In this article, we will discuss 14 different methods to hide rows in Excel based on different criteria utilizing the VBA macro.
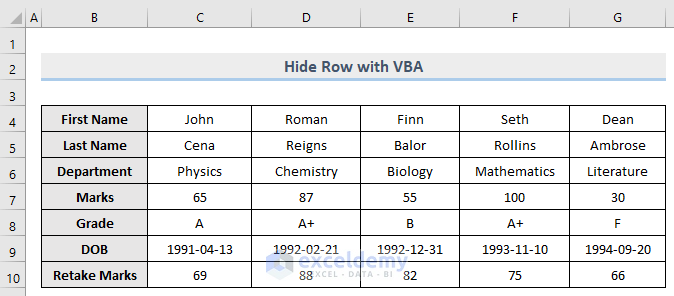
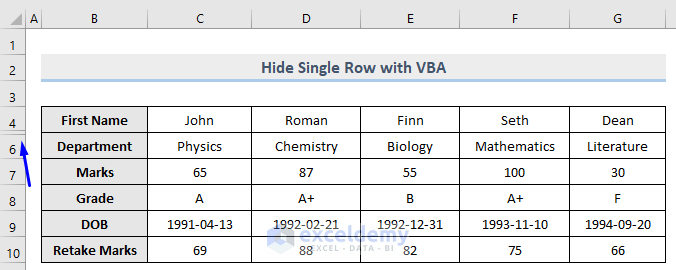
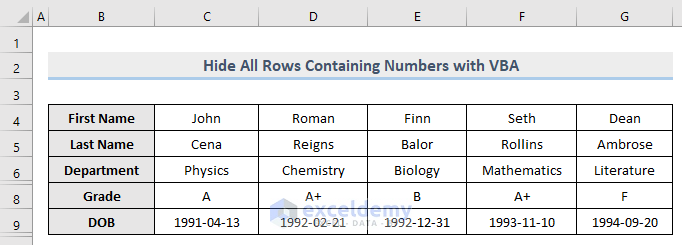
The sample dataset that we will be using is shown below.
Method 1 – Using a VBA Macro to Hide a Single Row
Let’s hide row 5 (Last Name) from our dataset.
Steps:
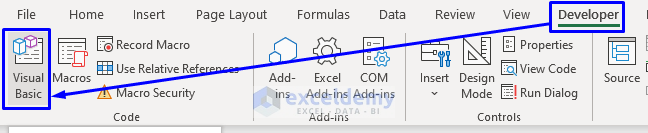
- Press Alt + F11 on your keyboard or go to the tab Developer -> Visual Basic to open Visual Basic Editor.
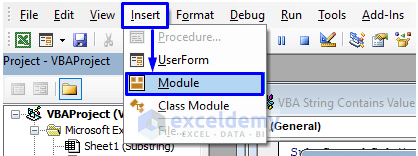
- In the pop-up code window, from the menu bar, click Insert -> Module.
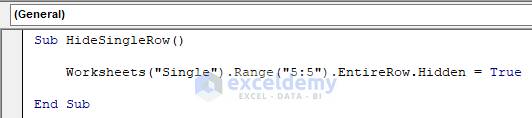
- Copy the following code and paste it into the code window:
Sub HideSingleRow()
Worksheets("Single").Range("5:5").EntireRow.Hidden = True
End SubThe code is now ready to run.
Here,
- Worksheets(“Single”) = Set the worksheet name.
- Range(“5:5”) = Pass row number 5 inside the Range method.
- Either press F5 on your keyboard; from the menu bar select Run -> Run Sub/UserForm; or just click on the small Play icon in the sub-menu bar to run the macro.
Row 5 is hidden after executing the VBA code.
Method 2 – Using a VBA Macro to Hide Contiguous Rows
Let’s hide rows 5 to 7 from our dataset.
Steps:
- Same way as before, open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
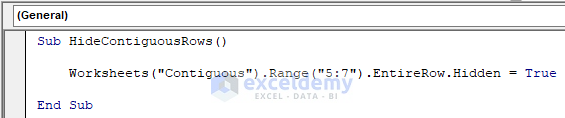
- Copy the following code and paste it in the code window:
Sub HideContiguousRows()
Worksheets("Contiguous").Range("5:7").EntireRow.Hidden = True
End SubThe code is now ready to run.
Here,
- Worksheets(“Contiguous”) = Set the worksheet name.
- Range(“5:7”) = Pass row number 5 to 7 inside the Range method.
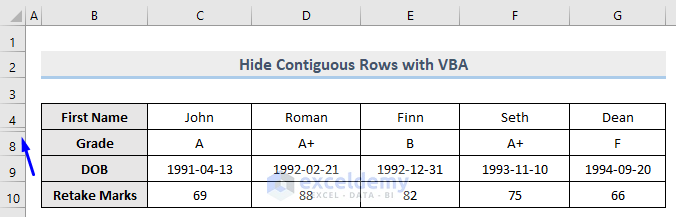
- Run this code.
Rows 5 to 7 are hidden now.
Read More: How to Hide the Same Rows Across Multiple Excel Worksheets
Method 3 – Using a VBA Macro to Hide Non-Contiguous Rows
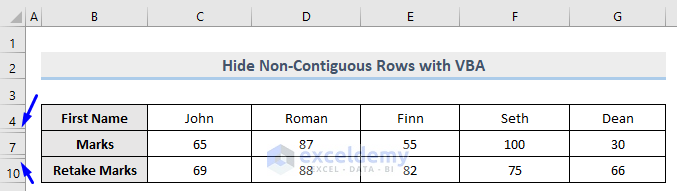
Let’s hide the non-contiguous rows 5, 6, 8 and 9.
Steps:
- As previously shown, open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- In the code window, copy the following code and paste it:
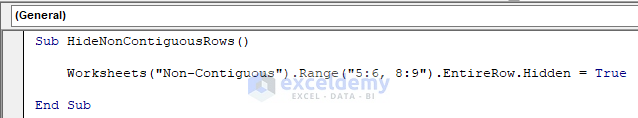
Sub HideNonContiguousRows()
Worksheets("Non-Contiguous").Range("5:6, 8:9").EntireRow.Hidden = True
End SubThe code is now ready to run.
Here,
- Worksheets(“Non-Contiguous”) = Set the worksheet name.
- Range(“5:6, 8:9”) = Pass rows 5 to 6 and 8 to 9 inside the Range method.
- Run the code.
Rows 5 to 6 and 8 to 9 are hidden.
Method 4 – Using a VBA Macro to Hide All Rows Containing Text
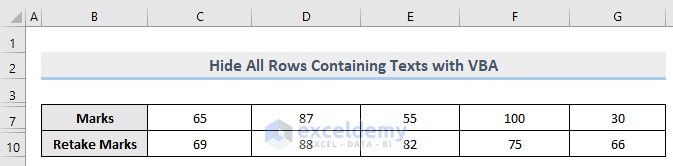
We can hide all rows that contain text values.
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- In the code window, copy the following code and paste it:
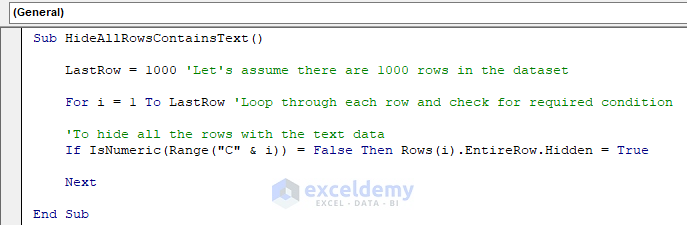
Sub HideAllRowsContainsText()
LastRow = 1000 'Let's assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset
For i = 1 To LastRow 'Loop through each row and check for required condition
'To hide all the rows with the text data
If IsNumeric(Range("C" & i)) = False Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
Next
End SubThe code is now ready to run.
Here,
- IsNumeric(Range(“C” & i)) = The data in our dataset starts from column C, so we passed C inside the Range method.
- Run this code.
All the rows containing text values are now hidden.
Read More: How to Hide Rows Based on Cell Value in Excel
Method 5 – Using VBA to Hide All Rows Containing Numbers
It’s a similar process to hide all rows containing numeric values with VBA code.
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- In the code window, copy the following code and paste it:
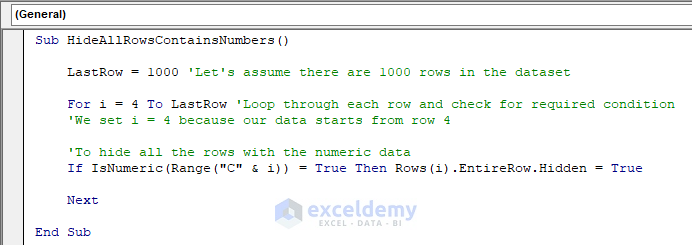
Sub HideAllRowsContainsNumbers()
LastRow = 1000 'Let's assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset
For i = 4 To LastRow 'Loop through each row and check for required condition
'We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4
'To hide all the rows with the numeric data
If IsNumeric(Range("C" & i)) = True Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
Next
End SubThe code is now ready to run.
Here,
- IsNumeric(Range(“C” & i)) = The data in our dataset starts from column C, so we passed C inside the Range method.
- Run the code.
All the rows containing numeric values are now hidden.
Read More: VBA to Hide Rows Based on Criteria in Excel
Method 6 – Using a VBA Macro to Hide Rows Containing Zero (0)
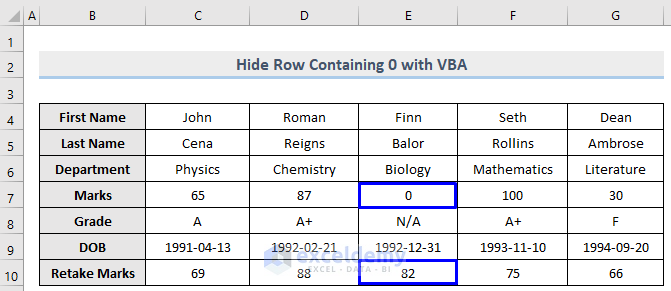
Extending the previous Method, we can hide rows that contain a specific numeric value only. Let’s hide only the row that contains a 0 (row 7).
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- In the code window, copy the following code and paste it:
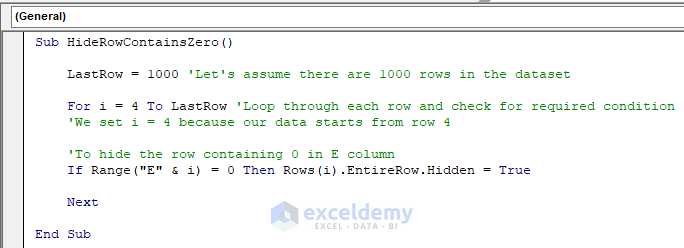
Sub HideRowContainsZero()
LastRow = 1000 'Let's assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset
For i = 4 To LastRow 'Loop through each row and check for required condition
'We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4
'To hide the row containing 0 in E column
If Range("E" & i) = 0 Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
Next
End SubThe code is now ready to run.
- Run this code.
The row (7) that contains 0 in column E is now hidden, whereas row 10 that is carrying 82 is unhidden.
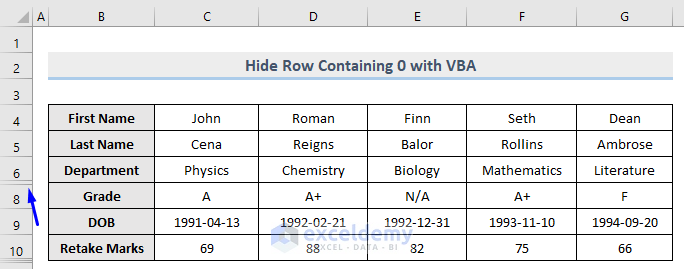
Read More: How to Automatically Hide Rows with Zero Values in Excel
Method 7 – Using a Macro to Hide Rows Holding Negative Values
Just as we can hide rows that contain zero from the same column, we can hide rows that hold negative values too. In column E which contains both negative and positive values, let’s hide only the row with the negative value.
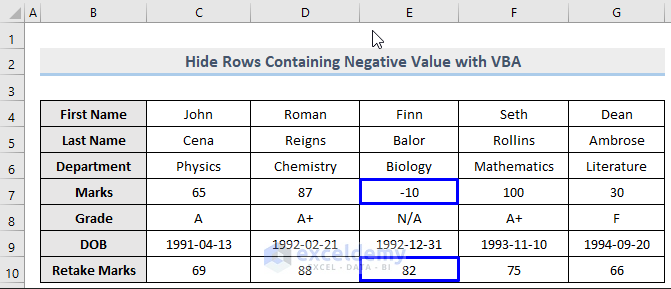
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- In the code window, copy the following code and paste it:
Sub HideRowContainsNegative()
LastRow = 1000 'Let's assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset
For i = 4 To LastRow 'Loop through each row and check for required condition
'We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4
'To hide the row containing negative values in E column
If IsNumeric(Range("E" & i)) = True Then
If Range("E" & i) < 0 Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
Next
End SubThe code is now ready to run.
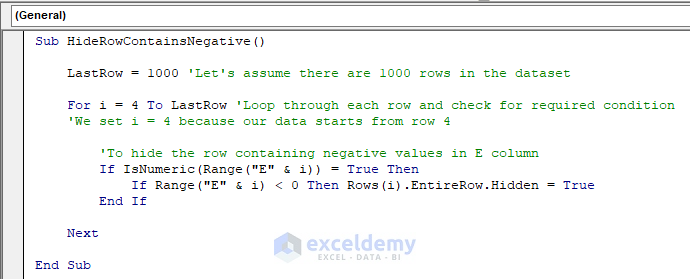
- Run the code.
Row 7 which contains a negative value (-10) in column E is now hidden, whereas row 10 that is holding the positive number 82 remains unhidden.
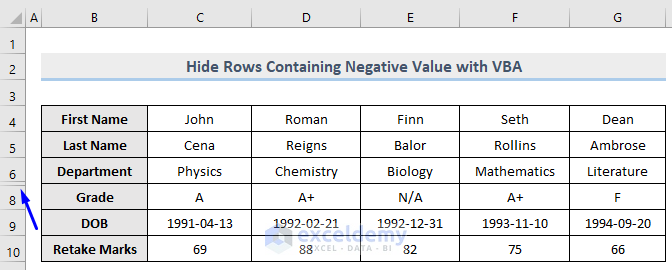
Read More: VBA to Hide Rows Based on Cell Value in Excel
Method 8 – Using VBA to Conceal Rows Containing Positive Values
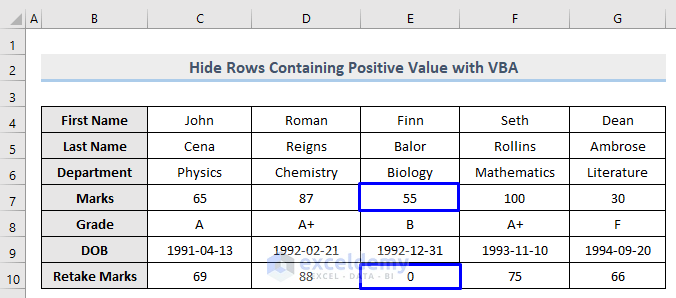
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- In the code window, copy the following code and paste it:
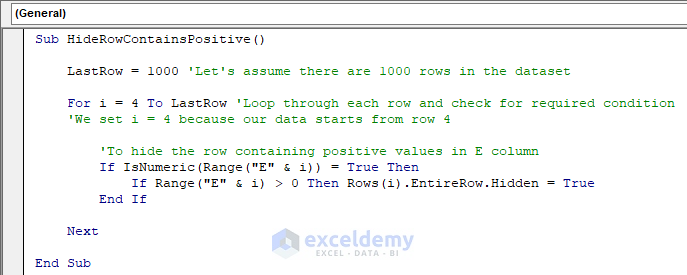
Sub HideRowContainsPositive()
LastRow = 1000 'Let's assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset
For i = 4 To LastRow 'Loop through each row and check for required condition
'We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4
'To hide the row containing positive values in E column
If IsNumeric(Range("E" & i)) = True Then
If Range("E" & i) > 0 Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
Next
End SubThe code is now ready to run.
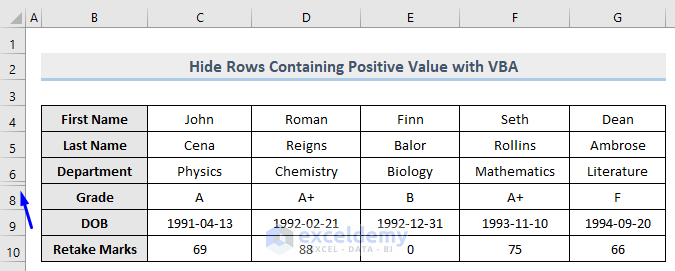
- Run the code
Row 7 which contains a positive value (55) in column E is now hidden, whereas row 10 which carries 0 remains unhidden.
Method 9 – Using a Macro to Hide Rows that Contain Odd Numbers
Column E holds both odd and even numbers in rows 7 and 10. Let’s hide the row that holds odd numbers only.
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- In the code window, copy the following code and paste it:
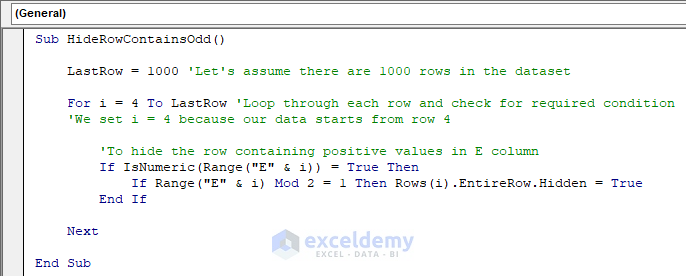
Sub HideRowContainsOdd()
LastRow = 1000 'Let's assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset
For i = 4 To LastRow 'Loop through each row and check for required condition
'We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4
'To hide the row containing positive values in E column
If IsNumeric(Range("E" & i)) = True Then
If Range("E" & i) Mod 2 = 1 Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
Next
End SubThe code is now ready to run.
- Run the code.
Row 7 which contains an odd number (55) in column E is now hidden whereas row 10 that is holding an even number (82) remains unhidden.
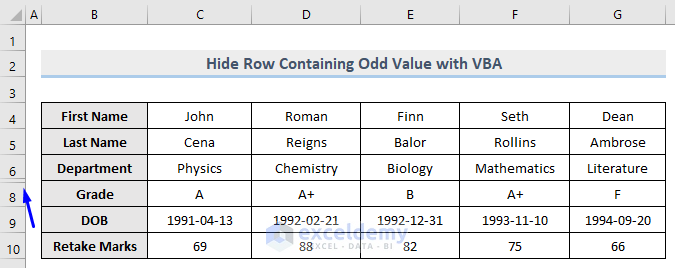
Method 10 – Using VBA to Hide Rows Containing Even Numbers
It’s an almost identical process to the previous Method to hide even numbers instead.
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- In the code window, copy the following code and paste it:
Sub HideRowContainsEven()
LastRow = 1000 'Let's assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset
For i = 4 To LastRow 'Loop through each row and check for required condition
'We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4
'To hide the row containing positive values in F column
If IsNumeric(Range("F" & i)) = True Then
If Range("F" & i) Mod 2 = 0 Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
Next
End SubThe code is now ready to run.
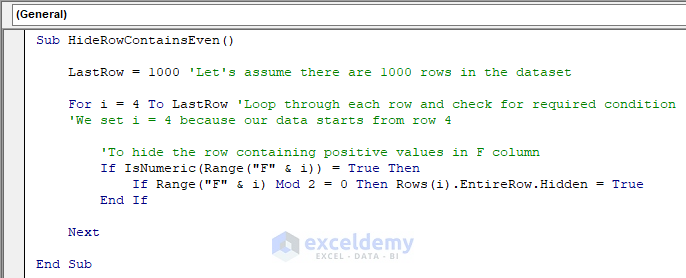
- Run this code.
Row 7 which contains an even number (100) in column F is now hidden, whereas row 10 that is holding an odd number (75) remains unhidden.
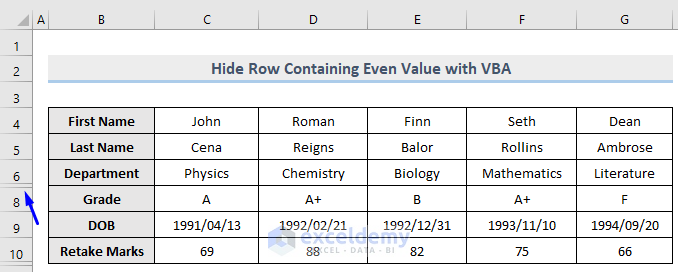
Method 11 – Using a Macro to Hide Rows that Are Greater Than a Specific Condition
Let’s hide the rows in column E where the value is greater than 80.
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- In the code window, copy the following code and paste it:
Sub HideRowContainsGreater()
LastRow = 1000 'Let's assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset
For i = 4 To LastRow 'Loop through each row and check for required condition
'We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4
'To hide the row containing positive values in E column
If IsNumeric(Range("E" & i)) = True Then
If Range("E" & i) > 80 Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
Next
End SubThe code is now ready to run.
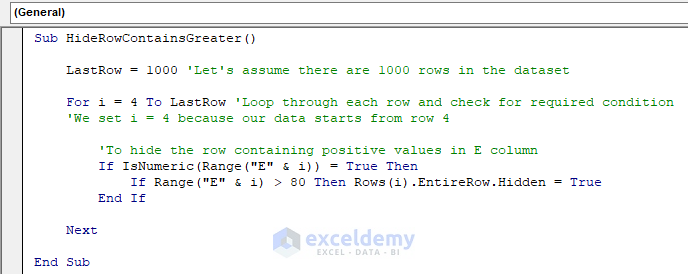
- Run the code.
Only row 10 which contains 82 (greater than 80) in column E is now hidden, whereas row 7 that is holding 55 remains unhidden.
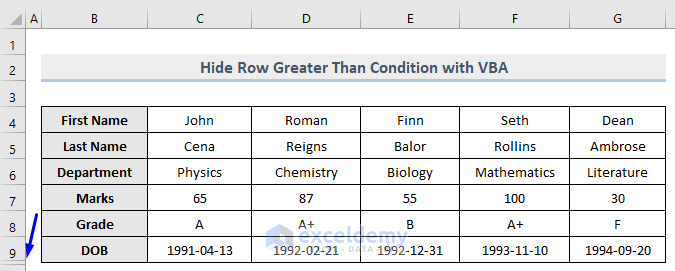
Method 12 – Using a Macro to Hide Rows that Are Less Than a Specific Condition
Now let’s hide the rows from column E where the value is less than 80.
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- In the code window, copy the following code and paste it:
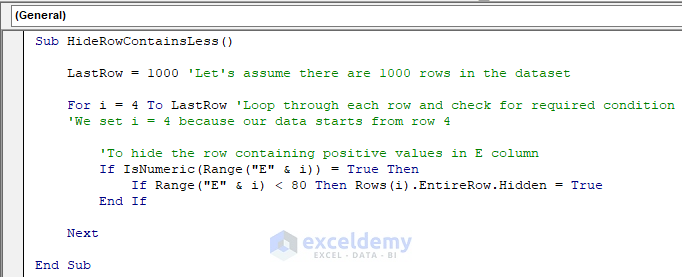
Sub HideRowContainsLess()
LastRow = 1000 'Let's assume there are 1000 rows in the dataset
For i = 4 To LastRow 'Loop through each row and check for required condition
'We set i = 4 because our data starts from row 4
'To hide the row containing positive values in E column
If IsNumeric(Range("E" & i)) = True Then
If Range("E" & i) < 80 Then Rows(i).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
Next
End SubThe code is now ready to run.
- Run this code.
- Only row 7 which contains 55 (less than 80) in column E is now hidden, whereas row 10 which carries 82 remains unhidden.
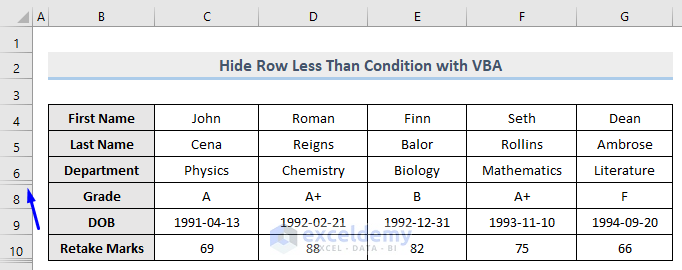
Method 13 – Using a Macro to Hide Rows Based on Cell Text Value
Suppose you want to hide a row that holds a specific text value. Let’s hide the row that contains the word Chemistry (row 6).
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- In the code window, copy the following code and paste it:
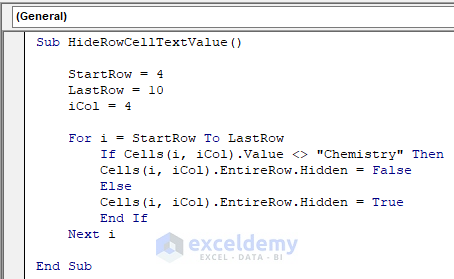
Sub HideRowCellTextValue()
StartRow = 4
LastRow = 10
iCol = 4
For i = StartRow To LastRow
If Cells(i, iCol).Value <> "Chemistry" Then
Cells(i, iCol).EntireRow.Hidden = False
Else
Cells(i, iCol).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
Next i
End SubThe code is now ready to run.
Here,
- StartRow = 4 -> First row of the dataset.
- LastRow = 10 -> Last row of the dataset.
- iCol = 4 -> The column address that holds the text value.
- Run this code.
Row 6 which contains the word Chemistry is hidden.
Method 14 – Using a Macro to Hide Rows Based on Cell Numeric Value
It’s a very similar process to hide a row containing a numeric value. Let’s hide the row that contains the numeric value “87”, row 7.
Steps:
- Open Visual Basic Editor from the Developer tab and Insert a Module in the code window.
- In the code window, copy the following code and paste it:
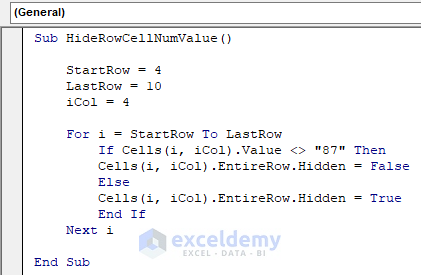
Sub HideRowCellNumValue()
StartRow = 4
LastRow = 10
iCol = 4
For i = StartRow To LastRow
If Cells(i, iCol).Value <> "87" Then
Cells(i, iCol).EntireRow.Hidden = False
Else
Cells(i, iCol).EntireRow.Hidden = True
End If
Next i
End SubThe code is now ready to run.
Here,
- StartRow = 4 -> First row of the dataset.
- LastRow = 10 -> Last row of the dataset.
- iCol = 4 -> The column address that holds the text value.
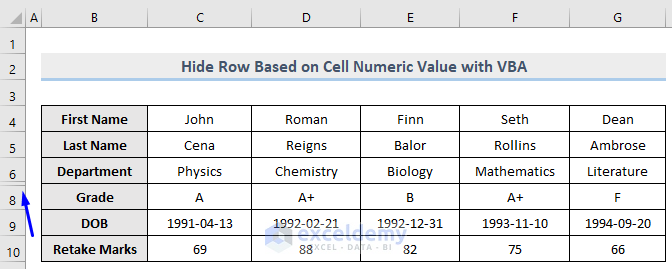
- Run this code.
Row 7 which contains the numeric value “87” is hidden.
Download Practice Workbook


