keyboard or clicking on Run.
This will select cell B5 in the worksheet.
1.2 – Entire Column
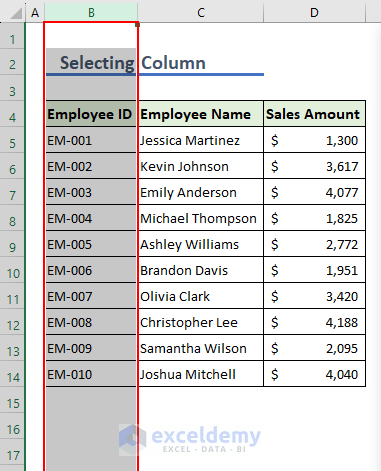
To select an entire column, use the following code:
Sub Select_Entire_Column()
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("B:B").Select
End Sub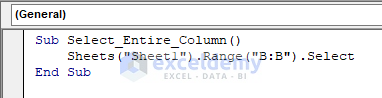
Running the above code selects column B in the worksheet.
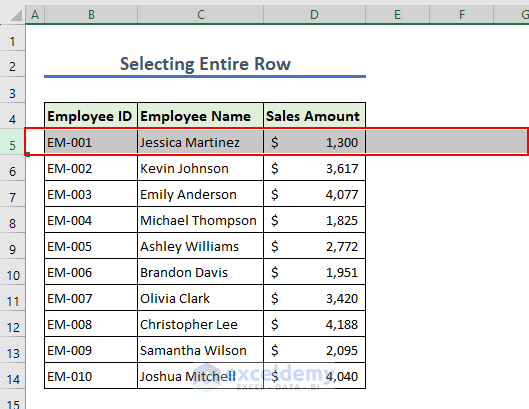
1.3 – Entire Row
The following code selects row 5 in the worksheet:
Sub Select_Entire_Row()
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("5:5").Select
End Sub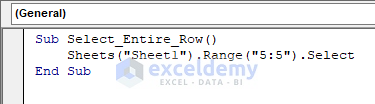
- Run the above code to select row 5.
Read More: Excel VBA: Set Range by Row and Column Number
1.4 – A Range of Cells
To select a range of cells, use the following code:
Sub Select_Two_Different_Ranges()
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("B5:D14").Select
End Sub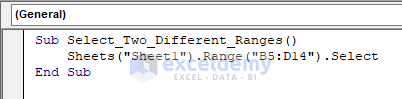
1.5 – Non-Adjacent Cells
To select a range of non-adjacent cells, use the following code:
Sub Select_Non_Adjacent_Cells()
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("B5,B7,D10").Select
End Sub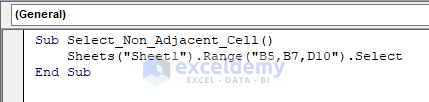
1.6 – Two Different Ranges
To select two different ranges, use the following code:
Sub Select_Two_Different_Ranges()
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("B5:B14,D5:D14").Select
End Sub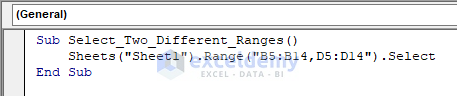
Modify this code to select multiple ranges.
Example 2 – Input Values
2.1 – Single Cell
The following code inputs the value Exceldemy in cell C6:
Sub Input_Values_Single_Cell()
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("C6").Value = "Ethan Rodriguez"
End Sub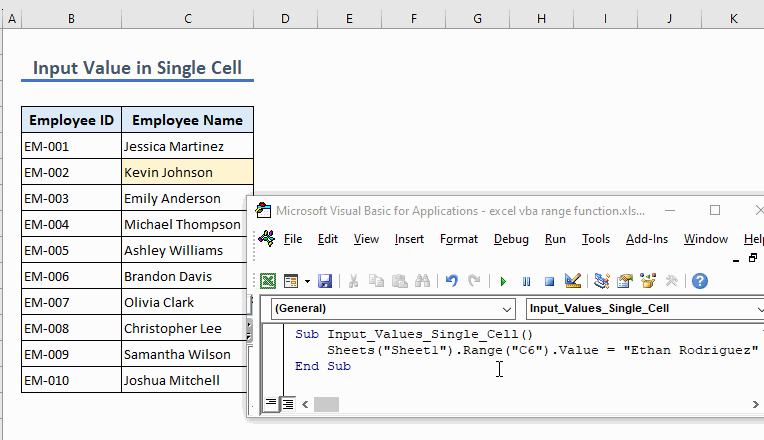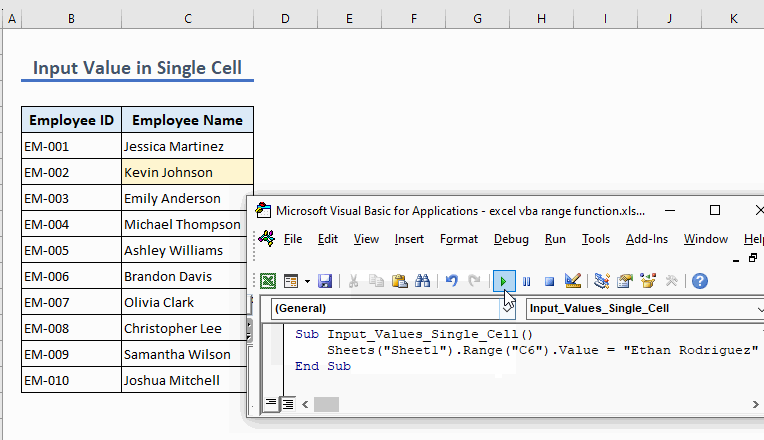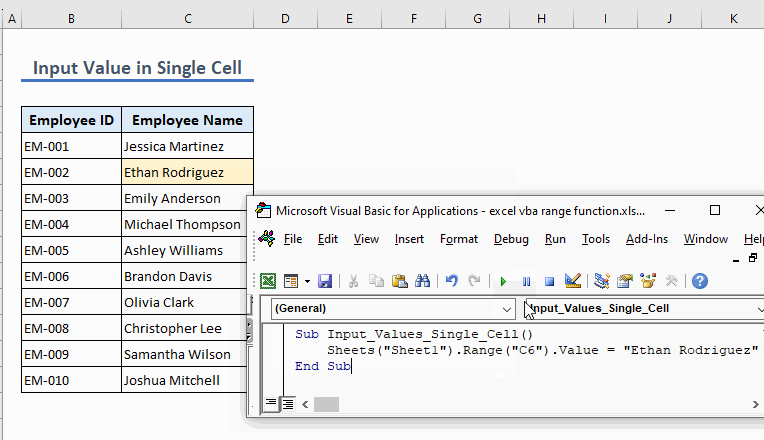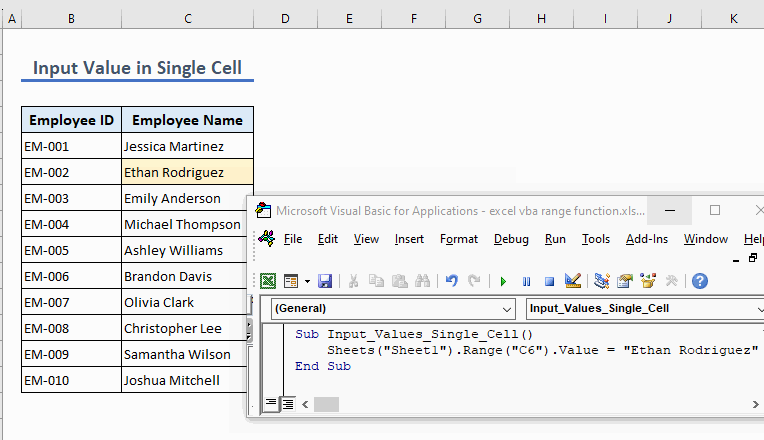
We don’t need to insert a quotation for a numerical value:
Sub Input_Values_Single_Cell()
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("D6").Value = 1950
End Sub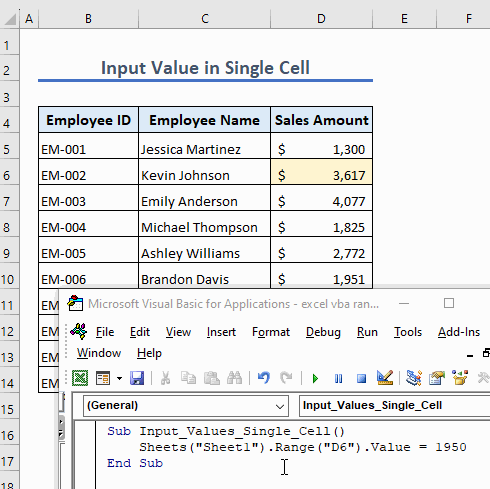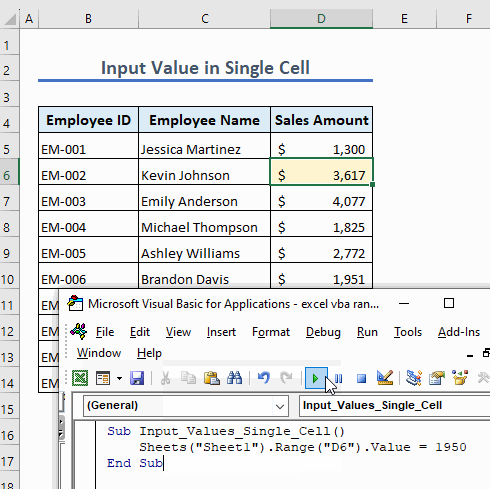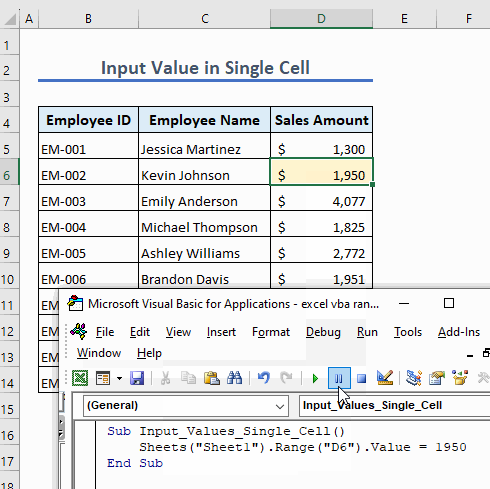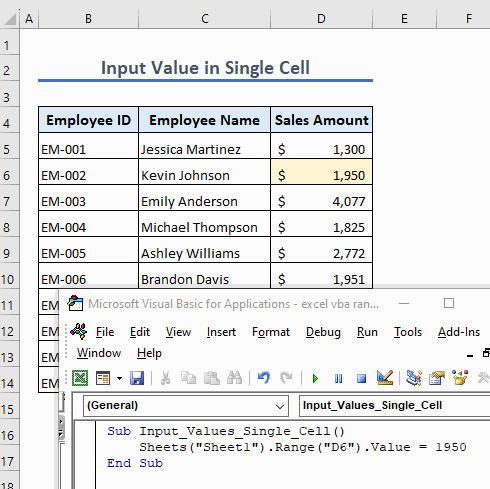
2.2 – Multiple Cells
Easily input a value in multiple cells or a range of cells using the following code:
Sub Input_Values_Multiple_Cell()
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("E5:E14").Value = “July”
End Sub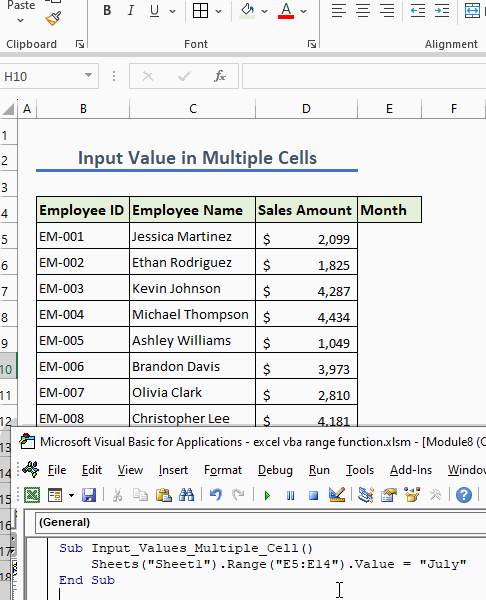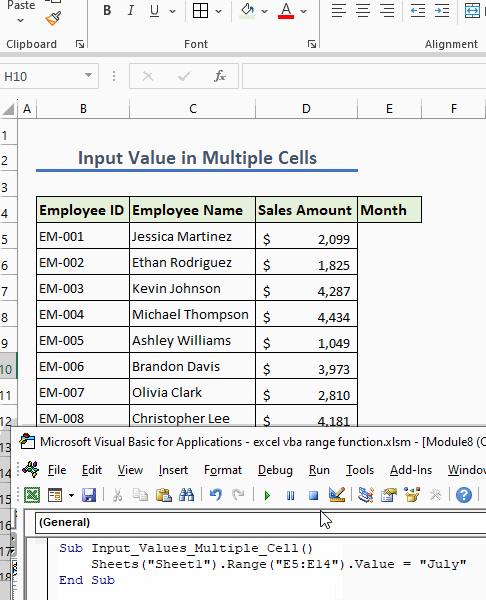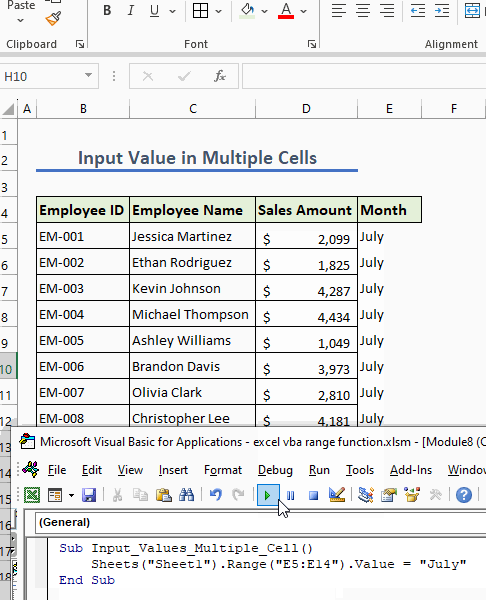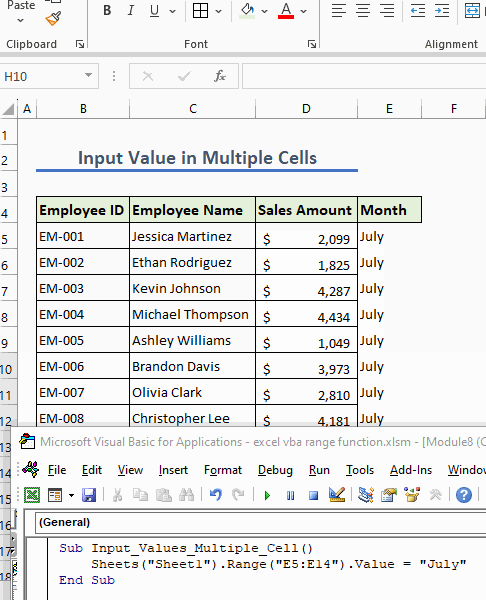
Example 3 – Merge Cells
To merge a range of cells use the following code:
Sub Merge_Cells()
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("B2:E2").Merge
End Sub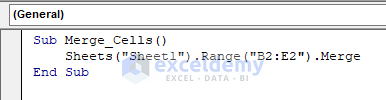
The above code merges cells B2, C2, D2, and E2 into a single cell.
Example 4 – Unmerge Merged Cells
To unmerge merged cells, use the following code:
Sub Unmerge_Cells()
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("B2:E2").UnMerge
End Sub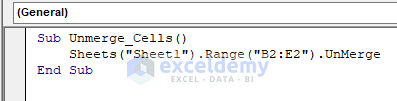
Example 5 – Clear Formatting from Cells
To clear formatting from a cell or a range of cells, use the following code:
Sub Clear_Formatting()
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("B4:D14").ClearFormats
End Sub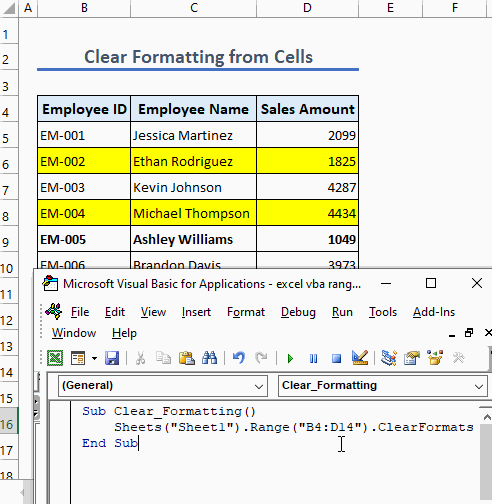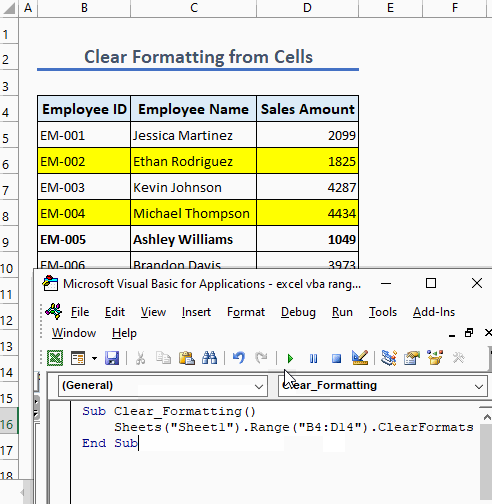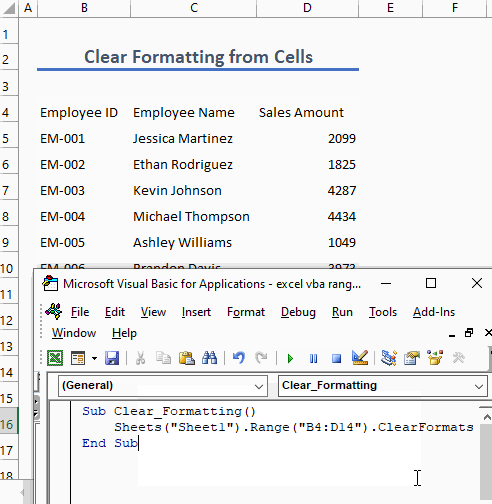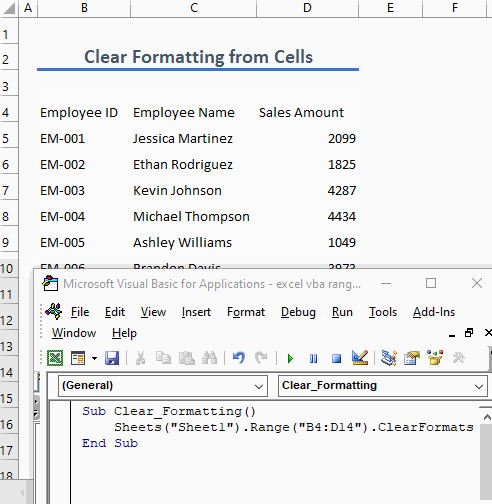
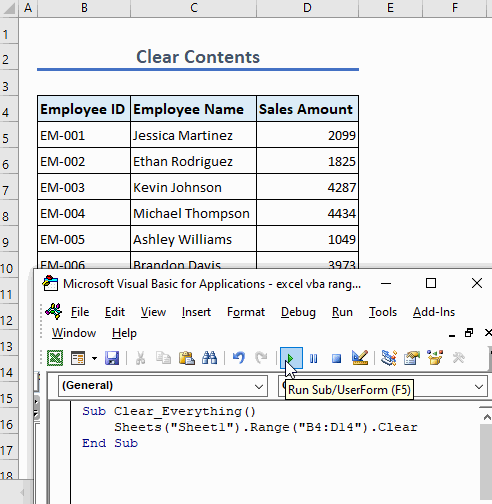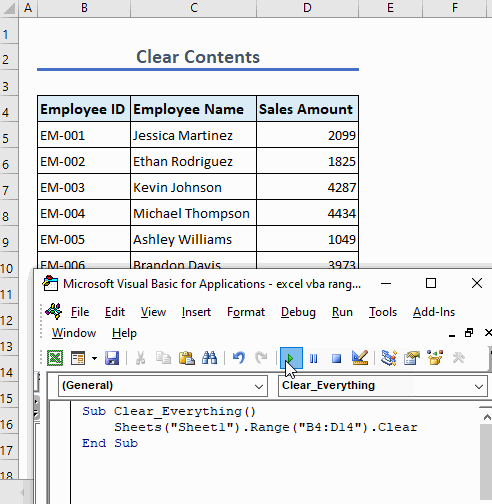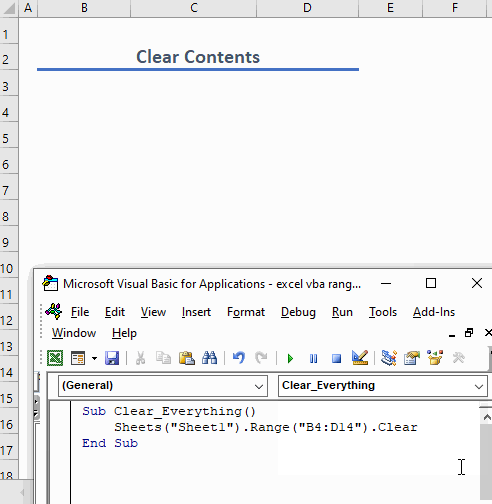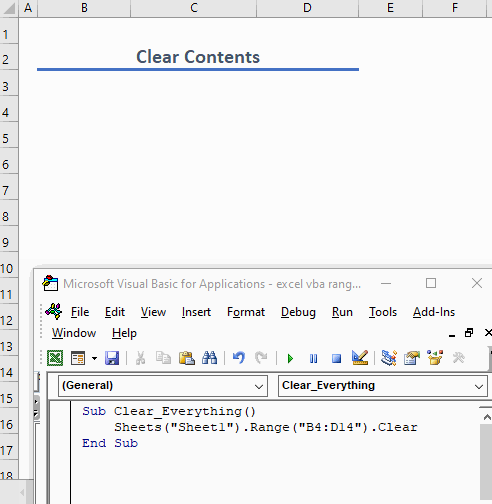
Example 6 – Clear a Range
Use this function to clear everything from a range:
Sub Clear_Everything()
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("B4:D14").Clear
End SubThe code clears all content from the range C5:D10 including formatting, formulas, values, etc.
Example 7 – Delete a Range
Delete a range using the following code:
Sub Delete_Range()
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("D5:D14").Delete
End Sub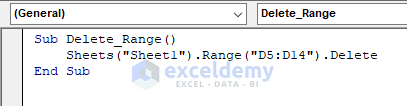
Example 8 – Find a Value Within Range
Use this function to find a specific value within a range and select the cell that contains the value:
Sub Find_and_Select_Cell()
Dim sValue As Variant
Dim sRange As Range
Dim foundCell As Range
sValue = "Ashley Williams"
Set sRange = Range("B5:D14")
Set foundCell = sRange.Find(sValue, LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlWhole)
If foundCell Is Nothing Then
MsgBox "The value '" & sValue & "' not found in the specified range."
Else
foundCell.Select
End If
End Sub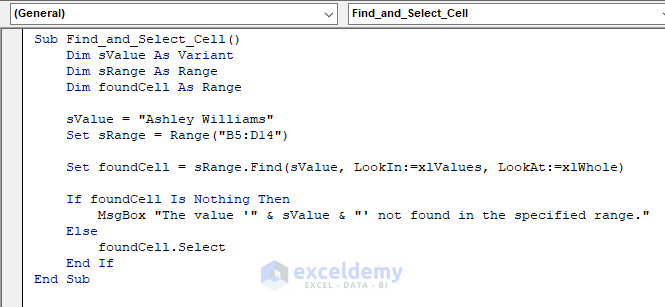
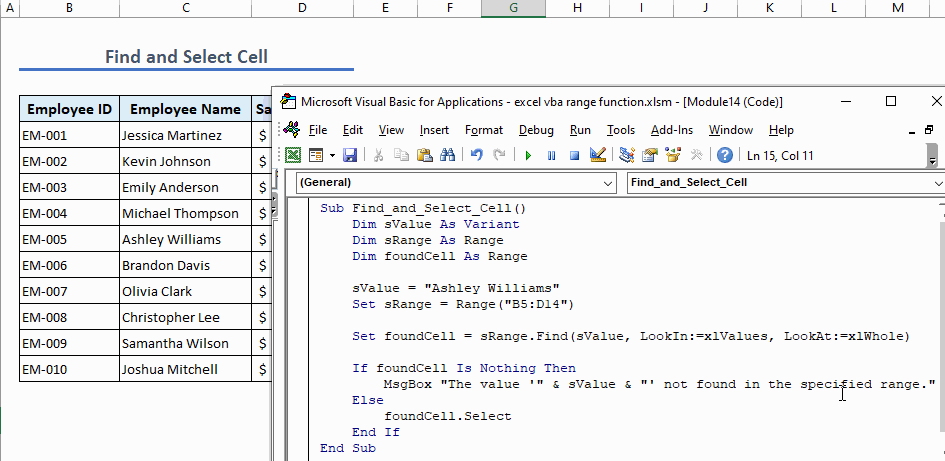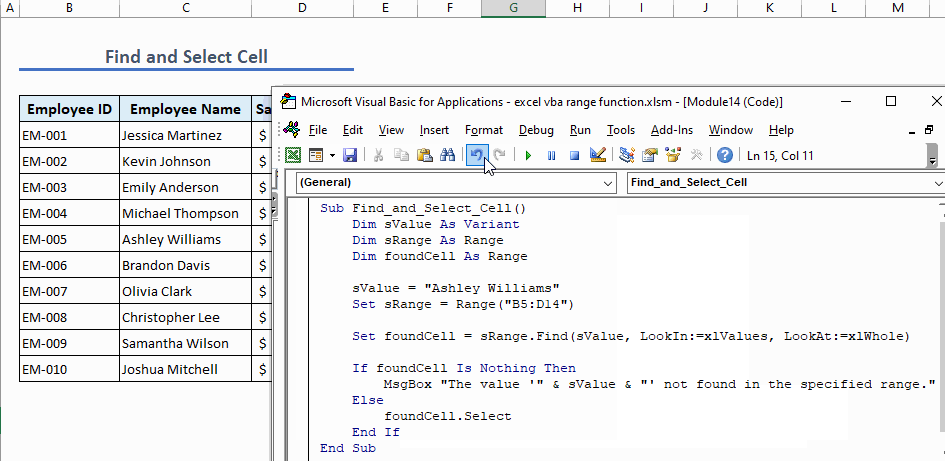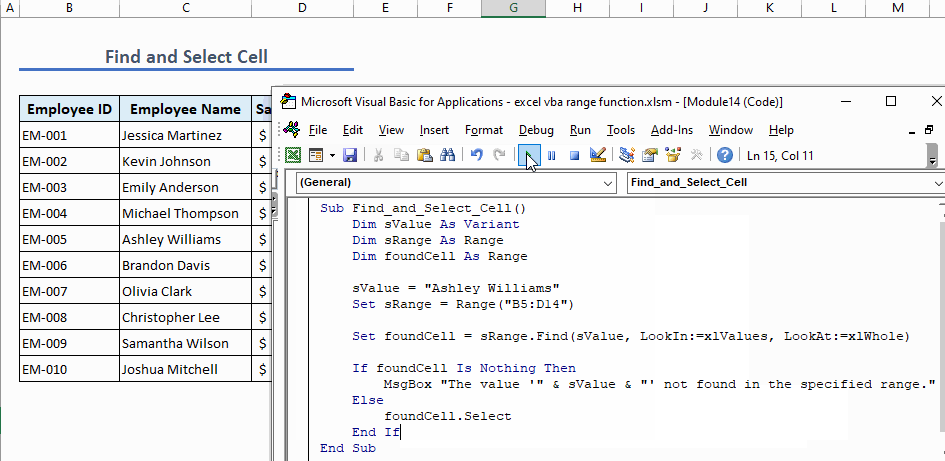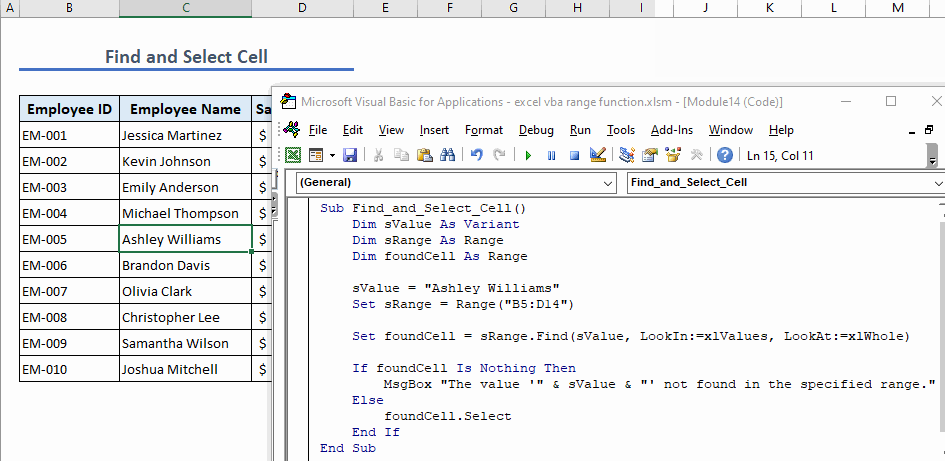
- Run the code to find the value and select the cell with that value.
Read More: Excel VBA: Get Range of Cells with Values
Example 9 – Sort a Range of Cells
Suppose we have the following dataset. Let’s sort it by a single column and then multiple columns.
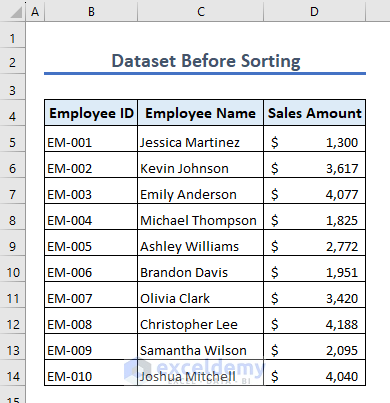
9.1 – Single Column
To sort the dataset based on the values in cell D5, use the following code:
Sub Sort_Single_Column()
Range("B5:D14").Sort Key1:=Range("D5"), Order1:=xlAscending, Header:=xlNo
End Sub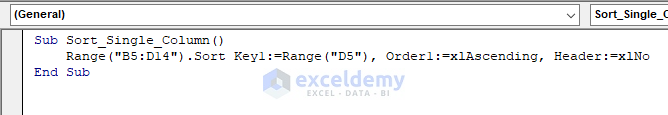
The dataset looks like this after sorting.
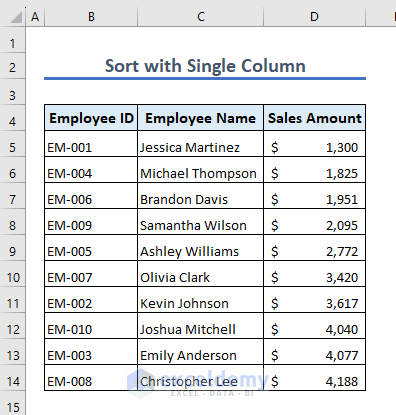
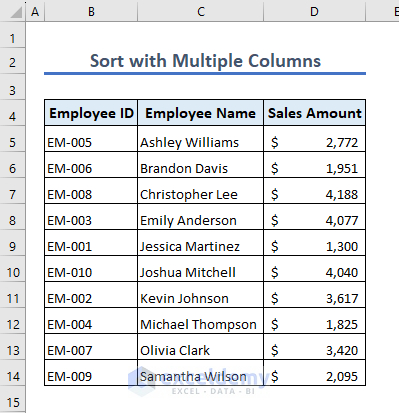
9.2 – Multiple Columns
Use the following code to sort a dataset by multiple columns:
Sub Sort_Multiple_Columns()
Range("B5:D10").Sort _
Key1:=Range("C5"), Order1:=xlAscending, _
Key2:=Range("D5"), Order2:=xlAscending, _
Header:=xlNo
End Sub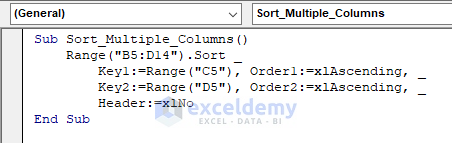
The dataset looks like this after sorting by multiple columns.
Example 10 – Copy and Paste Cell Values
To copy cell values and paste them into a specific range, use the following code:
Sub Copy_and_Paste_Values()
Range("E5:E9").Select
Selection.Copy
Range("C5").Select
Sheets("Sheet1").Paste
End Sub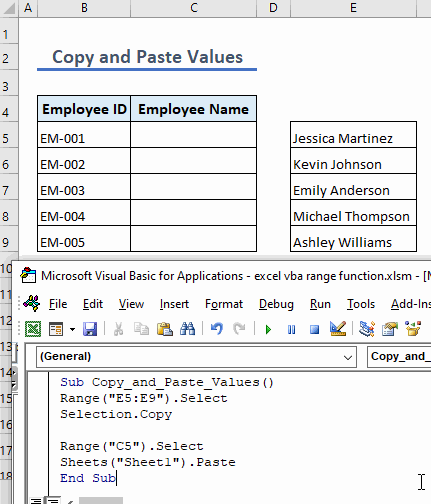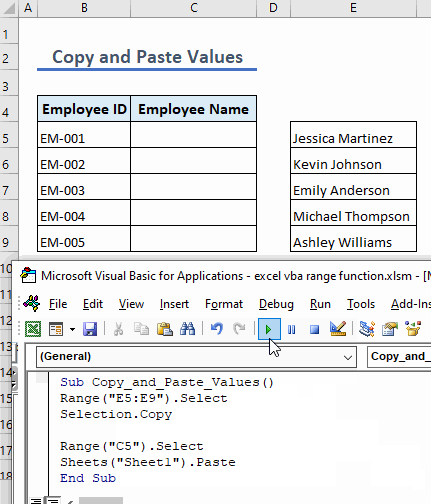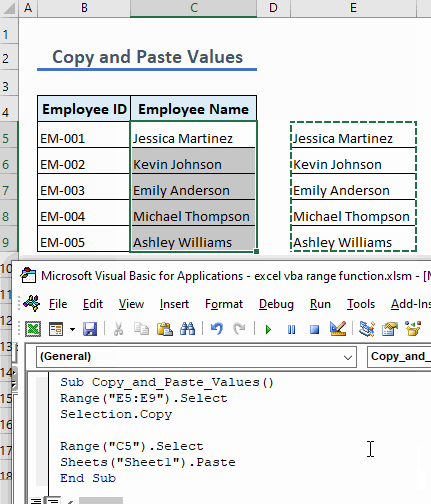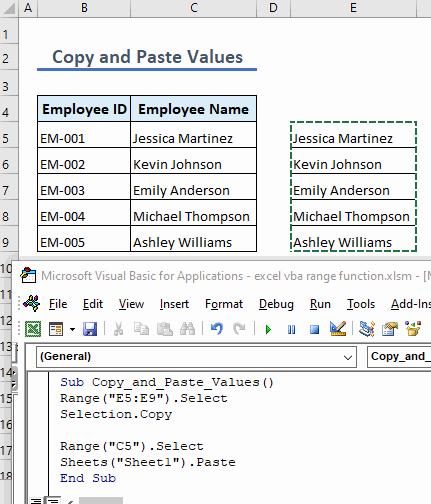
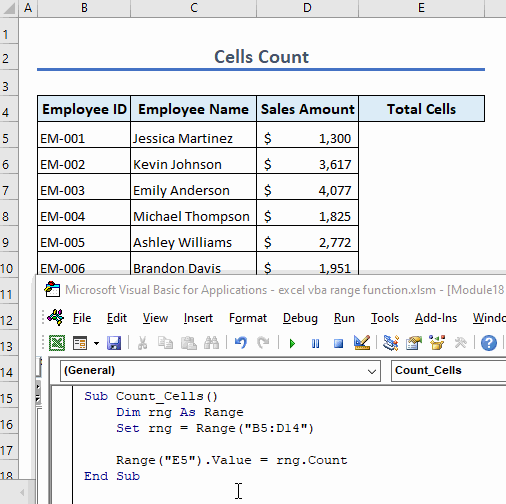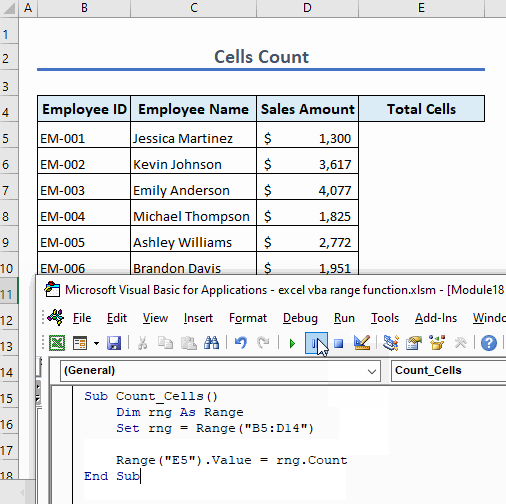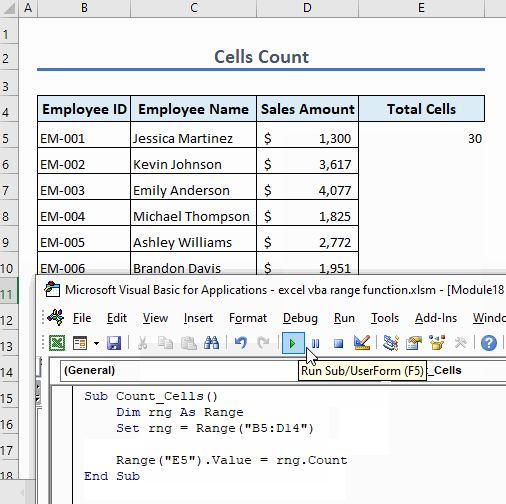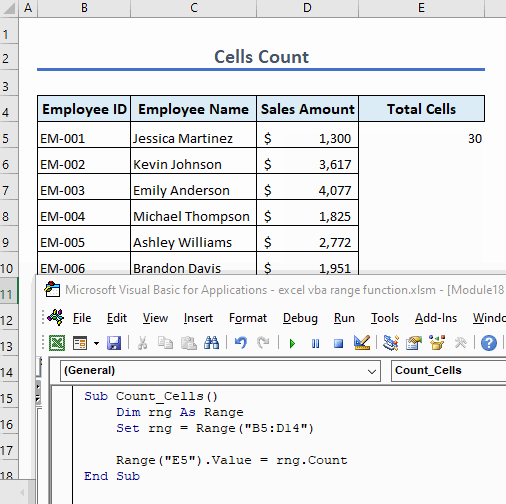
Example 11 – Count Cells in Range
To count the number of cells in a range, use the following code:
Sub Count_Cells()
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = Range("B5:D14")
Range("E5").Value = rng.Count
End SubThis code counts total cells in the range B5:D14 and shows the result in cell E5.
Example 12 – Customize Fonts
We can customize the fonts used in a range. For example, the following code makes the fonts in the range C5:C10 bold:
Sub Custom_Font()
Range("C5:C10").Font.Bold = True
End Sub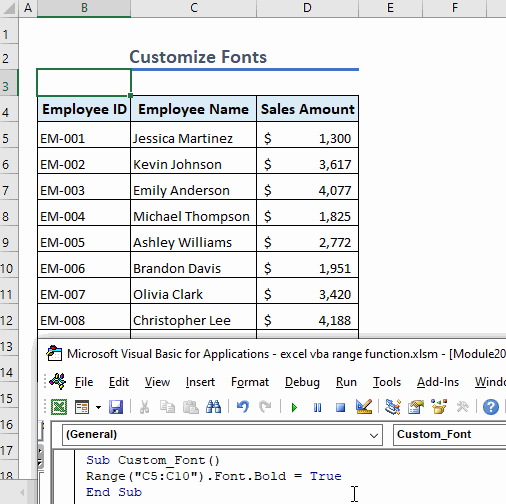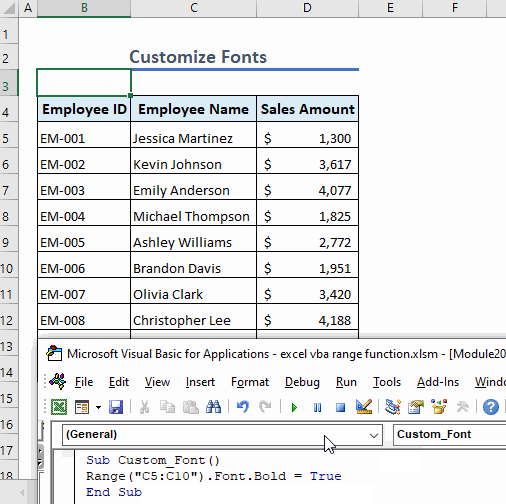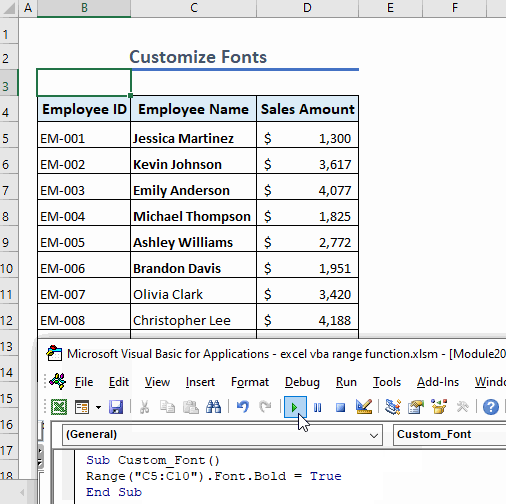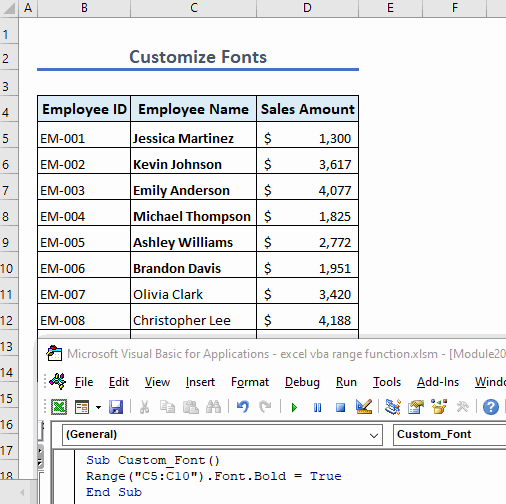
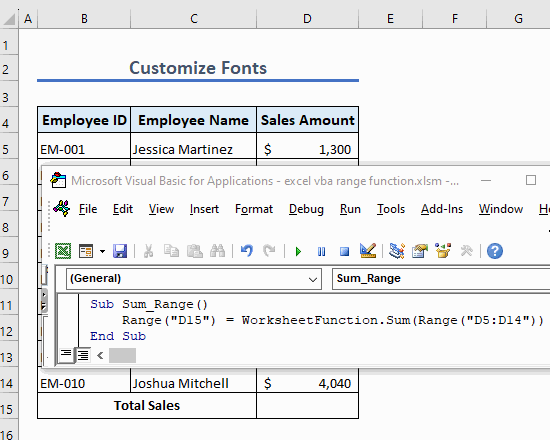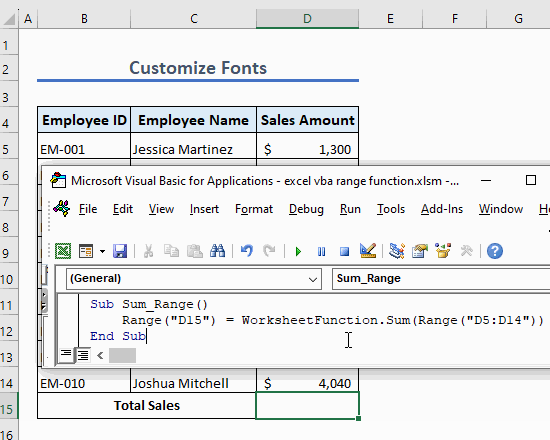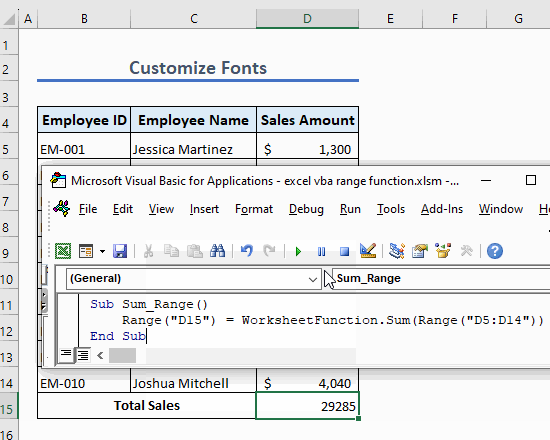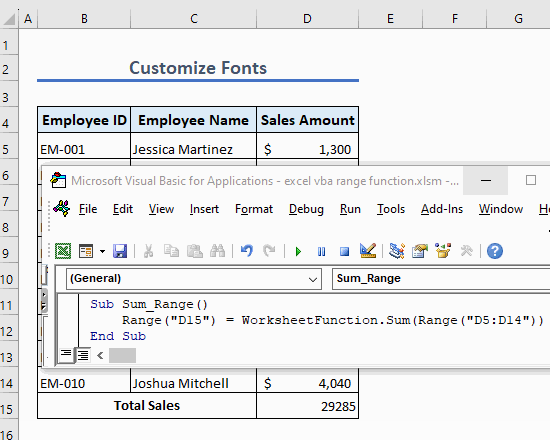
Example 13 – Sum a Range of Cells
Use the following code to sum a range of cells:
Sub Sum_Range()
Range("B14") = WorksheetFunction.Sum(Range("B5:B10"))
End SubThis code sums the values in cells B5 to B10 and shows the summation in cell B14.
Things to Remember
- Remember to save the Excel file as a macro-enabled workbook.
- The Range function can be used in conjunction with other VBA functions to create macros that automate tasks.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the Excel VBA Range function used for?
The Range function in Excel VBA is used to perform various operations on cells, such as reading or modifying values, formatting, and more.
2. Can I modify cell values using the Range function?
Yes, you can modify the cell values using the Value property of the Range object. An example is shown above.
Download Practice Workbook
Related Articles
- How to Use VBA to Set a Range Variable to Selection in Excel
- VBA Range with Variable Row Number in Excel
- How to Use Range with Variable Row and Column with Excel VBA


