Method 1 – Split Words of a String by Space Character
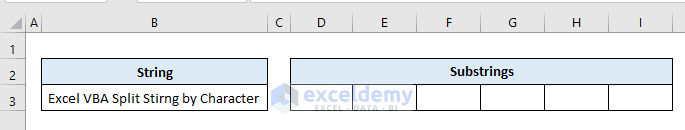
Task: Split a text string in cell B3 by space character and output the substrings in cells D3: I3 (the string in cell B3 has 6 words in it).
Solution: Use the Split function without any delimiter. As we know, if we omit the delimiter argument in the function, it’ll default use the space character as the delimiter.
Code: Insert the following code in the Visual Basic editor and press F5 to run it.
Sub SplitStringbyCharacter()
Dim SubStringArr() As String
SubStringArr = Split(Range("B3"))
For I = 0 To UBound(SubStringArr)
Cells(3, I + 4).Value = SubStringArr(I)
Next I
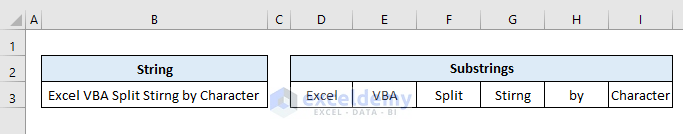
End SubOutput: The above code outputs all the substrings in cells D3:I3.
Method 2 – Specify the Number of Parts to Split a String by Character
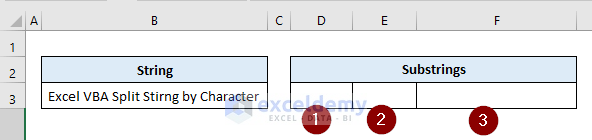
Task: Split a text string in cell B3 by space character and output the 3 substrings in cells D3: F3 (the string in cell B3 has 6 words in it)
Solution: To specify the number of substrings in the Split function, we must put the limit argument as 3 and use the Split function without any delimiter so that it uses the space character as the default delimiter.
Code: Insert the following code in the Visual Basic editor and press F5 to run it.
Sub SplitStringbyCharacter()
Dim SubStringArr() As String
SubStringArr = Split(Range("B3"), , 3)
For I = 0 To UBound(SubStringArr)
Cells(3, I + 4).Value = SubStringArr(I)
Next I
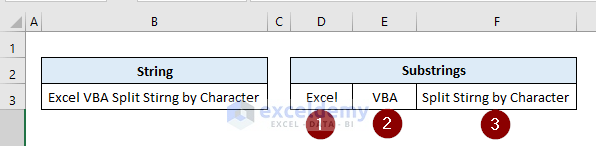
End SubOutput: The above code outputs 3 substrings in cells D3:F3.
Method 3 – Split a String by Character and Return a Specific Part
Task: Get the flat no from the addresses in cells B3:B5.
Problem Analysis: The address is a comma-separated string. Use the delimiter argument as a comma (“,”).
Solution: The Spit function returns a zero-based (start from 0) one-dimensional array. Each element of the array is a substring separated by a predefined delimiter. To solve the above task, we need to output the 2nd element of the array.
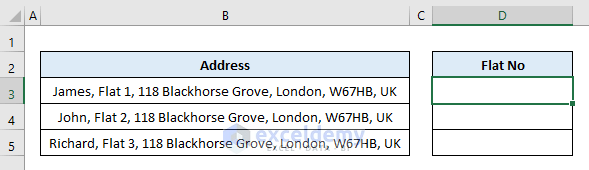
Code: Insert the following code in the Visual Basic Editor and press F5 to run it.
Sub SplitStringbyCharacter()
Range("D3").Value = Split(Range("B3"), ",")(1)
Range("D4").Value = Split(Range("B4"), ",")(1)
Range("D5").Value = Split(Range("B5"), ",")(1)
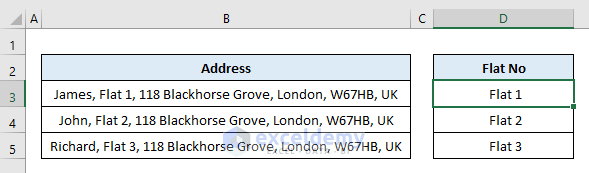
End SubOutput: The above code separated the flat numbers from the addresses and output in cells D3:D5.
Method 4 – Use of Non-Printable Character to Split a String
Task: Split a text string into substrings separated by a non-printable character Vbcrlf and output the substrings in cells B2:B4.
Solution: Here, the string is: “Excel VBA” & vbCrLf & “Split String by Character” & vbCrLf & “Non-printable”. We need to use the Vbcrlf (Visual Basic Carriage Return Line Feed) as the delimiter in the Split function.
Code: Insert the following code in the Visual Basic editor and press F5 to run it.
Sub SplitStringbyCharacter()
Dim SubStringArr() As String, SrcString As String
SrcString = "Excel VBA" & vbCrLf & "Split String by Character" & vbCrLf & "Non-printable"
SubStringArr = Split(SrcString, vbCrLf, , vbTextCompare)
For I = 0 To UBound(SubStringArr)
Cells(I + 2, 2).Value = SubStringArr(I)
Next I
End SubOutput: The above code separated the string and output in cells B2:B5.
Method 5 – Count the Number of Elements in a String Split by Character
Task: Count the number of words in the text string in cell B3 that is split by the space character.
Solution: Use the UBound function in the code to get the number of substrings in the input array.
Code: Insert the following code in the visual basic editor and press F5 to run it.
Sub SplitStringbyCharacter()
Dim SubStringArr() As String
SubStringArr = Split(Range("B3"))
Range("D3") = UBound(SubStringArr())
End Sub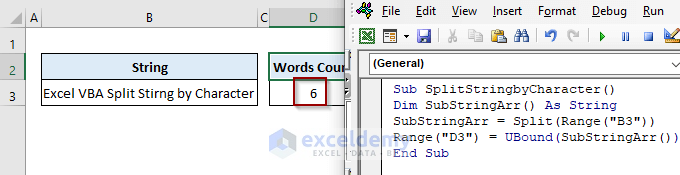
Output: In cell D3, we’ve successfully printed the number of words and the output is 6.
Method 6 – Split Cell Address to Get Row and Column Numbers of the Active Cell
Task: Get the row and column number of the active cell in the worksheet using the Split function in Excel VBA.
Problem Analysis: Run the following code in the editor to get the cell address of the active cell in the worksheet.
Sub GetRowColNumberfromCellAddress()
MsgBox Selection.Address
End Sub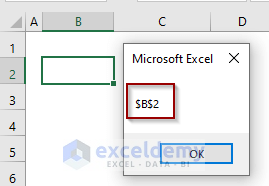
The cell address shown in the Msg Box is $B$2 in an absolute cell reference form.
Solution: We can use VBA Split function to split the cell address by the delimiter “$” to separate the row and column number.
Code: Insert the following code in the visual basic editor and press F5 to run it.
Sub GetRowColNumberfromCellAddress()
rowNumber = Split(Selection.Address, "$")(1)
colNumber = Split(Selection.Address, "$")(2)
MsgBox "Row Number: " & rowNumber & vbCrLf & _
"and" & vbCrLf & "Column Number: " & colNumber
End Sub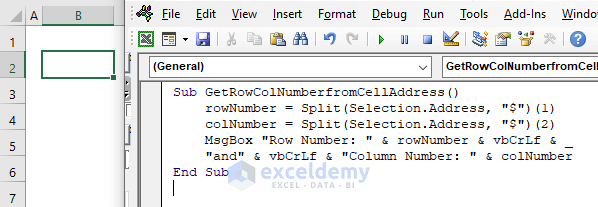
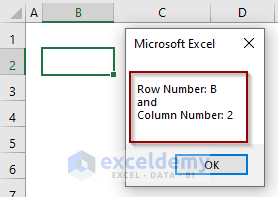
Output: We’ve successfully output the row and column numbers i.e., B and 2 of the active cell address B2 in the Msg Box.
Things to Remember
- If the specified delimiter doesn’t exist in the source string, the Split function will return the string as-is.
Download the Practice Workbook
Related Articles
- Excel VBA: Split String into Rows
- How to Split a String into an Array in VBA
- VBA to Split with Multiple Delimiters in Excel


