Knowing how to sort range using VBA in Excel saves time and effort in our daily calculations. Although Excel provides a sorting facility by default, using the Range.Sort method provides access to several useful additional parameters to sort a dataset.
Introduction to the Range.Sort Statement in Excel VBA
Objective: To sort a range of cell data.
Syntax:
expression.Sort (Key1, Order1, Key2, Type, Order2, Key3, Order3, Header, OrderCustom, MatchCase, Orientation, SortMethod, DataOption1, DataOption2, DataOption3)
The expression represents a Range object, such as a cell, a row, a column, or a selection of cells.
Arguments:
We need to provide three main parameters for the Range.Sort method. They are:
Key – The range of cells from single or multiple columns that we need to sort.
Order – The sorting order, either ascending or descending.
Header – Declare whether the columns to be sorted have a header or not.
In this article, we’ll use a list of peoples’ names with their date of birth and age as a dataset, and apply different methods to sort it using VBA.
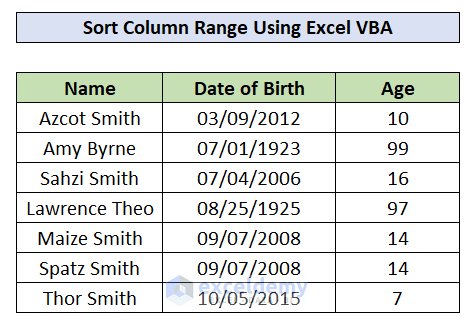
Method 1 – Sort a Single Column Range
In this example, we’ll sort people from oldest to youngest (descending order).
Steps:
- Go to the Developer Tab in the Excel Ribbon and click on the Visual Basic option.
- Select the Module option from the Insert tab to open a new module.
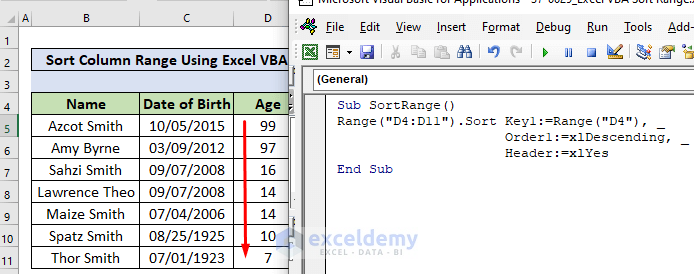
Now let’s insert our code to sort the Age column range.
1.1 – Column with Header
- Enter the following code in the visual code editor:
Sub SortRange()
Range("D4:D11").Sort Key1:=Range("D4"), _
Order1:=xlDescending, _
Header:=xlYes
End Sub- Press F5 or click the Run button to execute the code.
Explanation:
In the above code, we put:
Expression (Range object)=Range(“D4:D11”); the age column with a header in cell D4 and values in D5:D11.
Key = Range(“D4”); the key for sorting.
Order= xlDescending; as we want to sort values from largest to lowest, we set the sorting order as descending.
Header =xlYes; in the following screenshot, the dataset has a header for each of the columns.
1.2 Column without Header
- Enter the following code in the visual code editor:
Sub SortRange()
Range("D4:D10").Sort Key1:=Range("D4"), _
Order1:=xlDescending, _
Header:=xlNo
End Sub- Press F5 or click the Run button to execute the code.
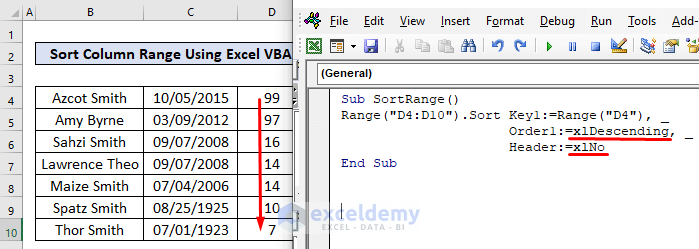
Explanation:
In the above code, we put:
Expression (Range object)=Range(“D4:D10”); the age column without a header has values in D4:D10.
Key = Range(“D4”); the key for sorting.
Order= xlDescending; as we want to sort values from largest to lowest, we set the sorting order as descending.
Header =xlNo; The dataset has no header.
Read More: Excel VBA to Sort by Column Header Name
Method 2 – Sort a Multiple Column Range
To illustrate sorting in multiple columns, we need to modify our dataset a little by inserting a few new rows. In the modified dataset, rows 7, 8, and 9 have the same values for the date of birth and ages, but three different names. These names are not in any specific order.
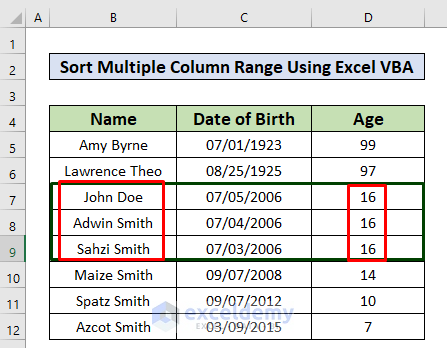
Let’s order the names in ascending order.
- Enter and run the following code in the visual basic editor:
Sub SortRange()
Range("B4:D12").Sort Key1:=Range("D4"), _
Order1:=xlDescending, _
Key2:=Range("B4"), _
Order2:=xlAscending, _
Header:=xlYes
End Sub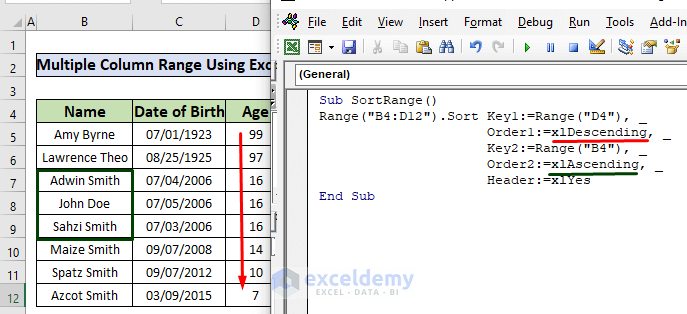
Explanation:
The ages in column D are sorted in descending order. We added two more parameters to our previous code:
Key2: =Range(“B4”), the key to sort names.
Order2: =xlAscending, the order for shorting names.
As a result, the names in rows 7, 8, and 9 are now alphabetically sorted in ascending order.
In the following screenshot, we changed the value of the Order2 parameter to sort the names in descending order.
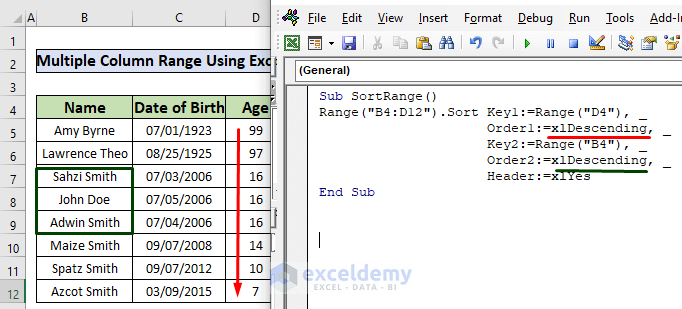
Read More: How to Sort Multiple Columns with Excel VBA
Method 3 – Double Click on the Header to Sort Column Range
Excel’s default sorting feature doesn’t allow to sort values of a column by double-clicking the column header. But using VBA code we can make it happen.
Enter and run the following code in the visual basic editor:
Private Sub Worksheet_BeforeDoubleClick(ByVal Target As Range, Cancel As Boolean)
Dim KeyRange As Range
Dim ColCount As Integer
ColCount = Range("A1:C8").Columns.Count
Cancel = False
If Target.Row = 1 And Target.Column <= ColCount Then
Cancel = True
Set KeyRange = Range(Target.Address)
Range("A1:C8").Sort Key1:=KeyRange, Header:=xlYes
End If
End SubIn this code we used the BeforeDoubleClick event to disable the usual double–click to start the editing mode of the cell. With this event running, if we double–click on any of the column headers, the column data will be sorted in ascending order.
Read More: VBA to Sort Column in Excel
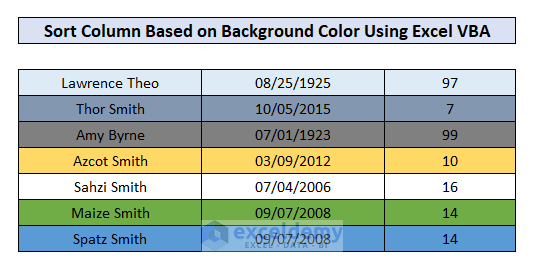
Method 4 – Sort Column Range Based on Background Color
To sort a range of cells in a column based on their background color, we need to add a parameter named SortOn which has a value xlSortOnCellColor. To demonstrate the sorting, we set different background colors to the rows of our dataset.
- In the visual basic code editor enter the following code and press F5 to run it:
Sub SortRangeByBackgroundColor()
ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("background").Sort.SortFields.Add2 Key:=Range("B4"), _
SortOn:=xlSortOnCellColor, Order:=xlAscending, DataOption:=xlSortNormal
With ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("background").Sort
.SetRange Range("B4:D10")
.Apply
End With
End SubThe dataset is sorted based on row background color.
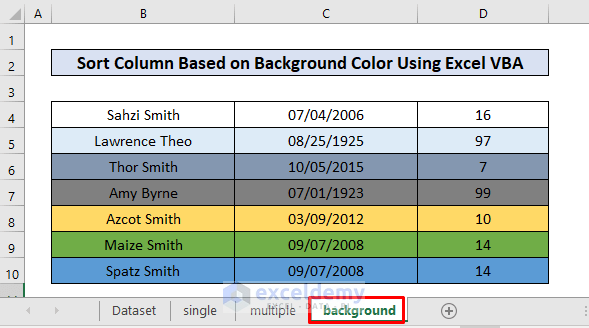
Explanation:
- We named the worksheet “background”, so we put “background” as our active worksheet name.
- We set B4 as the key and B4:D10 as the range. The code will sort data based on the key.
- As we didn’t specify the header parameter, the code uses the default no header.
- We set the order parameter as ascending, so the code sorted the data from lower to higher values.
Method 5 – Sort Column Range Based on Font Color
We can also sort our dataset based on their font color. Let’s color different rows to illustrate.
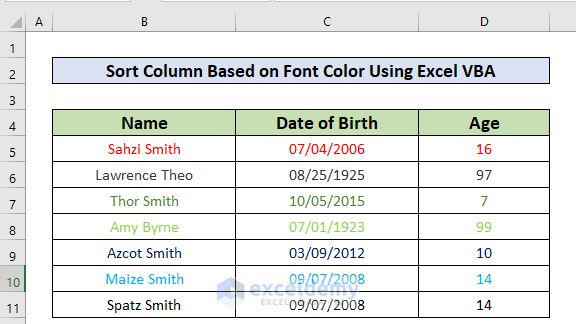
- Apply the code below to sort the dataset based on font color.
Sub SortRangeByFontColor()
ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("fontcolor").Sort.SortFields.Add(Range("B4"), _
xlSortOnFontColor, xlAscending, xlSortNormal).SortOnValue.Color = RGB(0, 0, 0)
With ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("fontcolor").Sort
.SetRange Range("B4:D11")
.Header = xlYes
.Orientation = xlTopToBottom
.Apply
End With
End Sub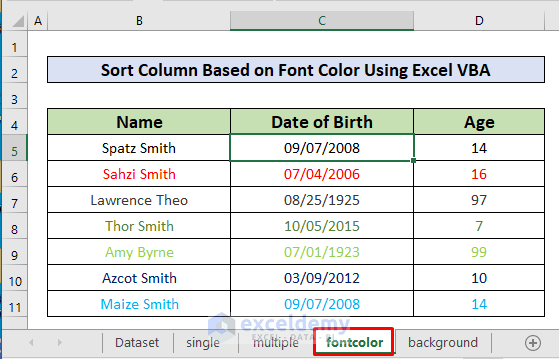
Explanation:
- We named the worksheet “fontcolor”. So, in the code, we put “fontcolor” as our active worksheet name.
- We set B4 as the key and B4:D11 as the range. The code will sort data based on the key.
- We specified the header parameter as xlYes.
- We set the order parameter as ascending, so it sorts the data from lower to higher values.
- The orientation parameter holds the value xlTopToBottom as it is mandatory.
- The Color to sort on is in RGB terms, which has a value from 0 to 255.
Read More: Excel VBA to Sort Column Ascending
Method 6 – Change Orientation to Sort Range
Using the orientation parameter, we can change the way we want to sort data. In this example, we transpose our dataset to sort it horizontally.
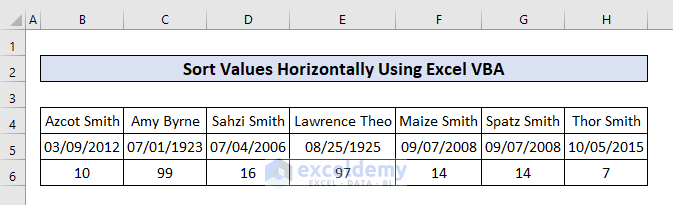
- Place the following code in the visual basic editor and press F5 to run it:
Sub Orientation()
Range("B4:H6").Sort Key1:=Range("B6"), _
Order1:=xlAscending, _
Orientation:=xlSortRows, _
Header:=xlYes
End Sub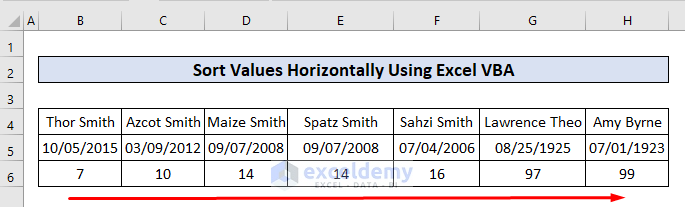
Here we sorted the data based on the age row in ascending order from left to right. In the code, we set the orientation parameter as xlSortRows.
Things to Remember
- The SortOn parameter that we used to sort column range based on background color and font color can only be used by a worksheet object. We cannot use it with a range object.
- The BeforeDoubleClick event sorts data only in ascending.
Download Practice Workbook
Related Articles
- Excel VBA Sort Named Range
- Excel Macro: Sort Multiple Columns with Dynamic Range
- Excel VBA Sort Range with Multiple Keys



At the beginning, Amy Bryne was 99. After first sorting 97. Not sure, whether this is wished sorting.
Hello RALF,
Thanks for your comment. I suppose you are mentioning the first method. Here, we have shown you how to sort a single column. We have sorted only the column which contains the Age and the other column values (Name, Date of Birth) remained the same. That’s why after sorting the age changed for Amy Bryne.
If you have any other suggestions or face any problems, please share them with us in the comment section.
Regards,
Arin Islam
Exceldemy.