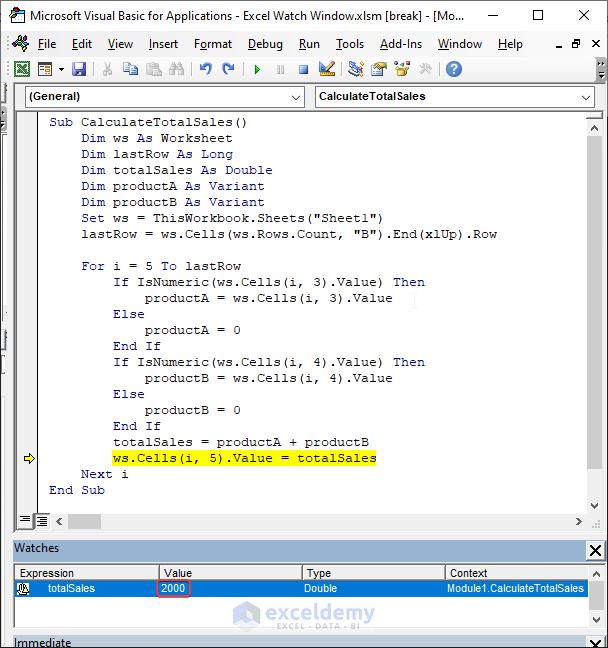
Below, you can see how the watch window monitors the variable value in Excel VBA.
How to Add a Watch Window
- Open the VBA code editor window.
- Go to View > Watch Window.
The watch window is displayed at the bottom of the VBA code editor window.
How to Use Watch Expressions in Excel
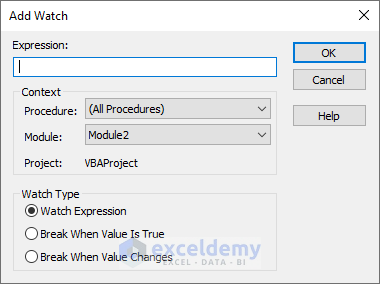
- Right-click the watch window and click Add Watch.
- The Add Watch… window is displayed.
- Enter the Variable you want to track in Expression
- Select Watch Expression in Watch Type.
- Click OK.
Read More: How to Monitor Cells Using Excel Watch Window
How to Use a Watch Window in Excel
Below, is a sample watch window:
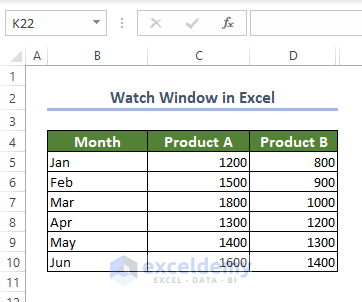
Get the summation of prices of product A and B.
Monitor the summation of the product values and the summation of the total price of products per month.
- Use the VBA code below.
Sub CalculateTotalSales()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim lastRow As Long
Dim totalSales As Double
Dim productA As Variant
Dim productB As Variant
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1")
lastRow = ws.Cells(ws.Rows.Count, "B").End(xlUp).Row
For i = 5 To lastRow
If IsNumeric(ws.Cells(i, 3).Value) Then
productA = ws.Cells(i, 3).Value
Else
productA = 0
End If
If IsNumeric(ws.Cells(i, 4).Value) Then
productB = ws.Cells(i, 4).Value
Else
productB = 0
End If
totalSales = productA + productB
ws.Cells(i, 5).Value = totalSales
Next i
End SubIt sums the values and presents the summation value in the next column.
Each time the totalSale variable value changes the watch window is updated.
- Add a watch window to add a watch variable.
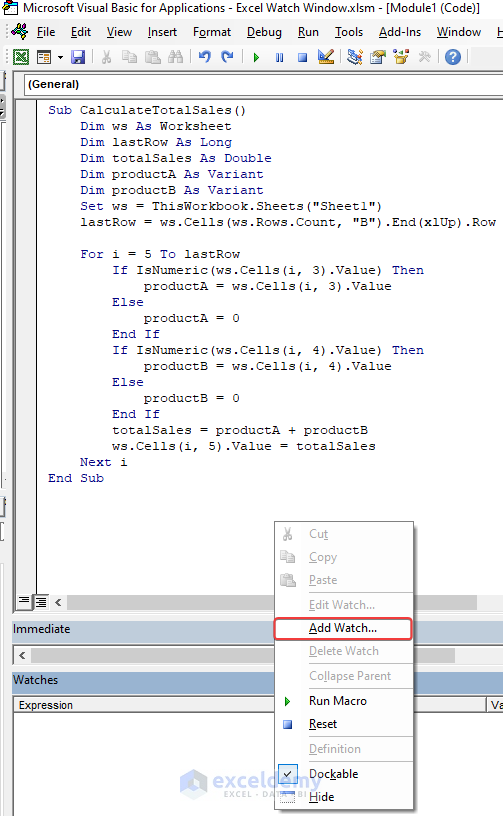
- In that Add Watch window, mention the variable name.
- Select Break When Value Changes.
- Click OK.
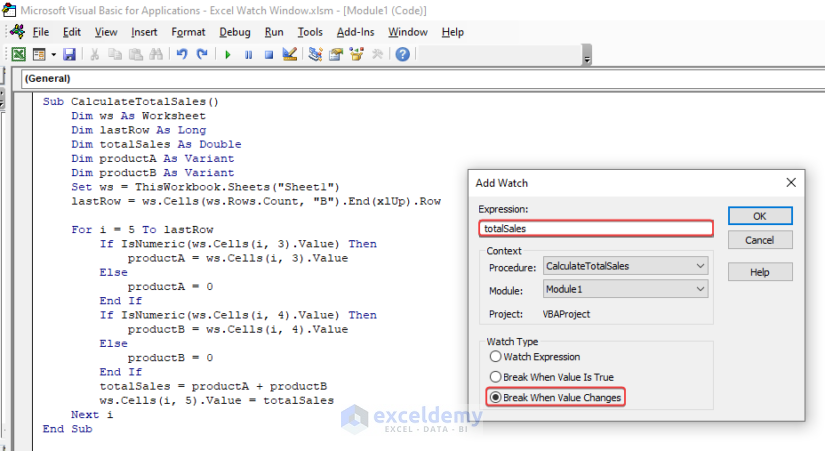
The totalSales variable is added to the variable list.
- If you try to run the code, you will see the variable totalSales is enlisted for tracking and updates.
- Running the code updates the variable value.
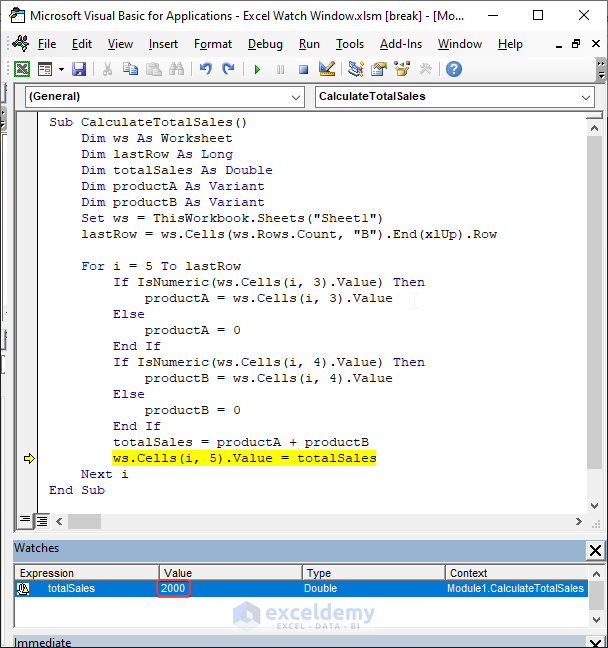
This is the value of totalSales after the second iteration.
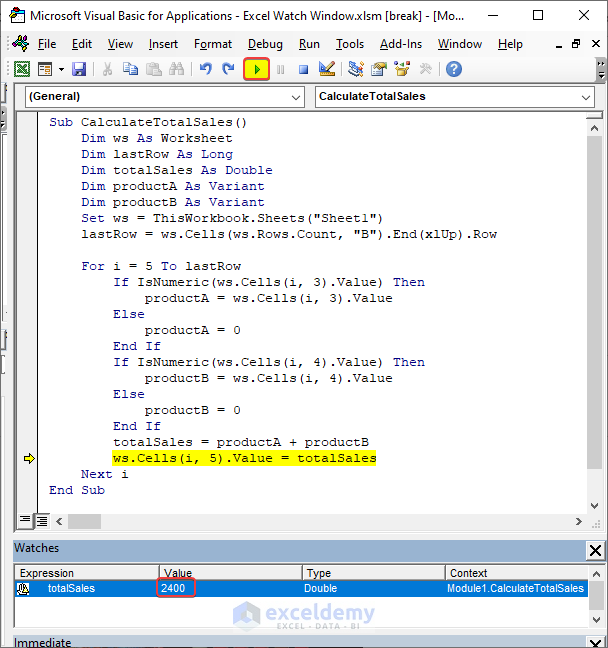
This is the value of totalSales after the code is Run.
Read More: How to Trace Errors in Excel
What Are the Benefits of Using a Watch Window?
Real-time monitoring
It helps understand how the variables change throughout the execution and identify unexpected behaviors.
Simplified Debugging
You can quickly pinpoint the source of issues and address them more efficiently.
Minimizes Repetitive Checks
It provides a central location to monitor multiple variables simultaneously.
No Code Modification
It allows you to inspect variables without altering the original code.
Supports Complex Data Structures
It can handle complex data structures, such as arrays, objects, or multi-dimensional arrays. You can expand it and inspect nested elements.
Pausing Code Execution
You can pause the VBA code execution and check the values of variables.
Efficient Tracking
It helps track progress and values of variables at different stages.
Variable Manipulation
You can change the value of a variable directly in the Watch Window while the code is paused.
Things to Remember
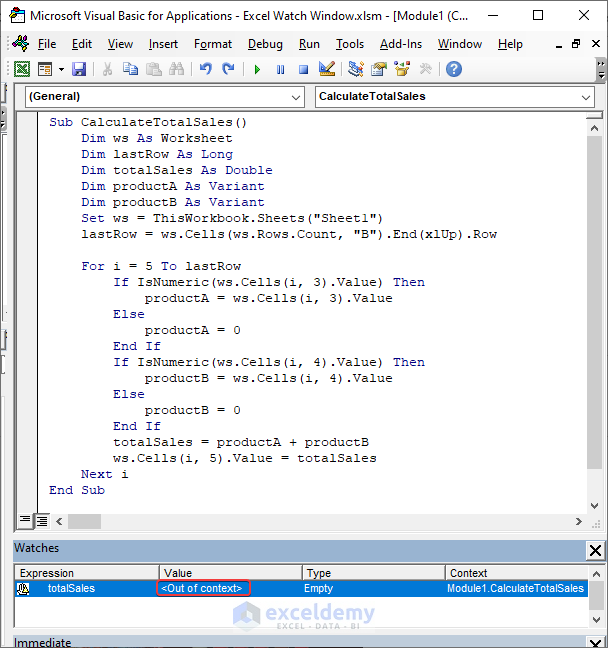
Variable scope: The Watch Window can only monitor variables that are in the current scope of the code.
Pausing code execution: To observe variable values accurately, you may need to pause code execution (using breakpoints or stepping through the code). Resume code execution after observing the variables.
Watch expressions: You can watch not only single variables but also expressions.
Updating the Watch Window: The values in the Watch Window update when the code is paused only. If you want to see updated values during th execution, you need to manually pause the code.
Memory usage: Adding multiple variables or complex expressions to the Watch Window can increase memory usage and slow down the debugging process.
Watch Window Limitations: It can display a limited number of variables simultaneously.
Tracking object properties: You can expand the object’s properties in the Watch Window. However, not all object properties are readable or update in real-time.
Datasets: Large datasets can cause the Watch Window to slow down or become unresponsive.
Floating-point accuracy: Be aware of potential floating-point precision issues, especially when comparing or calculating double or single-precision floating-point variables.
Disable Watches: Once you have finished debugging, consider disabling or removing unnecessary watches.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the shortcut for the watch window in VBA?
CTRL + SHIFT + W.
Q2. How do I activate a window in VBA?
Use the Activate method of the window object:
WindowObject.Activate
Replace WindowObject with the name of the window you want to activate.
Q3. What is the watch window function in Excel?
The Watch Window is a debugging tool available in the Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) editor.
Download Practice Workbook
Download the following workbook.
<< Go Back to Auditing Formulas | Excel Formulas | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!


All is fairly well presented except for no mention of displaying Public Variables which are supposed to be active in ALL procedures and modules. I put a Public Variable in to display in all procedures and I get an ‘out of scope’ kind of report. I was hoping for a thorough explanation.
Hello Peter Clarke
Thanks for reaching out and sharing your problems and suggestions. You put a Public Variable to display in all procedures but got an “out of scope” report. You want a thorough explanation.
This issue could arise due to several reasons:
I have demonstrated watching a Public Variable in the Watch Window. I am using three modules: one for the public variable, one for displaying the public variable, and one for watching the public variable.
VBA Code in Module1:
VBA Code in Module2:
VBA Code in Module3:
OUTPUT Overview:
Hopefully, the idea will overcome your situation. Good luck.
Regards
Lutfor Rahman Shimanto
Excel & VBA Developer
ExcelDemy