Why HLOOKUP Matters
HLOOKUP is a powerful tool for extracting specific information from large datasets, such as sales records or employee performance reports. Whether you’re a professional, analyst, or student, mastering HLOOKUP can significantly streamline your data analysis and reporting tasks.
Exercise Overview
These exercises cover various examples using not only HLOOKUP but also other related functions like MATCH, LARGE, and IFERROR. Regardless of your Excel version—whether it’s 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, or 365—these practice exercises are compatible. However, Exercise 7, which involves array returns, may require Excel 365.
Overview of HLOOKUP Function in Excel
Function Objective
The HLOOKUP function searches for a value in the top row of a table or array of values and returns the corresponding value from the specified row.
Syntax
=HLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, row_index_num, [range_lookup])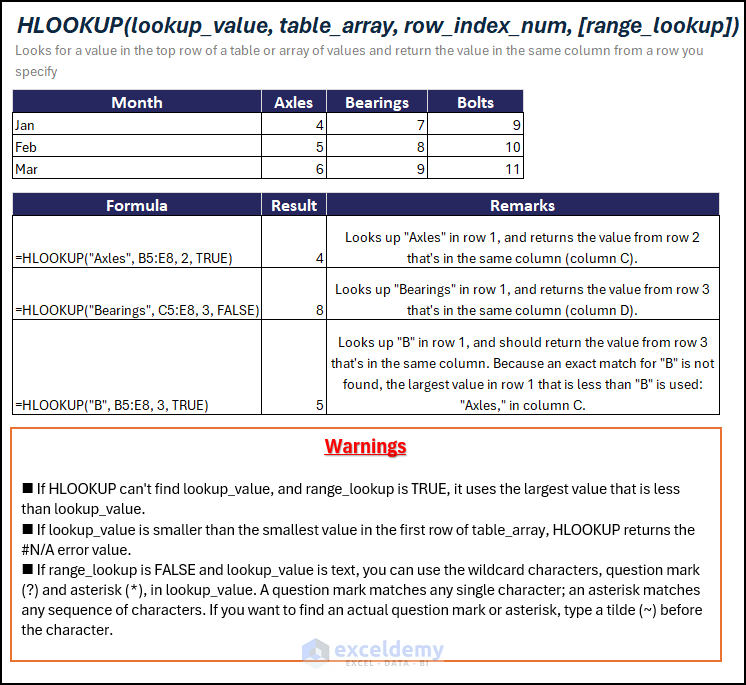
Practice Exercises
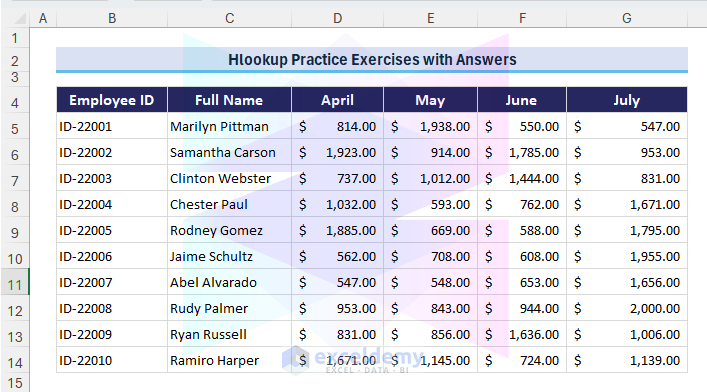
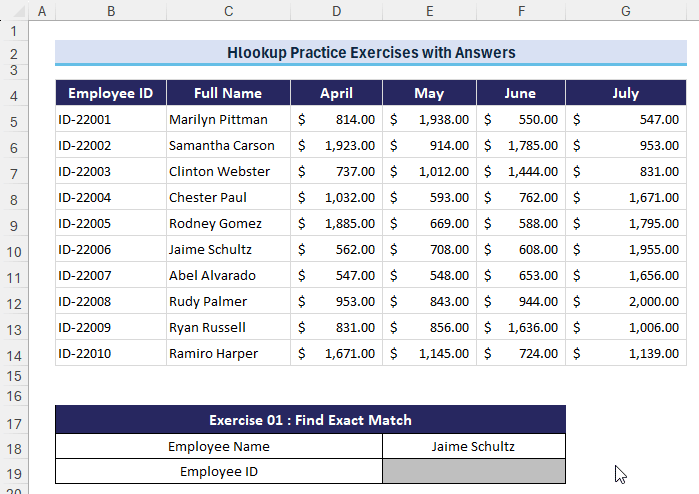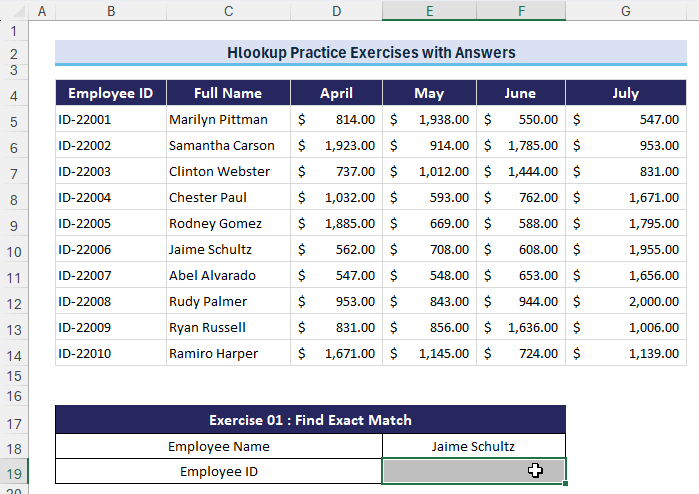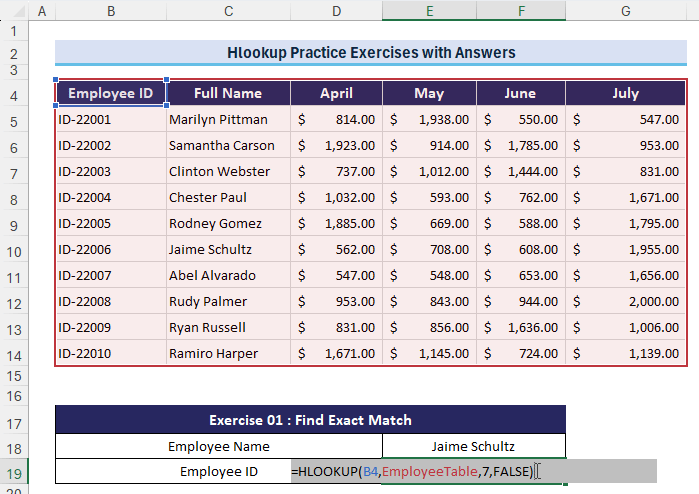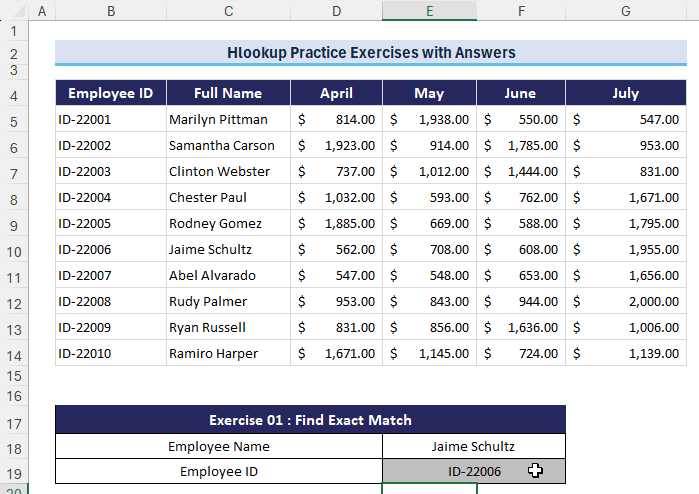
Let’s dive into the exercises based on a dataset containing information about employee sales for the months of April, May, June, and July. Each employee is identified by an Employee ID and Full Name, and their sales for each month are provided.
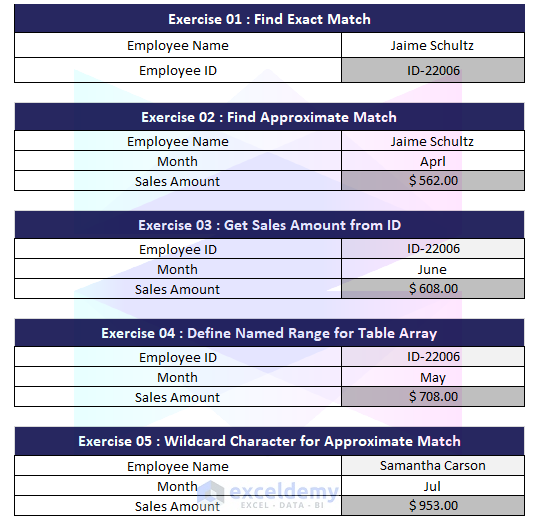
Exercise 1 – Find Exact Match
-
- Question: What is the “Employee ID” for Employee “Jaime Schultz”? Use HLOOKUP to locate the employee’s name and retrieve the corresponding Employee ID.
Exercise 2 – Find Approximate Match
-
- Question: What are the sales for the misspelled month “April” for Employee “Jaime Schultz”?
- Hint: Pay attention to the correct spelling of the month.
Exercise 3 – Get Sales Amount from ID
-
- Question: Find the sales for the month of “June” for the employee with Employee ID “ID-22006.”
- Hint: Use the MATCH function to locate the row number of the employee ID.
Exercise 4 – Define Named Range for Table Array
-
- Question: What were the sales for the employee with Employee ID “ID-22004” in the month of “May”?
- Hint: Defined a named range “EmployeeTable” for the range B4:G14?
Exercise 5 – Wildcard Character for Approximate Match
-
- Question: What were the sales for the employee with a Full Name containing “Samantha Carson” in the month of “Jul”?
- Hint: Utilize the Asterisk (*) wildcard for text/string values.
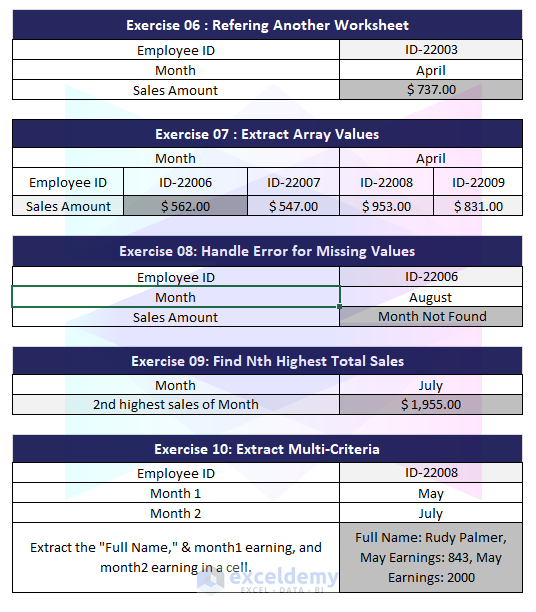
Exercise 6 – Referring Another Worksheet
-
- Question: How can you find the sales for the employee with Employee ID “ID-22003” for the month of “April” when the data is in a different worksheet named “Sales”?
Exercise 7 – Extract Array Values
-
- Question: Find the sales of the Month of April for Employee ID-22006, ID-22007, ID-22008, and ID-22009 as an array.
- Hint: Use curly brackets {} to create an array at the position of row values. Note that this exercise may require Excel 365.
Exercise 8 – Handle Error for Missing Values
-
- Question: Find the sales for the employee “ID-22006” in the month of August. If the month is not found, display “Month not found.”
- Hint: Employ the IFERROR function to manage errors.
Exercise 9 – Find Nth Highest Total Sales
-
- Question: Determine the sales for the employee with the second-highest total sales in July.
- Hint: Use the LARGE function to retrieve the second-highest sales.
Exercise 10 – Extract Multiple-Criteria
-
- Question: Extract the “Full Name,” “May” sales, and “July” sales for the employee with Employee ID “ID-22008.”
Get FREE Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions!


