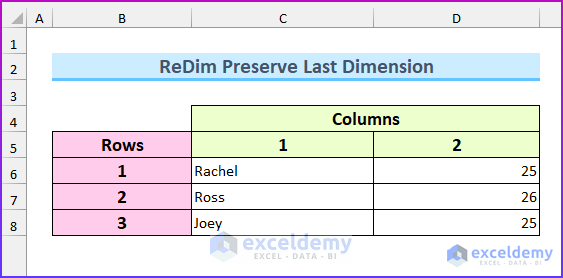
This is the sample dataset created from a 2D array with three rows and two columns.
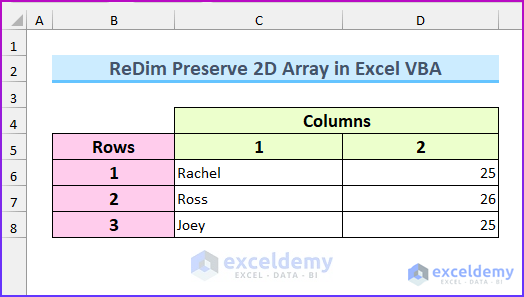
Method 1 – ReDim Preserve the Last Dimension of a 2D Array
- Press ALT+F11 to open the VBA Module window. Alternatively, go to the Developer tab → select Visual Basic.
- In Insert → select Module.
- Enter the following code in the Module window.
Sub Redim_Preserve_2D_Array_Row()
Dim Our_Array() As Variant
ReDim Our_Array(1 To 3, 1 To 2)
Our_Array(1, 1) = "Rachel"
Our_Array(2, 1) = "Ross"
Our_Array(3, 1) = "Joey"
Our_Array(1, 2) = 25
Our_Array(2, 2) = 26
Our_Array(3, 2) = 25
Range("C6:D8").Value = Our_Array
End Sub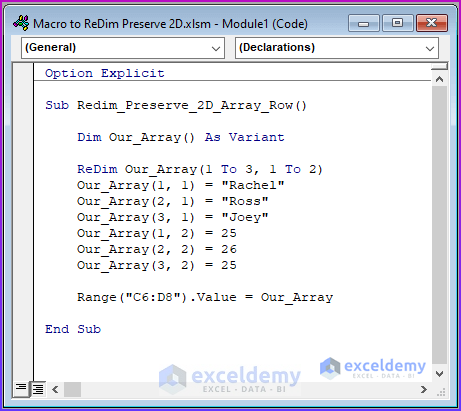
VBA Code Breakdown
- Call the Sub procedure “Redim_Preserve_2D_Array_Row”.
- Declare the variable Our_Array as a dynamic array.
- Define the size of the array. The lower bound is 3, the upper bound is 2, and both start from 1.
- Assign values to the array.
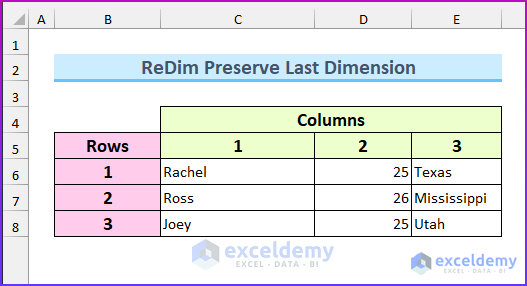
- Input the values to C6:D8.
It will return the values to the defined ranges: “Rachel” is in row 1 and column, which was defined as (1,1) in the VBA code.
- Resize the array.
- Add this to the previous code and remove the first Range.Value statement.
ReDim Our_Array(1 To 3, 1 To 3)
Our_Array(1, 3) = "Texas"
Our_Array(2, 3) = "Mississippi"
Our_Array(3, 3) = "Utah"
Range("C6:E8").Value = Our_Array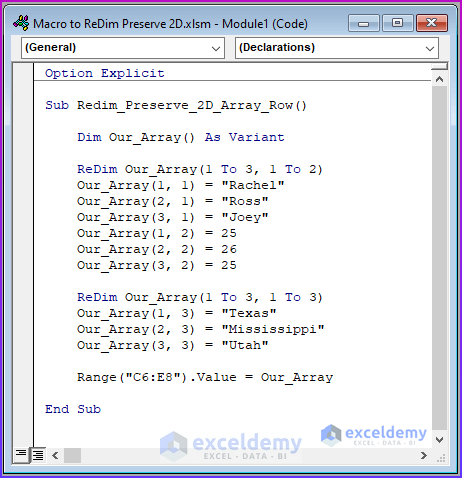
The upper bound was increased by 1 from (1 To 2) to (1 To 3).
The values were added to the array.
- If you execute the code, the previous values will return blank.
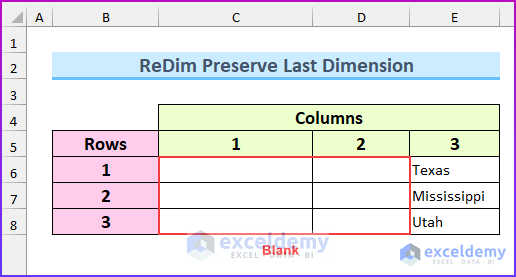
- Add the Preserve keyword into the ReDim statement:
Option Explicit
Sub Redim_Preserve_2D_Array_Row()
Dim Our_Array() As Variant
ReDim Our_Array(1 To 3, 1 To 2)
Our_Array(1, 1) = "Rachel"
Our_Array(2, 1) = "Ross"
Our_Array(3, 1) = "Joey"
Our_Array(1, 2) = 25
Our_Array(2, 2) = 26
Our_Array(3, 2) = 25
ReDim Preserve Our_Array(1 To 3, 1 To 3)
Our_Array(1, 3) = "Texas"
Our_Array(2, 3) = "Mississippi"
Our_Array(3, 3) = "Utah"
Range("C6:E8").Value = Our_Array
End Sub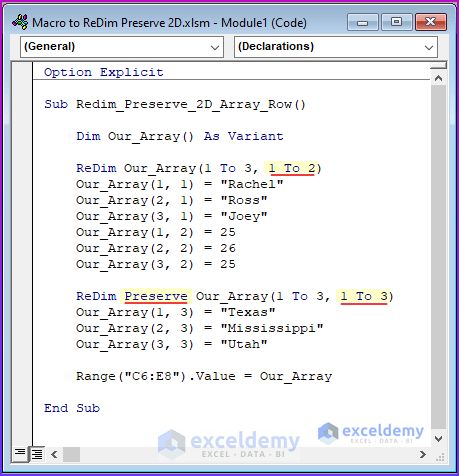
- Run the code.
This is the output.
Read More: How to Redim 2D Array with VBA in Excel
Method 2 – ReDim Preserve Both Dimensions of a 2D Array in Excel VBA
Steps:
- Open the Module window, as shown in the first method.
- Add the following lines of code to the first code.
Our_Array = Application.Transpose(Our_Array)
ReDim Preserve Our_Array(1 To 3, 1 To 4)
Our_Array = Application.Transpose(Our_Array)
Our_Array(4, 1) = "Monica"
Our_Array(4, 2) = 26
Our_Array(4, 3) = "New Mexico"
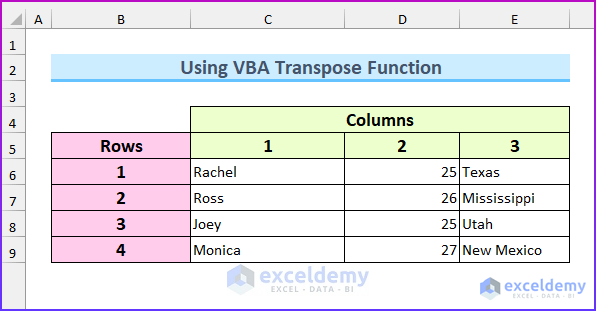
Range("C6:E9").Value = Our_Array
- This is the full code:
Option Explicit
Sub ReDim_Preserve_2D_Array_Both_Dimensions()
Dim Our_Array() As Variant
ReDim Our_Array(1 To 3, 1 To 2)
Our_Array(1, 1) = "Rachel"
Our_Array(2, 1) = "Ross"
Our_Array(3, 1) = "Joey"
Our_Array(1, 2) = 25
Our_Array(2, 2) = 26
Our_Array(3, 2) = 25
ReDim Preserve Our_Array(1 To 3, 1 To 3)
Our_Array(1, 3) = "Texas"
Our_Array(2, 3) = "Mississippi"
Our_Array(3, 3) = "Utah"
Our_Array = Application.Transpose(Our_Array)
ReDim Preserve Our_Array(1 To 3, 1 To 4)
Our_Array = Application.Transpose(Our_Array)
Our_Array(4, 1) = "Monica"
Our_Array(4, 2) = 26
Our_Array(4, 3) = "New Mexico"
Range("C6:E9").Value = Our_Array
End Sub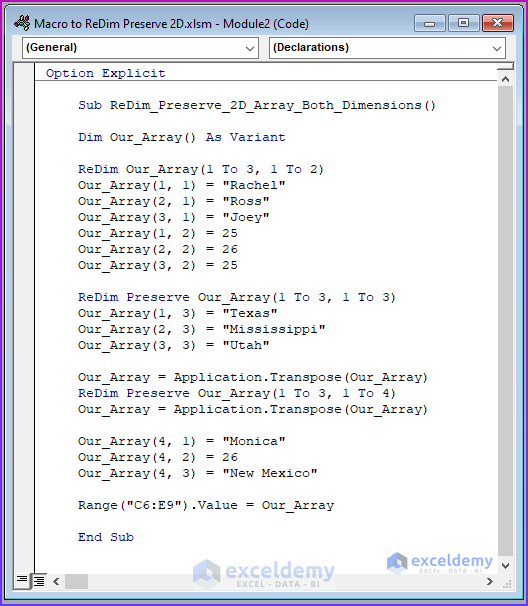
VBA Code Breakdown
- Call the Sub procedure “ReDim_Preserve_2D_Array_Both_Dimensions”.
- The rest of the codes up to the VBA Transpose function are the same as in the first code.
- Transpose the array.
- Increase the upper bound of the array.
- Transpose the array again. It will change the lower bound.
- Input the values for the resized array while preserving the old data.
- Enter the values to C6:E9.
- Run the code, as shown in the first method.
The code preserves a 2D array using the “ReDim Preserve” and the VBA Transpose function.
Read More: Excel VBA 2 Dimensional Array Initialization
Things to Remember
- ReDim Preserve cannot change the lower bound of the array. Use the Transpose function.
- Use ReDim on dynamic arrays.
Download Practice Workbook
Related Articles
- Excel VBA Multidimensional Array for Assigning Values
- Excel VBA Multidimensional Arrays
- How to Use UBound on Multidimensional Array with VBA in Excel
- Excel VBA to Declare Multidimensional Array of Unknown Size


