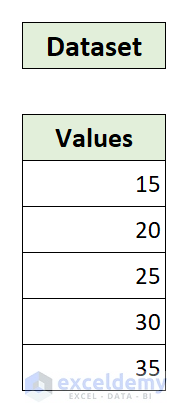
We will show you step-by-step instructions on applying a loop for each cell in a range using Excel VBA with a simple example. Look at this dataset below, which has some values in a column. We aim to loop through all of them and add five with each value.
Step 1: Open the VBA Editor in Excel
- Press Alt+F11. Select Insert > Module.
Step 2: Build the Code
- Enter the following code in the editor:
Sub add_five()
Dim cell As Range
For Each cell In Range("B5:B9")
cell.Value = cell.Value + 5
Next cell
End SubStep 3: Run the Code
- Press Alt+F8.
- Select add_five.
- Click Run. You will see this output:
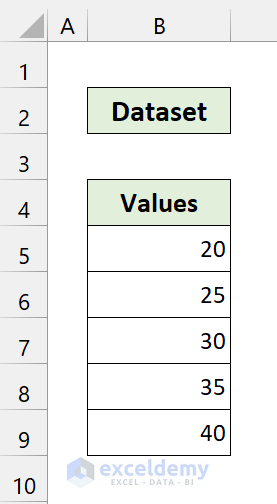
We have successfully added five with each of those numbers.
Breakdown of the Code
For each cell in Range(“B5:B9”): Here, our working range was B5 to B9.
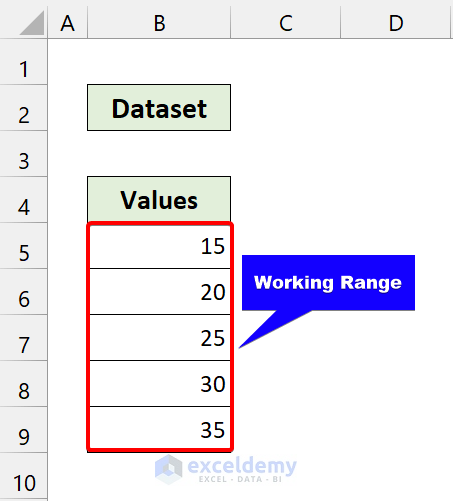
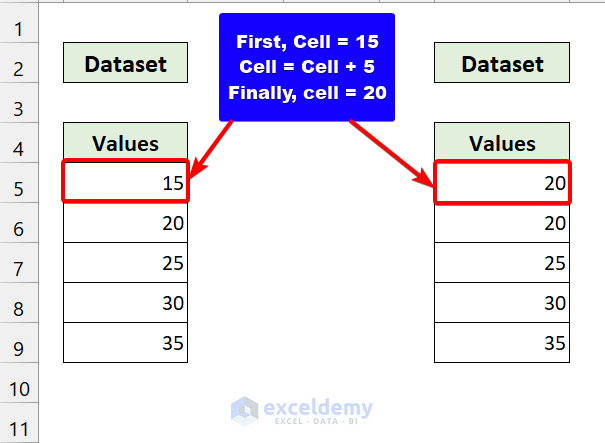
From that loop, our cell variable will point to cell B5.
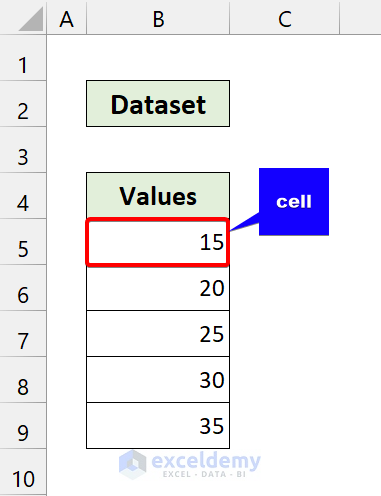
It will add 5 with the cell value and update it.
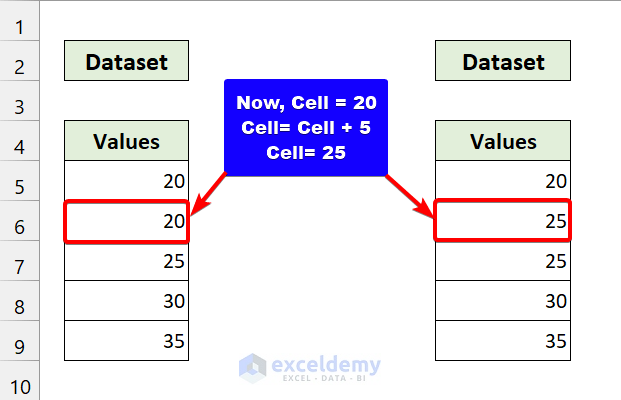
The cell variable will point to cell B6.
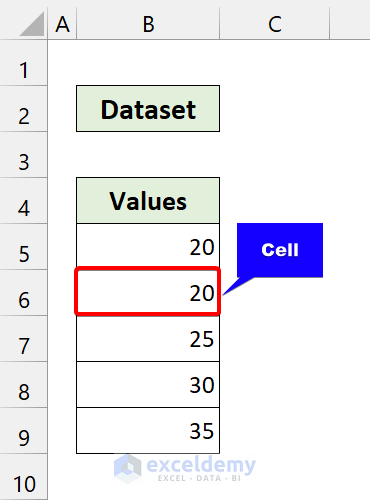
Similar to the previous steps, it will add five with the cell value and update it.
All the cells will go through this process, and the code will add five for each.
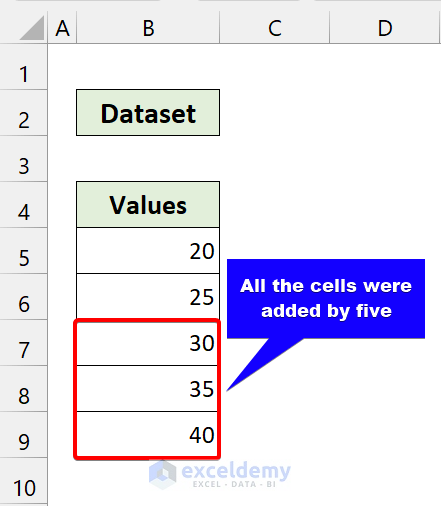
We successfully updated all the values using the “for each cell in range” loop.
Method 1 – Looping through an Entire Row
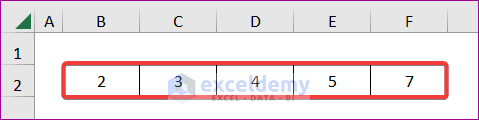
- If you don’t want to select a particular range but the entire row, enter the following code:
Sub entire_row()
Dim cell As Range
For Each cell In Range("2:2")
cell.Value = cell.Value * 5
Next cell
End SubIt will multiply each cell of row 2 with the value 5.
It will look like the following screenshot:
Read More: How to Use VBA for Each Row in a Range in Excel
Method 2 – Looping through an Entire Column
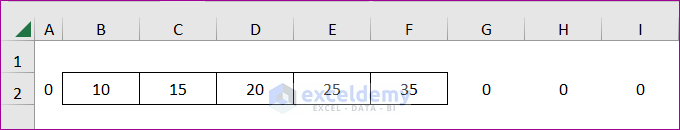
- If you want to loop through an entire column and perform something, enter the following code:
Sub entire_column()
Dim cell As Range
For Each cell In Range("B:B")
cell.Value = cell.Value * 5
Next cell
End SubIt will multiply each cell of column B with the value 5. After that, it will look like the following screenshot:
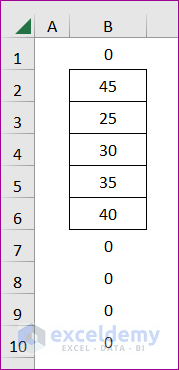
Method 3 – Looping through a User-selected Range in Excel
Steps:
- If you don’t want to specify the range of cells but choose with your mouse, enter the following code:
Sub user_selected()
Dim cell As Range
Set range_of_cells = Selection
For Each cell In range_of_cells
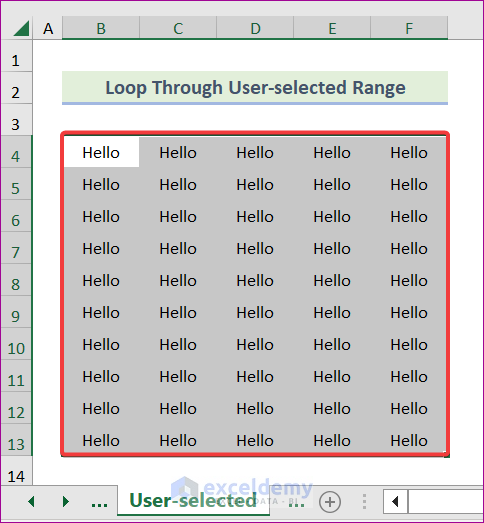
cell.Value = "Hello"
Next cell
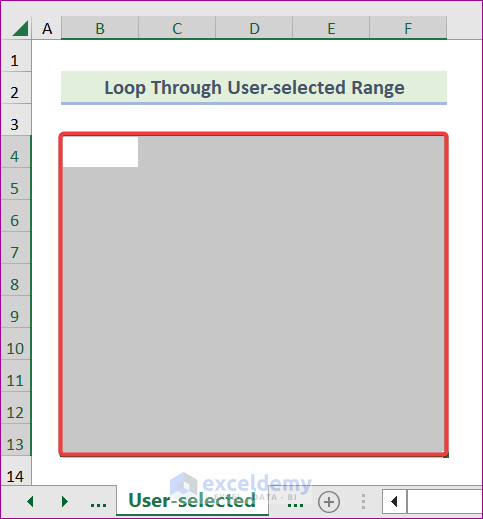
End SubThis code sets the cell’s value to “Hello”. Notice here that we didn’t specify any range of cells. Instead, we used Selection. It will perform this operation on a user-selected range. You can understand it by the following screenshot.
- Select a range of cells:
- Apply the macro. You will see the output.
Method 4 – Looping through an Array For Each Range
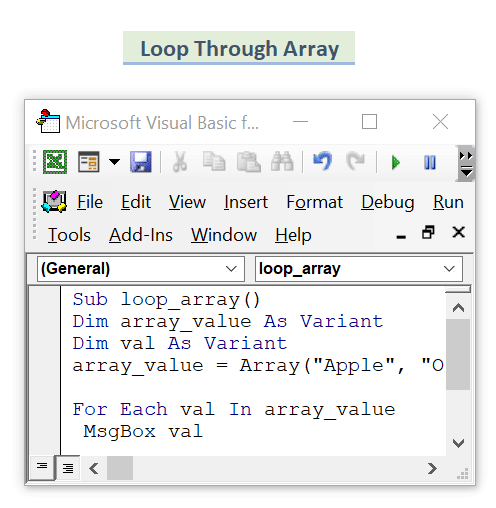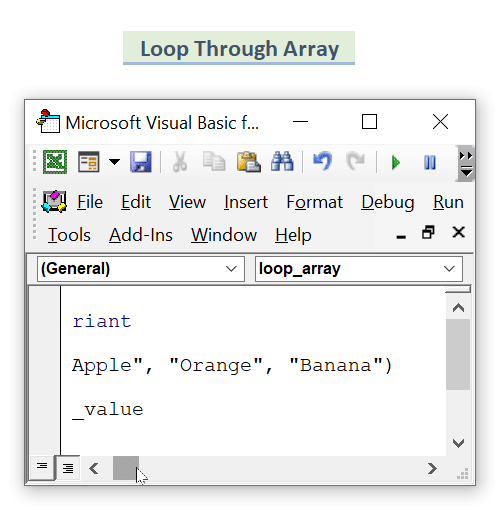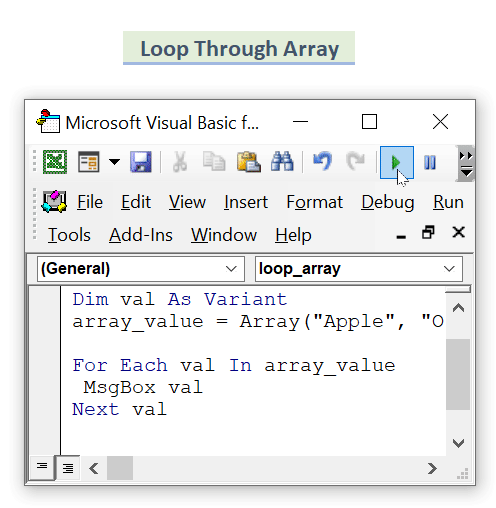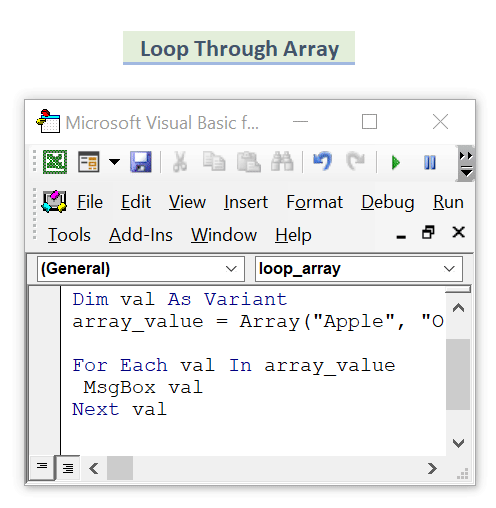
- If you have an array consisting of multiple items in it, enter this code to apply any kind of task:
Sub loop_array()
Dim array_value As Variant
Dim val As Variant
array_value = Array("Apple", "Orange", "Banana")
For Each val In array_value
MsgBox val
Next val
End SubHere, we have some values in an array. We take them in for each loop and show them in a message box in Excel.
Method 5 – Sheets as a Range in VBA
You can also select sheets as a range in VBA. We can perform operations across multiple sheets.
Sub loop_sheets()
Dim sheet As Worksheet
For Each sheet In Sheets
sheet.Visible = True
Next sheet
End SubThis code snippet will unhide all the sheets in a workbook.
Method 6 – Using Workbooks for Each Loop
The following code snippet will take workbooks as a range and close all the workbook at once.
Sub loop_workbooks()
Dim wBook As Workbook
For Each wBook In Workbooks
wBook.Close
Next wBook
End SubRead More: How to Use For Each Loop in Excel VBA
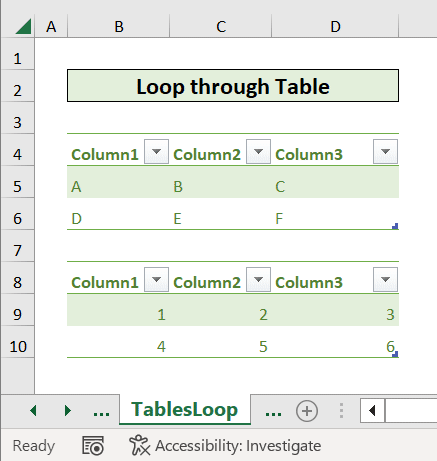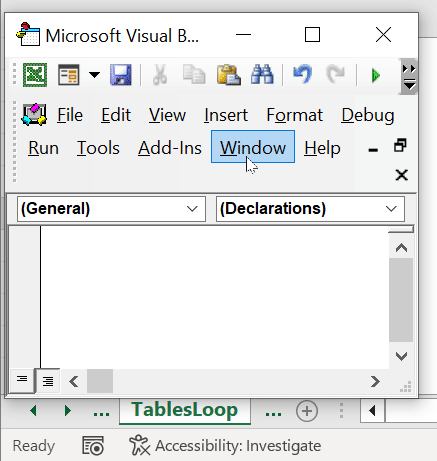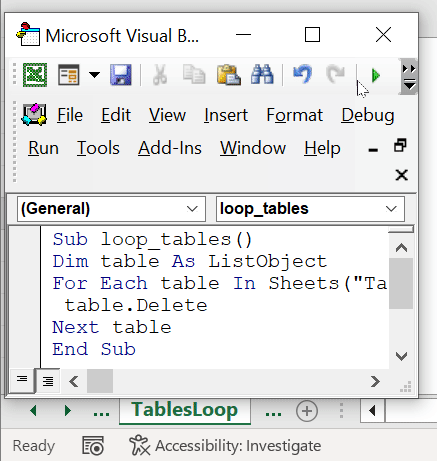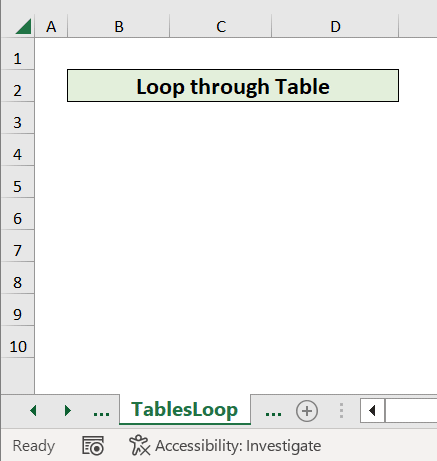
Method 7 – Looping through a Table in Excel
- Select tables as a range in our VBA codes.
Sub loop_tables()
Dim table As ListObject
For Each table In Sheets("Table").ListObjects
table.Delete
Next table
End Sub- This VBA code will take the table as a range from the sheet “Table” and delete it.
Method 8 – Using Conditions for Each Cell in Range with VBA
If you have an idea about the If condition in Excel, you mix it up with the for each loop. This is one of the important tasks in VBA. The following sample will give a clear idea about that:
Sub loop_if()
Dim cell As Range
For Each cell In Range("C5:C9")
If cell.Value < 33 Then
cell.Offset(o, 1).Value = "Failed"
Else
cell.Offset(0, 1).Value = "Passed"
End If
Next cell
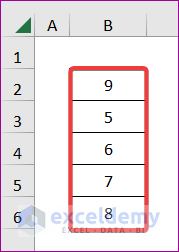
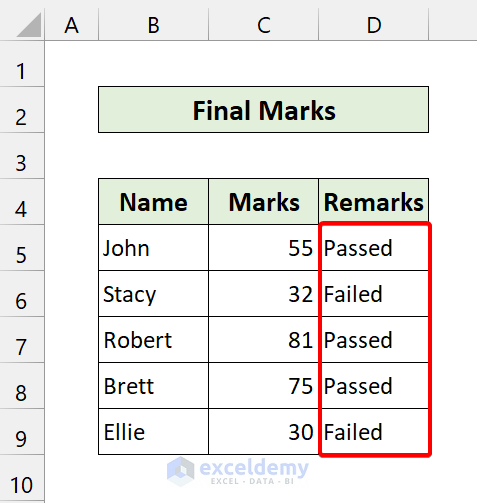
End Sub- Apply this code to the following dataset:
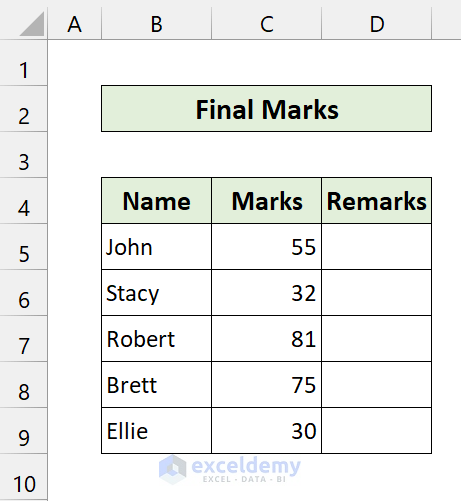
Here, we have a dataset of some students’ marks. Our goal is to analyze their marks and give a remark on whether they passed or failed. If someone scores more than 32, he/she gets passing marks. Otherwise, it will consider the marks as failed.
If we run the code, we will get the following result:
Read More: How to Use VBA for Each Cell in Range in Excel
Things to Remember
✎ Performing any operations throughout the whole columns or rows will change the whole columns/rows output.
✎ Your loop variable should be the same type as the Range type you selected. If your range type is Worksheets, your loop variable should be Worksheet type.
Download the Practice Workbook
Download this workbook to practice.


