Different Types of Workbook Related Events in Excel VBA
Excel has a number of different objects, including the application itself, workbooks, worksheets, charts, and so on. They can be classified into main six types.
- Event-related to Worksheet: These are the kinds of things that might happen as a result of the choices made in the workbook. These actions include things like double-clicking on a cell or right-clicking on a cell, altering the selection, etc.
- Events related to Workbook: Actions taken within a workbook would set in motion these occurrences. Creating a new worksheet, saving the workbook, opening the workbook, printing a selection or the complete workbook, etc. are all examples of such actions.
- Events related to Applications: This type of event deals with applications like closing a new application or switching/opening a new application.
- Events related to Userform: The user’s interactions with the ‘UserForm’ would set off these events. One such action is going to create a new UserForm or select a button on the UserForm.
- Events related to Chart: They are occurrences with relevance to the spreadsheet. One cannot compare a chart sheet to a spreadsheet. The goal of a chart sheet is to serve as a place to display a chart. Alterations to the chart’s series or size are two examples of such occurrences.
- OnTime and OnKey Events: There are two occurrences that can’t be classified as the ones listed above. We have provided the information in two distinct lists. In order to have some code run at a certain moment or after some elapsed time, you can use the “OnTime” event. The VBA OnKey Event lets you trigger code execution in response to the use of a single key or a sequence of keys.
List of Workbook Level Events in Excel VBA
| EVENT NAME | ACTION THAT EXECUTES THE EVENT |
|---|---|
| Activate | When the workbook is in the active state |
| AfterSave | After the workbook is in the active state |
| BeforeClose | When the workbook is in the active state, just before closing |
| BeforePrint | Just before printing any content of the workbook |
| BeforeSave | Just before the workbook is saved |
| Deactivate | When the workbook is not in the active state |
| NewSheet | When a new sheet is created in the workbook |
| Open* | When the workbook is in the open state |
| SheetActivate | When any sheet in the workbook is in an active state |
| SheetChange | When the user changes any worksheet |
| WindowActivate | When any window of the workbook is in an active state |
| WindowDeactivate | Any workbook window is in the active state |
Workbook_Open, Workbook_SheetActivate, Workbook_NewSheet, and Workbook_BeforeSave procedures have been in the ThisWorkbook code module.
Travel from one worksheet to another, save the workbook, create a new sheet and close the workbook. You will find the changes working under the scene.
Read More: Excel VBA Events
General Way of Adding Events in Workbook or Sheet
To add a VBA code that includes related events,
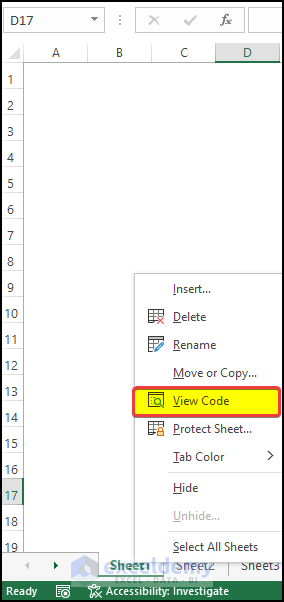
- Select the sheet where you want to enter the code.
- Right-click on the sheet and from the context menu, click on the View Code.
- An editor window will open. Enter your code included with the event attributes.
- Close the editor window.
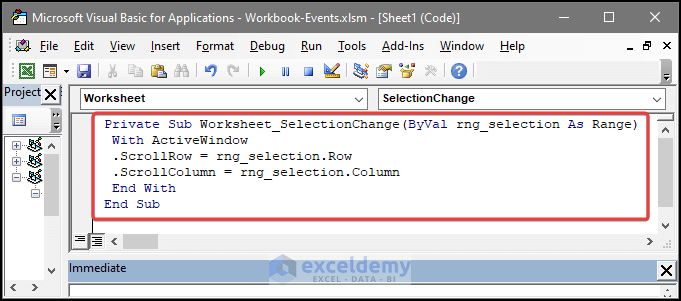
- After closing the editor window, you will notice that the sheet shows the exact function as instructed in the code.
13 Useful Workbook Level Events and Their Uses in Excel VBA
1. Workbook Event: Open
Open is one of the most important workbook events. This event executes when the workbook opens. The relevant procedure for this event is Workbook_Open.
You can design the Workbook_Open procedure to perform the following tasks:
- You can display a welcome message to the user.
- When a user is opening other workbooks.
- When a user is activating a specific sheet.
Caution
It does not give you confirmation that the Workbook_Open procedure will execute all the time. For two cases, the Workbook-Open procedure will not work:
- If the user makes the macros disabled.
- If the user holds the Shift key while opening a workbook.
We want to create a simple Workbook_Open procedure that will show a message box reminding the user to keep a file backup when it is Friday. If it is not Friday, nothing will show up.
Private Sub Workbook_Open()
If Weekday(Now) = 6 Then
Msg = "Today is Friday! Make sure you do your weekly Backup please!"
MsgBox Msg, vbInformation
End If
End SubA message box with some information or direction will pop up when you open your Excel file on Friday as shown in the image below:
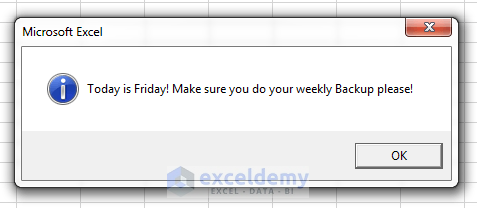
A message with some information popped up when I opened the Excel file on Friday.
You can do a series of actions when the workbook is in the open state. For example, we have made another VBA code to do the following jobs:
- It will maximize the workbook window.
- It will activate the worksheet DataEntry worksheet, if there is no sheet as DataEntry, there will an error.
- It will select the first empty cell in column A and enter the current date in this cell.
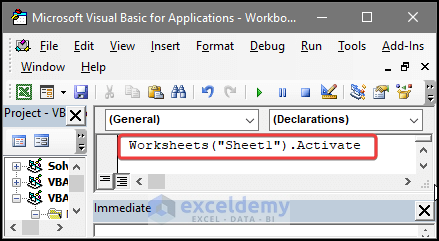
Private Sub Workbook_Open()
ActiveWindow.WindowState = xlMaximized
Worksheets(“DataEntry”).Activate
Range(“A1”).End(xlDown).offset(1,0).Select
ActiveCell.Value = Date
End SubRead More: Excel VBA Open Workbook Event
2. Workbook Event: SheetActivate
Workbook’s “SheetActivate” event executes when a user activates any worksheet in the workbook.
Whatever worksheet a user activates in the workbook, the following procedure will select cell B3. The “On Error Resume Next” statement makes the procedure to ignore the error that occurs if the activated sheet is a chart sheet.
Private Sub Workbook_SheetActivate(ByVal Sh As Object)
On Error Resume Next
Range("B3").Select
End SubThere is an alternative method to check whether the activated sheet is a worksheet or not. Use the following code:
Private Sub Workbook_SheetActivate(ByVal Sh As Object)
If TypeName(Sh) = "Worksheet" Then
Range("B3").Select
End Sub3. Workbook Event: NewSheet
The following procedure executes whenever a new sheet is new to the workbook.
The following NewSheet event procedure will check at first whether the new sheet is a worksheet or a chart sheet, if the new sheet is a worksheet, this procedure will insert the date and time stamp into cell A1.
Private Sub Workbook_NewSheet(ByVal Sh As Object)
If TypeName(Sh) = "Worksheet" Then
Range("A1") = "This Sheet added @ " & Now()
End If
End Sub4. Workbook Event: BeforeSave
The BeforeSave workbook event occurs before the User actually saves the workbook. We save Excel files by choosing the File ➪ Save command; this command displays the Save As dialog box. When the file is going to be in a save condition for the first time or the user only opens in read-only mode.
The Workbook_BeforeSave procedure has two arguments: SaveAsUI and Cancel. Both are Boolean-type arguments. See the following code:
Private Sub Workbook_BeforeSave(ByVal SaveAsUI As Boolean, Cancel As Boolean)
If SaveAsUI Then
MsgBox "Use the new file-naming convention to save your file."
End If
End SubWhen the save operation brings up the Save As dialog box, the SaveAsUI variable is TRUE and a message box with the information “Use the new file-naming convention to save your file.” is displayed.
The BeforeSave event procedure also has another argument named Cancel. By default, its value is FALSE. If the procedure sets this argument in such a way that it may be TRUE, the file is not saved.
5. Workbook Event: BeforeClose
The BeforeClose event occurs before a workbook is closed. You may use this event in conjunction with a Workbook_Open event handler.
For example, you may want to initialize some items in your workbook when the workbook is opened using the Workbook_Open procedure and clean up that initialization when you close the workbook using the Workbook_BeforeClose procedure.
If you try to close a workbook that hasn’t been saved yet, Excel displays a prompt that asks whether you want to save the workbook before it closes.
6. Workbook Event: Activate
The purpose of this event is to activate certain workbooks and execute certain tasks on the worksheet when they are activated. This code will automatically be generated when you activate a certain sheet.
Syntax
expression.Activate
Return:
Returns nothing specifically.
The code below will run when this certain sheet is selected, and will run the task below
Private Sub Workbook_SheetActivate(ByVal Sh As Object)
On Error Resume Next
Range("B3").Select
End SubThis code will execute whenever the workbook is activated by any means like manually activated or through any other kind of macro or VBA.
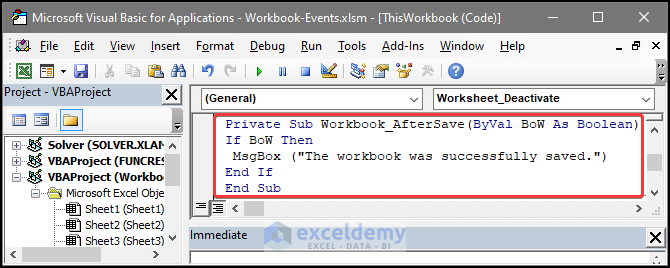
7. Workbook Event: AfterSave
This event can execute a certain task or warning message after the file is saved. This event can be used as a hint whether the file is actually saved or not.
In the image below, the event will execute a message box displaying “The workbook was successfully saved.” after the file is saved through manual input or by other means.
Private Sub Workbook_AfterSave(ByVal BoW As Boolean)
If BoW Then
MsgBox ("The workbook was successfully saved.")
End If
End Sub8. Workbook Event: BeforePrint
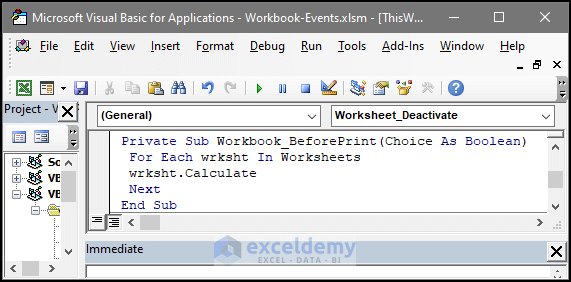
This event enables the user to execute certain tasks before they print. It depends on the parameter, whether it is Cancel or True. If it is true, then the code will not print the page after it the event executes. To continue printing, you need to set the parameter to Cancel.
In the image below, we have a before the print event, where Cancel is set to be the parameter. This worksheet will return the number of worksheets before printing.
Private Sub Workbook_BeforePrint(Cancel As Boolean)
For Each wrksht In Worksheets
wrksht.Calculate
Next
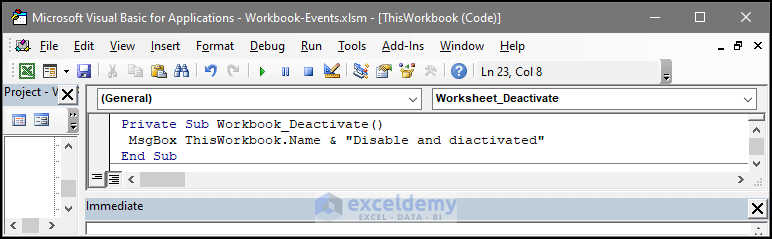
End Sub9. Workbook Event: Deactivate
This event will deactivate the workbook and complete tasks assigned in the event after the deactivation. The deactivation of the workbook will trigger when any of the following happens.
- If the user switches from an Excel application to another application like MS PowerPoint. If the user closes the workbook.
- Below we have a VBA code contains with the deactivate event. If the file is deactivated, then there will be a message box stating that “Disable and deactivated“.
Private Sub Workbook_Deactivate()
MsgBox ThisWorkbook.Name & "Disable and diactivated"
End Sub
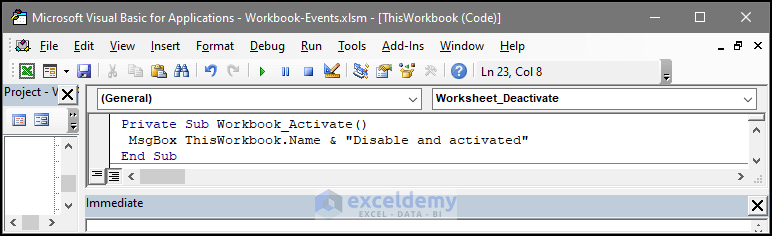
10. Workbook Event: Activate
In this workbook, the task executes after the workbook is in an active state. Two main reasons why a workbook can be deactivated are whether the user switch to another app or user closes Excel completely. In the same way, if the user wishes to switch back to the workbook, the workbook will open and activate once again. Each time the workbook is in an active state, the task with the event will also execute.
Below we have a VBA code containing the event. If the user reactivates the sheet, there will be a message welcoming the user with the workbook name and “Disable and activated”. Users can choose the task of their choice.
Private Sub Workbook_Activate()
MsgBox ThisWorkbook.Name & "Disable and activated"
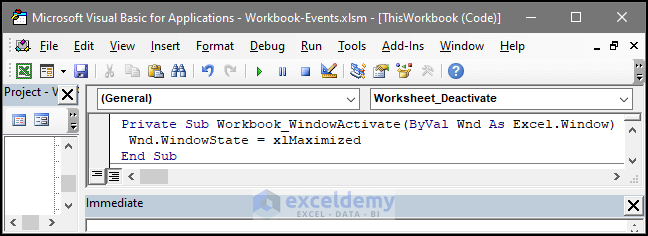
End Sub11. Workbook Event: WindowActivate
This event helps the user execute tasks after certain windows get activated. The window can be activated if the user previously switched to another sheet or workbook, and reactivate the window again.
The VBA code below contains the window activate event. If the user reactivates the window, the window will get a maximum.
Private Sub Workbook_WindowActivate(ByVal Wnd As Workbook. ByVal wndw as Window)
Wndw.WindowState = xlMaximized
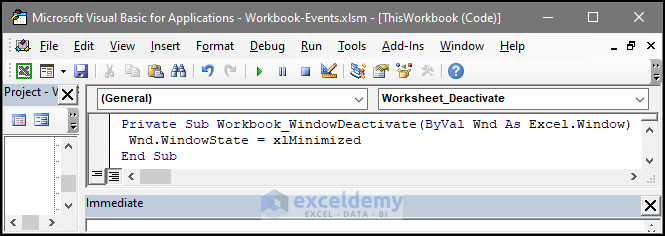
End Sub12. Workbook Event: WindowDeactivate
This event helps the user execute tasks after certain windows are in a reactive state. The window can be deactivated if the user switched to another sheet or workbook, or even close the workbook.
- The VBA code below contains the window activate event. If the user deactivates an active window, the window will get minimized and then go into a reactive state.
Private Sub Workbook_WindowDeactivate(ByVal Wnd As Excel.Window)
Wnd.WindowState = xlMinimized
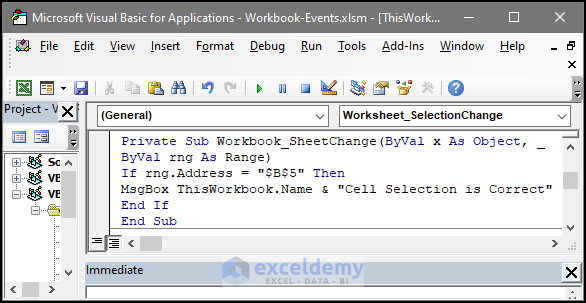
End Sub13. Worksheet Event: SheetChange
This event will allow the user to run certain tasks after any kind of change in the worksheet.
The code below contains the event sheetchange inside of it. If there is any change in the worksheet like value or format change, then the code will run the next task assigned to it.
The task here is that will check if there is any change in change in the worksheet, and then it will check the select cell address. If the address is $B$5, it will display a message box stating the workbook name and the “Cell Selection is Correct”
Private Sub Workbook_SheetChange(ByVal x As Object, _
ByVal rng As Range)
If rng.Address = "$B$5" Then
MsgBox ThisWorkbook.Name & "Cell Selection is Correct"
End If
End SubWhat to Do If Open Event Not Working in Excel?
- Make sure the Open event is inside the ThisWorkbok module, not inside another module from another workbook or class or sheet.
- “Application.EnableEvents = False” this event actually shuts all event activity in the workbook. Make sure that this is not before in the workbook
- Another reason could be that the macros are not enabled to run in the worksheet. To check this, Head to the Trust center and check for the macros integration, whether or not it is in a disabled state. If it is in disable condition, turn it on to allow the Open Event to work independently.