Step 1 – Prepare Your Dataset
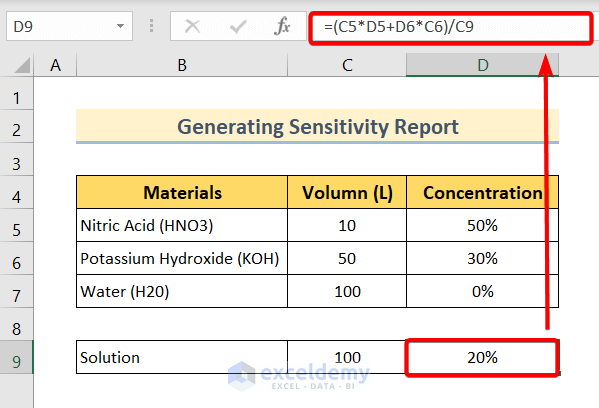
Suppose we want to make of solution of Nitric Acid, Potassium Hydroxide and Water. Our target volume of the solution is 100L with 20% concentration.
For example, we have the following materials:
- Nitric Acid (HNO3): Volume 10L with 50%
- Potassium Hydroxide (KOH): Volume 50L with 30%
- Water (H20): Volume 100L with 0%
Enter the following formula in cell D9.
=(C5*D5+D6*C6)/C9In this formula,
- C5 is the total volume of Nitric Acid.
- D5 is the concentration of Nitric Acid.
- C6 is the total volume of Potassium Hydroxide.
- D6 is the concentration of Potassium Hydroxide.
- And C9 is the target volume of the final solution.
This formula will return a 20% concentration of the final solution.
Step 2 – Set Solver Parameters
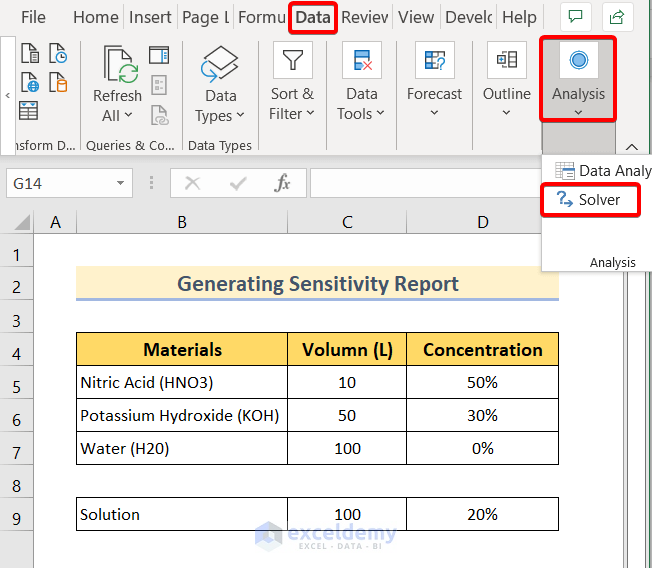
❶ Go to the Data tab first.
❷ Click on the Solver command in the Analysis group.
The Solver Parameters window will open.
❸ In the Set Objective box, insert the cell address of the target concentration of the solution which is cell $D$9.
❹ Select the ‘value of’ option and set the value as 0.2 which refers to the final concentration of 20%.
❺ In the ‘By Changing Variable Cells’ box, insert the cell range of the volume of the materials which is $C$5:$C$7.
❻ Click on the Add button to add constraints in the ‘Subject to the Constraints’ box.
We have used two constraints which are:
$C$5 <= 10$C$9 = 100The first constraint suggest that the volume of Nitric Acid can be less than or equal to 10L in the final solution.
The second constraint suggest that the volume of the final solution will be 100L.
❼ Press the Solve button.
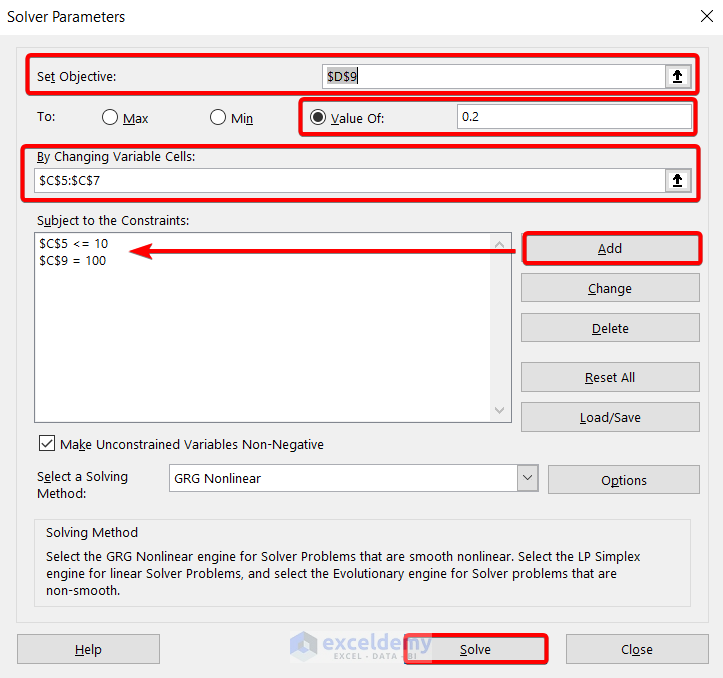
Note: You can choose a solving method from the Select a Solving Method drop-down field. We’ve kept GRG Nonlinear selected, you may need a different method for your scenario.
Read More: How to Do Sensitivity Analysis in Excel
Step 4 – Generate Sensitivity Report
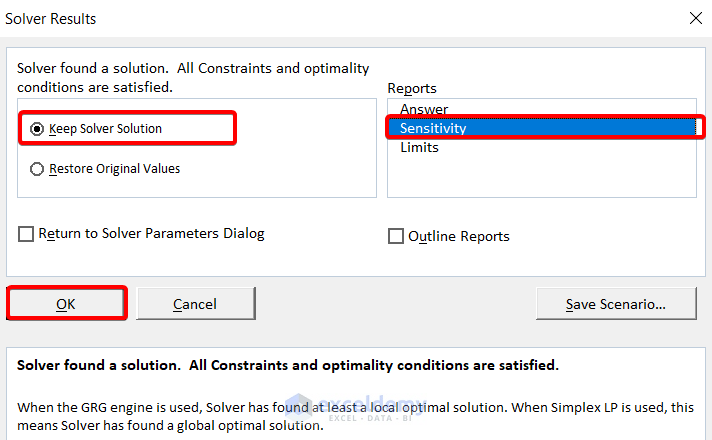
❶ Select the ‘Keep Solver Solution’ option in the left column of the Solver Results dialog box.
❷ Choose Sensitivity in the Reports section.
❸ Click the OK button.
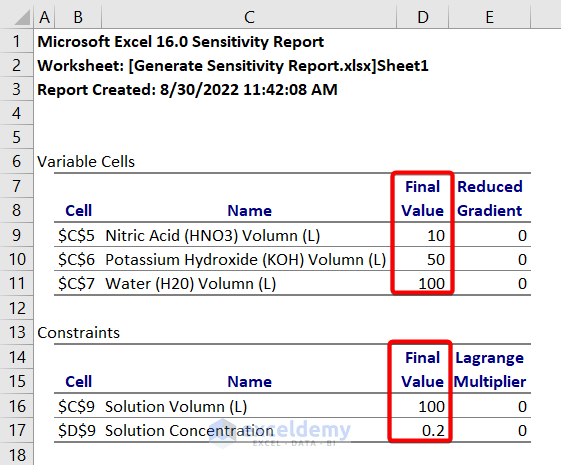
The sensitivity report will be automatically generated.
In this report,
You can see the names, corresponding cells, final values of the variable cells and constraints.
From this report, we can say that 10L Nitric Acid, 50L Potassium Hydroxide and 100L Water are used to make the final solution of 100L with 20% concentration.
The Lagrange Multiplier determines the sensitivity level of the constrained objective to any input changes.
Read More: How to Build a Sensitivity Analysis Table in Excel
Download Practice Workbook
Related Articles
- Sensitivity Analysis for NPV in Excel
- How to Do IRR Sensitivity Analysis in Excel
- How to Perform Sensitivity Analysis for Capital Budgeting in Excel
- How to Use What If Analysis in Excel
- What-If Analysis in Excel with Example
- What If Analysis Data Table Not Working
- How to Delete What If Analysis in Excel
<< Go Back to What-If Analysis in Excel | Learn Excel
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!

