How to Open the VBA Macro Editor in Excel
VBA is a programming language that may be used for a variety of tasks, and different types of users can use it for those tasks. Using the Alt + F11 keyboard shortcut, you can launch the VBA editor. In the last section, we will generate VBA code that makes it very easy to perform Vlookup with multiple criteria in Excel. Therefore, you can follow the simple steps to open the VBA editor.
Steps:
- Go to the Developer tab.
- Click on Visual Basic. You can also use the Alt + F11 keyboard shortcut.
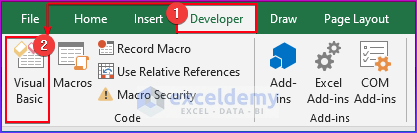
- The Visual Basic window will open.
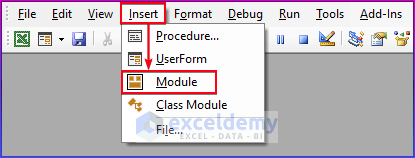
- Go to Insert and choose Module to write the VBA code.
Excel VBA VLookup with Multiple Criteria: 3 Examples
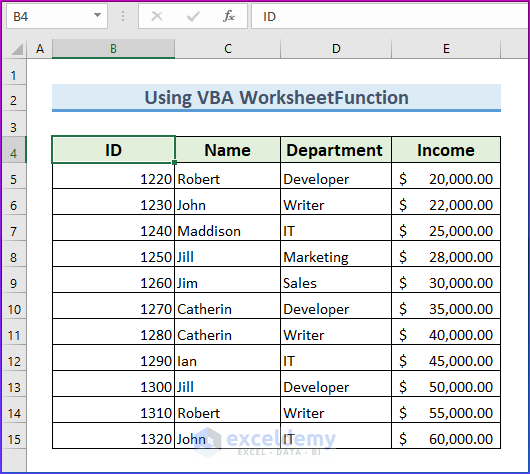
We’ll use a sample dataset, including the ID, Name, Department, and Income of different employees.
Example 1 – Using the VBA WorksheetFunction to VLookup with Multiple Criteria
We’ll show the individual income of all the employees by using the VBA VLookup function.
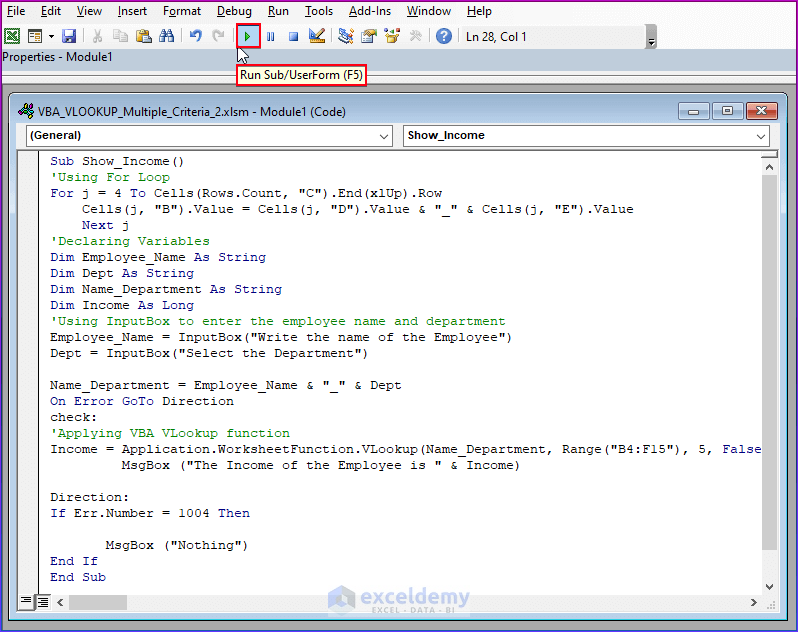
- Copy the following code and paste it into the above Module.
- Click on Run to see the output.
Code:
Sub Show_Income()
'Using For Loop
For j = 4 To Cells(Rows.Count, "C").End(xlUp).Row
Cells(j, "B").Value = Cells(j, "D").Value & "_" & Cells(j, "E").Value
Next j
'Declaring Variables
Dim Employee_Name As String
Dim Dept As String
Dim Name_Department As String
Dim Income As Long
'Using InputBox to enter the employee name and department
Employee_Name = InputBox("Write the name of the Employee")
Dept = InputBox("Select the Department")
Name_Department = Employee_Name & "_" & Dept
On Error GoTo Direction
check:
'Applying VBA VLookup function
Income = Application.WorksheetFunction.VLookup(Name_Department, Range("B4:F15"), 5, False)
MsgBox ("The Income of the Employee is " & Income)
Direction:
If Err.Number = 1004 Then
MsgBox ("Nothing")
End If
End SubVBA Breakdown
Sub Show_Income()- This is the name of the macro that we can use to call the function.
For j = 4 To Cells(Rows.Count, "C").End(xlUp).Row
Cells(j, "B").Value = Cells(j, "D").Value & "_" & Cells(j, "E").Value
Next j- The worksheet’s rows are iterated by using the For loop, which begins at row 4 and ends at the last non-empty row in column C. The code adds the values from columns D and E together for each row and then puts the result in column B.
Dim Employee_Name As String
Dim Dept As String
Dim Name_Department As String
Dim Income As Long- The Dim command declares three variables: Employee_Name as String, Dept as String, and Income as Long.
Employee_Name = InputBox("Write the name of the Employee")
Dept = InputBox("Select the Department")
Name_Department = Employee_Name & "_" & Dept
On Error GoTo Direction- The user is prompted to enter the name of an employee and choose a department using the InputBox function. The variables Employee_Name and Dept are each assigned the values entered.
- The concatenated value of Employee_Name and Dept is put into the variable Name_Department.
- The following code block uses the On Error GoTo statement to handle any errors that might arise.
Income = Application.WorksheetFunction.VLookup(Name_Department, Range("B4:F15"), 5, False)
MsgBox ("The Income of the Employee is " & Income)
Direction:
If Err.Number = 1004 Then
MsgBox ("Nothing")
End If- The output of the VLookup function, which looks for the value of Name_Department in the range B4:F15 and returns the value in the fifth column of the corresponding row, is set to the Income variable.
- The code jumps to the Direction label and determines whether the error code is equivalent to 1004 if the VLookup function returns an error. If so, a message box with the word “Nothing” is displayed by the code.
- The code shows a message box with the text “The Income of the Employee is” and the value of the Income variable if the VLookup function is successful.
Example 2 – Creating a User-Defined Function to VLookup with Multiple Criteria in Excel VBA
Case 1 – Vlookup with Two Criteria
We will create a User-Defined function using VBA and show the income of an employee based on two criteria.
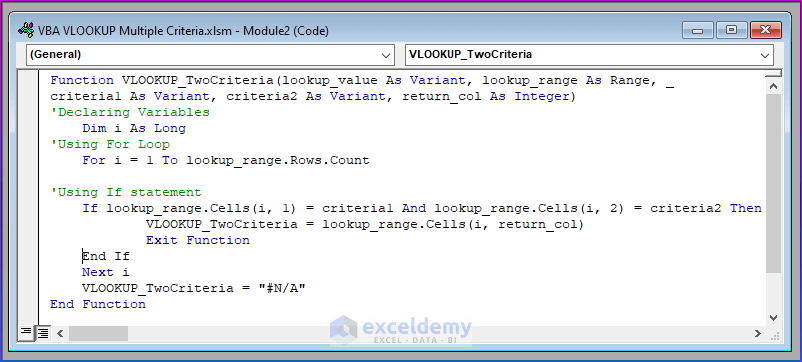
- Copy the following code and paste it into the Module, then save the file.
Code:
Function VLOOKUP_TwoCriteria(lookup_value As Variant, lookup_range As Range, _
criteria1 As Variant, criteria2 As Variant, return_col As Integer)
'Declaring Variables
Dim i As Long
'Using For Loop
For i = 1 To lookup_range.Rows.Count
'Using If statement
If lookup_range.Cells(i, 1) = criteria1 And lookup_range.Cells(i, 2) = criteria2 Then
VLOOKUP_TwoCriteria = lookup_range.Cells(i, return_col)
Exit Function
End If
Next i
VLOOKUP_TwoCriteria = "#N/A"
End FunctionVBA Breakdown
Function VLOOKUP_TwoCriteria(lookup_value As Variant, lookup_range As Range, _
criteria1 As Variant, criteria2 As Variant, return_col As Integer)- We will create a function named VLOOKUP_TwoCriteria, which is a user-defined function that will return a value when it is performed. This function has five arguments: lookup_value, lookup_range, criteria1, criteria2, and return_col.
Dim i As Long
'Using For Loop
For i = 1 To lookup_range.Rows.Count- We declare a variable for the For Loop. The For Loop iterates from lookup_range, starting from row 1 and ending at the last row in the given range.
If lookup_range.Cells(i, 1) = criteria1 And lookup_range.Cells(i, 2) = criteria2 Then
VLOOKUP_TwoCriteria = lookup_range.Cells(i, return_col)
Exit Function
End If
Next i- To determine whether the values in the first and second columns of the current row of the lookup range match those of criteria1 and criteria2, respectively, by using the If statement. If the values match, the function uses the Exit Function statement to leave and assigns the value of the cell in the return column of the current row to the VLOOKUP_TwoCriteria variable. The function moves on to the next row of the lookup range if the values are not the same.
VLOOKUP_TwoCriteria = "#N/A"- The function sets the VLOOKUP_TwoCriteria variable to the value “#N/A” at the end of the For loop if there is no match.
End Function- The End Function statement indicates the conclusion of the function operation.
- We want to know Robert’s income as a developer by applying the following formula in cell I6.
=VLOOKUP_TwoCriteria(G5,B4:E15,H5,I5,4)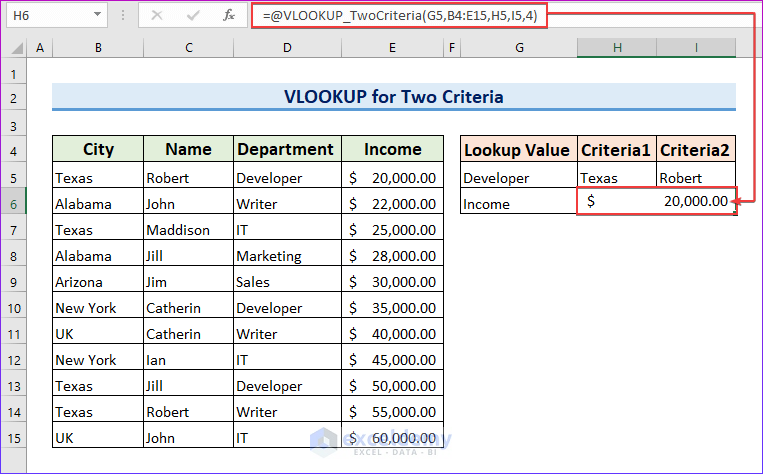
Case 2 – Vlookup with Three Criteria
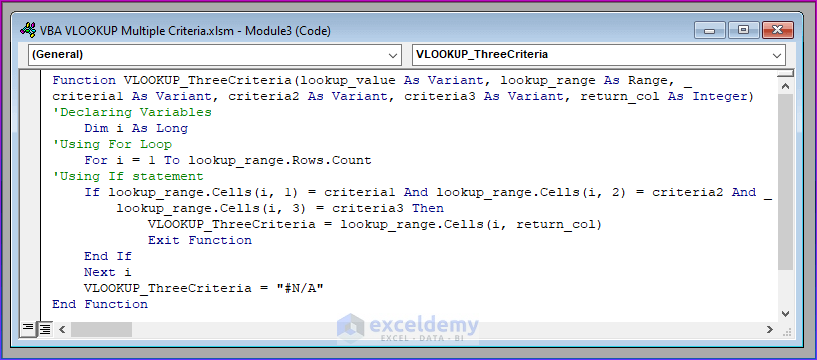
- Use the following code and paste it into the Module. Save the file and use the function in your dataset as if it were any other Excel function to see the output.
Code:
Function VLOOKUP_ThreeCriteria(lookup_value As Variant, lookup_range As Range, _
criteria1 As Variant, criteria2 As Variant, criteria3 As Variant, return_col As Integer)
'Declaring Variables
Dim i As Long
'Using For Loop
For i = 1 To lookup_range.Rows.Count
'Using If statement
If lookup_range.Cells(i, 1) = criteria1 And lookup_range.Cells(i, 2) = criteria2 And _
lookup_range.Cells(i, 3) = criteria3 Then
VLOOKUP_ThreeCriteria = lookup_range.Cells(i, return_col)
Exit Function
End If
Next i
VLOOKUP_ThreeCriteria = "#N/A"
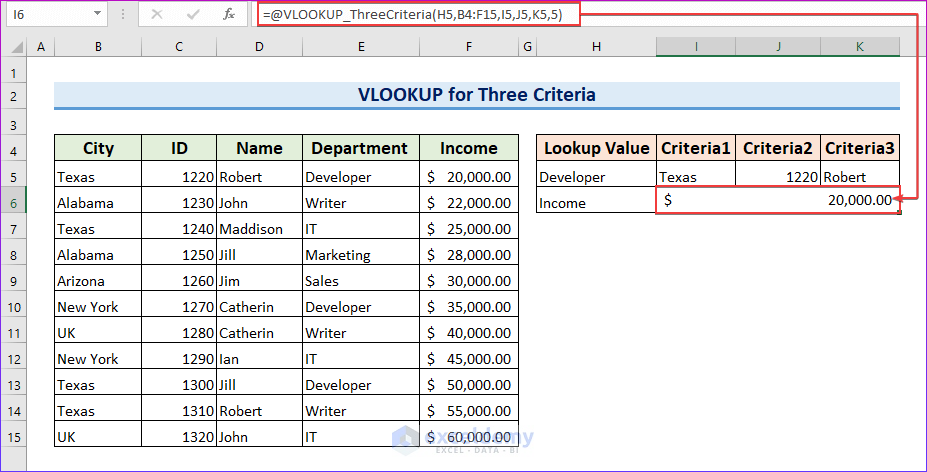
End Function- Here’s an example of using the formula in cell I6 to get the value based on the criteria listed in cells H5:K5.
=VLOOKUP_ThreeCriteria(H5,B4:F15,I5,J5,K5,5)
Read More: Excel VBA to Vlookup Values for Multiple Matches
Example 3 – Creating a UserForm to Vlookup with Multiple Criteria in Excel VBA
Here, we create a UserForm that contains a ComboBox and four TextBoxes. The ComboBox lists names, and when a name is selected, the TextBoxes display information associated with the name from a worksheet named Sheet2. The VLookup function looks up all the information with the selected name as the lookup value and the data range from column B to column F.
- Select the Insert option and click UserForm to open it.
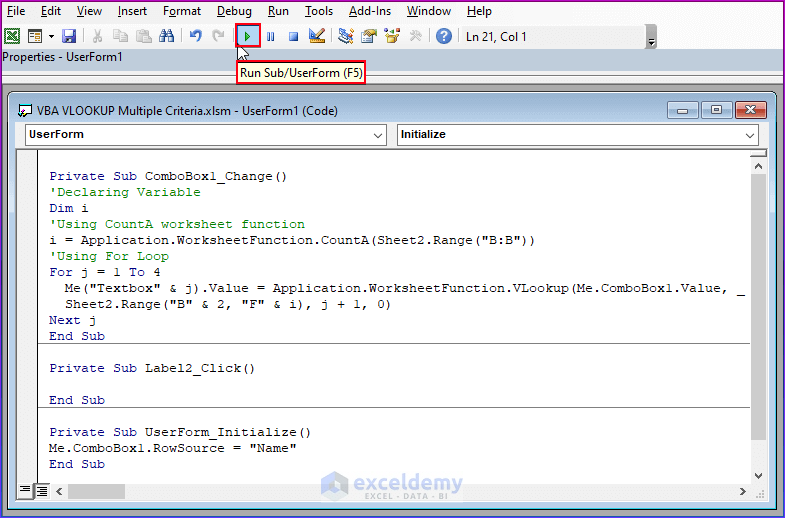
- Copy the following code and paste it into the above Module.
- Click on Run to see the output.
Code:
Private Sub ComboBox1_Change()
'Declaring Variable
Dim i
'Using CountA worksheet function
i = Application.WorksheetFunction.CountA(Sheet2.Range("B:B"))
'Using For Loop
For j = 1 To 4
Me("Textbox" & j).Value = Application.WorksheetFunction.VLookup(Me.ComboBox1.Value, Sheet2.Range("B" & 2, "F" & i), j + 1, 0)
Next j
End Sub
Private Sub Label2_Click()
End Sub
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
Me.ComboBox1.RowSource = "Name"
End Sub
VBA Breakdown
Private Sub ComboBox1_Change()
'Declaring Variable
Dim i
'Using CountA worksheet function
i = Application.WorksheetFunction.CountA(Sheet2.Range("B:B"))Code Breakdown
- We will define the first sub-procedure.
"ComboBox1_Change()".- We declared a variable i. It counts the number of cells that contain data in column B of Sheet2 using the COUNTA worksheet function and assigns the value to i.
For j = 1 To 4
Me("Textbox" & j).Value = Application.WorksheetFunction.VLookup(Me.ComboBox1.Value, Sheet2.Range("B" & 2, "F" & i), j + 1, 0)
Next j- The For loop runs for four iterations. Each iteration uses the VLOOKUP function to look up the selected name in the data range. It returns the value in the column that corresponds to the current iteration plus one (starting with column C). The value is then assigned to the corresponding TextBox (named “Textbox1” to “Textbox4“).
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
Me.ComboBox1.RowSource = "Name"- We will also define a sub-procedure “UserForm_Initialize()“.
- It sets the RowSource property of the ComboBox to “Name“, which means that the ComboBox gets its list of names from a named range called “Name“.
Read More: How to Use Excel VBA VLookup with Named Range
How to Use the If Else Statement to VLookup with Multiple Criteria in Excel VBA
We have introduced a Birthplace column to the author lists dataset. We want to find the birthplace of each writer that is listed in the “Birth_Place” sheet.
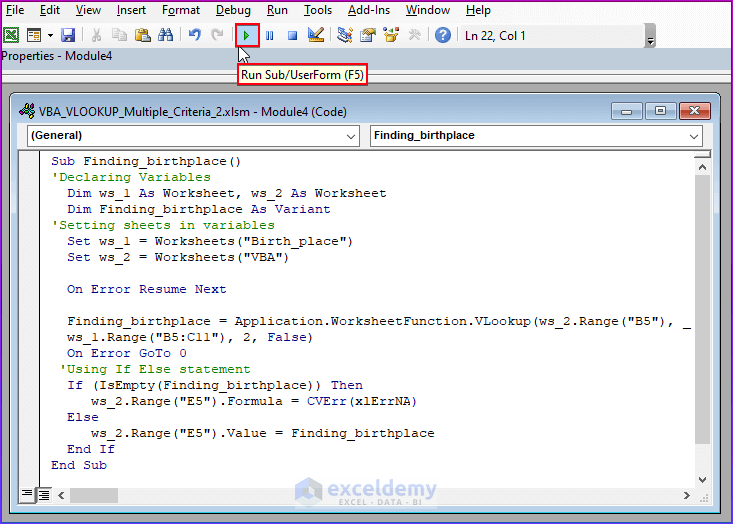
- Copy the following code and paste it into the Module.
- Click on Run to see the output.
Code:
Sub Finding_birthplace()
'Declaring Variables
Dim ws_1 As Worksheet, ws_2 As Worksheet
Dim Finding_birthplaceAs Variant
'Setting sheets in variables
Set ws_1 = Worksheets("Birth_place")
Set ws_2 = Worksheets("VBA")
On Error Resume Next
Finding_birthplace = Application.WorksheetFunction.VLookup(ws_2.Range("B5"), _
ws_1.Range("B5:C11"), 2, False)
On Error GoTo 0
'Using If Else statement
If (IsEmpty(Finding_birthplace)) Then
ws_2.Range("E5").Formula = CVErr(xlErrNA)
Else
ws_2.Range("E5").Value = Finding_birthplace
End If
End Sub
VBA Breakdown
Sub Finding_birthplace()Code Breakdown
- The Sub procedure is Finding_birthplace.
Dim ws_1 As Worksheet, ws_2 As Worksheet
Dim Finding_birthplaceAs Variant- The Dim statement is used to declare three variables: ws_1 and ws_2 as Worksheet objects, and Finding_birthplace as a Variant data type.
Set ws_1 = Worksheets("Birth_place")
Set ws_2 = Worksheets("VBA")- We apply the Set statement to assign the Birth_place and VBA worksheets to the ws_1 and ws_2 variables, respectively.
On Error Resume Next- By using the On Error Resume Next statement, we ignore any runtime errors that may occur during the implementation of the macro.
Finding_birthplace = Application.WorksheetFunction.VLookup(ws_2.Range("B5"), _
ws_1.Range("B5:C11"), 2, False)- We set the Finding_birthplace variable to assign the result of the VLookup function, which finds the value in cell B5 of the VBA worksheet in the table located in the Birth_place worksheet’s B5:C11 range. The function returns the value in the second column of the table (column C) that corresponds to the matching value in column B.
On Error GoTo 0- We apply the On Error GoTo 0 statement to turn off the error handling.
If Else statement
If (IsEmpty(Finding_birthplace)) Then
ws_2.Range("E5").Formula = CVErr(xlErrNA)
Else
ws_2.Range("E5").Value = Finding_birthplace
End If- We apply the If Else statement to check if the Finding_birthplace variable is empty. If it is, the code assigns the #N/A error value to cell E5 of the VBA worksheet using the CVErr function. If it is not empty, the code assigns the value of the Finding_birthplace variable to cell E5.
How to Use the XLOOKUP Function with Multiple Criteria in Excel
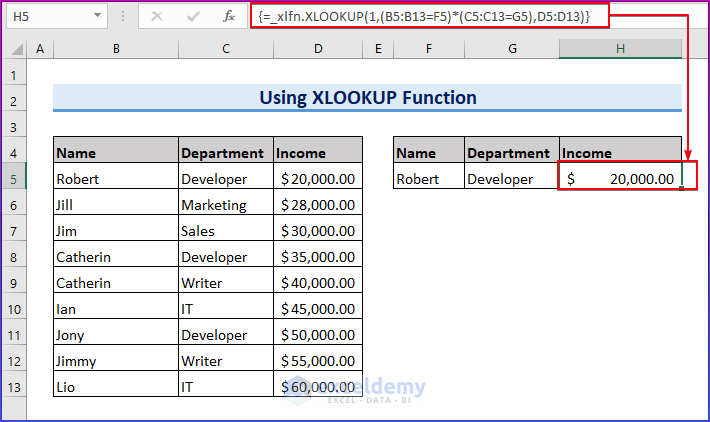
- The criteria for searching the table are listed in F5 (for the B column) and G5 (for the C column). We’ll fetch the value from the D column.
- Insert the following formula in the result cell.
=XLOOKUP(1,B5:B13=F5)*(C5:C13=G5),D5:D13)
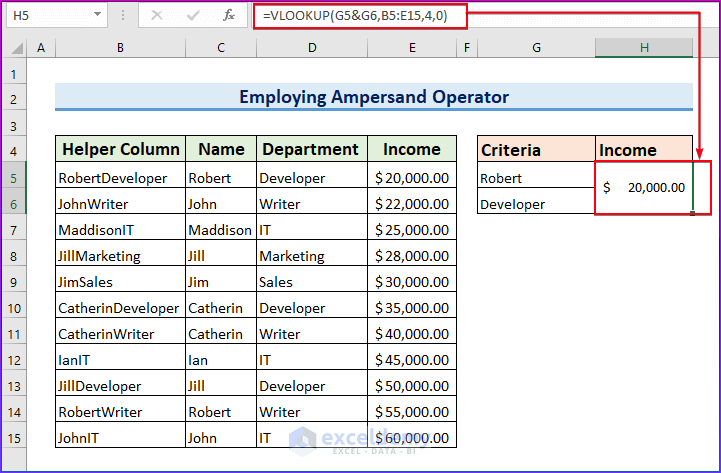
How to Use the Ampersand Operator to Join Multiple Criteria in VLOOKUP in Excel
- Column B represents a helper column which is the combination of the C and D columns.
- As the VLOOKUP function looks for a value in the first column, we have to keep this helper column in the first column of the lookup table.
- Put the criteria in cells G5 and G6 in the same order as they are in the table.
- Apply the following formula in cell H5.
=VLOOKUP(G5&G6,B5:E15,4,0)
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I lookup numerous values in Excel VBA?
To get numerous values in a single cell, we can generate a customized function in VBA that is very similar to the VLOOKUP function, and it checks each cell in a column to find the lookup value.
How can I use VLOOKUP to combine several criterion selections?
Follow these 3 steps to set up multiple criteria. VLOOKUP: Concatenate (join) values from columns you want to use for your criteria in a helper column. Configure VLOOKUP to use a table with the helpful column as a reference. The table’s first column must be the helper column.
Things to Remember
- In Excel VBA, the syntax of the VLookup function remains unchanged.
- When the VBA VLookup function cannot find any lookup value, it shows a 1004 error.
- If the VLookup function returns an error, we can handle it with a GoTo statement.
Download the Practice Workbook
Further Readings
- Use Excel VBA VLOOKUP to Find Values in Another Worksheet
- How to Use Excel VBA VLookup Within Loop
- Excel VBA to Vlookup in Another Workbook Without Opening
- Excel VBA: Working with If, IsError, and VLookup Together


